When to plant winter garlic in Siberia. When to plant winter garlic in Siberia: planting dates
The main harvest of garlic in my summer garden I get through the cultivation of winter garlic. His head grow larger than the spring. True, that they would start and grow normal size, you have to break out arrows, (my garlic is arrowed), but this is a small problem, especially since the young shooters are quite tasty and can be used as food.Precursors in the cultivation of garlic are very important. This year I planted garlic on the beds where tomatoes grew this summer. Moreover, the beds of garlic, I, as always, placed carrots between the future beds. This is what would be during the growing season of garlic harmful fly, infecting garlic (she do not tolerate carrot smell!), kept away from these places. He also took into account that this place next year, after harvesting garlic, would be suitable for planting young strawberry whiskers.
Before digging up the selected places for garlic, I made two buckets for each bed (5 sq.m.) sandtherefore, it didn’t bring it in there long ago, and the land turned out to be quite heavy there. But he didn’t add humus, as the amount applied to the previous crop (tomatoes) would be enough for garlic.
I select only the most seeds the best heads of garlic. These are the largest and most healthy heads from plants that have preserved the maximum varietal characteristics. All atypical (in terms of ripening, the type of heads, arrows, etc.) plants of garlic seeds never leave. I divide the heads of garlic into slices in advance, and I don’t use damaged teeth for planting. For the improvement of my entire mini-plantation of garlic, periodically (once every few years) I use the cultivation of garlic from bulbokhek.
Depending on the local growing conditions in different regions, they plant garlic for the winter at different times. In our area (Altai), the most acceptable time for planting winter garlic falls on the first of October. This season I planted winter garlic on October 2.
I plant garlic in rows. Row spacing 15-20 cm, and between plants in a row 10-15 cm. You can plant garlic and thicker, but I prefer to give him more space, so that he would grow better and fasten heads bigger. I make a special stick-planter planting nests-pits in the garden depth 5 cm (for different regions, the depth of landing may be different). In each prepared hole I drop a clove of garlic with the bottom (where the roots are) down, then you should pay attention - this is a must! After planting, gently level all the pits, and immediately fill up the garlic beds with previously prepared mulch. I use for this pine needles.

|

|
How to plant winter garlic
Garlic should be planted 45-50 days before the onset of cold weather, so that the soil at the time of planting has cooled to + 10 ° С. For the time of freezing of the soil, the planted teeth form roots with a length of 10-12 cm, which ensures them a good wintering.
Landing winter garlic: choice of location
It is better to grow garlic in beds 15-20 cm high and up to 1 meter wide. These beds are heated more by the sun, and the plants on them suffer less from waterlogging. In this case, rows of garlic should be located from north to south, so that in summer the plants would be evenly illuminated by the sun during daylight hours.
Under the autumn digging soil contribute to 1 square. meter for 1 bucket of compost and humus, 1 st. spoon superphosphate and potash fertilizers, 1 cup of ash. On acidic soils bring 200-300 g of lime-fluff (I repeat - it is better to do this under the previous culture).
In addition, on heavy clay soils, you need to make 1 bucket of sand and peat, on sandy ones, 1 bucket of peat and clay pounded into powder, and 1 bucket of loamy soil and sand — into peaty soils.
The best precursors of garlic are legumes, zucchini, pumpkin, cucumbers, tomatoes, early cabbage, green cultures, early harvested horse crops, but not potatoes. And after the potato plant garlic should not be, because it can become infected with fusarium or it can be damaged by nematodes. It is impossible to place garlic over garlic for two years in a row. Because of common pests and diseases, do not plant garlic after onions.
Winter garlic is propagated by bulbs or teeth. They start harvesting as soon as the film starts to crack, and the bulbs will get the color characteristic of the variety. They usually ripen in late September, in more northern areas by the beginning of winter. In this case, ripe bulbs should be maintained until spring.
Planting winter garlic: planting dates
Best term the landing of the bulbobok is the second half of September about a month and a half before the onset of sustained winter cold. On prepared beds, grooves are made with a depth of 3 cm when landing in spring and 4 cm when landing in autumn.
To protect garlic from diseases, many gardeners soak bulbs for 2-3 hours in one of the preparations: Immunocytophyte, Rizoplan, Zaslon, Barrier or in a warm solution of pink potassium permanganate before planting. Then the bulbs are laid out at a distance of 2 cm from each other and sprinkled with loose soil. Then the bed is mulched with peat or sawdust, which must be removed in the spring as soon as it begins to thaw the soil.
The maintenance of sowing bulbs next summer consists in loosening the soil, watering and feeding. In the phase of the second leaf, crops should be fed with a solution of mullein (1:10), consuming 2 liters per 1 square meter. meter beds. After two weeks feeding must be repeated.
In late July - early August, the tops of garlic fall down, the plants are podkapyvayut with forks, sevok dried in the sun, and when he begins to rustle, it is cleaned from the remnants of the roots and leaves. In case of direct cultivation, the sevaceous plants grown from the brooches are not dug, and it remains in the soil for the second winter.
On teeth select well-dried, typical for the type of onion. They are divided into teeth before planting so that the lower part of the teeth, where the roots are formed, does not dry out. To facilitate the division of the bulbs on the teeth can be a small pointed stick, which is introduced into the crack of the bulb.
Before planting, the teeth should be sorted by size, paying attention to the bottom: they should not have a dead part of the old bottom. It, like cork, prevents the germination and the formation of roots, so it should be removed.
To reduce the consumption of planting material, you can use single-teeth, which are obtained from the air bulb. This also contributes to the improvement of planting material. It is advisable to plant large teeth from full-fledged heads on one half of the bed, and to put one-teeth on the other. The landing rate is 40-50 teeth per 1 square. meter.
Plant sev or teeth rows in the grooves at a distance of 7-8 cm from each other and 20-25 cm between rows. The larger the teeth, the deeper they are planted. The depth of planting large cloves (the distance from the tip of the clove to the soil surface) should be 6-7 cm, and for smaller ones 3-4 cm. Fresh landings are mulched with humus or compost 2-3 cm.
The deep landing of large cloves contributes to their rapid strengthening and preservation from freezing. It is not necessary to press them with force into the bottom of the grooves, since this will delay the growth of the roots, and only fill it with loose earth and slightly condense. With the onset of cold landing, it is necessary to mulch the peat.
In the spring, the first loosening of the soil to a depth of 2-3 cm is done as soon as the soil allows. During the growing season, garlic must be fed 3 times. The first time they do this is 3-4 days after the snow melt with a solution of mullein (1:10), 2-3 liters per 1 square meter. meter or urea solution (1 teaspoon per 10 liters of water). The soil by this time has not yet had time to thaw, but the nitrogen nestles well into it with spring moisture.
The second feeding is carried out 2 weeks after the first feeding with a solution of mullein (1:10) with the addition of 1 bucket of 1 tbsp. spoon nitrophoska, consuming 3 liters per 1 square. meter beds. And the third time it is done after breaking out of the flower arrows with ash (1 cup per 10 liters of water). In the process of growth of garlic, you can additionally add to the soil and ash 1 glass per 1 square meter. meter.
If the spring is dry, the garlic should be watered abundantly (20-30 liters of water per 1 square meter), preventing the top layer of soil from drying out. He also needs abundant watering during the formation of the bulbs, but 2-3 weeks before cleaning, watering is stopped.
All floral arrows (if you do not need bulbs) should be broken out at the very bottom, when they grow 8-10 cm, otherwise good harvest can not count. Being late with breaking out the arrows or removing some inflorescences does not have an effect.
And in order for the ripe bulbs to crumble on the left peduncles, you should put a gauze bag on the inflorescence and not remove it until the bulb is ripe.
Many gardeners who pick up garlic spud up to a height of 3-4 cm, so that the bulbs are not overheated by the sun. And shortly before harvesting, the upper parts of the bulbs are freed from the ground, so they quickly gain mass.
When yellowing and lodging of the lower leaves proceed to harvesting garlic. If you are late with the collection, the cover scales fall off, the teeth are exposed and the bulbs crumble.
V.A. Loiko
Planting winter garlic
The success of winter garlic culture strongly depends on the quality of planting material, including the degree of ripening of cloves (ie, the content of dry substances and carbohydrates in them), and on the degree of shelter of garlic plantations with snow in severe winters with little snow.
The timing of planting winter garlic
When growing winter garlic, many gardeners most often complain that, despite all their efforts, the bulbs grew small. The main role in the cultivation of this crop is played by the preparation of the soil and the quality of planting material. In addition, both very early and too undesirable late landing winter garlic.
In different areas, the calendar dates of planting winter garlic are different. They should be determined in such a way that 45-50 days are left before the onset of stable winter cold. The planted teeth develop well before the soil freezes. root system 10-12 cm long, which provides them a good overwintering.
Soil for planting winter garlic
Garlic loves a sunny place and is very picky about the soil. It grows well on structural fertile soils with a low level of groundwater, best of all on sandy and light loams with a neutral reaction. Even with a slight increase in acidity, the plants feel depressed. But lime must be applied to the soil not in the year of planting garlic, but under the previous crop. Moist clay and dry sandy soils are unsuitable for its cultivation.
It is better to grow garlic in beds 15-20 cm high and up to 1 meter wide. These beds are heated more by the sun and the plants on them suffer less from waterlogging. In this case, rows of garlic should be located from north to south, so that in summer the plants would be evenly illuminated by the sun during daylight hours.
Under the autumn soil digging make 1 square meter for 1 bucket of compost and humus, 1 tbsp. spoon superphosphate and potash fertilizers, 1 cup of ash. On acidic soils bring 200-300 g of lime-fluff (I repeat - it is better to do this under the previous culture).
In addition, on heavy clay soils, you need to put 1 bucket of sand and peat on sandy soils - 1 bucket of peat and clay pounded into powder, and 1 bucket of loamy soil and sand into peaty soils.
Garlic is a plant of long daylight. Therefore, the bed set aside for him should be well lit throughout the day. It is noticed that long overcast weather adversely affects the development of plants.
The best predecessors of garlic are legumes, zucchini, pumpkin, cucumbers, tomatoes, early cabbage, green crops, early harvested roots, but not potatoes. And after the potato plant garlic should not be, because it can become infected with fusarium or it can be damaged by nematodes. It is impossible to place garlic over garlic for two years in a row. Because of common pests and diseases, do not plant garlic after onions.
Winter garlic is propagated by bulbs or teeth. They start harvesting as soon as the film starts to crack, and the bulbs will get the color characteristic of the variety. Usually they ripen in late September, in more northern areas - by the beginning of winter. In this case, ripe bulbs should be maintained until spring.
Before sowing bulbs should be sorted by size, because when sowing small bulbochka small odnozubki grow, in the second year - large odnozubki and only in the third year - commodity bulbs.
The best time for planting bulbs is the third decade of September, i.e. about a month and a half before the onset of sustained winter cold. On prepared beds, grooves are made with a depth of 3 cm when landing in spring, and 4 cm when landing in autumn.
To protect garlic from diseases, many gardeners soak bulbs for 2-3 hours in one of the preparations: Immunocytophyte, Rizoplan, Zaslon, Barrier or in a warm solution of pink potassium permanganate before planting.
Then the bulbs are laid out at a distance of 2 cm from each other and sprinkled with loose soil. Then the bed is mulched with peat or sawdust, which must be removed in the spring as soon as it begins to thaw the soil.
If you are going to grow this garlic in throat, i.e. you won't dig it up next fall, then the large bulbs are laid out after 4 cm, and the smaller ones - after 3 cm.
And the teeth are selected well dried, typical for the type of onion. They are divided into teeth before planting so that the lower part of the teeth, where the roots are formed, does not dry out. To facilitate the division of the bulbs on the teeth can be a small pointed stick, which is introduced into the crack of the bulb.
Before planting winter garlic, teeth should be sorted by size, paying attention to the bottom: they should not have a dead part of the old bottom. It, like cork, prevents the germination and the formation of roots, so it should be removed.
Large bulbs grow only from the largest cloves. Consequently, planting material must be selective. For planting it is necessary to take only external teeth, and internal (thin) to use only for food.
To reduce the consumption of planting material, you can use single-teeth, which are obtained from the air bulb. This also contributes to the improvement of planting material. It is advisable to plant large teeth from full-fledged heads on one half of the bed, and to put one-teeth on the other. The landing rate is 40-50 teeth per 1 square. m
Planted sevka or teeth rows in the grooves at a distance, depending on the size from 5 cm (small) to 8 cm (large) from each other and 20-25 cm between the rows.
The larger the teeth, the deeper they are planted. The depth of planting large cloves (the distance from the tip of the clove to the soil surface) should be 6-7 cm, and for smaller ones 3-4 cm. Fresh landings are mulched with humus or compost 2-3 cm.
When dividing the bulbs of winter garlic into teeth, which is carried out on the day or the day before planting, ensure that they do not contain parts of the old base of the mother bulb, which does not allow moisture to go to the base of the clove and interferes with its rooting.
The deep landing of large cloves contributes to their rapid strengthening and preservation from freezing. It is not necessary to press them with force into the bottom of the grooves, since this will delay the growth of roots, you just need to fill it with loose earth and slightly condense. With the onset of cold landing, it is necessary to isolate with peat or humus a layer of 1.5-2 cm.
And the shoots of winter garlic will appear in early spring, when all the snow has not yet melted. At this time, they acquire an unusual pink-purple color. When the soil is not yet thawed, the plants must be fed with nitrogen fertilizer at the rate of 1 teaspoon of urea per 1 square meter. m beds.
V. G. Shafransky

Garlic is a culture that grows in various climatic and soil conditions. Ideal soils for growing garlic are alluvial and humus. It is one of the oldest cultivated plants. , it was cultivated by the ancient Greeks, Jews, Romans for 4500 years BC. His homeland is one of the steppes of Central Asia, garlic came to Russia only in the Middle Ages, but in the rest of the world, it has been known for thousands of years. The characteristic aroma of garlic and taste made it the most valuable seasoning. But many avoid using garlic because of the smell that remains in the mouth. But nevertheless it is a small minus, which fades in the face of useful properties this plant and its beneficial effects on our body.
Garlic is distinguished not only by its excellent plant culture, used as a seasoning, but also widely known and famous for its healing properties. Because of their healing properties It is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry, and in its natural form it will include it in your diet, as it prevents sclerosis, fights against high blood pressure, cleanses the blood and supports the body’s natural immunity. Eating garlic helps get rid of the so-called "bad" cholesterol. It can be called the oldest antibiotic. Apparently, it was eaten by the builders of the Egyptian pyramids to protect themselves from diseases.
Hippocrates, the father of Jewish medicine, recommended garlic to stimulate the function of the digestive system and lung diseases. They knew this plant and the ancient Chinese. Today, China is the largest producer of garlic in the world. By and large, it is also grown in Egypt, India, South Korea and Turkey.
High yield is obtained, as a rule, on other soils, but they must be rich in good. On sandy and dry soils, the harvest will be less. Garlic, like other bulbous plants, reacts negatively to the weeds clogging the plantation. This is especially important during the germination of garlic and any discrepancy in the care leads to a significant reduction in yield.
What is the advantage of growing garlic in the winter?
Garlic, which is planted in the autumn period of time, undergoes natural hardening during the winter season. Planting winter garlic - this method is very common among gardeners. It allows you to get a harvest a few weeks earlier than those who planted garlic in the spring. By the middle of summer we will be able to provide our family with valuable nutrients. Moreover, during the autumn planting to build a greenhouse, there is no need.
Another advantage of this planting is that we do not need to create conditions for the storage of garlic in the winter.
Climate
Garlic is a strong and solid culture that easily tolerates low temperatures and can winter in soil provided it is timely. autumn planting (before the first frosts). It is resistant to spring frosts. After winter, it enters a phase of germination at a temperature of 3 to 5 degrees Celsius.
Landing
The timing of planting winter garlic, depending on the region, may vary. As a rule, the landing period begins in mid-October and lasts until the end of November. For planting garlic beds are suitable, from where already harvested. It should not be planted in a place where onions or garlic had previously grown. Garden beds for winter garlic are prepared about a month before planting.
However, you need to be very careful not to plant garlic too early, because it can germinate and freeze in winter. But garlic should have time for rooting before winter, but not so much to start growing up.
For more yield of winter garlic, it must be stored in a dry and cool place. The best material for planting will be medium or large onions. With small seeds and the harvest will be small. Garlic teeth are cultivated in the ground in an upright position, pointed end up. Garlic is planted in rows, the distance between them should be about 20-25 cm, and the distance from cloves to cloves in the same row is about 7 cm. Before planting garlic, process the soil with special solutions that can be purchased in specialized stores. Solutions will protect the chives from nematodes and fungi in the early stages of development.
Among the winter varieties of garlic can be distinguished: Arcus, Mega, Ceves, Harnas, Huzar, Ornak. Before the onset of frost, beds of garlic are lined with straw and covered with fir branches.
Winter garlic is planted in the soil to a depth of 5-6 cm, which is slightly deeper than spring garlic. For spring garlic optimal term The landing is the end of March or the beginning of April, as the weather permits. When the soil begins to thaw in the spring and dries out a little, it is necessary to cultivate the soil and plant garlic to a depth of about 3 cm.
In such beds it is necessary to add humus and compost, after which the soil should be dug up. Garlic is laid out on the garden in a checkerboard pattern, after which it is filled with compost from above. This is the most common method of planting winter garlic. There is another way to plant garlic in the fall. Garlic must be planted on the prepared bed with the first frost. In this case, the garlic has time to form a sufficiently powerful root system, which will contribute to obtaining a rich harvest. While preparing the beds for planting garlic, the soil must be well fertilized with manure.

Sandy soils are often used. They are fertilized with the help of humus. Immediately before planting, it is not recommended to bring fresh manure into the soil. It is not recommended to press garlic cloves into the ground when planting. Such planting can adversely affect the development of the root system. Also, the soil should not be too dense, otherwise it will push the garlic to the surface, where it will just freeze. In addition, the ground should not be too loose. When planting in loose soil, we can get a harvest with too small heads of garlic. Planting cloves of garlic is not deep enough, it can freeze, and an overly deep planting will adversely affect the development of the root system. It is imperative to mulch with peat and compost, they are layered. With the onset of spring, the layer of compost and peat from the bed must be removed to prevent the process of decay. When planting garlic for the winter, the main problem is to guess the planting date.
Garlic must be planted when the temperature of the earth reaches plus 2-3 degrees Celsius. If you plant the garlic too soon, then in the fall it will begin to germinate from the ground, and when frost comes, the seedlings will die. It is for this reason that in the fall garlic is planted in a slightly frozen ground. With such planting, the garlic tolerates even the harsh winter well and in the summer it pleases the gardener with a rich harvest.
Planting winter garlic in Siberia is somewhat different from planting in middle lane. Here, winter garlic is planted a little earlier. For example, in Western Siberia, the planting of winter garlic begins in mid-September and ends around October 5. Having planted garlic in the above period of time, the teeth or sets, have time to take root in the ground, form a root system, the length of which can reach 7-10 centimeters, but leaves do not have time to form. Such garlic is able to tolerate even big frosts. When planting for the winter nonstartling varieties, they must be planted to a depth of about 6 centimeters. Shooting varieties are planted at a depth of 8 centimeters. The distance between rows when sowing should be from 25 to 30 centimeters, and in a row, between the plants themselves from 8 to 10 centimeters. Regardless of weather conditions, immediately after planting garlic, garden beds should be watered well. Watering will increase the winter hardiness of garlic and the formation of a good root system.
Top dressing
With the onset of spring, as soon as the snow melts, it is necessary to feed the garlic. Fertilizing is carried out by ammonium nitrate. On 1 square meter is used about 20 grams. During the summer, the field from 3 to 4 times must be drilled or loosened to a shallow depth. At the same time, the plants themselves do not pile up so as not to damage them. When the garlic leaves begin to germinate, it is necessary to water it abundantly. We water 3-4 times. In order to increase the mass of the bulb in the arrow grades, the arrow that appears by the end of the first summer month must be removed. The arrow can simply pull out, but it is best to remove all the inflorescence. Thus, the weight of the bulbs will increase by 30 to 40 percent. We start harvesting of non-strepling winter varieties of garlic when at 75 percent of the plants the leaves turn yellow and become poles.
As for the shooter varieties, the time for their cleaning will come when the inflorescences are cracked and the aerial bulbs begin to crumble. In no event should harvest be delayed. If you are late with the harvest, the quality of the harvest will decrease. We select the bulbs from the soil very carefully, so as not to injure, carefully remove the stuck earth from them.
Garlic Harvesting
Harvesting garlic should be started when more than half of the garlic has planted stalks on the plantation. If the garlic is planted in the fall, it is harvested at the beginning of July. Another sign of maturity is dry leaves. Garlic collected too late will be poorly stored, and the head will disintegrate into individual teeth that are poorly covered with husk. Such garlic is more susceptible to disease. To harvest on garden plots The best tools are “American Forks”. After harvesting the garlic and cleaning the heads from the ground, leave them to dry in the same area. Usually this process takes several days.
Storage
After the stems and leaves are completely dry, you can transfer the garlic to the room or basement storage room, after shortening the stem .. The room should be dry and well ventilated. The recommended temperature for storage is 0 degrees Celsius, humidity 65-70%.
Magic garlic
The magic component of garlic is allicin, with the result that garlic acts as an antibiotic and effectively inhibits the growth of many bacteria. The structure of the plant includes vitamins such as: A, B1, B3. Various types of decoctions and infusions of garlic help in the environmental control of plant pests.
There are two types of garlic: producing flowering shoots, not producing flowering shoots.
From the inflorescences of the first type, excellent planting material is obtained in the form of small oblong onion.
Garlic is not just a good seasoning for any dish and a must-have in delicious pickles. It is also a proven one. folk remedy, strengthens the immune system and helps to cope with all sorts of unpleasant diseases, from the common cold to bronchitis. Therefore, the cultivation of garlic, especially in cold Siberian regions, is an extremely popular occupation among gardeners. But in order for the venture to take place, and the harvest turned out to be rich, you need to figure out how and when to plant garlic for the winter. This is the question we will look at in the article, as well as help to deal with the technology of planting this culture in Siberia.
Siberian temperatures are quite severe, because it is quite important to understand the varieties of winter garlic, before taking up the landing.
It is worth remembering the difference between winter varieties and spring varieties and not to confuse: summer culture can hardly withstand frosts, while winter crops can easily wait out the cold in winter under a snowy hat. Next, consider the most popular varieties of winter garlic.
Gribovsky Jubilee - arrowed mid-season variety of culture. The garlic head usually weighs up to 45 grams and can hold up to 10 cloves covered with cream scales with purple veins. The acuteness of this variety is not very pronounced. While the Gribovsky 60 is a variety of arrows, but early, very sharp. Its bulb is larger, often reaches 60 grams and consists of large cloves from 5 to 12 in the bulb.
Yelenovsky is also a shooter, a very fertile variety, characterized by high yield and increased frost resistance, as well as resistance to bacterial diseases. In the white bulbs (about 50 g) is only 4-7 teeth. The same resistance and fecundity are characterized by the variety Spas. Its bulbs are twice the size of Elenovsky (up to 100 g), but there are also few cloves in it - from 7 to 10 pieces per onion. There is another variety - Sofiyevsky. Like Spas, it is resistant to frost and nematode. Its head weighs 120 grams on average and gives about 8 teeth.
Alcor is a mid-season variety that produces small bulbs covered with purple scales. Weigh garlic heads up to 40 grams, each of them has up to 6 cloves. One of the most popular varieties - Lyubasha. It gives large heads up to 130 g in weight with large teeth from 4 to 7 in one bulb.

Features of planting winter garlic
Before you plant garlic for the winter in Siberia, you need to decide what kind of result you want to achieve: collect big harvest or withdraw good grade. If the first, then your seeds will be the teeth. If the second - then bulbs.
It is important to understand how one differs from another. The cloves are the "fruits" of garlic, closely adjacent in the bulb to the stem in winter varieties. Bulbs are, conditionally speaking, “seeds” that ripen in the seed box on the arrow. In the first year after sowing, the bulbs give out bulbs with one clove (the so-called sevok), which only next year grow into a full onion. Such a plant is grown in two seasons, but it guarantees a high-quality and rich harvest.
When the decision is made, it is worth doing the selection of seed and its preparation. Garlic teeth for landing are selected large and intact. This will be the key to good, proper growth. Such teeth must be hardened - kept in a solution of potassium permanganate, ash solution or solution of copper sulphate.

Bulbs should be dried and treated with a strong solution of potassium permanganate or ash solution by spraying just before planting.
Timing
Winter garlic in Siberia is worth planting when you have completely cleared a selected piece of land from a previous crop and prepared the ground. All this should happen at the end of September or the beginning of October, approximately 50 days before frosts. During this time, the tooth placed in the ground will have time to develop a good root system and begin its proper development. So the plant is the most adaptable and will be ready to wait the winter.
Choice of place
A landing site is also an important issue. It is important to take into account many points, choosing the right plot for sowing garlic. It is worth remembering that the culture loves loamy soil with low acidity. The earth should not accumulate a lot of moisture - it damages the development of planted teeth, moreover, it can lead to an undesirable result: garlic can simply rot.

Determine the place in advance, even before harvest predecessors. Remember that the type of plants that grew on the site before, will depend on how well the new soil will take root in the culture. By the way, it is not recommended to plant a plant on the same plot twice in a row, since the previous sowing will take too many nutrients and the new crop will turn out to be rather poor.
When you have decided on the land and removed all organic residues from the soil, you need to go to the stage of fertilizing the soil.
Proper soil saturation will help garlic survive the winter, even in Siberia.
It is best to fertilize the earth with a mullein or horse manure, feed it with phosphates and potassium. Fertilizer should be applied to the ground at 20 cm - the maximum depth of the root system of garlic. It is also recommended to treat the soil with a solution of copper sulphate.
After the earth has been treated, hold it for a while under polyethylene or roofing felt. The soil needs to warm up and accumulate moisture. However, the shelter must be removed for the winter so that the garlic in the ground does not overheat.

Landing technology
Before planting, after the ground cover has been removed, the soil should be slightly damp. Now that everything is ready, you can proceed directly to the landing. There are several options for planting garlic, and the choice of the actual depends on the size of the land allotted for planting:
- You can feed the earth with a solution of yeast, and then divide the furrows, leaving between them at 25 centimeters. Cloves are planted in these furrows with an interval of 10 centimeters, and then covered with earth.
- If in a small area you want to grow as much garlic as possible, you can plant a crop in two tiers. The technology is similar: it is necessary to dig furrows up to 20 cm deep, to lay the first tier of teeth. Then cover the ground for 5-6 centimeters, land the second tier and prikopat again.
- The third way for those who do not want to once again dig and mark the grooves, take care of their depth. In this case, the beds are simply distributed at a distance of 25 cm from each other, garlic cloves are sown and covered with earth.
It should be remembered that in all cases after planting the culture is recommended to be mulched with leaves or grass.

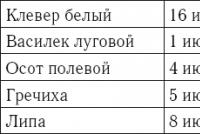
Garlic Precursors
Returning to the question of predecessors, it is worth clarifying a few important details. It is best to know after which crops the sowing of garlic will produce a rich harvest, and after which - poor. Of course, the first rule that is easy to observe (if we are talking about winter varieties) is not to plant a crop two times in a row.
However, it is unlikely gardeners will give the site to stand idle in the summer. Because something you are sure to sow. And so it is important to think that it is. After potato, Jerusalem artichoke, rare carrot and garlic teeth will not develop too well - there will be too few useful elements in the ground. But after melons, cabbage and legumes, the land, in contrast, will be sated with useful nutrients for the growth of garlic.