Variety of vegetables. What is a vegetable culture
Vegetable crops are herbaceous plants grown for the production of heads, root crops, bulbs, leaves, and fruits. 120 kinds of vegetable plants are cultivated. The most common of them belong to 10 families: crucifers - cabbage, rutabaga, turnip, radish, radish, horseradish, watercress; umbrella-carrots, parsley, parsnip, celery, dill; pumpkin-cucumber, pumpkin, melon, watermelon; Solanaceae - tomato, pepper, eggplant, physalis; legumes - peas, beans, beans; lily-onion, garlic, asparagus; Asteraceae - salad, chicory, artichoke, tarragon; maryovye - beets, spinach; buckwheat - rhubarb, sorrel; cereals - corn.
There are annual, biennial and perennial vegetable crops.
Annuals complete the life cycle (from seed to seed) in one year. Among them are plants of the family Solanaceae, legumes and pumpkin, as well as radishes, dill, lettuce, spinach, Peking and cauliflower.
The biennials in the first year of life form the vegetative organs — onions, roots, head, etc., and in the second - seeds. These include: onion and leek, garlic, root vegetables (except radishes), cabbage (except cauliflowers and Peking), artichokes. By winter, they lose their leaves, and often the roots, retaining only the organs in which nutrients are stored.
Perennial vegetable plants are rhubarb, sorrel, asparagus, horseradish, tarragon, onion-batun, chives, multi-tiered onions. In the autumn, all the above-ground part of them dies off, and the roots, in which nutrient reserves are laid, are preserved until spring of the next year.
Every year in spring these plants resume their growth.
Vegetables - the main source of vitamins, they contain important nutrients: proteins, fats and carbohydrates. But due to the high water content (70-95%) they are low-calorie. Taste and pleasant smell of vegetables depend on various combinations of Sugars, organic acids, aromatic and mineral substances contained in them. Sugar in vegetables during fermentation and pickling is fermented, forming lactic acid, which protects them from rotting. Dill, parsley, garlic, onion, radish, horseradish contain many phytoncides-substances with bactericidal properties. Mineral salts contained in vegetables, enhance the physiological processes in the human body. The Institute of Nutrition of the Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR has established an average annual rate of consumption of vegetables - 122 kg per person.
Soviet breeders created more than 700 varieties and hybrids of vegetable crops, which are zoned in various climatic zones of the country.
The homeland of most vegetable crops is the country of warm, tropical and subtropical climate. Therefore, many of them are thermophilic, demanding on soil moisture. But some species are cold-resistant, which makes it possible to grow them in the north, in the central regions and in the winter in subtropical regions. Seeds of some when underwintering begin to germinate already under snow at a temperature of about 0 °, and others - at a temperature not lower than 13-14 °. Some plants tolerate hot and dry weather, and in the case of wet, rainy die, others, on the contrary, do not tolerate heat.
All this testifies to a large variety of biological features of vegetable crops. Therefore, to obtain a high and high-quality crop of vegetables, it is necessary to create a set of conditions that meet the needs of vegetable plants.
The best time for tillage is autumn. It is necessary to clear the soil from the rhizomes of perennial weeds, larvae of the May beetle. Careful and deep (with a full bayonet of shovels) treatment allows moisture to easily penetrate into the soil and accumulate in it. In spring, it is enough to dig up the soil by 15-20 cm. At low, damp places, you need to arrange ridges or ridges.
Vegetable crops respond very well to fertilizers, especially on podzolic and gray forest soils. The most common organic fertilizer is manure (preferably rotted), fecal matter, peat, bird droppings. Horse manure is introduced at the rate of 6–12 kg per 1 m, cattle manure - 7–14 kg, slurry - 10–20 kg, feces - 4–8 kg, peat - 10–20 kg, dead leaves - 10- 20 kg. Excrements are used only in a mixture with fine peat and rotted.
When mineral fertilizers are applied, not only the yield increases, but also the quality of products improves, the ripening of tomatoes, cucumbers, onions, and early cabbage is accelerated. Valuable potassium fertilizer-wood ash. Here are the average application rates of mineral fertilizers: wood ash-200-500 g per 1 m, ammonium sulphate-20-30 g, ammonium nitrate-12-15 g, phosphate rock - 180-200 g, superphosphate - 40-80 g , potash salt - 40-60 g. Lime is applied on acidic soils every 4-6 years.
The same vegetable crops should not be grown all the time in the same place — this increases the risk of pests and diseases. It should be noted that good predecessors for cabbage are all leguminous crops, potatoes, tomatoes; root vegetables - potatoes and cabbage; cucumbers, onions, leguminous vegetables, cabbage, potatoes, root vegetables, tomatoes; green vegetables (parsley, celery, etc.) - cabbage, potatoes, tomatoes, cucumbers.
Vegetable plants are sown in autumn, spring and summer. In the fall, 3-5 days before the onset of frosts, it is recommended to sow carrots, parsley, parsnip, dill, 10-15 days - garlic. Sown seeds in the fall should not germinate. In the spring, vegetables begin to sow as early as possible. Immediately after preparing the soil, seeds of onion, radish, radish, spinach, lettuce, turnip, peas, carrots, parsley are sown in the soil, beetroot later, and later all beans and cucumbers. The depth of seeding depends on their size, soil condition, the needs of plants in moisture and heat. But you should not close them very deeply. Small seeds (turnips, carrots) are best covered up to 1-2 cm; medium (beets, cucumbers) - by 2-3 cm, large (beans, beans) - by 3-5 cm. Small seeds are sown in shallow grooves. Do not sow them thickly.
Many vegetable crops (cabbage, swede, tomatoes, pumpkin, zucchini, cucumbers, beets, celery, leek, onion on a turnip, asparagus, rhubarb, etc.) can be grown from seedlings.
Caring for plants begin before germination. If the soil thickens and a crust forms, it is loosened with a harrow or hoe. In the spring, autumn and early crops are harrowed, for weed control, they row between rows, weed them out in rows and near plants, protect plants from pests and diseases, spud and thin out plants, pinnify (stop plant growth by removing their tops), mulch the soil (cover its sawdust, straw cutting, mulch paper and other materials). Cauliflower, tomatoes, cucumbers, onions and seed plants of vegetable plants are especially responsive to soil mulching. Plant nutrition is of great importance.
The average rate of irrigation on sandy and sandy soils is 10-12 liters per 1 m2 in 2-3 days, and on loamy humus - 20-30 liters in 5 days. The need of plants for watering is determined by the degree of soil moisture and the condition of the plants.
Terms of harvesting vegetables depend on their destination. So, early vegetables (lettuce, spinach, dill, onions for greens, sorrel, radishes, early cabbage and cauliflower) are harvested as they ripen: lettuce and spinach in a stage of 5-6 leaves; dill with a plant height of 10-40 cm; sorrel, green onions in the period of the greatest development of green mass. Cauliflower is picked selectively. Harvesting cucumbers and tomatoes begins as they ripen from mid-summer. The harvest of late vegetables (cabbage, root crops) is harvested in the fall (see Harvesting and storage of the crop).
Vegetable plants - quite capacious concept, which has a very blurred boundaries. They have become so firmly established in our lives that we don’t even think about what can be attributed to them and where they came from. In gardening, the main purpose of their cultivation is to get vegetables in the end.
Classification of vegetable plants
Signs on which it is possible to classify vegetable plants, a great many. They can be distinguished not only by morphological signs, but also by the duration of the life cycle, as well as growing conditions, harvesting periods, and many other signs. However, all of the above makes more sense for farmers, but the average consumer is more interested in the classification of the part that can be eaten.
Despite the fact that vegetable plants at first glance seem completely different, they have a number of common features that make it possible to define them in groups. It is important not only for farmers, but also for cooks, merchandise experts, botanists.
Botanical classification
(vegetable), examples of which many of us can bring in abundance from daily practice, can be classified according to belonging to a particular family or botanical class. In our country, mainly vegetables belonging to the family of nightshade, pumpkin and legumes are grown. You can also meet representatives of cruciferous, amaryllis, celery and mariyevyh.
The advantage of botanical classification is that it allows cultivated plants (vegetable) in all their diversity to be attributed to related crops, which is important for their cultivation. However, for consumers this distribution is very inconvenient, as well as for ordinary gardeners.
Lifetime classification
This classification is most convenient for ordinary amateur gardeners who do not have in-depth knowledge of botany. According to this division, the type of vegetable plant is defined as annual, biennial and perennial.
Annuals are distinguished by the fact that their life cycle, starting with sowing and ending with the formation of seeds, takes place within one year. These include: melons, eggplants, watermelons, cucumbers, zucchini, radishes, etc. Most of them are familiar to us from childhood and are present on our table almost daily.

In biennial plants in the first year only a rosette of leaves can be formed, as well as productive organs in which a certain amount of nutrients can accumulate. Then, when the external climatic conditions become unfavorable, they enter the so-called quiescent period. But already in the second year of life, the plant begins to form the stem and blossom, after which the fruits are formed and mature. These include: beets, onions, cabbage, carrots, parsley and other familiar and familiar vegetables.
Perennials are not so common on the territory of our country and are grown mainly in small quantities. Plants of this species in the first year of life form only the root system, leaves and buds. But they form their productive organs mainly in the second or third year of life. Many of them are ways to live for three to five years. Perennials are similar to biennials in that by winter they enter a period of rest and begin to redistribute nutrients.

For perennials include garlic, Jerusalem artichoke, horseradish, asparagus, sorrel, onions, and many others. Interestingly, many annuals can also be grown as perennials. For example, if you use cultivation in greenhouses. It is also possible reverse. For example, with a lingering and cold spring, carrots and beets can begin to bear fruit in the first year.
Classification by duration and method of cultivation
Vegetable plants, examples of which are given in this article, can also be classified according to the length of their growing season. In this connection, early, middle and late varieties can be distinguished. But the method of growth can be divided into two main types: soil and greenhouse-greenhouse.

Soil vegetable plants are intended for cultivation in open ground, but greenhouse greenhouse plants are exclusively for growing in greenhouses or in greenhouses. At the same time in the greenhouse can grow only stunted vegetables. However, at present, soil is used less and less for growing plants in greenhouses. Most often, the roots of the plant are placed in a special solution, which consists of a mixture of essential nutrients. But there is a perception that vegetables grown in this way are not only not useful, but even vice versa - they can harm the human body. The most valuable are still ground vegetables.
Classification of keeping quality and used in the food
Longevity determines the ability of the vegetable to be stored. In this regard, it is possible to distinguish vegetable plants, which tend to move to a state of rest, and those that do not have such properties.

According to how much of the plant can be eaten, two large groups can be distinguished: fruit or generative vegetables, and vegetative ones. Vegetable grain plants, pumpkin and solanaceous plants can be attributed to the first group. But to the second, root crops, tuberous, bulbous, deciduous and sprout crops, which are familiar to all of us, are ranked.
This classification is the most convenient for both ordinary consumers and distributors of vegetables.
Fruit Vegetable Plants
A distinctive characteristic of these vegetables is considered to be the factor that their fruit is a vegetable. Some of them can give it in the phase of botanical ripeness, others - in the phase of technical ripeness. This can be attributed to all your favorite watermelons, tomatoes, melons, squash and many others. These plants need to create conditions so that they begin to bloom and form fruits as soon as possible. At the same time, it is worth it regardless of the degree of ripeness of their fruits.
Features of growing vegetable plants
Cultivated plants (vegetable), examples of which can be found in this article, have some peculiarities of cultivation. First of all, it should be noted that not the last place is played by the layout of the site. Before you implement it, you need to try to study the agricultural practices of those vegetables that you plan to cultivate in your plot.
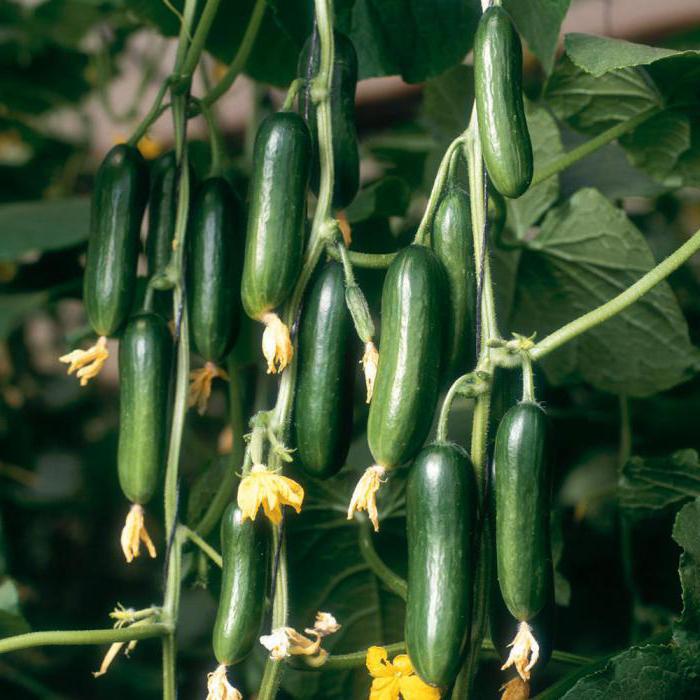

The biological characteristics of certain plants also contribute to the fact that it is necessary to select the natural and climatic conditions for a particular vegetable. Vegetable plants have one common requirement in their cultivation: for several years it is impossible to plant the same or related plant in the same place. The remaining requirements for cultivation are selected individually, as well as the soil composition and the amount of fertilizer required for the application.
Classification V.I. Edelstein
The Soviet scientist Edelstein developed a special classification, which makes it possible to divide vegetable plants not only by biological, but also by agrotechnical conditions. According to this classification, our vegetables can be divided into: cabbage, root, tuber, bulbous, fruit, leafy, perennial, and mushrooms.

In each of these classes, families are also distinguished.
General classification
In general, this classification can hardly be called scientific, the more it is intended specifically for consumers. Vegetables are not grouped by any attribute in it, however, such species as tuber crops, root crops, rhizomatous plants, cabbage, leafy, spicy, bulbous, tomato, pumpkin, bean, cereal, dessert are distinguished. But the pineapple, to everyone's surprise, scientists have not yet determined neither to vegetables nor to fruit.
Continuing the theme of the ornamental garden, today we will talk about the decorative placement of vegetable plants. Possibilities of placement of garden plants depend, first of all, on the area of the site, its relief, general design and are determined by the diversity of the range. Its range is very wide and includes flowering, decorative and leafy, beautiful, high and low plants, forming carpet coverings and, on the contrary, climbing high upwards on supports, drought-resistant and growing in water, sun-loving and preferring exclusively shady places with a short growing season (ephemeroids) and evergreens, etc. Let us consider in more detail the main decorative properties of vegetable plants.
Groups of ornamental vegetable plants by life expectancy
The period of decorativeness of vegetables is determined primarily by the life cycle and the phase of plant development. Among the traditional vegetable crops and vegetables are wild plants, most of which are herbaceous plants, annuals, biennials and perennials are found.Annual plants include plants that bloom during the same growing season, form mature seeds and die. This group includes the majority of traditionally grown vegetables: cucumber, tomato, pepper, pumpkin, zucchini, squash, dill, beans, watermelon, cantaloupe, etc.
Annual vegetable plants:
amaranth, anguria, anise, watermelon, basil, okra, marigolds, stone-shredded females, beninkaza, beans, borage, water chestnut, mustard, melon, Moldavian serpentine head, zucchini, calendula, Chinese cabbage, K. pekinskaya, chyrocorye, cabbage, cabbage, calendula, Chinese cabbage, K. pekinskaya, ch. coriander, watercress, crouton, maize, lagenaria, garden quinoa, luffa, samoseyka, corn capitate, momordika, cucumber, squash, pepper, sunflower, purslane, radish, summer radish, lettuce, tomato, pumpkin, dill, bean common, glutenopod physalis, f. pubescent, chrysanthemum, cyclantera, chicory salad, savory garden, Chernushka, spinach.
Biennials include plants whose life cycle lasts two years. In the first year, a shortened stem with leaves develops, most often in the form of a rosette. In the second year, a flowering sprout grows, the plants bloom, bear fruit and, forming mature seeds, die off. The biennials include: parsley, celery, common goat, chicory salad, etc. Many biennial plants are grown as annuals, harvesting in the first year of their lives (cabbage, carrots, parsnips, beets, etc.), and if necessary, get seeds, their continue to grow in the second year.
Biennial vegetable plants:
tuberiferous butenbill, common goatskin, half-flowered mullefruit, forest kupyr, oslinnik biennial, parsley, radish, winter radish, turnip, celery, cumin, fennel, physalis ordinary, salad chicory, garlic, spinach.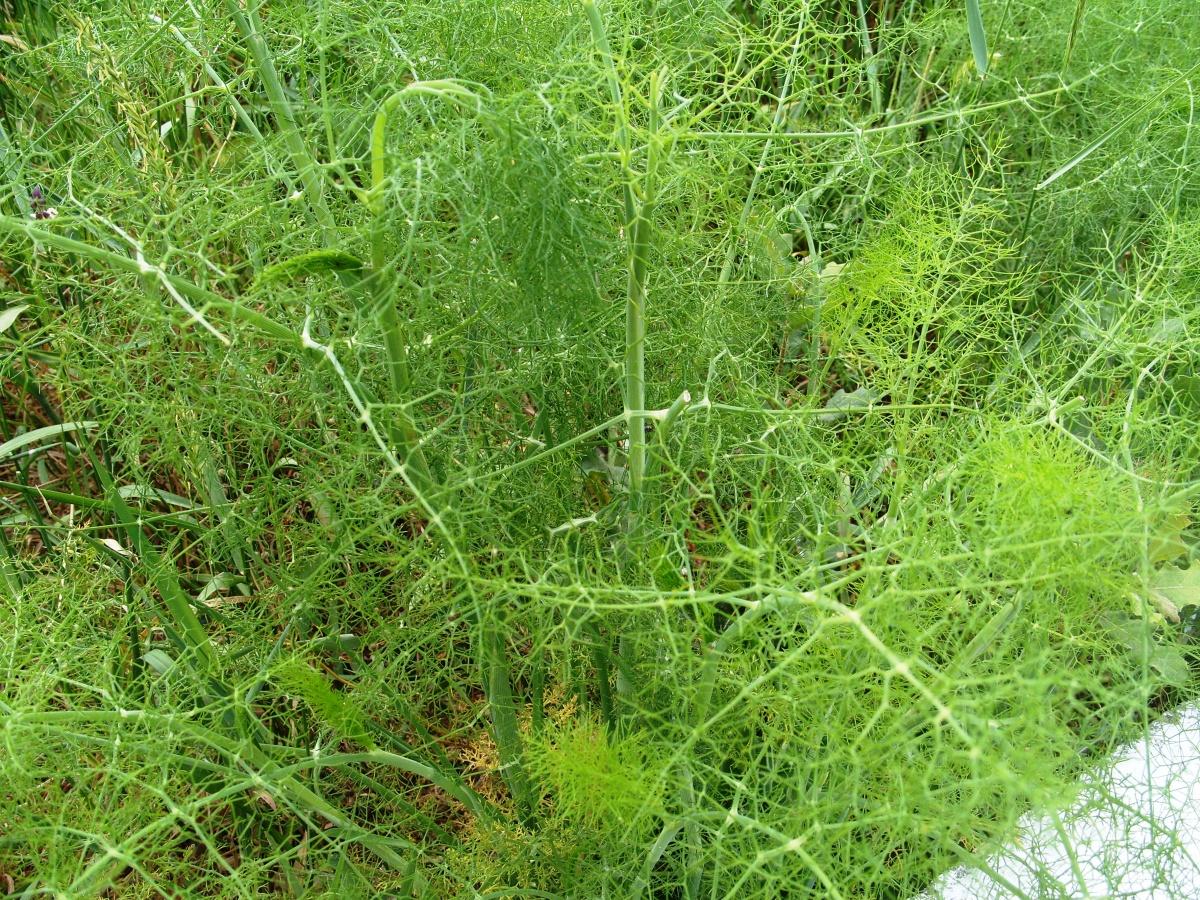
Biennial vegetable plants grown as annuals:
rutabaga, daikon, cabbages, carrots, parsnips, table beets, p. chard, fennel, onion, garlic.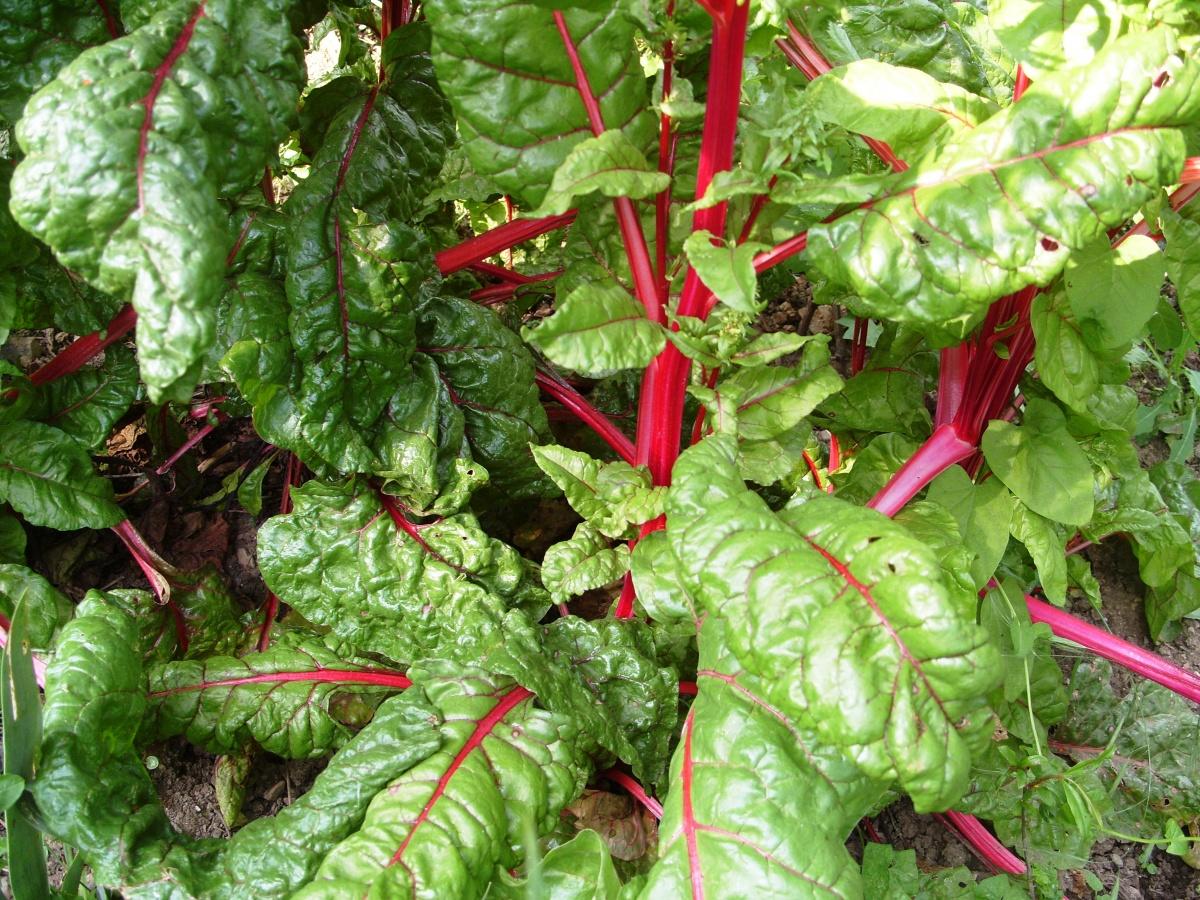
Perennials include plants whose life expectancy is more than two (many) years. At the same time, every winter, the aerial part of them dies off, and in the spring, flowering shoots from the underground organs, on which there are renewed buds, flowering, the plants bloom, bear fruit, and die again in winter. The first flowering of these plants begins with the second or third year of life, or later, if the plants were grown from seeds. This should be taken into account when composing the compositions and not focusing on the decorativeness of the flowers or fruits of the vegetable perennials in the first years of life. The vast majority of perennials among vegetable plants are various types of onions, some spicy-flavoring plants, wild plants.
Perennial vegetable plants:
calamus, marshmallow, artichoke, badan, hogrichevik, budra, small basilus, Veronika, large rooting geranium, yellow gentian, Russian gorzey, river gravilat, yellow goose onions, tall man, anchor Germanic marsh marsh marigold, lake reed, balsamic canuper, Tatar quatra, common oxis, creeping clover, bell, catnip, chemotherapist, white waterlily, bunt, forest kupyr Goaty fennel, Anzur onion, L. Roundhead, L. Long-fresh, L. Pobedy, L. Reeking, L. Hard, L. Angled, L. Shalot, L. Skorot (chives), lovage, perennial daisy, mother- coltsfoot, medunitsa medicinal, lemon balm, fragrant myrrh, young roofing, duckweed, mint, common bird, common bracken, common stonecrop, red fenugreek, primrose, tansy, evading peony, tarragon wormwood, forest mallow, prymma, prymma, peony deviating, tarragon wormwood, forest mallow, prymma, prymma, peony deviating, tarragon wormwood, forest mallow, prymma, prymma, peony deviating, tarragon wormwood, forest mallow, prymma, prymma, peony deviating, tarragon wormwood, forest mallow, prymma, prymma, peony deviating, tarragon wormwood, forest mallow, pvarna, pryvma, pivma, pion , Rhodiola rosea, core, Serpuha crowned, asparagus, arrowhead, susak umbrella oh, syt edible, tladiant, Jerusalem artichoke, common cane, yarrow, cry, fennel, hamenerion Echinacea purpurea.
Perennial vegetable plants grown as annuals:
artichoke, eggplant, sweet potato, garden clove, medicinal herb, potato, castor oil, Spanish goatling, batun onion, L. delushy, L. plover, L. skoroda, nasturtium large, perilla, red-fire beans, chayot, Siebold cleaner.Vegetable crops are herbaceous plants grown for the production of heads, root crops, bulbs, leaves, and fruits. 120 kinds of vegetable plants are cultivated. The most common of them belong to 10 families: crucifers - cabbage, rutabaga, turnip, radish, radish, horseradish, watercress; umbrella-carrots, parsley, parsnip, celery, dill; pumpkin - cucumber, pumpkin, melon, watermelon; solanaceous - tomato, pepper, eggplant, physalis; legumes - peas, beans, beans; lily - onion, garlic, asparagus; Asteraceae - salad, chicory, artichoke, tarragon; maryovye - beets, spinach; buckwheat - rhubarb, sorrel; cereals - corn.
There are annual, biennial and perennial vegetable crops.
Annuals complete the life cycle (from seed to seed) in one year. Among them are plants of the family Solanaceae, legumes and pumpkin, as well as radishes, dill, lettuce, spinach, Peking and cauliflower.
Biennials in the first year of life form vegetative organs - bulbs, roots, cabbages, etc., and in the second - seeds. These include: onion and leek, garlic, root vegetables (except radish), cabbage (except
color and Beijing), artichoke. By winter, they lose their leaves, and often the roots, retaining only the organs in which nutrients are stored.
Perennial vegetable plants are rhubarb, sorrel, asparagus, horseradish, tarragon, onion-batun, chives, multi-tiered onions. In the autumn, all the above-ground part of them dies off, and the roots, in which nutrient reserves are laid, are preserved until spring of the next year.
Every year in spring these plants resume their growth.
Vegetables - the main source of vitamins, they contain important nutrients: proteins, fats and carbohydrates. But due to the high water content (70-95%) they are low-calorie. Taste and pleasant smell of vegetables depend on various combinations of Sugars, organic acids, aromatic and mineral substances contained in them. Sugar in vegetables during fermentation and pickling is fermented, forming lactic acid, which protects them from rotting. Dill, parsley, garlic, onion, radish, horseradish contain many phytoncides-substances with bactericidal properties. Mineral salts contained in vegetables, enhance the physiological processes in the human body. The Institute of Nutrition of the Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR has established an average annual consumption rate of vegetables of 122 kg per person.
Soviet breeders created more than 700 varieties and hybrids of vegetable crops, which are zoned in various climatic zones of the country.
The homeland of most vegetable crops is the country of warm, tropical and subtropical climate. Therefore, many of them are thermophilic, demanding on soil moisture. But some species are cold-resistant, which makes it possible to grow them in the north, in the central regions and in the winter in subtropical regions. Seeds of some when underwintering begin to germinate already under the snow at a temperature of about 0 °, and others - at a temperature not lower than 13 -14 °. Some plants tolerate hot and dry weather, and in the case of wet, rainy die, others, on the contrary, do not tolerate heat.
All this testifies to a large variety of biological features of vegetable crops. Therefore, to obtain a high and high-quality crop of vegetables, it is necessary to create a set of conditions that meet the needs of vegetable plants.
The best time for tillage is autumn. It is necessary to clear the soil from the rhizomes of perennial weeds, larvae of the May beetle. Careful and deep (with a full bayonet of shovels) treatment allows moisture to easily penetrate into the soil and accumulate in it. In spring, it is enough to dig up the soil by 15-20 cm. At low, damp places, you need to arrange ridges or ridges.
Vegetable crops respond very well to fertilizers, especially on podzolic and gray forest soils. The most common organic fertilizers are manure (preferably rotted), fecal matter, peat, bird droppings. Horse manure is made at the rate of 6-12 kg per 1 m2, cattle manure-7-14 kg, manure-10-20 kg, feces-4-8 kg, peat-10-20 kg, leaves parted, 10- 20 kg. Feces are used only in blends.