Pot climbing roses on the plot. Indoor roses live in the garden
The seedlings with a closed root system are very popular because of their convenience. These roses are already planted in a container and have their own advantages. So that they quickly got accustomed, it is necessary to observe simple technology. Transplanting roses to open ground is quite simple, and even a beginner can handle it.
Care of seedlings before planting
Rose saplings in containers do not require immediate planting in open ground. If you provide them with good conditions, then they can grow up to several years. It is best to place the seedlings in the garden where there is no strong wind, and the sun will not be able to seriously dry the earth. Due to the fact that the seedling is in the container, an abundance of sunlight can overheat its roots, and a strong wind will accelerate their drying. A good option would be to dig containers into the ground or into sawdust.
Saplings need frequent regular watering before transplanting. (again, the reason for the small amount of land). It will be useful sometimes to spray the leaves with water. If planting is delayed for a long period of 1 month, then you should start feeding seedlings with liquid or soluble fertilizers that are recommended for seedlings. In this case, special fertilizers for roses will not work, because they are designed for bushes that grow in open ground, and at saplings in pots can burn roots. Therefore, in the case of a delay, you should consider feeding in advance.
Preparation of a sapling for an open ground
If the rose sapling was kept indoors or in greenhouse conditions, then before transplanting it into the garden, it should be allowed within 1-2 weeks to get used to outdoor conditions. To do this, you need to put a container with a rose for some time in the open air on the balcony or garden ploteach time increasing his time on the street. If the procedure was successful without harm to the flower, then you can proceed to the next step.
Before planting, remove the seedling from the pot or container to ensure the health of its root system. The best option in such cases will be the saplings of those firms that use metal inserts in the form of a grid, because then you will not have to destroy the earthen room to see the roots
Root system must cover the whole earth and have young white roots. Such a plant will not require additional processing, it will be enough to soak it in water for a couple of hours before planting. The metal mesh, if any, may not be removed. It will decompose without any harm to the plant within 2-3 years, without limiting the growth of the roots.
A more popular packaging method is the cardboard liner. It is somewhat difficult to check the roots of the future decoration of the garden, if they have not yet sprouted through the walls. When there is no possibility to verify the proper quality of the plant, or the root system was underdeveloped, then we can resort to using root growth stimulants. It should be diluted according to the instructions and soak the seedlings in the resulting solution for several hours.
Place for Rose
At one place the rose bush can grow up to ten years, which increases the requirements for site preparation.
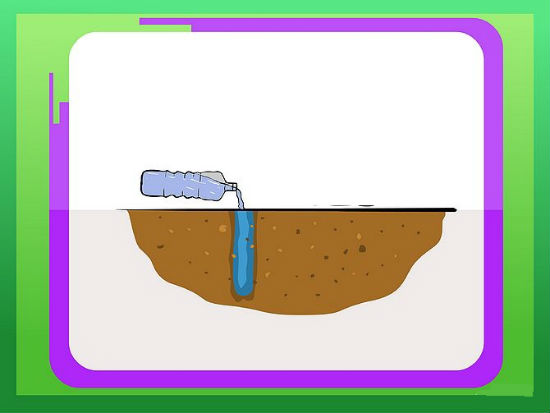
First, you need to prepare the landing hole. Its depth should be about half a meter, and the length and width of about 50-60 cm. From the upper fertile layers should not get rid of, and the bottom is better to remove. The main thing for any rose is a fertile, loose earth, therefore, humus, compost or peat should be added to the soil of the upper layer. You will also need sand and superphosphate (as a rule, the recommended dose is indicated on the package). To equalize the acidity of the soil, you can add a little wood ash or dolomite flour. All listed ingredients mix well, and the landing pit is filled with the mixture.
After filling in the pit, a recess is made so that when the coma with a seedling is dipped, its edges are below the edge of the pit by about 5 cm. Roses can be planted in a metal grid or in a cardboard insert. The only thing, it is better to remove those areas of the cardboard where the roots did not have time to germinate, otherwise it will slow down the growth by 1-2 weeks.
Next, the remaining space in the well is filled with a fertile mixture. It is obligatory to water about 8-10 liters of water so that the soil in the planting pit and around it is well soaked. After watering, the planting level is adjusted - the ground is poured, or the seedling is gently pulled to the desired level. After all operations, the surface is mulched with peat so that the earth crust does not appear. If the weather is too hot, then the seedling in the first couple of weeks is better to apply.

Roses, symbols of love and beauty, have existed for thousands of years, both in the wild and in gardens. To grow gorgeous roses, it is important to choose varieties that are suitable for your climate and help them thrive season after season.
In this article, you will learn how to grow this exquisite flower and what care is needed for their successful cultivation in budding roses.
Planting roses - preparing the soil
What would be right in the spring, the first thing is to take care of the soil for a comfortable growth of roses. The best soil for growing roses is loam. It consists of sand, silt, clay and organic material. Therefore, before determining the place for planting roses, you should find out the composition of the soil on your site, and change the composition to ensure maximum comfort for your roses.
The clay soil retains water well, but does not allow it to stagnate. This is usually a strongly alkaline substrate, and requires the addition of organic matter. So adding chalk or lime will improve the clay soil and provide good drainage.
The sandy soil well passes water, but demands frequent watering. It will also need to be amended in the form of organic additives, such as peat.
Very organic soil (peaty), as a rule, and very acidic. It will also have good drainage and retain moisture. You can add lime to raise the pH.
Compost can be purchased at garden centers or use cut grass and fallen leaves. Bring them into the soil in autumn or spring as soon as you wake up. Preparing the soil in the garden for roses in the fall will allow the organic matter to decompose over the winter.
Aeration - loosening and digging up the soil in the rose garden should be done every season - in spring and autumn. If you already have growing roses, work the soil around the bush, but be careful not to damage the rose bush.
Before adding additional components to the soil for improvement, make sure that the soil in the future rose garden is dry and loose (it crumbles easily). Take a handful of earth and squeeze it. Too wet soil will stick together in a lump, and dry crumble.
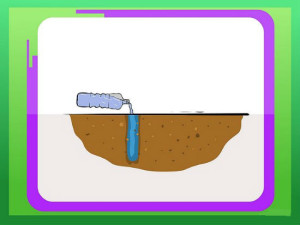 Check the soil for drainage - dig a hole 30 cm deep and fill it with water. Water should be absorbed into the soil in about 15 minutes. If it takes much more time, or vice versa, it happens too quickly, it may be necessary to make several amendments to the composition of the soil under the rosary.
Check the soil for drainage - dig a hole 30 cm deep and fill it with water. Water should be absorbed into the soil in about 15 minutes. If it takes much more time, or vice versa, it happens too quickly, it may be necessary to make several amendments to the composition of the soil under the rosary.
Make sure the soil under the roses has a pH of about 6.5, which is slightly acidic. Such soil is usually located in the forest.
- You can raise the pH by adding lime, or wood ash, if the soil is too acidic. If it is too alkaline, add pine needles, peat or rotted leaves. If your roses grow poorly and there are yellowed leaves, it may mean that the soil is too alkaline, either.
Add other additives, such as bone meal or complex fertilizers (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium). The proportions are 1: 2: 1.
- Phosphorus helps roses to bloom. Avoid excess nitrogen, this will cause even greater foliage growth and fewer buds.
- Alfalfa, salt or manure are also good additions to the soil.
You can buy a special primer for roses. Its soil already has the desired composition and fertilizer. To save you can only add to the hole with roses a certain amount of soil during planting.
How to plant roses
Choose your favorite variety of roses. Do you know that there are more than 13,000 varieties! Not all roses grow the same in different regions. Investigate the specific nature of the plants in your area, and then choose roses, with suitable characteristics that you will like. Assess their shape, size and color when choosing varieties for cultivation.
Varieties of roses
- Beautifully-shaped hybrid tea roses are colorful roses that are often used in flower shops as part of bouquets.
- Floribunda - roses are the brightest of all varieties. Each bush has many flowers, and not just one on the stem.
- Grandiflora is a cross between hybrid tea and floribunda. They grow quite tall, with several branched stems.
- Climbing roses can be pulled out like ivy, along fences and walls.
- Miniature roses are very tiny, including ideal for planting in a container.
- Spray and park (street) roses are quite hardy, resistant to pests and diseases. They have a wide variety of color shapes and sizes.
- Tree roses require a little more care than some other roses.
- Hybrids.
What are rose seedlings
![]() Once you have chosen the variety of roses that you want to plant, decide in what form you want to buy them. Bare cuttings with the roots of roses, which are planted directly in the ground or seedlings of young roses, which are already planted in a small pot, and transplant them to the ground or another pot. Any type can be purchased in the nursery. Rare varieties of roses can be found on the Internet.
Once you have chosen the variety of roses that you want to plant, decide in what form you want to buy them. Bare cuttings with the roots of roses, which are planted directly in the ground or seedlings of young roses, which are already planted in a small pot, and transplant them to the ground or another pot. Any type can be purchased in the nursery. Rare varieties of roses can be found on the Internet.
- Bare root roses are planted in early spring, giving them time to take root before they germinate a few weeks later, when the weather sets.
- Pot roses can spend the winter in the apartment, and then planted in the ground in the spring.
Rose Care Tools
To start a successful work in the rose garden, purchase some of the necessary tools for the job:
- Gardening scissors. Pruning roses keeps them healthy, encourages the growth of new shoots, and keeps them in beautiful shape. Scissors are essential for growing roses. Get small curved scissors and large loppers.
- Garden gloves. Protect yourself from spikes with thick gloves.
- Fertilizer. Roses should receive fertilizer several times per season. You can buy fertilizers specifically designed for roses, but this is not strictly necessary.
- Mulch. Soil mulching will help repel pests and preserve more nutrients in the soil. Use wood chips, pine needles, peat, or another type of mulch suitable for your area.
- Compost or humus. Add it to the soil when planting roses, it will help their growth.
- Shovel and spatula. With their help, you'll make pits prb planting roses.
Planting roses
Planting roses means choosing a place that receives at least 6 hours of good sunshine per day. It should not be crowded with roots or plantings of other plants and trees. The soil should be loose and have good drainage, if the soil is heavy and clayey, loosen it and add chalk or gypsum granules before planting.
- Roses grow best when the soil has a pH of 6.3-6.8.
- To determine if the drainage is good in the selected area, walk around it after the rain. If the soil is wet but not swampy, it will be loose. If you see puddles or large mud spots on the plot, choose another place or process this to make it more conducive to growing roses.
If you plant seedlings, soak them in a bucket of water for several hours before planting. If you plant roses from pots, carefully spill the soil with water and leave for 30 minutes to soak the earthy clod. After this, pass the flower along with a clod of earth into the prepared hole.
Preparation of holes for planting roses
For each rosebush, prepare a separate hole. Dig a hole 50 cm in diameter and 50 cm deep. The dimensions of the pits are approximate, but such a wide one and depth will be suitable for most varieties of roses. Mix the soil from the dug hole with the compost and pour part of it into the middle, forming a hillock inside the hole. Add some fertilizer for roses.
- If you plant several bushes, leave between them a space of about a meter, for the free growth of the root system, the volume of rose roots can be from 1 to 2.5 m.
Planting roses in the ground
Place a rose stalk or a pot bush on top of a hill in the hole. Fill the hole with soil. The share bud of a rose should be located at a depth of 5 cm below ground. If you live in a cold region, you may need to plant roses deeper to protect them from low temperatures.
- If you are planting roses from a pot, gently squeeze its walls so that the roots come out with a clod.
- Make sure the soil fits the roots tight, press it with your hands to remove any air pockets.
- Careful watering of the planting site will help to consolidate the soil at the roots. Make sure that the moisture after planting is sufficient.
- Lay the mulch around the roses. If you have planted a shrub pot, place the mulch around the stem, this will keep the temperature constant and protect the roses at an early stage of growth.
How to grow roses successfully
Watering roses in the summer, when they need plenty of water, will help the rose bushes grow healthy. Do not allow the soil to dry out, if you see dust on the buds, then the roses should be given a deep watering. Depending on your region, roses should be watered about once a week.
Top dressing roses
After planting, the roses need to be fed several times during the growing season. Use fertilizer (liquid or granules) in early spring, when the first leaves appear. Use it again after the first flowering, and again if the roses bloom again. Finish dressing at the end of the summer, around September.
- Some fertilizers have a slower absorption (granules), so they should not be used often.
- Excessive fertilizer of roses, can lead to diseases.
Ash top-dressings are good - we drop ash in the near-stem circle at a distance of 15-20 cm from the stem. This feed can be repeated from early spring to autumn, thus, performing the procedure 5 times per season.
For better flowering of roses, you can feed them with infusion onion peel - lay the husks in 3 - x liter jar and pour boiling water over, insist day. The resulting solution is further diluted with water 1:10 and we water the roses. By the way, such a top dressing is good for indoor plants.
An excellent source of potassium and magnesium as a top dressing for roses, is -! Dig in the spring banana skins near the roots of roses within a radius of 25 cm.
Pruning roses
 Pruning roses keeps them beautiful and healthy. The purpose of pruning is to remove excess foliage and open a shrub, which helps prevent rotting and disease. The pruning strategy differs depending on the season, but the pruning technique is always the same - prune a little higher than the branching of the stems, above the annular thickening on the stalk.
Pruning roses keeps them beautiful and healthy. The purpose of pruning is to remove excess foliage and open a shrub, which helps prevent rotting and disease. The pruning strategy differs depending on the season, but the pruning technique is always the same - prune a little higher than the branching of the stems, above the annular thickening on the stalk.
It should be cut and the power of the buds, which would give the opportunity to bloom new. This is a rather pleasant moment, because a beautiful bouquet is the best interior decoration. You can find out what to do so that roses and other cut flowers stand in a vase longer.
- Trimming is very useful for air circulation.
- In late winter or early spring, dry branches should be pruned. Cut off the stepson processes that are smaller than the branches of the main stem, so that they do not take nutrients from the bush. Leave about 8 cuttings, trimmed to 1/3 of their height. This will promote healthy growth, with the onset of spring.
- In the summer, be sure to remove faded buds. This stimulates the growth of new ones.
Wintering roses
Roses that have not been cut for the winter can be damaged by strong winds and frost. Trim the stems to a height of 60 to 70 cm. Tie them together with twine, and in the northern regions wrap agrofiber over the top to help protect them from the weather. Spray the roots with the compost around the base of the bush, and then lay a layer of straw on top. When in spring the ambient temperature is set above 10 - 12 ° C, roses can be opened by removing the compost and shelter.
How to plant a rose video
website ideas for giving
To print
Peter Verigin 04/17/2014 | 4227
There was a time when climbing roses were considered rare and exquisite decorations of palace parks. Now they are braiding the walls of houses, covering arches and pergolas, winding around the trunks of old trees on the backyards of country houses.
AT middle lane The most common are two varieties of these plants: many-flowered and large-flowered.
Multicolor roses grow sprawling shrubs with arched lashes from 2 to 5 meters long. Their branches are covered with medium-sized, odorless flowers of various degree of terry up to 3 cm in diameter. The flowers are collected in the brush. These roses bloom more than a month. Flowers are formed on last year's shoots. In the spring they are not cut. After flowering, remove only those withered shoots that are more than 2 years old.
Large-flowered roses - it is shrubs with lashes up to 3 m. They bloom throughout the summer with terry fragrant flowers, similar to the flowering varieties hybrid tea roses. Brush inflorescences have from 4 to 10 flowers.
Decorative properties of climbing roses
The splendor of the proud climbing beauty sometimes creates a desire to grow them not only in the ideal conditions for a sunny flower garden, but also on paved grounds, on the terrace, next to a chaise lounge for rest or in any other places. To do this, growers planted roses in tubs, pots or hanging pots. Due to their decorative effect, they are ideal for growing in pots. Their long, picturesquely hanging shoots become a magnificent living decoration of terraces and balconies. Twisting the supports made of metal rods, they form luxurious flowering hats.
Climbing roses grown in pots and containers can also be used for vertical gardening of walls. In the cramped conditions of flower pots, climbing beauties require special attention, but they grow quite well and respond to care with long, rapid flowering.
Rules for planting roses in containers, pots and tubs
For growing grafted roses clay containers with dimensions of 40x40 cm and a depth of at least 60 cm are suitable. Small, in comparison with the grafted plant, the root system own-rooted bushes allows you to plant a rose in a less deep pot, but its height should not be less than 40 cm.
Before disembarking roses in a container must be removed with pruning shears, dead roots and weakened shoots, and also a little to shorten healthy roots and strong shoots, and then place the seedlings in room temperature water, in which the root formation stimulator is dissolved in a proportion of 2 g per 10 l of water. The root system of roses should be in this solution for about 10 hours.
The quality of the soil is well suited German earthwalk "Greenworld". In a clay pot that allows the roots to breathe, drainage holes are made that cover with shards or flat stones, and a drainage layer of sand or expanded clay is poured in from above. The pot is partially filled with soil, in which a rose is planted so that the roots do not bend. The ground is filled until the grafting site is covered by 3-5 cm. The soil is well compacted and shed with water with a root-stimulator, in which the roots are soaked.
Wintering tub climbing roses
Roses in pots, pots and pots are much easier to ensure wintering, as there will be no need to hide them for the winter. Enough capacity move to the basement for the period of cold weather and put it on a sheet of foam.
A wintering rose is not required. shine. Perfect temperature for it - from +8 to -5 ° С. Wrap placed in the basement of the plant is not necessary, it is enough to pile upto close the vaccination site, and give him rest until spring. In such conditions, the rose is easier to survive the cold.
If the roses cannot be moved to the basement or lowered into a hole, they are moved to the wall of the building and shelter straw, dry leaves or spruce branches. If this cannot be done, then the tubs are lined with foam and wrapped with sacking, and the plants are wrapped with spruce leaves.
Features care for climbing roses in spring and summer
Spring tubs with roses taken out to the open air and placed in any places open to bright sunlight, with good ventilation. In the sun, plants dry out quickly from rain, which is a natural prevention of fungal diseases.
Water and feed up potted roses are needed more often than unpaved. Once every 2 weeks they are fed with liquid fertilizers, using half the dosage from the standard indicated on the package.
Prevention of climbing roses
So that fallen petals and withered shoots do not become a source of fungal spores or aphids, they must be cleaned immediately. Withered flowers should also be regularly removed, making a cut under the first pair of leaves under the flower.
From gall nematodes Roses will protect the marigolds or geraniums planted next to them. It will strengthen plants well and give them strength to resist diseases. spraying leaves and stems decoction of dry grass of horsetail (enough 200 g per 1 bucket of water).
Due to lack of fresh air or excess moisture, leaves may become covered. mealy dew. In these cases, roses are sprayed with a solution of sulfur soap.
To print
In the horticultural centers and local nurseries roses with an open root system are sold in pots. By the time of flowering, the clod of earth is already “stitched” with new roots, which is not bad for a transplant. It is better to spend it on an overcast day, after making sure that the sapling is watered enough and not depressed.
In the case of potted roses, the graft site is always high above the ground. In cold areas, the graft site after transplant should be hidden underground. A pot with a rose is put in a landing hole to determine approximately the location of the vaccination. If necessary, deepen the pit.
To transplant a rose after purchase, you need to remove it from the pot, take it under the area under the grafting site and, swaying the pot, carefully remove it. such as New Generation, gently pull out of the pot, keeping the seedlings as close as possible to the base. They can be placed in the ground at the same level as they were in the seedling pot, and then sprinkle the soil.
If the roses in the pots are bought at the very beginning of spring, they will have to be transplanted as plants with, because after extracting the seedling, the entire substrate will remain in the pot.

Often, when the roses are extracted from the pot, the roots are wrapped around the base of the coma, and then they should be cut before planting, otherwise they will not go into the soil, but continue to grow in a circle. Gardening centers in order to save use small pots. This exacerbates the problem of weak growth caused by twisting the roots. Matted roots are cut so that the rest are easily separated from each other. A rose prepared in this way can be transplanted.
If the garden is heavy soil or insufficient drainage, it is better to grow roses on. Hanging out of them, ground cover plants look very impressive. On a raised flowerbed looks impressive. Caring for miniature roses in a high bed, do not have to bend over much. But do not plant roses on the raised bed of roses, otherwise they will become less winter-hardy.
As a frame for a raised bed, it is preferable to use wooden structures, but not railroad sleepers. They are treated with creosote, and if it gets into the soil, it will damage the plants. The soil for the raised flower bed is harvested from garden land. For a bed miniature roses suitable land, which remained after the construction of a small. Sold in stores and horticultural centers, the soil dries quickly, so you need to add special organics to it.
Roses on raised beds require more watering. Here is effective; You can also put irrigation hoses in the flowerbed. Near the frame of the raised flower bed, you must additionally cut the grass so that its roots and seeds do not harm the seedlings.
For roses, which were originally in the pot, it is useful to have a uniform drip from the hose. It happens that a rose that has grown beautifully in a pot, after being transplanted into the ground, will fade, despite all efforts. To remedy the situation, it is recommended to prune the plant for several days; it is also useful to resort to drip irrigation.
In some horticultural centers, potted roses are grown in greenhouses - to accelerate flowering. These roses are usually crammed with synthetic fertilizers, and after the greenhouse conditions they need to be given several days to acclimatize in the garden. It is best to keep them this time in the shady place and water regularly.
Acclimatization of roses from pot to garden
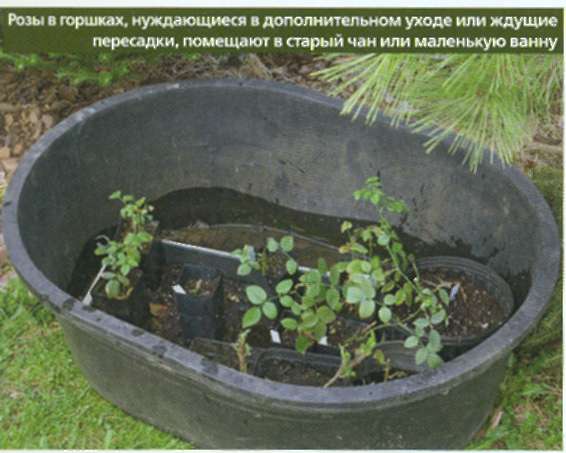
Many valuable varieties garden rosesthat you really want to breed, you can only get in specialized nurseries, making an order by mail. Kornes own roses are delivered in pots. When purchasing small plants, it is important to bear in mind that before transplanting they will have to be carefully cared for. Even in a mature form, extremely hardy and unpretentious, they are not ready to immediately move into the garden of tiny pots. A little extra attention after delivery will pay off over the years the joy of flowering.
Specialized nurseries supply roses at the beginning or middle of the growing season. Almost always these plants have leaves, and sometimes buds. Having received roses in small pots or containers, you first of all need to place them in an old vat, small bath or other suitable container, where the sun peeks only two or three hours a day. Rain water should get into the tank so that the flowers, most of the time in the shade, are sufficiently moistened. After a few days, small roses are transplanted into larger pots. Pre-check whether the roots appeared near the bottom of a small pot. If this is so, then the rose is actually a rooted own, and not just a rooted cutting that will require special care.

Own rosé roses from small pots are recommended to be transplanted into large ones with a capacity of 1 liter, and after six weeks into four-liter ones. These large pots are placed in a vat or other container and left there until new leaves appear. During the acclimatization period, fertilizing is carried out with fish emulsion (highly diluted) and / or liquid seaweed extract.
With the beginning of growth, large pots with roses are transferred to a sunny place, where they are fed with slow-acting fertilizer (1 tablespoon each) and watered daily. Flower growers that do not use synthetic fertilizers can continue to feed the roses in portions of fish emulsion and seaweed extract.
As soon as it becomes clear that the sapling is healthy and grows well in a four-liter pot, it is transferred to the garden. Even the most hardy and unpretentious rose at first needs to be looked after, like an immature patient. Such plants are recommended to be replanted in September, to be closely monitored, so that until the end of the growing season they are always well watered and weeds do not oppress them. Before the first wintering, they should be highly detrimental, even if they do not need shelter for the winter. should be carried out in any garden where there is a threat of freezing of roses in harsh winters. A hill of soil poured around the seedling will protect the clod at the roots, still loosely connected with the surrounding soil, from drying out during alternation of frosts and thaws.
Selection rules planting material
Preparing a place for planting roses
Benefits: own-rooted or grafted roses?
Autumn transplant of roses from pots