What are the types of acacia: description and photo varieties. Robinia: photos and species, growing and caring for a tree
Robinia pseudo-acacia. Under this complex name hides one of the most beloved and common plants, growing abundantly in urban gardens, parks, squares and just in the courtyards. In everyday life, pseudo-acacia (or robinia pseudoacation) is simply called acacia. This deciduous tree-bush from the legume family has firmly taken root in urban culture, tolerates heat, irregular watering, polluted air and other “delights” of survival in the city.
Calling Robinia a false acacia "acacia" is not entirely correct. There are many plants united by the common name “acacia”: both silk acacia (albition), yellow acacia (tree-like caragun) and other members of the genus Robinia. We, first of all, speak of white acacia, namely Robinia pseudo-acacia.
 Robinia pseudoacathy
Robinia pseudoacathy White acacia, like many other plants, moved to us from North America. Robinia genus includes more than twenty species of tree cultures growing in the Americas.
The seeds of a Pseudo-Cacania robinia were brought to Europe by the court gardener of the French king Louis XIII. Vespasian Robin. When laying the pharmacy garden in the royal park in 1635, he planted the seeds of Robinia. Later, this pharmaceutical garden turned into a botanical garden in Paris, and this is the first tree still alive. And the name of the gardener was immortalized in the scientific name of this plant.
Very soon, Robynia quickly went beyond the royal gardens and firmly settled on the streets of French and then European cities. Despite the fact that white acacia is traditionally considered a southern plant and does not differ in winter hardiness, it can also be found in temperate latitudes of the middle zone, where outwardly coarse acacia trunks twisted from cold winds hide in beams and ravines, in fences and in front gardens. At the beginning of the 19th century, Robinia, pseudo-acacia, expanded the collection of the Nikitsky Botanical Garden in the Crimea, where she was able to demonstrate her beauty and tenderness with full force.
A white acacia tree reaches a height of thirty-five meters and a crown span of up to twenty meters. The peculiarity of acacia is the most powerful root system. The roots penetrate the ground to a depth of twenty meters and firmly hold the tree even on steep slopes. It is this quality of white acacia that is often used for strengthening the slopes of ravines, for anti-landslide work, for building expensive in mountainous terrain, when it is crucial to strengthen the soil and prevent it from slipping.
Robinia has a pseudoacacia coarse, wrinkled with deep cracks and a grayish bark. Wood is a little susceptible to rotting and abrasion, and therefore is very much appreciated by cabinetmakers. It is surprising that at the same time, the acacia does not look so massive like, for example, oak or maple.
Due to the structure of the branches and the foliage features, the tree is as if penetrated by the sun's rays. Acacia leaves resemble a veil in their structure: they are long, pinnate, with multiple pairs of ellipse-like leaves of rich green color. Bottom leaves have a silvery shade. At the base of the leaves are hiding powerful needles, which are altered foliage.
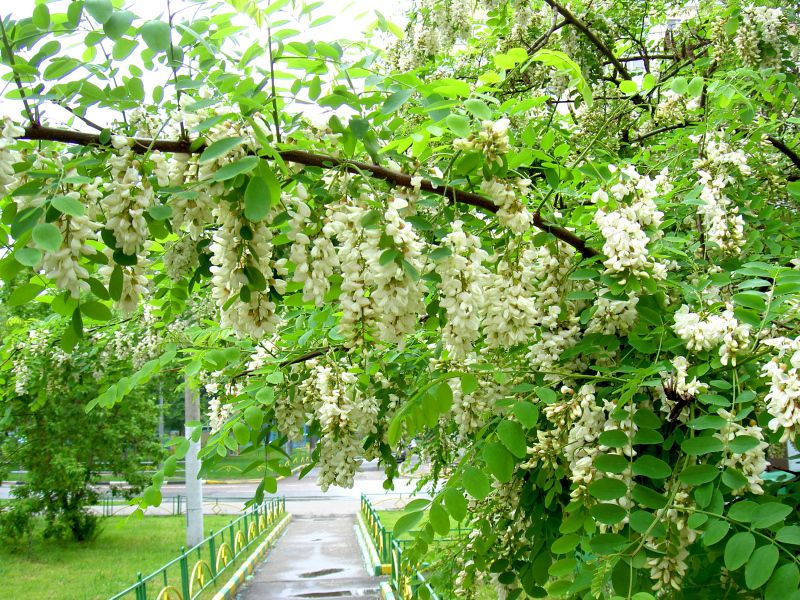
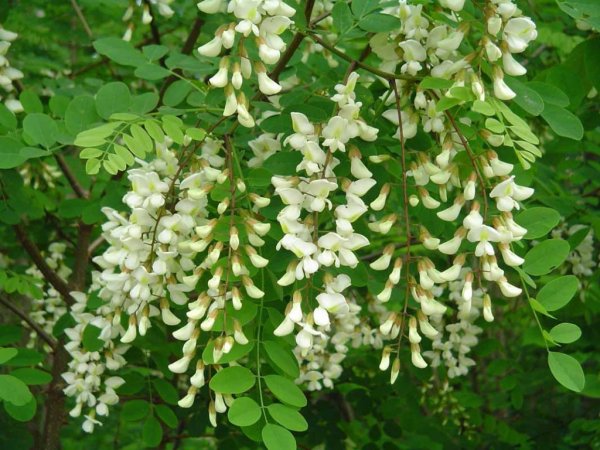
But the main aesthetic value of Robinia is Pseudo-Acacia in its amazing flowering. How many romances, songs and poems composed of white acacia! And all this is due to the luxurious, with a dizzying aroma of abundant blooms, which pleases us Robynia in May and June. Acacia flowers are milky white, sometimes with a yellowish or greenish tint. They are assembled in heavy drooping racemes, reaching a length of up to twenty centimeters. The aroma of flowers is similar to the aroma of wisteria and lilies, it may seem too rich, but every year we again and again admire this bloom.
After the end of flowering, in the place of peduncles, pods-beans are formed, in which seeds are hidden. Seeds ripen by November, but the pods do not fall off and continue to hang on the tree, giving it a special winter charm.

Application
In addition to the exceptional decorative qualities of Robinia pseudo-acacia, people have long known and appreciated the other useful qualities of this plant.
- Due to its chemical composition, the color of white acacia has long been used in traditional medicine. Acacia flowers contain sugars, organic acids, essential oils, vitamins, flavonoids and tannin. The bark of young branches is rich in routine, fatty acids, tannins, phytosterols. All this has a powerful therapeutic effect on the human body, helping to fight colds, edemas, gynecological diseases, kidney diseases, the nervous system, the gastrointestinal tract. First of all, the exceptional antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties of acacia flowers, which in some countries are officially recognized as a drug, deserve attention. For example, in German medicine, tincture of acacia flowers is recommended to treat gastritis with low acidity. Herbalists also advise acacia teas to people who are depressed, as well as to particularly conflicted patients.
- The healing properties of acacia honey deserve special attention. This tree is very revered by beekeepers, because in three weeks of flowering on average, it is possible to get up to eight kilograms of honey from one tree. Acacia honey is light, transparent, with a delicate aroma and amazing healing qualities. It is used in cooking, in medicine and in cosmetology, does not crystallize for a long time, which also attracts consumers.
- White acacia flowers are rich in essential oils, the extract of which finds its application in the perfumery and cosmetic industry.
- Wood and the inner layer of seed pods are valued by craftsmen using the exceptional decorative properties of these materials.
White acacia in everyday life is called Robinia pseudoacacia (Robinia pseudoacacia), and we published material about it. Readers were inspired that these "fragrant clusters" can grow not only in the south, and are asked to tell in more detail how to grow this plant. Will it grow in the Moscow region, near St. Petersburg, in Nizhny Novgorod? To avoid a repetition, we decided to tell more about the acacia pink. All pictures were taken in Central Russia.
The genus was named after Vespasian Robin, who first brought this plant to Europe from America in 1620. Includes up to 20 North American species of deciduous trees and shrubs. The leaves are large, pinnate, with stipules, modified into powerful spines. Butterfly flowers, white or pink, mostly fragrant, gathered in large drooping brushes. Fruits flattened from the sides of the beans.
The tree looks very decorative, even without flowers. Due to the large feathery leaves it looks pleasing. Openwork crown gives the tree lightness and does not give a big shade, any flowers grow perfectly under it.
Robinia is of low fertility and soil moisture, prefers limestone. Noticed that
grows well in cities near houses where there is often a lot of construction waste in the ground (broken bricks, whitewash, etc.). On wet, heavy soils, it often suffers from frost. Very light-requiring and drought-resistant.
HOW TO REPLACE THE ACTION
The easiest way to dig out the root growth. But sometimes gardeners say that the tree grows singly and does not give seedlings.
Robinia and seed propagated. It is better to collect them from the local, most winter-hardy plants. In the middle zone, robinia seeds ripen normally and are suitable for sowing.
Seeds are sown usually in the spring after a month-long stratification or scalding with boiling water (5-7 seconds, and then in cold water). This is necessary in order to break from the temperature drop rugged seed coat. After processing in boiling water, the seeds are left for 12 hours in water until complete swelling.
Scalded seeds are sown immediately: in April in a box, in May in a greenhouse. For successful germination and growth of young Senets, the temperature must be above 20 C.
In the first season after sowing the shoots need to be well looked after: weed, water, not allowing drying, feed.
The first half of the summer, you can give nitrogen supplements (infusion of manure, grass), as well as complex fertilizers. From the second half of summer, nitrogen should be excluded and only phosphate-potassium fertilizers should be added (complex fertilizers with the prefix "autumn" can be used). All legumes love alkaline soil, so ash and dolomite flour will be useful. This mode of dressing will allow you to grow strong plants that will not fatten and perezimuet well.
ACACIA WINTER PRIORITY
It should be noted that young plants are poorly winter-hardy, so you need to sow more seeds. After the first winter will survive the strongest.
If the seedling is purchased, then for reliability, you can build around it a shelter of 34 laths and wrap it with a double layer of spunbond. Compress the roots with compost or earth.
With age, the hardiness of Robinia increases, but sometimes, at very low temperatures, the plants are damaged to the level of snow. Due to the high pobegoobrazovatelnuyu ability, subject to the preservation of the roots and root collar, the plants are quickly restored.
WHITE ACACIA
Robinia pseudoacacia, or pseudoacacia (R. pseudoacacia L.) first appeared in the catalogs of the Botanical Garden of St. Petersburg in 1796, but until 1887 (and possibly longer) was noted only in greenhouses and pottery arboretum. Tests in open ground began, presumably in the 30s of the last century. In the Botanical Garden of St. Petersburg, in the park, specimens of this species have been growing since 1954, are well restored after frosting, and bloom regularly.
In Moscow, robinia can be seen in large numbers in the Kuzminsky Park near the Veterinary Academy.

In Nizhny Novgorod, robinia, pseudoacation grows in the Botanical Garden of UNN, and is also used in gardening the city in several places, particularly in the center of Sormovo, near the Transfiguration of the Savior Cathedral.
In addition, the "white acacia" can be found in the forests of the Nizhny Novgorod region (Borsky district), where it naturalized and reproduces independently.
It is clear that if in the botanical gardens some acacia leaves go, then in the forests it grows, prone to all natural disasters: both to droughts (it survived the anomalous heat of 2010) and to frost.
It blooms very plentifully, the sweet aroma in the evening intensifies, and the acacia fully responds to the poetic lines: "With the fragrance of a tender head turns around" ...
Robinia pseudoacacia has several garden forms with different crown shapes and leaf color. The trees are very beautiful with fresh bright green foliage. There are also forms with white and pink flowers (with different color intensity). They bloom in the same time as white acacia. White and pink acacia can be seen in the UNN Botanical Garden in late May and early June (photo 3). Pleasant aroma attracts a lot of bees and bumblebees.
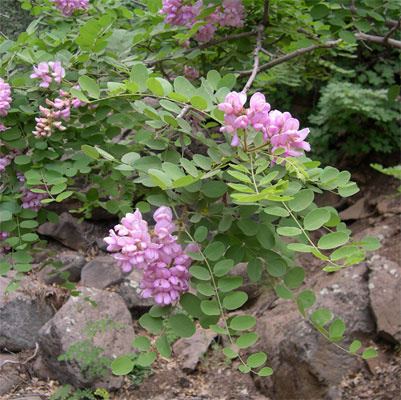
PINK ACACIA
This species is much less common than the white acacia, the botanical name Robinia gummy (Robinia viscosa Vent.). However, in Nizhny Novgorod there is still pink acacia. And, of course, in the collection of Sergey Marinkov, where all the interesting wonders are collected.
The tree is grown from cuttings grafted on the stock of acacia. Now grown above four meters, has a lush crown, richly blooms.
Unlike white acacia, which blooms only in spring and early summer, Robinia gummy blooms twice. In late May-June, gives abundant flowering, and then takes a three-week break. Recovering strength, begins to bloom in July and continues until frost. Repeated flowering is not so abundant, but the flowers last longer due to the fact that there is no bright sun and strong heat.
The aroma of pink acacia is weaker than that of white, but bumblebees fly to it from everywhere, unmistakably catching its sweet vibes.
Robinia gummy has received its specific name for the fact that shoots, leaf stalks and inflorescences are densely covered with glandular, sticky hairs (photo 2). The spines are very small or absent altogether.

Robinia is believed to be less drought and frost-resistant than a false white one. But in Sergei Marinkov, the tree grows outside the garden, near the fence, and does not receive any special care (photo 6). Nevertheless, its pink acacia suffered several frosty winters with temperatures below 34C and anomalous heat of 2010.
LANDING ACACIA
The choice of a landing site for Robinia is determined by its need for light. Under the sun, it develops better. On shaded areas, it will also grow, but it does not bloom so much and may suffer from frost. Natural pink protection from the north wind (wall of a house, shed or fence) is also desirable for pink robinia.
All Robinia should be planted in the spring, before bud break. When planting in autumn, the soil is too cold and wet, damaged roots may rot. The root neck is not buried, so that it does not undermine.
Sand (if the soil is clayey), humus and necessarily some alkaline component of slaked lime, ashes, dolomite flour, and lime rubble are brought into the landing pit.
In general, these plants feel better on the soils of the poor, but loose, than on the rich and clay.
That's all the wisdom when growing Robin. And yet, it is more pleasant to call them acacias. Just think about how wonderful it sounds: "The acacia has bloomed ..." as if the dream of a warm and blessed south had come true.
N. Petrenko,
photo by S. Marinkov and from the collection of the UNN Botanical Garden
Robinia are often used for landscaping. A single tree or a small group can be an ornament to the backyard. Forms with golden foliage look great against the background of dark coniferous rocks.
Representatives of the genus - deciduous trees (up to 30 m tall) or shrubs (up to 4 m tall). A number of species on the branches have sharp, strong spines - modified stipules.
The leaves are large, characteristic of many legumes: pinnate, consist of 7-21 obovate or elliptical leaves. The flowers are gathered in lush racemes, usually drooping. The flowers are white or pink, in some species - with a strong pleasant aroma. Fruit - bean.
Robinia genus, or Pseudoacacia (Robinia), belongs to the family Legumes (Fabaceae) and includes from 4 to 10 species (according to different scientists), common in North America.
The scientific name is given in honor of the French gardeners, the father and son of Robins (Jean Robin and Vespasien Robin), who brought the seeds of this plant to Europe and successfully grew the first copies.
Robinia pseudoacathy
Robinia pseudoacacia, or white acacia (R. pseudoacacia), is found in nature in eastern North America, where it forms part of deciduous forests. C X !! century widespread in Europe as a landscape gardening culture, suitable for landscaping cities, creating forest belts in the southern regions.
 The tree is 12–30 m tall, with a laced sprawling crown, which becomes irregular and “ragged” with age. Young branches and shoots are in addition to the leaves of large sharp spines. The upper surface of the leaves is dark green, the bottom is light, so the trees look especially attractive in the wind. In autumn, the foliage is painted in pure light yellow tones, although it can only be observed in the southern regions.
The tree is 12–30 m tall, with a laced sprawling crown, which becomes irregular and “ragged” with age. Young branches and shoots are in addition to the leaves of large sharp spines. The upper surface of the leaves is dark green, the bottom is light, so the trees look especially attractive in the wind. In autumn, the foliage is painted in pure light yellow tones, although it can only be observed in the southern regions.
In the middle lane, the leaves fall green after the very first frost. Flowering occurs in June and lasts 7-10 days (depending on the weather). The flowers are white, sometimes slightly pinkish or slightly greenish, very fragrant, gathered in lush drooping racemes 10-20 cm long.
Winter hardiness
In regions with warm winters, lacquer is a very unpretentious plant. In the middle belt conditions, its winter hardiness increases with age. Young plants in severe winters often frost themselves to the level of snow, but quickly restored.
Experience shows that Robinia pseudoacacia can be grown without shelter even near Petersburg (Karelian Isthmus). Under these conditions, the tree will be low (3-5 m). in severe winters, the plant is frosting up, flowering does not occur every year, but with age it becomes more frequent. Tassels of flowers develop not very large, but just as gentle and fragrant as in the south.
False attack tolerates anti-aging pruning, and quickly recovers from freezing winters.
Special properties
 It has a heavy, very durable, very resistant to rotting wood, which is used for the manufacture of furniture, floors, all sorts of panels and pillars. The ability of the tree to form long rhizome shoots with offsprings makes it especially valuable for soil consolidation and erosion control. You should know that the leaves, bark and wood of this tree contain substances that are poisonous to humans and cattle (including horses).
It has a heavy, very durable, very resistant to rotting wood, which is used for the manufacture of furniture, floors, all sorts of panels and pillars. The ability of the tree to form long rhizome shoots with offsprings makes it especially valuable for soil consolidation and erosion control. You should know that the leaves, bark and wood of this tree contain substances that are poisonous to humans and cattle (including horses).
Decorative forms
There are a number of decorative forms, the most famous and common of which is “Frisia” with golden yellow foliage. Of interest are also the following forms.
“Lace Lady”, also known as “Twisty Baby”, - a small tree or shrub with twisted twigs and “curly” leaves, is very effective not only in summer, but also in winter. Suitable for growing in containers, responds well to trimming formation. The variety was patented in 1996 under the name “Loce Lody”, currently sold under the commercial name “Twisty Baby”;
"Purple Robe" - a low tree with bright pink-purple flowers, young foliage has a spectacular bronze-red tint.
"Pryamidalis" - a tree with a narrow columnar crown, unfortunately, rarely and not much flowering.
Our reference
Robinia lzheakatsiya durable, can live up to 300 years. It is very resistant to air pollution, so it is widely used for urban greening, creating plantings along highways. Great honey plant.
Robinia bristle haired
Robinia (pseudoacacia) bristled hair (R. hispida) is common in the southeastern regions of the United States. In a culture known from the middle of XU !!! Century.
 Shrub 1-3 m tall, due to numerous root offspring forming dense thickets. All parts of the plant except the petals and leaf plates are covered with numerous long setae.
Shrub 1-3 m tall, due to numerous root offspring forming dense thickets. All parts of the plant except the petals and leaf plates are covered with numerous long setae.
Shoots without spines. The flowers are pink, odorless, collected by 3-9 in loose hanging brush. It blooms in June for 2-3 weeks, possibly re-bloom in July and August.
Very decorative look, especially suitable for group park plantings and hedges. The Cherokee Indians used this type of Robinia differently. Infusion of the roots was used to treat toothache. The leaves were fed to cattle as a tonic. Wood was used to make bows, to build fences and hedges, and even to build houses.
Our advice
Top dressing with organic fertilizers is most effective in the summer, before flowering and immediately after it.
For this, diluted extracts of mullein or bird droppings are used.
In the fall, nutrient compost is scattered in tree circles, in the spring - complex mineral fertilizer.
It should be noted that in the case of Robinia, top dressing should not be abused - this tree develops well and blooms even on poor soils.
Robiniya is sticky
Robinia (pseudoacacia) is a sticky (R. viscose) in nature common in the eastern United States. In a culture from the end of HU !!! Century.
 The tree is up to 12 m tall, the crown is wide, often almost rounded. Young shoots, leaf stalks, flower stalks and calyx flowers are covered with thick glandular hairs, for which the species got its name. The spines are small. Sometimes completely absent. Flowering occurs at the end of May-June. The flowers are pink or pink-lilvye, odorless, clustered in racemes 5-10 cm long.
The tree is up to 12 m tall, the crown is wide, often almost rounded. Young shoots, leaf stalks, flower stalks and calyx flowers are covered with thick glandular hairs, for which the species got its name. The spines are small. Sometimes completely absent. Flowering occurs at the end of May-June. The flowers are pink or pink-lilvye, odorless, clustered in racemes 5-10 cm long.
This species is less frost and drought-resistant than Robinia pseudoacation. There are a number of decorative forms, including those with larger, intense pink flowers.
Robinia New Mexican
Robinia (pseudoacacia) New Mexican (R. neomexicana) in nature is found in the southwestern United States and in the northwestern regions of Mexico. In culture from the first half of the twentieth century.
Shrub or small tree 2-12 m tall. Shoots with prickles and hard pubescence. Flowering occurs in June. The flowers are white or pink, hanging in racemes 5-10 cm long.
Despite the southern range, rather winter-hardy, characterized by rapid growth. It tolerates air pollution, drought, salinity, unpretentious to soil conditions.
A place under the sun
In mid-band conditions, robinia requires a sunny, sheltered from strong, cold winds of location.
This tree is very unpretentious in relation to soil conditions, able to tolerate drought and salinization, it can feel good on poor sandy substrates, as well as on clay, but grows best on fertile loams with good drainage. Does not tolerate stagnant water in the soil. Robiria, like all legumes, due to root bacteria is able to accumulate nitrogen in the soil. Resistant to air pollution.
How to care
Caring for an adult tree is simple. Pruning is carried out as needed: remove dried branches or those that interfere with other plantings. Robinia does not need to form the crown, since it has a neat form by nature.
False attack tolerates anti-aging pruning, quickly recovering from freezing winters. Watering is also not a necessity, it is important only for newly planted specimens.
It is useful to keep tree trunks free from weeds — mulching with sawdust or crushed bark with a layer of 4-6 cm will help here.
 In the conditions of Russia, the acacia is practically not subject to diseases and pests.
In the conditions of Russia, the acacia is practically not subject to diseases and pests.
Robinia breed by seeds and root offsprings. Seed propagation pseudoacre easy.
Seeds before planting are scalded with boiling water for 5-10 seconds and immediately placed in cold water. These measures violate the integrity of the peel and significantly accelerate germination.
Mechanical stratification is possible: grinding with coarse sand, sandpaper processing.
Scalded seeds are immediately sown in the ground. The best time for this is April-May.
If weather conditions do not allow, sowing is done in boxes on the windowsill, in warmer weather, you can use a greenhouse. For germination and development of seedlings need a temperature not lower than +20 degrees. Planting young plants in the ground is possible as soon as the threat of frost has passed. They are placed on a dedicated solar bed.
Care of seedlings
 The soil should be prepared in advance: make nutrient compost, wood ash. The distance between the specimens must be at least 30 cm.
The soil should be prepared in advance: make nutrient compost, wood ash. The distance between the specimens must be at least 30 cm.
Young plants are weeded, watered regularly, fed with complex mineral fertilizer.
Careful intensive care in combination with warm weather will allow to receive saplings of meter height with side branches by the autumn.
In the spring they can be planted in a permanent place.
Root scions and cuttings
Reproduction by root suckers is even easier: you should dig up a young plant with a piece of maternal rhizome and plant it in a new place.
Reproduction by root cuttings is possible. To do this, with the onset of warm weather, usually at the beginning - mid-May, one or more side roots are dug up in an adult tree, from which cuttings are cut.
Their diameter must be at least 0.5 cm, length - at least 20-25 cm.
Our reference
The main problem in the cultivation of Robin is the numerous root scions that require removal. They grow in considerable quantities, often at a distance of several meters from the maternal trunk. This may harm nearby landings.
Root cuttings are planted obliquely in loose nutrient soil.
In this case, the upper cut of the root should be at the level of the soil surface. With favorable running conditions, in 2-3 weeks young shoots will appear, which by the autumn can reach a meter height.
It should be noted that under the conditions of the middle band, the green cuttings of Robinia do not root well, and the plants obtained from them are usually badly damaged in the very first winter. In this regard, it is better to multiply Robinia root suckers.
The best time for planting a false attack is spring, until the buds are picked. Autumn planting gives good results only in the southern regions with warm winters.
According to the magazine "Favorite Dacha"
The beauty of this southern tree with delightfully fragrant white flowers sang in the classic romance, popular songs, lyric poems.
White Acacia became the name of the Soviet operetta, which was shot on the same feature film.
In contact with
In the end, she became the symbol of the most picturesque southern city in the USSR - Odessa. What does this plant have in common with peas or clover habitual in our latitudes?
 No matter how strange it may seem, but peas, clover and southern tree are relatives in the botanical systematics, and belong to the same legume family.
No matter how strange it may seem, but peas, clover and southern tree are relatives in the botanical systematics, and belong to the same legume family.
This is not hard to guess if you wait for fruiting acacia - it will be a long pod, like peas, filled with seeds.
And here is another stereotypewhich science destroys: white acacia is not acacia at all, the name of this plant according to the international classification of flora - "locust". So, in the 18th century, the Swede K. Linnei named her in honor of the famous botanists from France - father and son Robin. He was the first to give a scientific description of a tree grown from seeds brought from North America by the royal gardener Vespasian Robin.
Interesting. Now the French copy of Robinia is already four hundred years old, but even now it safely turns green not far from Notre-Dame de Paris. The French carefully backed it up with a concrete crutch and recorded on the tablet the date of their appearance on the Gallic land - 1602 year.
There is one more an interesting feature of acacia is white: it grows well both in the regular park and along the roadsides. Today, robinia (pseudoactivity) has 750 species, to their birth was put a hand and a man. The creation in the process of selection of decorative forms on a wild-growing stock has replenished a collection of varieties of exceptional flowering beauty, as well as plants that can change the southern regions for the harsh climate of the Vologda region.
 The wild-growing species of Robinia, introduced from the New World, is usually supplemented with clarifying names: pseudoactivity, false attack, robinia, false attack, pseudo attack or ordinary.
The wild-growing species of Robinia, introduced from the New World, is usually supplemented with clarifying names: pseudoactivity, false attack, robinia, false attack, pseudo attack or ordinary.
Since there are acacias and genuine, growing in the tropical climate of the southern hemisphere.
This type of plant came to Russia at the beginning of the 19th century and was widely distributed in its southern regions, since its main attachment to sunlight in these latitudes was completely satisfied. In the 20th century, the dendrologist and breeder, A.S. Yablokov received frost-resistant varieties of Robinia, able to resist the forty-degree frost. And they began to use the pseudoacaction in creating forest belts, to protect the roads from winter drifts in the forest-steppe part of the country.
In landscape design, in the last 20 years, decorativeness of Robinia was naturally appreciated:
- The crown of white acacia, which happens:
- pyramidal;
- spherical;
- umbrella;
- weeping.
- Features of leaf cover:
- univalent;
- small-leaved;
- sloping;
- dissected leaf.
- Coloring inflorescences:
- white and pink;
- dark pink;
- golden;
- lilac.
- In terms of flowering:
- ever flowering
- By the presence or absence of thorns.
The most common decorative varieties:
The tender beauty of Robinia is reliably protected by large, sharp spines - modified by stipules. But breeders have also created varieties in which this natural weapon of the plant has been eliminated.
Note. The theologians, investigating the circumstances of the last days of Christ, came to the conclusion that the wreath, which had scratched his brow, was woven from the branches of Robinia. The Jewish tradition, which endowed the sacred tree for the Jews, the acacia with the sign of immortality, also inclines to this conclusion.
Exceptional features of the southern tree
- White Acacia Root Systemthat goes deep into the ground and at the same time branching out in a diameter of 15 meters, it allows you to extract moisture even during the drought period and to keep tightly under gusts of wind on the mountain slopes.
- Acacia is exceptional growth rates, especially in the first years of their life: the increase for the season is 1.5 meters. This property is used to create forest belts and urban greening.
- Robinia has the ability accumulate nitrogen in the soil extracted from the air. With group plantings, the process of diazotrophy is particularly pronounced. From the neighborhood with white acacia in the joint planting benefit other plants.
- Leaf cover he feels fine in the conditions of gas pollution of city streets, he is able to survive with an excess of smoke in the atmosphere.
- Plant does not suffer from soil salinity, even being landed on the embankment of the seaside boulevard.
- Sunshinethe plants can also be seen in the peculiarities of the “behavior” of the leaves, which are located at right angles to the rays during the sunny day, lean down in the evening, and with an intense burning stream of light turn the sheet plate edge to the light source.
- Duration of bloomi white acacia (from mid-May to October) makes it a wonderful honey plant.
- Despite the external unpresentability of the trunk, covered with thick cracked bark, robinia's wood is a bit like oak, not afraid of prolonged exposure to water, which is very popular in shipbuilding.
- All parts of the tree - drives and keepers of useful substances: essential and fatty oils, tannins and flavanoids, tannins and sugars, organic acids and vitamins. Among them are substances that are effective in the prevention of cancer, and dangerous to humans, categories - poisons.
- Aroma of a blossoming tree able to positively influence a person’s emotional mood, relieve depression, negative effects of stress, replenish bio-energy reserves, especially for women.
Interesting.The sacred artifact - the Ark of the Covenant, according to the descriptions in the Bible was made of Robinia wood, and decorated with gold plates on top.
Description and photo
White acacia - it is a strong-growing deciduous plant, common as a result increasing its winter hardiness, throughout the European territory of our country.
- Wild tree reaches heights of 25 meters and even higher (in thick plantings). Krona has a spreading, openwork, tiered. Crown shape rounded at the top, cylindrical. The thickness of the trunk - from 30 cm to 1 meter in diameter. Lifespan up to 300 years.
- Powerful root systembranched with a strong central root extending into the depths.
- At a young age tree trunk covered with gray-brown smooth bark, with growth, the bark becomes thicker, it cracks, making the gray-brown trunk prominently from the furrows.
- Shoots have a smooth light green cover, which eventually becomes covered with spikes and becomes reddish-brownish. The growth of shoots is especially evident in the first year - up to 1.5 meters and further, up to 10 years - 80 cm in length.
- Kidney two speciesc - vegetative and generative very small and inconspicuous.
- White Acacia Leaf has a characteristic structure for this species: pinnate, alternately arranged. Each leaf cutting has up to 20 elliptical leaf shapes, the color of which varies depending on the growth phase of white acacia: from yellow-green with a silky edge in the summer, to dark green in the autumn. The modified stipules at the base of each such branch form long and very sharp thorns.
- Scented flower White acacia belongs to the zygomorphic (irregular), like the rest of the plants of the legume family. The five-leafed flower is formed only along the vertical axis and forms the “flag” of the upper, largest petal, the “wings” of the 2 lateral ones, and the bottom (coalescent) form the boat with androceum and gynetsy. The complex shape of the flower dictates selectivity in pollination: bumblebees and a bee take bribes well, but small insects do not have access to the fruit.
- The period of active flowering plants comes on the 6th year of his life. Most varieties bloom at the beginning of summer (from May to July).
- As a result fertilization ovary by autumn, fruits appear in the form of long (up to 12 cm) flat pods, and when ripe they turn brown. Each such horn has ten hard flat shiny seeds in the range of green, brown, black flowers. Seed pods can stay on the tree all winter.
Flowers of white acacia form inflorescences in the form of a drooping brush that attracts insects with a strong aroma. The color of the brush varies from pristine white to all shades of pink.
Reference. Plant material can be all parts of a plant. His collection for consumer purposes requires knowledge of the terms and conditions of security: when harvesting Robinia bark, more or less serious symptoms of poisoning are possible.
Visually familiarize yourself with the White Acacia tree (Robinia) or the false acrimony can be in the photo below:
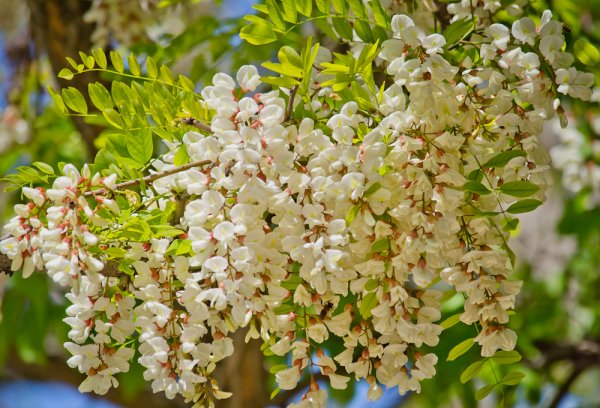
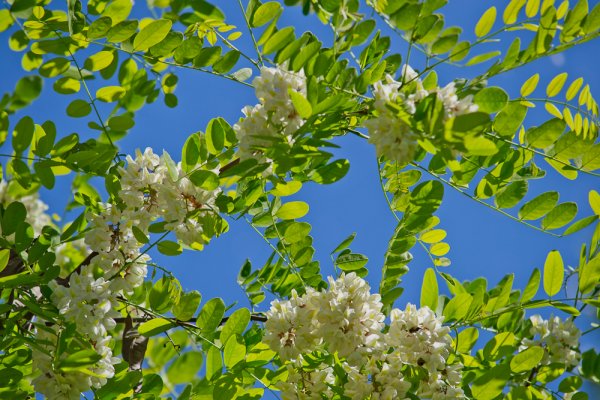
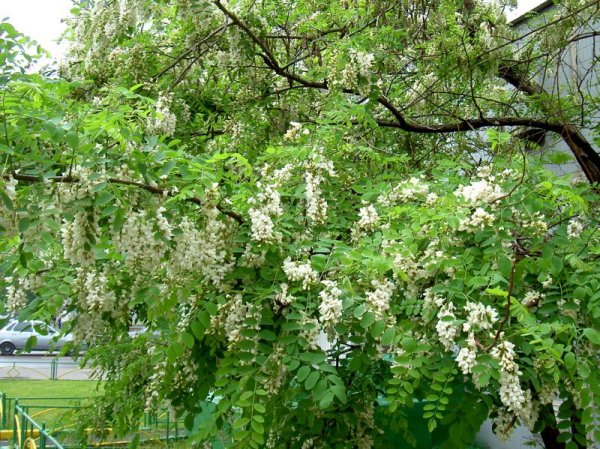
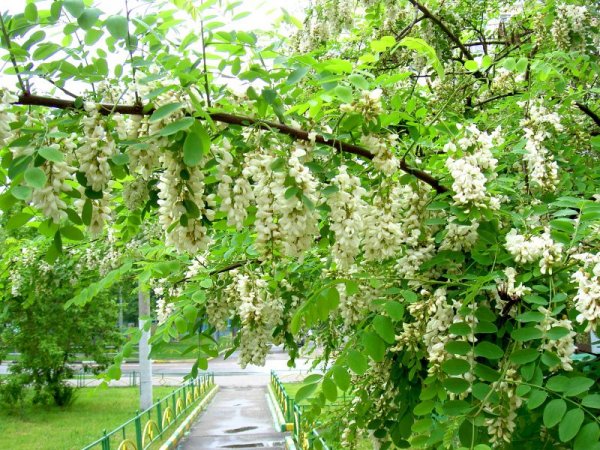









Application
What is useful acacia white?
The beneficial properties of white acacia make its application indispensable in the most various areas of production and consumption:
- it is used in decorative plantings, hedges and when creating windbreaks; in order to strengthen the slopes and grip sandstones;
- wood goes on constructionsailing ships and yachts, bridges and barns; piles and sleepers are made of it, supports for trellis plantings, parquet flooring and elements of piece guns;
- the beauty of the texture of a false assault was appreciated. in furniture and souvenir production;
- essential oils use in the production of toilet water and scented soap;
- acacia honey to all its taste qualities - the only one that, having bypassed the crystallization process, remains in liquid form for a whole year;
- leaves and flowers of white acacia eat cattle feed and used in the production of tea collections, coffee substitute, as a flavoring wines, the basis for dessert and jam;
- widely used possibilities of the chemical composition of the plant for medical purposes (in allopathy, homeopathy and traditional medicine).
Interesting. The inhabitants of the Caucasus invented a recipe for the original delicacies of acacia flowers: they dip a flowering brush into the batter and throw it into the boiling oil, as they do with donuts.
Healing properties
For the first time the healing properties of white acacia found their use in traditional medicine, which used both flowers, and bark, and leaves, and seeds of a white acacia for receiving tincture, decoctions, spirit tinctures, rubbing.
Acacia White Treatment
Traditional medicineand considered the chemical composition of pseudoacacies still insufficiently studied, since, along with undoubtedly useful substances, it contains toxins (for example, the alkaloid of robinin) that pose a threat to human life.
But homeopathy, working with meager doses, and treating “similar to similar”, took into use the healing arsenal of Robinia:
- as an antispasmodic;
- antipyretic;
- used in the treatment of colds;
- diuretic;
- expectorant;
- with internal bleeding;
- in the early stages of hypertension;
- external remedy for thrombophlebitis and varicose veins, myositis and radiculitis.
Reference. The system of homeopathic treatment involves the administration of microdose medications on an hourly schedule in close connection with meals and the exclusion of a number of tonic drinks and spices from the diet. The main task of homeopathy is to strengthen the immune system.
Read more about what acacia treats and how to prepare the tincture in the video below:
Planting and care
Casualty wild forms of white acacia to growing conditions does not mean that it does not need care and care at all. The first thing to take care of is the right choice of the place where the tree will reach its full bloom.
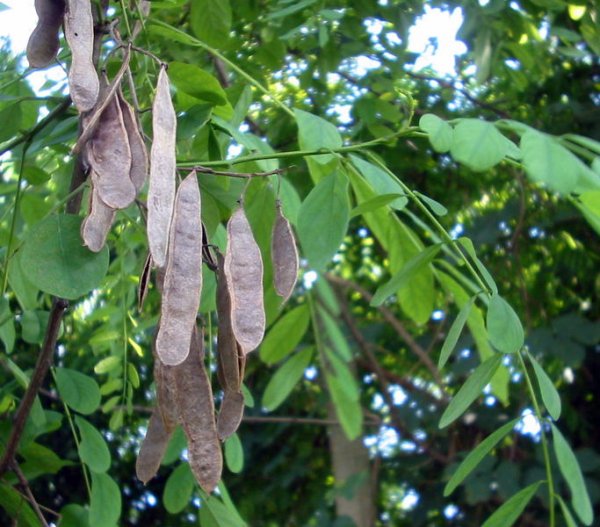

Useful video
Read more about white acacia (robinia) in the video below:
Attention, only TODAY!
In contact with
See inaccuracies, incomplete or incorrect information? Do you know how to make an article better?
Want to propose to publish photos on the topic?
Please help us make the site better! Leave a message and your contacts in the comments - we will contact you and together make the publication better!
One of the most beautiful trees belonging to the genus Robinia is acacia. Robinia pseudoacacia has another name - white acacia. However, it may not only be white. Depending on the type and variety of the plant, acacia flowers are red and lilac.
Robinia pseudoactivity: description
Robinia pseudoactivity is a beautiful decorative tree. During the flowering period, fragrant white flowers appear on it. Acacia can reach a height of up to 25 meters. The thickness of the barrel is 1 meter. The crown of the tree is open and spreading. On the trunk of an acacia bark is thick with longitudinal cracks. The leaves of the ornamental tree are arranged alternately and consist of egg-shaped leaves. They are green with a slight silvery shade, in length they can reach up to 25 cm. The flowers are small, fragrant, usually white, gathered in large inflorescences. Robinia blooms inactivity in May and June. Nectar in a flower stands out in large quantities over several days. Therefore, we can speak of high acacia medoproduktivnosti.

In the autumn, the fruits of the acacia begin to ripen - flat. In winter, when there is no foliage on the tree, spikes can be found on the shoots. A young plant is quite sensitive to low temperatures. With age, frost resistance increases. Robinia has an extensive root system. At the roots of acacia are tubers that contain bacteria. Thus, the soil is enriched with nitrogen. Acacia is successfully used in the food industry, medicine, and perfumery.
Main varieties and types of robinia
There are about 20 species of Robinia. The most common are the following:
Robinia pseudoacathy. Deciduous tree, which differs in various decorative forms. There is a pyramidal or umbrella crown, the form of a leaf is univalent or dissected. Flowers may be white or pink. Robinia is a new mexican. The height of the tree is no more than 12 meters. The leaves of Robinia of this species are large, about 20 cm in length.
The flowers are pinkish, odorless. Robinia is sticky. The tree has a rounded crown and can reach up to 11 meters in height. On the petioles of the leaves, shoots and inflorescences there are sticky hairs hence the name - sticky. There are no spikes on the shoots or they are not visible at all. The flowers of sticky robinia are pink with a violet tinge; they are odorless. Robinia is bristly haired. Low height of about 3 meters. The entire shrub is covered with reddish-colored setae. Robinia flowers are pink. Flowering begins in mid-June and until the end of September.
How to grow Robinia pseudoacacia
Robinia is mainly propagated by root suckers or seeds. Seed harvesting should be done in early November. They should be stored in the refrigerator. Before planting, seed is processed: immersed in boiling water, and then in cold water. After this procedure, the seeds should immediately. For this you can use the boxes. Seeds should be planted in mid-April or May. Pre-apply compost, ashes and nitrogen fertilizers into the soil.

In order for the seedlings to grow well, the temperature must be high. If the spring is cold, then it is recommended to plant in the greenhouse. Propagate root suckers easier than seeds. To do this, dig a young plant with a rhizome and transplant it to a permanent place. Seedlings well take root and grow in full sun. The soil mixture should consist of sod land, peat and sand in a ratio of 3: 2: 2.
The most effective way is reproduction by cuttings. In spring, when the weather is warm, take cuttings from several lateral roots of a healthy adult plant.
The length of the cutting should be at least 20 cm, and a diameter of about 5 mm. Next, land in the prepared nutrient substrate. Cut the root should be treated with crushed coal. Do not forget that the cut must be on the surface of the soil. In warm and humid weather, the appearance of shoots can be observed after a few weeks. All types of Robinia should be planted in the spring. If you plant in the fall, the roots of the plant may rot from cold or too wet.
Features care for white acacia
After planting, young seedlings require special care. They need to be watered and fed regularly, as well as weeds removed. After planting, in order for the plant to stick well, it should be watered liberally. Pseudoactivity is unpretentious in care, it grows quite quickly on any soil. The soil around the plant needs to be mulched. For this you can use peat, sawdust or small pebbles.
Because of the stagnation of water, the roots may die, so this should be avoided. It is better to use organic fertilizers in the form of manure or bird droppings, which are diluted with water. In the summer, robinia shrubs are recommended during and after flowering. If necessary, pruning old shoots. Next to the acacia can not plant fruit plants - apples, pears. Since the acacia has a highly developed root system, it will suppress other trees. With proper cultivation and care, decorative Robinias will decorate a country house or a country house and will delight you with their beautiful flowering and fragrant aroma.
Robinia fake on video: