Catalpa bloom. Catalpa, types, photos, growing conditions, care
Catalpa is a very beautiful tree in height from 5 to 30 m, which attracts views from early spring to late autumn. Its homeland is the southeastern part of North America, where it grows in abundance along the banks of rivers. In the 18th century, the catalpa was introduced to Europe, and today it is widespread also in Russia, China, India and Japan. In total, the plant counts 10 species, but in our country they usually grow Catalpa bignonioid (Catalpa bignonioides) and excellent Catalpa (Catalpa speciosa).
Large round leaves of catalpa secrete it from the total mass of trees throughout the season. Flowering plant for 3 - 4 weeks, starting in mid-June. During the flowering period, the catalpa is covered with large inflorescences of white or cream flowers with apple flavor, and the fruits that appear by autumn in the form of long pods up to 40 cm long decorate the branches of the tree almost all winter, which gives it an extremely unusual look. Another difference catalpa from most trees is that in the fall it almost does not turn yellow and sheds green leaves when the temperature drops below zero.
Growing catalpa
Catalpa is preferably planted in a sunny place, well protected from the wind, which can damage its delicate leaves. The plant is usually planted to a depth of 1 - 1.2 m. A soil mixture consisting of three parts of humus, two parts of leafy ground, two parts of sand and one part of peat is well suited for it. When planting, it is desirable to fertilize the ground with wood ash and add superphosphate. It is better if the acidity of the soil is neutral. Before planting, you need to carefully shed a hole with water. With proper care, the young tree will bloom in the fifth year.
Catalpa is quite cold-resistant, but young plants are often more susceptible to frost. Their trunks for the winter should be wrapped with spruce leaves or sacking, and the ground under them should be covered with a layer of dry leaves. Shelter need to clean up in the spring, when the threat of prolonged frost will be reduced to zero.
Despite the good frost resistance, the younger shoots are often frosting over at catalpa. This problem can be successfully fought by cutting off branches in the early spring that were tainted by frost. Catalpa tolerates pruning and it is possible to combine such a forced haircut with a decorative one, creating the crown of a tree of the desired shape.
Growing a catalpa, you should promptly remove the weeds under it and loosen the soil to a depth of 30 - 35 cm. Watering is sufficient once a week, but plenty of water.
As for fertilizing fertilizer, the rotted manure is ideal for catalpa. Feed should be at planting, and then about once a month during the growing season.
Catalpa Reproduction
Catalpa propagated by seeds and cuttings. To increase the germination of seeds, you should soak them in warm water for 7 to 12 hours. Seeds are sown in February or March, sprinkled with a thin layer of earth and covered with glass or film. Having provided them with a place with diffused sunlight, a temperature of 15 - 25 ° C and regular watering, we can hope for the emergence of shoots within a month. Then the shelter should be removed and continue to care for seedlings until May. When stable warm weather is established, seedlings can be planted in open ground.
 If it is possible to obtain catalpa cuttings, they should be cut 10 cm long in the second half of summer. They are planted in a mixture of peat and sand, and look after them in the same way as in seed reproduction. When a seedling sprouts appear and a root system is formed, you can plant it in open ground.
If it is possible to obtain catalpa cuttings, they should be cut 10 cm long in the second half of summer. They are planted in a mixture of peat and sand, and look after them in the same way as in seed reproduction. When a seedling sprouts appear and a root system is formed, you can plant it in open ground.
Catalpa Pests and Diseases
Catalpa is highly resistant to diseases and pests, but sometimes it is still affected by the Spanish fly, which can be eliminated by a double spraying with kinmiks, decis or karbofos. If insects have appeared in the still not blooming buds (Comstock worms), then the tree should be treated with insecticides before bud break, otherwise the young shoots will be deformed. If the soil is too compacted, there is a danger of infection by the fungus of the genus Verticillus, which causes drying and death of the plant. Therefore, the soil should be sufficiently loose and well water flowing.
A man who has planted a catalpa on his plot acquires a beautiful, powerful tree, which for many years will delight with its unusual appearance, and on hot summer days, shelter in the shade of thick and spreading branches.
indasad.ru
Catalpa tree
 Catalpa General information
Catalpa General information
Botanical name: Catalpa (Catalpa), a genus of the family Bignonium.
Catalpa homeland: North America.
Lighting: light-requiring
The soil: fertile, moist, slightly acidic, fresh.
Watering: abundant.
Maximum tree height: 30 m.
Tree's average lifespan: up to 100 years.
Landing: seeds, cuttings.
Spherical catalpa

Deciduous tree with a spherical crown. The leaves are large, heart-shaped, whorled 30 cm long and 17 cm wide. In the autumn do not turn yellow.

Funnel-shaped flowers, up to 7 cm, fragrant, have a pleasant apple aroma, white, sometimes cream with dark spots, gathered in erect inflorescences - panicles. Flowering begins in mid-June and lasts up to 4 weeks.

The fruit is a long box, up to 40 cm, filled with seeds - volatile. Fruits hang on trees throughout the winter, which gives the tree an unusual look.
The wood is soft, flexible, not rotting. Catalpa prefers well-moistened soils and bright places. Hardy. When the temperature drops, the tree sheds green foliage. All types of catalps are decorative.
Landing and care for catalpa
Landing catalpa produced in a well-lit area, protected from the wind. Plant the plant at a depth of 1 - 1.2 m. For planting suitable soil mixture of humus, leaf soil, sand and peat. Before planting, the ground should be fertilized with wood ash and superphosphate and pour plenty of water over the pit. Soil acidity should be neutral. With proper care, flowering will begin in the fifth year.
Young plants are often exposed to frosts. For the winter period their trunks are wrapped with spruce branches or burlap. The ground under the tree is covered with a thick layer of leaves. The coating is removed in early spring, when severe frosts stop. In early spring, pruned branches pruned.
Catalpa care consists in timely removal of weeds under it and loosening the soil to a depth of 30 cm. The plant does not require frequent watering, it is enough to water the catalpa once a week. Top dressing is done during planting and during the growing season. As a top-dressing suitable rotted manure.
Reproduction of catalpa seeds and cuttings
Catalpa propagated by seeds and cuttings. Before planting, seeds are pre-soaked in warm water for 7-12 hours. Sowing is done in February - March in place with diffused sunlight. Seeds are sprinkled with a thin layer of earth and covered with a film or glass. With regular watering and a temperature of 15-25 degrees, seedlings will appear within a month. After the emergence of shoots shelter removed. Care of seedlings continues until May, then the seedlings are moved into the open ground.
Cutting of catalpa is done in the second half of summer. Cut cuttings 10 cm long, plant them in a mixture of peat and sand. Care is the same as in the reproduction of catalpa seeds. When sprouts appear in saplings and a formed root system, they are transplanted into open ground.
Catalpa Pests and Diseases
The catalpa tree is resistant to pests and diseases. The main pest of the plant is Spanish fly. You can get rid of it by sprinkling the tree with kinmiks or decis. When insects appear on the kidneys, the catalpa should be treated with insecticides before bud break. Otherwise, the shoots are deformed. In order to avoid infection with the fungus Verticillus, you need to monitor the condition of the soil. It should be sufficiently loose, unconsolidated and well water flowing. The fungus leads to drying and death of the plant.
Sick tree catalpa pictured:

Common types of catalpa
Below you can see the most common types of catalpa. The obtained information will help you choose the right tree for your garden.
Bignonium catalpa
 Bignonia catalpa (Catalpa bignonioides) is a tree up to 20 m high. Spreading branches form a wide-round crown. The bark is light brown, thin-lamellar.
Bignonia catalpa (Catalpa bignonioides) is a tree up to 20 m high. Spreading branches form a wide-round crown. The bark is light brown, thin-lamellar.
The leaves are large, 20 cm long and 15 cm wide, resemble lilac leaves. From above naked, light green, pubescent from below.
The flowers are white, with red-brown specks and yellow stripes inside, up to 5 cm long. Possess weak aroma.
Blossom begins in the fifth year of life. Flowering lasts up to 25 days.
Fruits - narrow, pod-shaped boxes with numerous seeds and thin walls. Grows catalpa bignonevidnaya very quickly. Hardy to the soil is not demanding. Young individuals can freeze at low temperatures, so they are warmed for the winter.
Bignonia catalpa - a beautiful tree, often used for soliternyh plantings. It gains decorative value during flowering and in autumn, when the leaves turn golden. In winter, Bignonia catalpa look unusual, as its branches adorn the boxes of fruits.
This type of catalpa is used in single and group plantings, when planting alleys, parks and squares.
Looks winning on the gardens in the middle of a green lawn. The tree is combined with oak and magnolia, herbaceous perennials and bulbous flowers, unpretentious in care: crocuses, tulips and narcissuses.

Decorative forms of catalpa: gold, Ken, low (dwarf). Bignonia gold catalpa is distinguished by yellow leaves. A variety of catalpah Kene interesting bright yellow leaves with a dark green spot in the middle and green veins. Low bignonevidny catalpa or dwarf catalpa has a spherical crown and a height of 2 m.
Catalpa Nana
 Low tree, reaching 4-6 m in height. The krone is dense, dense, spherical. The leaves are light green, heart-shaped. Flowers are not tying. Prefers lighted places, protected from the wind. Requires fertile, fertilized soil. Suitable for planting and fresh loam. It grows slowly. Juveniles are less hardy than adults; they can be damaged at the first frost.
Low tree, reaching 4-6 m in height. The krone is dense, dense, spherical. The leaves are light green, heart-shaped. Flowers are not tying. Prefers lighted places, protected from the wind. Requires fertile, fertilized soil. Suitable for planting and fresh loam. It grows slowly. Juveniles are less hardy than adults; they can be damaged at the first frost.
Catalpa Nana does not tolerate high temperatures and excessive dryness, so on hot days you should be abundant and often water the plant. The crown of the tree is susceptible to damage. Digging up, loosening and replanting a tree should be very careful. Catalpa Nana is used for landscaping public areas and gardens.
Beautiful catalpa
 Ornamental tree with a wide pyramidal crown. The height of the beautiful catalpa reaches up to 35 m. The trunk is gray, with thin lamellar cortex. The leaves are large, 30 cm long and 15 cm wide, on thin, long petioles, smooth on top, light green, white underneath, pubescent. The flowers are white and cream-colored, with yellow stripes and purple-brown dots inside, large, up to 7 cm. They have a pleasant aroma. Duration of flowering 20 - 25 days. Blossom begins at the age of 10-12 years. Fruits - seed boxes. Appear in the middle of summer. Propagated by seeds, cuttings and layering. It grows in deep, fertile, moist soils. Well tolerated transplant. Planting is done in early spring. More hardy than other types of catalps. It is used in single, group plantings and to create alleys.
Ornamental tree with a wide pyramidal crown. The height of the beautiful catalpa reaches up to 35 m. The trunk is gray, with thin lamellar cortex. The leaves are large, 30 cm long and 15 cm wide, on thin, long petioles, smooth on top, light green, white underneath, pubescent. The flowers are white and cream-colored, with yellow stripes and purple-brown dots inside, large, up to 7 cm. They have a pleasant aroma. Duration of flowering 20 - 25 days. Blossom begins at the age of 10-12 years. Fruits - seed boxes. Appear in the middle of summer. Propagated by seeds, cuttings and layering. It grows in deep, fertile, moist soils. Well tolerated transplant. Planting is done in early spring. More hardy than other types of catalps. It is used in single, group plantings and to create alleys.
Spherical catalpa
 A tree with spreading branches forming a wide-round crown, up to 20 m in height. The bark is light brown, thin-lamellar. The leaves are large, up to 20 cm long, up to 15 cm wide. Bare, light green above, white pubescent from below. When rubbing emit a characteristic smell. The flowers are white, fragrant, up to 5 cm long, with two yellow stripes and dark brown spots inside. Flowering plant spherical catalpa 20-25 days. Fruits - narrow pods with seeds.
A tree with spreading branches forming a wide-round crown, up to 20 m in height. The bark is light brown, thin-lamellar. The leaves are large, up to 20 cm long, up to 15 cm wide. Bare, light green above, white pubescent from below. When rubbing emit a characteristic smell. The flowers are white, fragrant, up to 5 cm long, with two yellow stripes and dark brown spots inside. Flowering plant spherical catalpa 20-25 days. Fruits - narrow pods with seeds.
The leaves fall green immediately after the first frost. Autumn color does not change. It grows slowly. Hardy. Demanding on soil moisture. Used in single and group plantings, for landscaping streets and creating parks. Serves to decorate the garden plots.
Catalpa bigonic
 Tree up to 10 m tall. Crohn asymmetric, shoots are arranged in the form of a funnel. The leaves are large, heart-shaped, up to 20 cm, the color is pale yellow. By the period of flowering become green. The flowers are white and yellow with crimson specks, up to 30 cm. The fruits are pods, up to 40 cm. By the end of summer they turn brown. Keep on the tree until frost.
Tree up to 10 m tall. Crohn asymmetric, shoots are arranged in the form of a funnel. The leaves are large, heart-shaped, up to 20 cm, the color is pale yellow. By the period of flowering become green. The flowers are white and yellow with crimson specks, up to 30 cm. The fruits are pods, up to 40 cm. By the end of summer they turn brown. Keep on the tree until frost.
Under natural conditions, it grows in southeastern North America. Settles in deciduous forests and river valleys. Prefers moist, fertile, moderately acidic soil. The root system is deep, unbranched, sensitive to damage.
Used on garden plots, as an exotic, unusual tree.
Catalpa is great
 Ornamental tree up to 30 m. Crohn dense, wide pyramidal. The bark is gray, thin-lamellar. The leaves are large, 30 cm long, 15 cm wide, on long petioles. The flowers are large, up to 7 cm, fragrant. The color of the flowers is white and cream with two yellow stripes and purple-brown dots inside, with wavy edges.
Ornamental tree up to 30 m. Crohn dense, wide pyramidal. The bark is gray, thin-lamellar. The leaves are large, 30 cm long, 15 cm wide, on long petioles. The flowers are large, up to 7 cm, fragrant. The color of the flowers is white and cream with two yellow stripes and purple-brown dots inside, with wavy edges.
Duration of flowering tree for 20-25 days. The fruit is a seed box that resembles a long pod of dark brown color. Seeds are stored in paper envelopes or bags in a dry, dark room. Shelf life of seeds 2 years.
Sowing is done in autumn or early spring. For spring sowing, seeds are soaked in water for two days. Place for landing catalpa should choose a well-lit and protected from the wind. Juveniles grow quickly. Growth per year is up to 1 m. Catalpa is magnificently frost-resistant, drought-resistant, but on dry days it requires abundant and frequent watering. Flowering begins on the 12th year of life of the tree, lasts from late July to early July. Spectacular catalpa gorgeous used in landscaping urban parks and squares.
Catalpa ordinary
 Slender deciduous tree with a height of 6-8 m. It blooms from June to July. In the middle of summer fruits appear - pod-shaped boxes with brown seeds. Collect the fruits of catalpa ordinary in autumn and spring. The best time to collect is October - November.
Slender deciduous tree with a height of 6-8 m. It blooms from June to July. In the middle of summer fruits appear - pod-shaped boxes with brown seeds. Collect the fruits of catalpa ordinary in autumn and spring. The best time to collect is October - November.
The tree prefers fertile, cultivated fresh soil. On dry and compacted soil it grows very slowly. The plant is drought-resistant, but on hot days requires frequent watering. In good conditions, catalpa vulgaris rapidly grows and develops. In severe winters, annual shoots suffer, so they are wrapped in material for the winter period.
The plant is planted in early spring before bud break. Autumn planting is made before the onset of frost. Before planting, they dig a shallow hole, the excavated earth is mixed with humus. When planting, care should be taken to ensure that the root collar is above the soil surface at a level of 2-3 m. Care for young seedlings consists in monthly soil loosening, mulching, timely pruning of affected seedlings and branches.
Hybrid catalpa
 Ornamental tree up to 20 m tall. The crown is wide-round with spreading, long branches. The leaves are large, 20 cm long and 15 cm wide, light green, pubescent below. Inflorescences loose, erect with white flowers, inside which there are two yellow stripes and red - brown specks. Duration of flowering up to 25 days. Blooms profusely every year. Fruits - narrow boxes.
Ornamental tree up to 20 m tall. The crown is wide-round with spreading, long branches. The leaves are large, 20 cm long and 15 cm wide, light green, pubescent below. Inflorescences loose, erect with white flowers, inside which there are two yellow stripes and red - brown specks. Duration of flowering up to 25 days. Blooms profusely every year. Fruits - narrow boxes.
For landing hybrid catalpas are recommended well-lit places, protected from wind and drafts. Soils rich in organic fertilizers with weak acidity are preferred. Young seedlings need regular and abundant watering, loosening the soil and mulching. After pruning, intensive growth of shoots is noted.
The hybrid catalpa tree is combined with oak and magnolia. Looks equally impressive in group and single plantings. Used to create alleys and street plantings.
Use of catalpa
The tree serves as an excellent honey plant. In the paint industry, catalpa is also valued, from the seeds of which a drying oil is obtained. In many localities and large cities, the plant serves for landscaping public places, decorating private gardens and house territories. Widely used in traditional medicine.
Photo gallery: catalpa (click on image to enlarge):
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
udec.ru
Catalpa in the Russian garden
Catalpa vulgaris, or bignonioid (Catalpa bignonioides) comes from the southeastern part of North America, where it occurs along river banks.
In its natural habitat, catalpa is a picturesque deciduous tree up to 15 m high; in Russia, the height of an adult catalpa tree is on average 6–7 m. And also a catalpa can grow as a luxuriant multi-trunk shrub.
Catalpa in landscape design
The catalpa has a rounded and rather sprawling crown, which gives a lot of shade. Its large petiole leaves (they are arranged oppositely, sometimes whorled) whole, velvety, heart-shaped; up to 30 cm long and 17 cm wide. In the fall, the leaves of catalpa remain green almost until the onset of cold weather and fall only after frost.
Grown from seed or propagated by cutting, catalpa develops rather quickly. Therefore, the first flowering of a young plant can be observed already at the age of five.
Catalpa bloom occurs in June. At this time, the plant is literally strewn with large paniculate inflorescences - they are erect, resembling candles. The flowers of the catalpa are creamy-white, funnel-shaped, up to 5 cm long (see the title photo). Inside the flower, in the throat, there are red spots, dots and two yellow strokes; The edges of the petals are slightly corrugated.
The fruit of the catalpa is a dark brown box about 40 cm long, hanging down and resembling a pod, with volatile seeds inside. Fruits, even after the opening of the valves and seed eruptions, remain hanging on the branches, giving the catalpa a very unusual and original look.
In gardens and parks, catalpa looks interesting both as a tapeworm and as an element of various ornamental groups of local plants. In the southern regions, the catalpa goes well with magnolias, holly, oriental liquidmarie.
Decorative forms of catalpa
Breeders deduced several decorative forms of catalpa bignoniform with elegant leaf color: - catalpa Bignoniform "Aurea" (“Golden”) with bright yellow leaves, often grown as a seedling; - catalpa Bignoniform «Koehnei"(" Kene ") - has yellow leaves with a dark green spot in the center of the leaf blade and eye-catching green veins.
Of particular interest to Russian gardeners. catalpa bignonevidnaya "Nana" ("Dwarf"). It is more winter-hardy than species plants, therefore it is promising for growing in central Russia. Dwarf catalpa is often grafted onto the strain.
Growing conditions and care for catalpa
Catalp light-requiring, but can grow in partial shade. For soil conditions, these plants are not very demanding, although they prefer fresh, well-hydrated, drained, organic-rich, loamy soils with pH = 7.
When choosing a catalpa for decorating a garden, in addition to its decorativeness, it is valued that this plant is drought-resistant and heat-resistant, it practically does not suffer from diseases and pests. And also the catalpa feels good in difficult urban conditions.
With regular watering catalpa develops better, gives more gains. This plant responds well to fertilizing with mineral and organic (for example, slurry) fertilizers.
Wintering catalpa
The experience of the introduction of a bignonecatalpa in Russian botanical gardens has shown that the winter hardiness of representatives of this species largely depends on the geographical origin of the seeds and cuttings from which the seedlings were grown. Therefore, for the garden in the first place you should look for already acclimatized plants grown in the surrounding areas.
In terms of winter hardiness, catalpa can be attributed to zone 5. Under conditions of the Moscow Region, growths of young plants often freeze slightly, but in summer, catalpa restores the crown. With age, the winter hardiness of catalpa improves, and yet for the winter, young trees are better tied with spruce branches. In the spring of damaged shoots must be cut.
Yellow-leaved varieties of catalpa (“Aurea”) can freeze to the ground in winter and grow back in the summer. Therefore, this variety in regions with cold winters is usually a low shrub.
Catalpa Reproduction
Catalpa can be propagated by seed or vegetatively - summer cuttings.
Seeds of catalpa are sown (in autumn or spring) in the greenhouse or directly in open ground.
Catalpa cuttings cut in summer rooted under the film; their rooting rate without the use of growth stimulants is about 50 percent.
gardenia.ru
Catalpa ordinary
Catalpa ordinaryOr Bignonium - slender deciduous tree, which reaches a height of 6-8 meters. Flowering plant in June and July. During the flowering period, the plant looks like a huge beautiful bouquet. After flowering, the fruits of a long-shaped box are fastened. The plant grows every year and abundantly. Our fruits are not edible. Fruits can be harvested from autumn to spring, although many crack and seeds spill onto the ground. And the optimal time for collecting seeds is October - November.
Catalpa ordinary - photophilous, it grows on soft, deeply cultivated, fertile soil, and on dry and dense soil it develops poorly. The catalpa is rather drought-resistant, but in strong heat it requires watering, to which it responds well with fast good growth. But the presence of close groundwater, adversely affect the plant, and the tree may even die. The heat and frosts of up to - 27 hail the plant tolerates well, but in severe winters annual shoots can freeze.
Growing a catalpa is easy. Planted the plant in a permanent place in a prepared pit (50x50x50cm), do it in the spring before bud break. Can be planted in the fall, but after all the leaves fall and before the onset of frost. Before planting, prepare the pit, dig it well and add humus, and only then plant the plant. At the same time it is necessary to ensure that the root neck is 2-3 cm above the level of the soil surface.
And in the first year of planting it is necessary to mulch, straw, sawdust or manure. Good propagated by catalpa seeds.
Seed catalpa breeds easily. Seeds ripen in October - November, and do not lose their germination for about 2-3 years. Plant seeds do not require any treatment before planting, but it is better to just soak them in clean running water for a day or two. And if you wish, you can use any growth stimulant.They are sown in the fall, freshly harvested, and in the spring. Autumn crops will need to be mulched for the winter, and spring crops are sown on a bed about 3-4 cm deep, watered. Mass shoots appear in May and June. Caring for seedlings is the easiest, during the entire vegetative period they are watered, loosened and weeded. Catalpa from seeds, it develops very quickly and already within a year it grows up to 40 cm in height.
The catalpa grown from seeds has one peculiarity; when transplanting, the plant produces crooked trunks. To get a slender tree, the plant in the first year of life or in the next (it does not matter), cut to the stump, which leads to the stimulation of the appearance of powerful even shoots. From these shoots choose the most powerful, and the rest are removed. If a young sprout weakly develops in thickness, and is strongly drawn out, then it is simply pinched or the top of the trunk is cut off. This method can grow a beautiful, well-shaped seedling in 2-3 years.
Catalpa the beautiful (Catalpa speciosa) family of Bignonium is a large, spectacular tree with a very beautiful large lime heart-shaped foliage (up to 15-30 cm long). Originally from America, where it grows to 30 m.
In the Moscow region, catalpa usually does not grow above 3–5 m, freezes, although reference books claim that it can reach 10–15 m. In total, there are about 11 species in nature. Catalpa blooms in early to mid-July paniculate inflorescences, which consist of large, sweet-smelling orchid-like flowers. The flowers of the catalpa are white outside, and the inside with purple stripes and yellow stamens. When they fade, fruits appear - long pods that can hang until the end of winter. Catalpa is often called macaroni, because its fruits (up to 55 cm) are like hanging pasta.
Garden reference books write that in very hot weather the catalpa sprays juice around itself, which leaves out, and then a circle is formed, very similar to the haloes above the heads of the saints on the icons. Therefore, catalpa and called "God" or "heavenly" tree. In the Moscow region, unfortunately, I have never seen anything like this; probably the heat is not enough for this phenomenon.

Location, soil
The landing site for the catalpa should be warm, sunny, protected from the north winds. It must be remembered that the tree (bush) freezes over, and in severe winters it can freeze out completely to the ground. Do not be afraid of this, catalpa grows to 1.5 m already in the current season. If possible, for the winter you can wrap any covering material (lutrasil, spanbond). It is not necessary to plant on the front seat, as the plant from the series of surprises - it is not clear how it will look this year, how frozen it is. My catalpa grew a tree for 3 years, only the tips of the branches were cold. And after one I will not say that the severe, winter of the tree is gone. I think that the summer was not warm enough, and the catalpa did not have time to finish the growing season and prepare for winter. In mid-June, young shoots came out at the bottom of the trunk (which was trimmed before the shoots). Now the catalpa grows a bush.
Catalpa can grow well in a container that is removed to the basement in late autumn. In this case, it will have to be transplanted annually in a larger pot.
Landing
If the catalpa is planted with seeds, then there is a high probability that freezing will be minimal. But the bloom in this case will be at 5 - 7 year.
Planted catalpa in a mixture of peat, humus (compost), sand and leaf earth in a ratio of 1: 1: 0.5: 1. To this mixture, 80-100 g of total mineral granulated fertilizer, 50 g of wood ash, 40-50 g of dolomite (phosphate rock) flour are added and mixed well. It is recommended to prepare the landing pit in advance, at least 2 weeks in advance. The top layer of garden soil 20cm can be used for the preparation of planting soil. In catalpa branched powerful, and somewhere in the surface root system. The pit should be prepared rather wide than deep (70x40 or 80x50, for example).
If a catalpa is bought in a pot, then it should be soaked before planting in a solution of any stimulator (epine, root, etc.) or simply in water until air bubbles cease to appear on the surface of the water. You plant the plant as it grew in a pot, the root collar (who does not know what it is, look in the dictionary) can be buried no more than 2 cm. After planting and watering, the soil around the trunk is necessary.

Pruning
Catalpa is recommended, and it is necessary, to form a trim. Catalpa wakes up late, when other shrubs are already dissolving leaves, so hurry with pruning is not worth it. Somewhere in early to mid-July, frozen parts are cut over the last living kidney. Slices of more than 1 cm are recommended to cover (for example, “RanNet”).
Breeding
Catalpa propagated by seed or green cuttings. Seeds are planted in March-April. From the seeds, shoots up to 50 cm grow already this year. When propagating with green cuttings, all the qualities of the mother plant are preserved. Cuttings cut from mid to late June. The lower leaves are removed, the upper (you can leave one) shortened, leaving 1/3 of the sheet. The lower oblique cut is made under the lower sheet (which is then cut off), the upper even cut is 1 cm above the last upper sheet. The lower section is dipped first into water, then into a root formation simulator (root, heteroauxin, etc.) and planted into a mixture of peat and sand in a ratio of 1: 0.5. Young saplings in the first winter, and in the second too surely cover. If the cuttings were taken from catalp growing in the areas close to yours, then the plants that grew from them will be more winter-hardy.
Pests, diseases
I did not notice any pests or illnesses in catalpa. Sometimes at the end of the summer can be affected by powdery mildew. Control measures: or spraying with phytosporin.
Application in landscape design
Catalpa as an exotic plant will look good next to the same rare plants in the Moscow region as magnolia, red oak, seven-blade calopanax and ginkgo. In my area, the catalpa grows next to Diabolo and Aurea, and its lime-colored foliage contrasts remarkably well with the yellow and purple foliage of the bladders.
Varieties and types
In the southern regions of Russia, bignoneiform or southern catalpa is also grown and the egg-shaped catalpa. These species can tolerate short-term lowering of temperatures to -20-25 degrees, so in the suburbs they can be grown only in containers.
The standard Nana form adapts well to the conditions of the middle lane and winters well without shelter. In the first year, the vaccination site and the root system are covered. The plant grows with a crown that grows wide. You need to form an annual haircut.
Catalpa is a plant from the Bignoniev family. It is a deciduous tree in height from 5 to 30 m, characterized by a special decorative effect and attracting views almost all year round.
I fell in love with catalpa for beauty during the flowering in summer, when other ornamental shrubs and trees are already fading. Flowers of catalpa are large inflorescences (up to 50 flowers), extraordinarily beautiful flowers, very similar to orchid flowers, and even with an apple scent.
The fruit of the catalpa is a hanging box-pod up to 40 cm long. It is interesting that the fruit hangs on the branches almost all winter, giving the tree a rather original look and arousing the curiosity of the passers-by.
There is a legend that the catalpa is a tree of elephants and monkeys, when the elephant's ears and monkey tails, on the quirk of the Buddha, merged into this peculiar tree.
Description
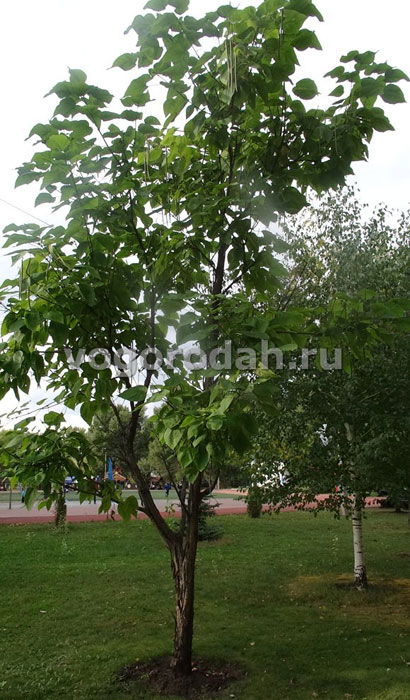

Large, heart-shaped leaves of catalpa do not turn yellow almost until frost.
Catalpa blooms from mid-June and lasts about 4 weeks, fragrant flowers, have a delicate apple flavor.
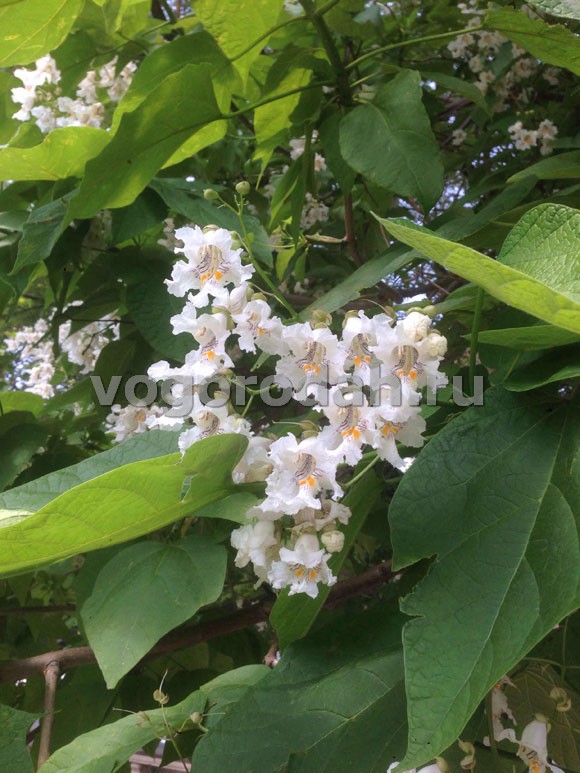

The fruits are long pods, filled with seeds, batts that can hang on a tree all winter.
Catalpa is frost resistant, but young plants need to provide shelter for the winter.
Grown catalpa seeds or cuttings.
Types of catalpa
There are 11 types of catalpas that are well adapted to the conditions of central Russia, withstand cold, and even quite strong. Three types of catalpas have become well-established on the territory of Russia:
- ovoid - shrub with several trunks with a short growing season.
- magnificent - a ten-meter tree with a wide crown and large leaves, fast-growing,
- bignoneiform or common - blooming up to 1.5 months with spreading branches and rounded crown, catalpa.
In turn, the bagony-like catalpa, according to the elegance of the foliage, is distinguished into four varieties:
Aurea - sprouting culture with golden-yellow foliage at the beginning of the growing season;
Nana - a tree up to 4 meters in diameter, with a ball-like crown;
Kene - catalpa, different from other varieties of dark green middle and veined on yellow leaves;
Purpurea - at the time of blooming the leaves have red-brown shades.
Growing catalpa from seed
The seeds of catalpa are peculiar, similar to bean pods. Therefore, this plant is called "bean tree"
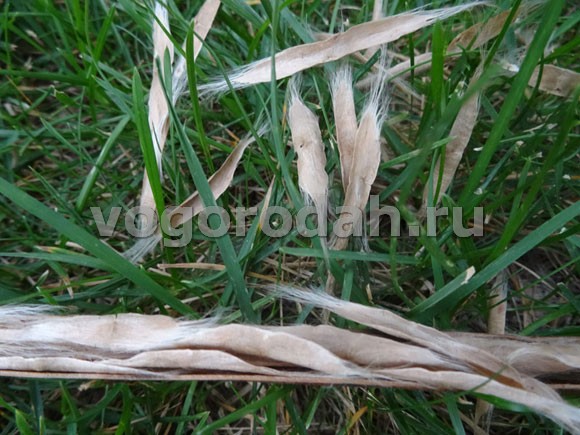

Sowing catalpa seeds occurs in March, before sowing, you can put the seeds in the water for several hours. Seeds are laid out on the surface of the soil and sprinkled with a thin layer of earth, then placed under the film. At a temperature of 20-25 degrees, catalpa seeds germinate within 3-4 weeks. Care of seedlings continues immediately before transplanting into open ground in a place protected from drafts.
A plant grown from seed develops quite quickly, giving a rise in the meter per year.
If you want to purchase catalpa seeds, then you can do it in my group, “Flowers for home and garden” in Odnoklassniki.
Planting catalpa seedlings
Catalpa perfectly conveys the acclimatization properties of its place of cultivation. Therefore, it is best to take a catalpa seedling in a nursery located in the same climatic zone - then the catalpa will be maximally acclimatized for cultivation in its area.
For example, the seedlings that I sell are grown in the southern Urals, in the zone of temperate continental climate. In the summer the air here warms up to 40 or even 43 degrees, and in winter the temperature can drop to - 45 degrees.

Optimal for planting take annual catalpa seedling. It is suitable as a place lit by the sun, and partial shade (you can along the garden paths, in the center of the lawn or near the reservoir). It is also worth considering that large leaves and branches of the catalpa may break due to gusts of wind, therefore when planting a tree it is better to choose a place protected from the winds.
Catalpa is not very demanding for soil features. Preferably - moist, enriched with organic matter, not too acidic, and drained soil.
The optimal time for landing catalpa - early spring.
For planting seedlings digging a hole, a depth of up to a meter. If you want to plant the catalpa trees in a row, then you should leave a distance of about 3 meters between them.
The current time, when compared with other geological epochs, is by no means the best either in climatic conditions or in the richness of flora and fauna. It could be called the era of gray mediocrity.
This fully applies not only to ancient groups of plants and animals, which have become extinct completely or only a few survived to this day, but also the most evolutionarily advanced angiosperms. Magnolia, tulip trees, catalpas, horse chestnuts, lilacs and other beautifully flowering trees and shrubs of the Tertiary period have been replaced by birch, aspen, willow, with their small leaves and inconspicuous flowers. And our deciduous trees - oak, beech, maple, elm, ash, are also pollinated by the wind and have ordinary-looking flowers. Similarly, giant mammals, represented in the Tertiary period by numerous species of elephants, rhinos, indrikoteriy, cave bears, saber-toothed feline replaced mice, rats and other trifles.
The main reason for the drastic depletion of flora in temperate latitudes was a sharp cooling in the Quaternary, accompanied by a grandiose glaciation. Glaciers have destroyed the luxurious tertiary flora in Europe and most of Asia. Cooling forced the plants to retreat farther south, until on their way an insurmountable obstacle did not become the mountain ranges stretching in the latitudinal direction (from west to east), seas and straits. Only in two regions of the northern hemisphere - in East Asia and in the east of North America, where such natural barriers were absent, the tertiary flora was able to retreat to the south, and then, when the climate warms, return to temperate latitudes. Of course, in a more impoverished state - not all species survived the “great migration”, many died out, unable to withstand the sharply intensified competition. Nevertheless, in the modern forests of China, Korea, Japan, and the east of the United States, we can imagine what the ancient Tertiary forests looked like.
A typical tertiary forest tree is catalpa. One glance at her is enough to be convinced of its antiquity, so it differs from our birches and aspens. Large beautiful "burdock" leaves, gorgeous bell-shaped flowers with a beautiful pattern, collected in large candelabrabropy inflorescences, unusual long fruit - boxes, reaching half a meter or more in length and resembling pods. The modern distribution of catalpa and a small number of species that survived to our time, also indicate its antiquity.
Remnants of luxury
Now botanists have only 11 types of catalps. Some of them grow in the tropical mountain forests of the West Indies - in Cuba, Jamaica, Haiti. In temperate latitudes, only 6 species are known in nature, 2 of which grow in the eastern United States, and 4 in China.
American species
– CatalpabignonioidesWalter.Americans call it Southern Catalpa, because it grows south of another local species, the catalpa, beautiful. A small tree, in the homeland up to 15 m, in a culture rarely above 4–5 m, with a low stem, sometimes begins to branch almost from the ground. The bark is light brown; leaves are large, 15–20 cm long and the same in width, from heart-shaped to ovate, usually with two lateral lobes, less often entire, below, with short pubescence, dark green, when rubbed with an unpleasant odor. The inflorescence is a strongly branched large panicle with numerous flowers, in this species the most multi-flowered inflorescence. The flowers are small, pale yellow, rather nondescript. It sets numerous fruits, a box up to 35 cm long, but usually much shorter, of a cylindrical shape, oval seeds, up to 2.5 cm long and 0.7 cm wide. It blooms in mid-summer.
– Catalpaspeciosa (WarderexBarney)DEngel.The American local name is Northern Catalpa. Quite a large tree up to 30 m tall at home, in culture usually 10–15 m, with brown furrowed bark. The leaves are large, 15–30 cm long, heart-shaped, densely pubescent below, glabrous above, light green, when rubbed without odor. The inflorescence is paniculate, the flowers in it are much smaller than those of Bignonium catalpa, the flowers are large, a rim up to 5 cm in diameter, pure white with purple spots and yellow stripes in the throat, very beautiful, with a light aroma like the smell of horse chestnut flowers. Fruits sets significantly less than the previous form. The boxes are cylindrical, long - up to 55 cm, and thick, reach the thickness of a human finger, the seeds are elongate-oval, large, 2–3 cm long and up to 1 cm wide, blooms in the first half of summer.
Chinese species
Catalpa ovoid – CatalpaovataG.Don.The Chinese name Ji - River tree. A medium-sized tree, at home up to 15 m tall, not more than 10 m in culture. The leaves are large, up to 20–25 cm in length and width, broadly ovate, usually with two lateral lobes, bare or slightly pubescent along the veins from above, green. Inflorescence - candelabrous multicolored panicle. The flowers are medium in size, light yellow, with corrugated edges, inside with two yellow stripes and numerous small purple dots, fragrant, with a fairly strong pleasant aroma, reminiscent of the smell of lily of the valley. The fruits are tied abundantly, a box up to 20–30 cm long, thin, only 5–7 mm thick, often curved, sometimes even curling. Seeds are oblong-oval, small, 6–8 mm long and about 3 mm wide. It blooms in mid-summer. Widely distributed in northern China, especially in Shandong Province, which in ancient times was called the Country River Tree. Now it is difficult to establish the initial natural range, since it is widely cultivated as a forest and ornamental tree.
Catalpa Bunge – CatalpabungeiC.A.Meow The Chinese name Chui-su - Autumn tree. The tree in the homeland is 8–12 m tall, with a dense crown. Leaves compared to other species of medium-sized: up to 15 cm in length and 8 cm in width, triangular-ovoid or oblong-ovoid, entire or with 1-4 pairs of teeth at the base; when blooming red, then turn green. The inflorescence is a corymbose few-flowered brush, the number of flowers is from 2 to 12. The flowers are medium and large, of various colors - white, dark pink, light red to light purple, with dark purple spots and stripes on both sides. Decorative quality is high, especially in forms with brightly colored flowers. Fruits fastens rarely, the box is quite long - up to 45 cm, but thin - about 6 mm. The seeds are narrow, elongated-oval, small, about 1 cm long and up to 2 mm wide. It blooms in the homeland in the first half of summer. Distributed in northern and eastern China from Beijing in the north to the lower Yangtze River in the south, in the west to Gansu province.
– CatalpafargesiiBurr.Close to the previous view. Quite a large tree, at home 25-30 m tall. Leaves of medium size - up to 20 cm long and 12 cm wide, ovate or triangular-heart-shaped, thick, leathery, bottom with thick yellow pubescence or bare, slightly pubescent from above. The inflorescence, as in the previous species, is a corymboid brush, slightly more many-flowered, consists of 7–15 flowers. The flowers are medium and large, from light pink to light purple, with purple spots on top. The box is cylindrical, tapering towards the end, very long, up to 80 cm, but narrow - 5–6 mm, the seeds are elongate-oval, small, about 9 mm long and only about 2.5 mm wide. Blossoms in the first half of summer. Due to the large, brightly colored flowers is very decorative. It grows wildly in the mountains of southwestern China, in the provinces of Sichuan and Yunnan, and is widely cultivated from Beijing in the north all the way to the southern tropical provinces.
European botanists secrete a species from catalpa Farghez Duclos – f.duclouxii (Dood)Gilmourwhich is different ovoid-pointed, at a young age, three-bladed, fluffy leaves. The flowers are slightly larger than the typical species, with red spots from the bottom, purple. Chinese botanists refer it to the main species.
Tibetan catalpa – CatalpatibeticaForest.This species, close to the ovoid catalpa, was described later than the others - in 1921. Shrub or small tree about 5 m tall. The leaves are similar to the leaves of ovoid catalpa, broadly ovate in shape, rather large - about 22–25 cm in length and width, dark green, naked above, pubescent from below. Inflorescence of corymbose-paniculate, large, up to 25 cm long, hairless. The flowers are large, up to 5 cm in diameter, yellowish-white with light purple spots in the throat. Fruits are cylindrical, tapered towards the end, striped, about 30 cm long and 1 cm in diameter.
Seeds are oval, up to 2.5 cm long and up to 6 mm wide. Blossoms in the first half of summer. It grows in mountain forests and thickets in the south-east of Tibet and north-west of Yunnan Province at an altitude of 2400–2700 m.
Catalps in Russia
In our country, the catalpa in culture has been known for about 100 years, but it has been widely spread only in recent decades. Now it can often be found in parks and on the streets of cities and towns in the Central Black Soil Region and to the south.
Often found in the Belgorod region, especially in its west. Here it is completely winter-hardy, does not suffer from frost even in the most severe winters. It grows a low-stem tree with a rounded crown. It blooms in mid-July, the inflorescences are large, many-flowered, but rather nondescript yellowish in color. Early in the flowering season, in the nursery often in the third year, low, well-branched seedlings, barely reaching 1 m in height, bloom and bear fruit.
East and North, in the Voronezh region, dominates beautiful catalpa . This is the most winter-hardy species, in the extremely harsh winter of 2005–2006, when at the end of January the temperature dropped to -40. -42 ° C and many fruit-trees were very cold; neither young nor old trees suffered from the beautiful catalpa. In the gardens and parks of Voronezh, catalpa trees over 50 years old now grow, reaching 10 m or more in height. Most likely, this species came to Voronezh from the Forest-Steppe Experimental Station, where the well-known domestic plant breeder N. K. Vekhov worked a lot with catalps in the 1930–1950s of the last century. Now beautiful catalpa is intensively propagated in municipal and private nurseries of the Voronezh region.
According to the number of trees planted in parks and on the streets, for example, Rossosh, it takes a leading place among other plants. Beautiful catalpa blooms in the third decade of June - two or three weeks earlier than bignoneiform catalpa. Her inflorescences are smaller, but the flowers themselves are large and very beautiful. Among the minuses of the beautiful catalpa is its lack of drought tolerance: in hot and dry weather, trees growing without irrigation, luxurious large leaves tangle and wilt.
A catalpa is quite common in the south of European Russia, especially in the Rostov region, in the Kuban, Stavropol, and the republics of the North Caucasus. I collected its seeds in the Rostov region (Novocherkassk), the Krasnodar Territory (Krymsk), in the south-east of Ukraine (Donetsk region) and sowed in my garden. Catalpa is a very good subject for research, as it grows quickly and starts blooming early. It turned out that in the southern areas we have a common hybrid species, one of whose parents is a beautiful catalpa. Regarding the second species, I do not have complete certainty; equally it could be catalpes bignonevoid and ovate. Such hybrids have long been known. The hybrid between the oval-shaped catalpa and the beautiful catalpa is called catalpa Galle (C.x galleanaDode).In the 1940s, N. K. Vekhov received such hybrids at the Forest-Steppe Experimental Station, while the hybrids between catalpes of bigny-shaped and beautiful bloomed, but did not bear fruit, while the hybrids between catalpa ovoid and beautiful not only blossomed, but also abundantly bore . Therefore, I am inclined to believe that hybrid catalpes that are common in the Kuban region, in the Rostov region and in the south-east of Ukraine belong to the Galle catalpa species. Depending on the place of cultivation in trees of hybrid catalpa, the signs of parental species are expressed to varying degrees.
The north of its cultivation area, the more pronounced the signs of beautiful catalpa are: the leaves are light green, the inflorescences are smaller and contain fewer flowers, the flowers themselves are larger, the flowering is earlier (though later the catalpes are beautiful), the fruit-boxes are longer and thicker. Conversely, more southerly forms bloom late, in mid-July, their inflorescences are very large, multi-tiered, the flowers themselves are smaller, although they look more like flowers of a beautiful catalpa, the boxes are shorter, but the thickness is closer to the boxes of a beautiful catalpa. In late-flowering forms, the leaves are rubbed with an unpleasant odor. The hybrid origin of plants is indicated by the heterogeneity in the progeny of each of the geographical forms, it also splits, although the magnitude of variability is smaller than when comparing seed progeny from different forms.
All types of catalps have 40 chromosomes, and they quite easily form hybrids when crossed between themselves. The ability to easily form hybrids between distant species is characteristic of ancient groups of plants, so this is yet another proof of the antiquity of the genus. I did not have to meet Chinese types of catalps on the streets and in the parks of Russia. Catalpa ovoid got into my garden under curious circumstances. I have long dreamed of having a pink catalpa - Bunge or Forgeza. Therefore, when visiting China in September 2003 and 2004, I intensively searched for their seeds. I didn’t have to meet Catalpa Forgez in Northern China even in the botanical gardens, but Catalpa Bunge, as the tablets showed, was pretty ordinary. But there was no fruit anywhere on its trees, since this species has very poor fruit bearing (which may indicate its hybrid origin). In one of the botanical gardens of Shandong Province, a whole grove of Bunge catalpa trees grew, but there was not a single “pod” on them, although there was a lot of egg-shaped “pods” in the nearby grove of catalpa. Finally, after a long search, on the ground managed to find one box. Trees grown from seeds first bloomed in 2008, and, alas, it turned out to be an egg-shaped catalpa. Of course, it is also interesting for its “pocky” because of the numerous purple dots with fragrant flowers, but they are pale yellow, not pink. So Catalpa Bunge still remains an impossible dream. Apparently, it is absent in our country, as well as the catalptic Farghez and Tibetan.
A few words about catalpa widely discussed on Internet forums Duclos from the Sochi Arboretum. I saw it long ago, back in 1980, at the end of May, when its tree was in full bloom, and without any exaggeration it was then the most beautiful in the whole garden. A rather large leafless tree was covered with large standing panicles of bright purple flowers.
But the long fruits, characteristic of catalpa, are boxes, absent both on the tree and under it. I very much doubt that this is really a catalpa, perhaps this is some kind of Chinese paulownia with bare leaves, different from the widespread felt paulownia. Paulownia and catalpa are very similar in appearance to the tree, wood structure, leaves, inflorescences and flowers. You can distinguish them by fruit and seed. In paulownia the fruits are round or oval, often with a toe at the top, and the seeds are very small, surrounded by a narrow wing. The absence of fruits and seeds in Sochi trees does not allow using this important distinguishing feature. But one more peculiarity of paulownia is to bloom in spring before leafing (unlike catalpa, which blooms in summer when the leaves are fully opened), allows us to assume with sufficient confidence that the Ducallo arboretum's catalpa is actually paulownia.
A few words about catalpa winter hardiness. In the majority of reference books on gardening, they are recommended only for the most southern regions of the European part of Russia, where the absolute minimum does not fall below -20 ... -25 ° C. As I noted above, this is not true.
In regions with long and hot summer, the catalpa trees are beautiful, bignonic, ovoid, and their hybrids withstand frost temperatures down to -35 ° C or even less. But winter hardiness is formed gradually. In seedlings, especially those grown from seeds of southern origin, in the first or second years of life, before the onset of cold weather, the wood in the upper part of the growth does not have time to ripen, and they frost up. Gradually, the growth of shoots and their maturation begin to adapt to the peculiarities of the local warm season, and frosting stops. Sometimes this “adjustment” can last long enough. So, one of the seedlings of the hybrid catalpa from seeds collected in the Donetsk region, froze heavily annually in my garden for 5 years. After another severe frosting in the provocative winter of 2003–2004, when after long warm frost-free weather in late February, the frost hit, and the temperature dropped at night to -28 ... -30 ° C, I decided to uproot it and throw it out of the garden. However, because of the employment of the hand, they did not reach it, the tree recovered over the summer and then safely overwinter. In the summer of 2005, it bloomed for the first time, and the next, extremely harsh winter of 2005–2006, to my great amazement, did not suffer at all. Obviously, the cause of freezing was not the genetically programmed ability of the plant to tolerate only moderate frosts, but its slow adaptation to the vegetative period of the new homeland. As soon as his growth began to "fit" in our growing season, the plant was able to prepare well for the winter and stopped freezing.
Therefore, I believe that the main cause of catalpa freezing in the northern regions is not winter, but short and cool northern summer. In order for the plant to adapt more quickly to it, it is better to grow it from seeds. In the middle - end of August, the seedlings need to pinch the top of the head for better aging of the wood. This procedure, if necessary, should be repeated for several years. For safety net, you can grow a tree in a container - from spring in the open air, and in the late fall to clean the basement. At the same time, he also needs to pinch the top, and after 2–3 years to land in open ground.
It is undesirable to grow seedlings for open ground in a greenhouse, because there both summer temperatures and the length of the growing season are very different from the conditions of open ground. And the plant at a young age adapts precisely to greenhouse conditions. I repeatedly had to observe a strong freezing in the first years after planting seedlings of winter-hardy fruit and ornamental crops grown in the greenhouse into the open ground.
Catalpa breeds very easily. Seeds do not require stratification, and germinate in spring sowing. Light is necessary for seed germination, so they are sown on the surface of a well-moistened soil, lightly sprinkling with peat, compost or sand. Then the ridge is covered with a loosely fitting polyethylene film, preferably matte, which is removed after germination. Seedlings grow quickly, and in the first year they reach 30–40 cm. The following spring they are planted in the nursery for further rearing, and a year later some of them begin to bloom.
A.I. Sychov
author Kulakhmetova I., photo of the authorCatalpa ordinary, or bignoniform (Catalpa bignonioides) comes from the south-eastern part of North America, where it occurs along the banks of the river. In its natural habitat, the catalpa is a picturesque deciduous tree up to 15 m high; in Russia, the height of an adult catalpa tree is on average 6–7 m. And also a catalpa can grow as a luxuriant multi-trunk shrub.
Catalpa in landscape design
The catalpa has a rounded and rather sprawling crown, which gives a lot of shade. Its large petiole leaves (they are arranged oppositely, sometimes whorled) whole, velvety, heart-shaped; up to 30 cm long and 17 cm wide.
In the fall, the leaves of catalpa remain green almost until the onset of cold weather and fall off only after frost. Grown from seeds or propagated by grafting, the catalpa develops rather quickly. Therefore, the first flowering of a young plant can be observed already at the age of five. The flowering of catalpa occurs in June.
At this time, the plant is literally strewn with large paniculate inflorescences - they are erect, resembling candles. The flowers of the catalpa are creamy-white, funnel-shaped, up to 5 cm long (see the title photo).
Inside the flower, in the throat, there are red spots, dots and two yellow strokes; the edges of the petals are slightly corrugated. On the photo: branches of catalpa with fruits. Catalpa's fruit is a dark brown box about 40 cm long, hanging inside and resembling a pod, inside which there are volatile seeds. Even after disclosing the leaves and seed eruption, the fruits remain hanging on the branches, giving the catalpa a very unusual and original look. It looks interesting in catalpa gardens and as a tapeworm, and as an element of various ornamental groups of local plants. In the southern regions, the catalpa goes well with magnolias, holly, oriental liquidmarie.
Decorative forms of catalpa
Breeders deduced several decorative forms of catalpa bignoniform with elegant leaf color: - catalpa Bignoniform "Aurea" (“Golden”) with bright yellow leaves, often grown as a seedling; - catalpa Bignoniform «Koehnei"(" Kene ") - has yellow leaves with a dark green spot in the center of the leaf blade and eye-catching green veins. Of particular interest to Russian gardeners catalpa bignonevidnaya "Nana" ("Dwarf"). It is more winter-hardy than species plants, therefore it is promising for growing in central Russia. Dwarf catalpa is often grafted onto the strain.
Growing conditions and care for catalpa
Catalp light-requiring, but can grow in partial shade. For soil conditions, these plants are not very demanding, although they prefer fresh, well-hydrated, drained, organic-rich, loamy soils with pH = 7. When choosing a catalpa for garden decoration, in addition to its decorative effect, it is practically drought- and heat-resistant that does not suffer from diseases and pests.
And also the catalpa feels good in difficult urban conditions. With regular watering, the catalpa develops better, gives more growth. This plant responds well to fertilizing with mineral and organic (for example, slurry) fertilizers.
Wintering catalpa
The experience of the introduction of Bignone catalpa in Russian botanical gardens showed that the winter hardiness of this species depends to a large extent on the geographical origin of the seeds and cuttings from which the seedlings were grown. Therefore, for the garden, in the first place, it is necessary to look for already acclimatized plants grown in the nearest areas. According to the winter hardiness, catalpa can be attributed to zone 5. In the conditions of the Moscow region, the growth of young plants often freezes, but in summer the catalpa restores the crown.
With age, the winter hardiness of catalpa improves, and yet for the winter, young trees are better tied with spruce branches. In the spring, damaged shoots must be cut. Yellow-leaved catalpa varieties (“Aurea”) may freeze to the ground in winter and grow back in the summer. Therefore, this variety in regions with cold winters is usually a low shrub.
Catalpa Reproduction
Catalpa can be propagated by seed or vegetatively - summer cuttings. Catalpa seeds are sown (autumn or spring) in the greenhouse or directly into the open ground. Catalpa cuttings cut in summer are rooted under the film; their rooting rate without the use of growth stimulants is about 50 percent.
How to grow a tree "catalpa"
Want to surprise friends and acquaintances? Plant a tree with the name of catalpa (if climate allows, of course, about this below). The catalpa is useful as a dacha decoration, there is no “fruit” benefit from it, and the catalpa also has no useful qualities and properties. But here are its decorative qualities on high.
Catalpa grows very quickly, resistant to a variety of adverse conditions, requires a minimum of care. It will look good in the foreground as a single planting and as a component in the alleys plantings. The large flowers of catalpa are beautiful and delicate, from a distance they are very similar to the flower of a foxglove, and the inflorescences in which they are collected do not differ from chestnut trees (meaning blooming horse chestnut) .Thanks to the large leaves of the heart-shaped catalpa, it was called the “tree with elephant ears”.
Biological features of the tree
Catalpa (Latin Catalpa) is a plant that belongs to the bignonium family. There are a total of 10 types of catalps. Of these, only 4 in our country are grown in the southern regions. All members of this genus are very beautiful and, as a rule, deciduous (less often evergreen - much depends on climatic conditions) plants.
The crown is almost all round, very shady because of the large leaves. The decorativity of the catalpa lies in the fact that its leaves do not turn yellow in the fall but stand green almost until frost. The colors of the catalpa are white or creamy. Collected in large inflorescences.
The fruit is also amazing - a green pod resembling an icicle and containing a large number of seeds flying after opening that resemble dandelion seeds. Fruits of catalp containing seeds can hang throughout the winter.
In the courtyards, cottages and plots are most often found and. Both of them are brought from North America, their homeland. I must say that there they can reach a height of up to 30 meters!
In our conditions, it is rare to find a catalpa whose tree exceeds 10-12 meters. The stem of a magnificent catalpa is almost always slender, covered with gray bark with thick plates. The crown is pyramidal, wide, very thick. The leaves of the magnificent catalpa bloom earlier than in other species.
Veleklepolnaya catalpa grows very quickly - growth can reach one meter per year. This species is relatively light-requiring and drought-resistant, therefore it does not tolerate close groundwater, as well as any flooding, including spring water. So if your site is located in the flood zone, it is not recommended to plant a catalpa. Read also: Japanese Spirea - photo, planting, cultivation and care - the view is characterized by its spreading branches and a wide round crown.
The bark, in contrast to the catalpa, which is magnificent in bignoniform light brown color, is also lamellar, however, the plates are thinner. The leaves are very large and wide, pubescent and naked above. Growth to. Bignoniavaya slower.
Unlike its predecessor, it places higher demands on moisture. It also tolerates frost well. The most famous catalpa cultivar is the beautiful “Pulverolenta”, “Aurea” (better known as shrub grown in parks up to 2 meters high), “Koehnei” and “Nana” (a dwarf form of catalpa, spherical, characterized by winter hardiness in the conditions of the South of Russia, is successfully grown by gardeners even in the middle lane, Moscow region). In gardening gardens and plots, the other two catalpes are most often used - the Chinese "" (Catalpa ovata) and (Catalpa hybrida) which is nothing more than hybrido m catalpa bignonevidnoy and K. ovoid.
Catalpa bloom
Catalpas begin to vegetate actively in mid-second half of May and stop active growth at the end of August. Most catalp species fall off preserving the green color of the leaves. The catalp flowers are very beautiful and fragrant, often pure white, but they are also cream-colored. Read also: Scented , pleasantly smelling plants for the garden. Flowers are large (5-7 centimeters), often covered with dotted spots. The panicles in which the flowers are collected can even reach 20 centimeters in length if the care of the catalpa is correct. Catalpa most often (depending on the region, of course) begins to bloom in the 5th year after planting in late June or early July, which is good for gardeners. these terms are no longer blooming with other trees. The pods (because of which the plant was called “the pasta tree) with catalpa seeds can grow almost to half a meter in length, usually 35-40 centimeters. If there are no strong winds, then almost all of them are hanging on a tree all winter. Photo 2: From left to right: Bignonemic catalpa flowers, gorgeous catalpa leaves, hybrid catalpa pods
Catalpa - how to grow care
Place for planting catalps choose a sunny, protected from cold winds - drafts, especially frost - the main enemy of not only young catalpa seedlings, but even a fully grown tree. The seedling is planted in a hole to a depth of 70 to 120 centimeters. For planting catalpas, a garden mixture of peat, sand, humus and leafy soil (ratio 1-2-3-2) is well suited. Do not be lazy to add 5-7 kilograms of wood ash to your catalpa seedling when planting, you can add a little phosphate flour - it will be more reliable, all the same, the tree is fastidious. For planting catalpa seedlings, it is recommended to choose sunny, protected from the wind places, since the large and delicate leaves, characteristic of all species, are heavily damaged in drafts.
Plants are planted to a depth of 0.8-1.2 m. Reference: Growing dogwood is useful, beautiful and tasty The best acidity of the soil for catalpa is ph7. Catalpa easily tolerates transplant, which is best done in the spring, and early.
Catalpa can be propagated by layering, cuttings and seeds, which it has in abundance. Watering is not frequent or abundant - 15-18 liters under a tree, no more than once every seven days, if there is no prolonged drought. Catalpa is very good at feeding. (growth accelerates very significantly). Top dressing bring one, two maximum three times in one season.
As fertilizers use the same slurry (approximately 5 liters per tree). Cutting the catalpa should be done annually, in the spring it is necessary to remove dry branches affected by frost. After cutting the catalpa, it restores the crown just before the eyes, so grasp the secateurs to form it without fear. It is better to protect young seedlings of catalpa from frosts with burlap, and to ground the ground in tree trunks. In severe frosts, young seedlings should be covered completely, for example, just like covering roses from frost At the very least, cover the same burlap. The older the catalpa becomes, the less it will need antifreeze protection. The experience of growing catalpes clearly and repeatedly showed that their winter hardiness and cold resistance depends on those seeds and cuttings from which the seedlings are grown. Therefore, for planting, try to buy seeds and seedlings of catalpa from the region closest to you (when it comes to ordering seeds by mail).
Below are other entries on the topic "Cottage and garden - do it yourself
Catalpa is a very beautiful and spectacular deciduous tree, reaching a height of 5-6 meters in the climate of the Central strip. It grows without problems on rich, light and well-drained soils, in fully lit places, moisture-loving.
Duration of flowering 25-30 days (from mid-June). Each inflorescence contains up to 50 flowers. Fruits, thin long (up to 40 cm) green "icicles", remain hanging on the branches for most of the winter, giving the tree an original look and arousing curiosity of passersby.
The genus includes 10 species. Basically, three varieties are cultivated. Catalpa is beautiful (Catalpa speciosa).
- Homeland - the United States, where it reaches 35 m in height. In central Russia, grows a small tree or large shrubs. Beautiful, large, up to 7 cm, fragrant flowers of creamy white color, with a wavy edge, inside with two yellow stripes and numerous purple-brown dots. Fruits, up to 45 cm long, decorate a tree from the second half of summer. Resistant in urban environments to dust, smoke and gases.
Beautiful Catalpa (Northern Catalpa) Bignonia catalpa, or ordinary (Catalpa bignonioides).
- Originally from southeastern North America. Tree up to 20 m tall, with spreading branches forming a wide-round crown. It grows pretty fast. The first bloom - in the fifth year of life.
Bignoniform catalpa (Southern Catalpa) Catalpa ovoid (Catalpa ovata).
- Comes from China. In height reaches 6-10 meters. Crown spreading. Flowers are fragrant, creamy-white, in panicles, up to 25 cm long. It blooms in July and August. Light-requiring, demanding of moisture and soil fertility.
Catalpa ovoid (Yellow Catalpa)
Landing features
Using: catalpa successfully combined with oak, deciduous magnolias, but looks spectacular in single plantings. Location: recommended sunny places protected from the wind, as large and delicate leaves of catalpa in drafts are severely damaged (the distance between plants is 4-5 m). The root neck should be at ground level, and the root ball should be 10-20 cm above the level land (after planting occurs subsidence and compaction of the soil).
Before planting, the root system must be saturated with moisture. Soil mix: humus, leaf soil, peat, sand (3: 2: 1: 2). When planting, ashes (5-8 kg) and phosphorus flour (50 g) are also introduced. Mulch with peat (5-7 cm).
Top dressing: In a season, feed 2-3 times with slurry (1:10), 1 bucket for each adult plant. One dressing with organic matter can be replaced by Chemira-wagon (120 r / sq. M). Before dressing - abundant watering.
Watering: In the heat it is watered once a week for 2 buckets per plant. If summer is not hot, watering can be reduced to 2-3 times a month. Loosening: on a spade bayonet, while removing weeds.
Haircut, trimming: dry and damaged branches are cut out in spring. Diseases and pests: stable. Occasionally Spansky cannon damage (spraying: kinmiks, detsis, karbofos - twice).
Preparing for the winter: Young plants should be tied with spruce branches and covered with dry leaves (removed in spring). To protect frost from standard plants, wrap in two layers of sackcloth or lutrasil.
In adult trees, it is desirable to mulch pristvolny circles (dry leaf layer of 15 cm). Vegetation: from the middle of May. Shoot growth stops in August.
Fall foliage comes after frost. The leaves fall completely green. Breeding: catalps successfully multiply without any special treatment with seeds and summer cuttings (survival rate of about 50%). Materials used:
- Desktop log grower " I love flowers»# 1 January 2009
Please rate this article in our ranking:
11 comments
Botanical name: Catalpa (Catalpa), a genus of the family Bignonium. Catalpa homeland: North America. The soil: fertile, moist, slightly acidic, fresh.
Watering: abundant. Maximum tree height: 30 m. Tree's average lifespan: up to 100 years. Landing: seeds, cuttings.
Spherical catalpa
Deciduous tree with a spherical crown. The leaves are large, heart-shaped, whorled 30 cm long and 17 cm wide. In the autumn do not turn yellow.
Funnel-shaped flowers, up to 7 cm, fragrant, have a pleasant apple aroma, white, sometimes cream with dark spots, gathered in erect inflorescences - panicles. Flowering begins in mid-June and lasts up to 4 weeks.
The fruit is a long box, up to 40 cm, filled with seeds - volatile. Fruits hang on trees throughout the winter, which gives the tree an unusual look. The wood is soft, flexible, not rotting.
Catalpa prefers well-moistened soils and bright places. Hardy. When the temperature drops, the tree sheds green foliage.
All types of catalps are decorative.
Landing and care for catalpa
Landing catalpa produced in a well-lit area, protected from the wind. Plant the plant at a depth of 1 - 1.2 m. For planting suitable soil mixture of humus, leaf soil, sand and peat.
Before planting, the ground should be fertilized with wood ash and superphosphate and pour plenty of water over the pit. Soil acidity should be neutral. With proper care, flowering will begin in the fifth year. Young plants often undergo frost.
For the winter period their trunks are wrapped with spruce branches or burlap. The ground under the tree is covered with a thick layer of leaves. The coating is removed in early spring, when severe frosts stop.
In early spring, pruned branches are pruned. Taking care of a catalpa consists in the timely removal of weeds under it and loosening the soil to a depth of 30 cm. The plant does not require frequent watering, it is enough to water the catalpa once a week.
Top dressing is done during planting and during the growing season. As a top-dressing suitable rotted manure.
Reproduction of catalpa seeds and cuttings
Catalpa propagated by seeds and cuttings. Before planting, seeds are pre-soaked in warm water for 7-12 hours. Sowing is done in February - March in place with diffused sunlight.
Seeds are sprinkled with a thin layer of earth and covered with a film or glass. With regular watering and a temperature of 15-25 degrees, seedlings will appear within a month. After the emergence of shoots shelter removed.
Caring for seedlings continues until May, then the seedlings are moved to the open ground. Catalpa cutting is done in the second half of summer. Cut cuttings 10 cm long, plant them in a mixture of peat and sand. Care is the same as in the reproduction of catalpa seeds.
When sprouts appear in saplings and a formed root system, they are transplanted into open ground.
Catalpa Pests and Diseases
The catalpa tree is resistant to pests and diseases. The main pest of the plant is Spanish fly. You can get rid of it by sprinkling the tree with kinmiks or decis.
When insects appear on the kidneys, the catalpa should be treated with insecticides before bud break. Otherwise, the shoots are deformed. In order to avoid infection with the fungus Verticillus, you need to monitor the condition of the soil.
It should be sufficiently loose, unconsolidated and well water flowing. The fungus leads to drying and death of the plant. Sick tree catalpa pictured:
Common types of catalpa
Below you can see the most common types of catalpa. The obtained information will help you choose the right tree for your garden.
Bignonium catalpa
Bignonia catalpa (Catalpa bignonioides) is a tree up to 20 m high. Spreading branches form a wide-round crown. The bark is light brown and thin-lamella. The leaves are large, 20 cm long and 15 cm wide, resemble lilac leaves.
From above naked, light green, pubescent from below. The flowers are white, with red-brown specks and yellow stripes inside, up to 5 cm long. They have a weak aroma. The flower starts in the fifth year of life.
Flowering lasts up to 25 days. Fruits are narrow, pod-shaped boxes with numerous seeds and thin walls. Grows catalpa bignonevidnaya very quickly. Hardy to the soil is not demanding.
Young individuals can freeze at low temperatures, therefore they are warmed for the winter. Bignonese catalpa is a beautiful tree, often used for soliter plantings. It gains decorative value during flowering and in autumn, when the leaves turn golden.
In winter, Bignonium catalpas look unusual, as its branches adorn the boxes of fruits. This type of catalpa is used in single and group plantings, when planting alleys, parks and public gardens. It looks advantageous in garden plots in the middle of a green lawn. The tree is combined with oak and magnolia, grassy perennials and bulbous flowers unpretentious in care: crocuses, tulips and daffodils. Decorative forms of catalpa: golden, Ken, low (dwarf).
Bignonia gold catalpa is distinguished by yellow leaves. A variety of catalpah Kene interesting bright yellow leaves with a dark green spot in the middle and green veins. Low bignonevidny catalpa or dwarf catalpa has a spherical crown and a height of 2 m.
Catalpa Nana
Low tree, reaching 4-6 m in height. The krone is dense, dense, spherical. The leaves are light green, heart-shaped. Flowers are not tying.
Prefers lighted places, protected from the wind. Requires fertile, fertilized soil. Suitable for planting and fresh loam. It grows slowly. Juveniles are less hardy than adults; they can be damaged at the first frost.
Catalpa Nana does not tolerate high temperatures and excessive dryness, so on hot days you should be abundant and often water the plant. The crown of the tree is susceptible to damage. Digging up, loosening and replanting a tree should be very careful.
Catalpa Nana is used for landscaping public areas and gardens.
Beautiful catalpa
Ornamental tree with a wide pyramidal crown. The height of the beautiful catalpa reaches up to 35 m. The trunk is gray, with thin lamellar cortex. The leaves are large, 30 cm long and 15 cm wide, on thin, long petioles, smooth on top, light green, white underneath, pubescent.
The flowers are white and cream-colored, with yellow stripes and purple-brown dots inside, large, up to 7 cm. They have a pleasant aroma. Duration of flowering 20 - 25 days. Blossom begins at the age of 10-12 years.
Fruits - seed boxes. Appear in the middle of summer. Propagated by seeds, cuttings and layering. It grows in deep, fertile, moist soils. Well tolerated transplant.
Planting is done in early spring. More hardy than other types of catalps. It is used in single, group plantings and to create alleys.
Spherical catalpa
A tree with spreading branches forming a wide-round crown, up to 20 m in height. The bark is light brown, thin-lamellar. The leaves are large, length up to 20 cm, width up to 15 cm.
From above naked, light green, from below pubescent white. When rubbing emit a characteristic smell. The flowers are white, fragrant, up to 5 cm long, with two yellow stripes and dark brown spots inside.
Flowering plant spherical catalpa 20-25 days. Fruits - narrow pods with seeds. The leaves fall green immediately after the first frost. Autumn color does not change. It grows slowly.
Hardy. Demanding on soil moisture. Used in single and group plantings, for landscaping streets and creating parks.
Serves to decorate the garden plots.
Catalpa bigonic
Tree up to 10 m tall. Crohn asymmetric, shoots are arranged in the form of a funnel. The leaves are large, heart-shaped, up to 20 cm, the color is pale yellow. By the period of flowering become green.
The flowers are white and yellow with crimson specks, up to 30 cm. The fruits are pods, up to 40 cm. By the end of summer they turn brown. Keep on the tree until frost.
Under natural conditions, it grows in southeastern North America. Settles in deciduous forests and river valleys. Prefers moist, fertile, moderately acidic soil. The root system is deep, unbranched, sensitive to damage.
Used on garden plots, as an exotic, unusual tree.
Catalpa is great
Ornamental tree up to 30 m. Crohn dense, wide pyramidal. The bark is gray, thin-lamellar. The leaves are large, 30 cm long, 15 cm wide, on long petioles. The flowers are large, up to 7 cm, fragrant.
The color of the flowers is white and cream with two yellow stripes and purple-brown dots inside, the edges are wavy. The flowering time of the tree is 20-25 days. The fruit is a seed box that resembles a long pod of dark brown color.
Seeds are stored in paper envelopes or bags in a dry, dark room. Shelf life of seeds 2 years. Sowing is done in autumn or early spring.
For spring sowing, seeds are soaked in water for two days. Place for landing catalpa should choose a well-lit and protected from the wind. Juveniles grow quickly.
Growth per year is up to 1 m. Catalpa is magnificently frost-resistant, drought-resistant, but on dry days it requires abundant and frequent watering. Flowering begins on the 12th year of life of the tree, lasts from late July to early July. Spectacular catalpa gorgeous used in landscaping urban parks and squares.
Catalpa ordinary
Slender deciduous tree with a height of 6-8 m. It blooms from June to July. In the middle of summer fruits appear - pod-shaped boxes with brown seeds. Collect the fruits of catalpa ordinary in autumn and spring.
The best time to harvest is October - November. The tree prefers fertile, treated fresh soil. On dry and compacted soil it grows very slowly. The plant is drought-resistant, but on hot days requires frequent watering.
In good conditions, catalpa vulgaris rapidly grows and develops. In severe winters, annual shoots suffer, so they are wrapped with material for the winter period. Plantations are planted in early spring before bud break.
Autumn planting is made before the onset of frost. Before planting, they dig a shallow hole, the excavated earth is mixed with humus. When planting, care should be taken to ensure that the root collar is above the soil surface at a level of 2-3 m. Care for young seedlings consists in monthly soil loosening, mulching, timely pruning of affected seedlings and branches.
Hybrid catalpa
Ornamental tree up to 20 m tall. The crown is wide-round with spreading, long branches. The leaves are large, 20 cm long and 15 cm wide, light green, pubescent below.
Inflorescences loose, erect with white flowers, inside which there are two yellow stripes and red - brown specks. Duration of flowering up to 25 days. Blooms profusely every year.
Fruits - narrow boxes. For landing the hybrid catalpa, well-lit places, protected from wind and drafts, are recommended. Soils rich in organic fertilizers with weak acidity are preferred.
Young seedlings need regular and abundant watering, loosening the soil and mulching. After pruning, intensive growth of shoots is noted. The hybrid catalpa tree is combined with oak and magnolia. Looks equally impressive in group and single plantings.
Used to create alleys and street plantings.
Use of catalpa
The tree serves as an excellent honey plant. In the paint industry, catalpa is also valued, from the seeds of which a drying oil is obtained.
In many localities and large cities, the plant serves for landscaping public places, decorating private gardens and house territories. Widely used in traditional medicine.