Formation and pruning of fruit trees and shrubs. The best time to trim a garden in spring. Red currant pruning
This book is intended for gardeners of the middle zone of the Soviet Union. It describes the characteristics of the development of fruit breeds and varieties mainly in this zone.
The large-scale commercial gardening developing in our country requires well-trained personnel, armed with the knowledge of modern gardening science. In particular, sovkhoz and kolkhoz gardens need skilled cutters, on the skill of which the success of gardening largely depends on the productivity of the gardens, the timing of their entry into fruiting, the durability of the plantations.
Offered to the attention of the reader the book is intended primarily for young gardening personnel specializing in pruning. But not only for them. For each collective and state farm grower, no matter what work he performs, it is useful to master the complex, important and, one can say, fascinating work of correct formation of fruit trees and berry bushes, a matter requiring not only knowledge and skill from the grower, but also great observation.
In order to properly trim the plants, the gardener must first of all be well versed in the biological characteristics of fruit plants. He must be clear that the plant is constantly changing. It is known, for example, that shoots develop from the leaf bud. They, in turn, turn into branches and branches (the difference between these concepts will be clarified). The branches in the process of tree development are covered with branches of various types. The changes that occur with each part (or organ) of a fruit and berry plant are so significant that as these parts develop, their names change.
Well, having understood all this and learned it, the gardener will understand freely in numerous terms that are called essentially the same part of the tree as it develops and becomes more complex. So, escape, branch, branch, branch - all these are the names of the same parts of the tree at different stages of their growth.
The tree, according to the figurative expression of Professor P.G. Shitt, is its own recorder. We must learn to read these records, or, more simply, to understand what is happening in the tree crown. Without this, correct pruning is impossible. Reading the literature on gardening, getting acquainted with books describing the structure of plants, find directly on living objects, trees, bushes, their separate parts and organs, look for traces of fruiting, determine age, type of fruiting and other properties of the breed and variety. This will greatly assist you in mastering the trimming technique described in the book.
It is very useful if a young gardener will observe how an experienced worker leads pruning. However, you can not learn pruning, just watching her. When the basic features and rules of pruning become clear to you even in the most general terms, proceed to pruning and carefully observe the results of your work. In a large garden there will always be plots or individual plants on which young cadres, under the supervision of experienced workers, will try their hand and hone their skills.
It goes without saying that the role of the book, which is a manual for pruning, is to some extent limited. She can not equip obrezchika necessary practical skills. But in it the reader will find a description of a number of sections of plant biology that are directly related to pruning, practical guidelines for pruning all the main species of fruit and berry plants in connection with their biological features, the rationale for individual pruning techniques. Without this, mastering the art of pruning is also impossible.
Strong theoretical knowledge in combination with practical skills is the main condition for the success of pruning, which can rightfully be regarded as one of the most important agro-technical measures in gardening.
Popular articles of the site from the section "Food and Health"
Can I lose weight with green coffee?
Not all advertised products really help to lose weight, but absolutely all of them swear to help. Today, green coffee is at the peak of popularity. What is so special about it and why has green coffee become the number one tool for weight loss?Popular articles of the site from the section “Dream Interpretation”
Why do we dream of people who have died?
There is a strong belief that dreams about dead people do not belong to the horror genre, but, on the contrary, are often prophetic dreams. In a whole series of dream books, various roles are assigned to different roles ...When do prophetic dreams occur?
Clear enough images from a dream make an indelible impression on a person. If after a while the events in the dream come true, people are convinced that the dream was prophetic ...If you had a bad dream ...
If you have a bad dream, it is remembered by almost everyone and does not go out of your head for a long time. Often a person is frightened not so much by the contents of a dream, but by its consequences, because most of us believe that we do not see dreams in vain ...Popular articles from the section "Holidays and Gifts"
|
Corporate Party Scenario
|
Pruning and nipping trees and shrubs in the country
Regular pruning is one of the elements of care for garden trees and shrubs. It is of great importance for plants. Depending on the method, degree and timing, age and condition of plants, weather conditions and varietal affiliation, various effects can be achieved by pruning.
❧ According to the Guinness Book of Records, the world's largest apple has grown the size of a soccer ball. The mass of a beautiful red fruit was 1.8 kg. An apple was grown in the Japanese city of Hirosaki by Chisato Iwasaki.
Why do you need to prune trees and shrubs
There are several types of trimming.
1. Formative pruning. She spend more often in young trees. She forms a strong skeleton of a tree with evenly distributed branches. Pruning is subjected to semi-skeletal and overgrown branches. Old trees are removed tops. After such pruning, the lighting inside the tree crown improves and the trees start to bear fruit earlier.
2. Crop to improve yields. This type of pruning causes an update on overgrown branches. After it, the trees give a consistently good harvest.
3. Anti-aging pruning. It is carried out at those Trees that cease to grow.
4. Restorative pruning. Carried out in the event that the tree suffered from frost or mechanical damage to the crown. Pruning restores the crown of trees.
5. Sanitary pruning. This is the removal of dry, broken, diseased branches and their parts.
In young plants, branches are pruned to form a crown, in adults - to maintain the shape of the crown, remove dry and diseased branches. Old trees and shrubs are pruned with a rejuvenating goal. Many valuable varieties of fruit trees need to be pruned each year to get a good harvest.
Pruning reduces plant height, the number of harmful insects on them and the frequency of diseases. It makes the fruiting periods of trees and shrubs more uniform. Gross harvest of fruits during pruning may decrease, but the size and quality of fruits increase. For example, coloring of fruits improves. After pruning, the general condition of the plant is improved, the light-air mode is optimized. This makes trees and shrubs more resistant to pests and diseases without the use of chemicals.
When is it best to prune trees and shrubs?
Pruning trees and shrubs carried out at different times. In early spring pruning done in March - before the movement of the juices in the plants. Otherwise, the plants will lose a lot of nutrients during pruning and weaken. At this time, prune crops (pears, apples) are usually pruned. Red and black currants are pruned as soon as the snow depth is reduced.
From March to May, mainly in March-April, most of the fruit trees are pruned. First pome, then stone fruit cultures.
Mature trees can be pruned at a later time - from May to June. They are cut even during the flowering period and after it. Reducing the crown in adult trees reduces the cost of recovery after winter and growth.
Some fruit trees, such as apricot, can be pruned in summer. As a result, they will bloom next year. This will help protect the crop from spring frosts.
In the summer, from June to July, pinching (pinching) and breaking the shoots are carried out. This removes unnecessary shoots. They will be completely removed at the next spring pruning.
In the fall, they usually carry out sanitary and anti-aging pruning. They are carried out after the beginning of leaf fall. It is in autumn that old and neglected trees are cut, as well as berry bushes - all types of currants, raspberries, gooseberries, etc.
In winter, fruit trees are pruned only in the southern regions, where there is no likelihood of frost damage to the trees. In central Russia, in the winter, they occasionally carry out forced pruning of trees. At the same time, the protective sections of the branches are left on the tree. With such pruning, the branches damaged by adverse effects (strong wind, rain with icing, etc.) on the trees are removed. This reduces the load on the trees and prevents fractures and splitting of the branches in the future.
Pruning trees and shrubs carried out with the following objectives:
✓ get a small healthy tree with a compact crown, which would be excellent fruit every year;
✓ create a tree with a strong skeleton - branches evenly spaced in space;
✓ maintaining crown size at a certain level;
✓ creation of a good illumination in the crown;
✓ regulation of growth and fruiting, reducing plant height and fall of fruits;
✓ increase the quality of fruits - mass and size, color;
✓ easier harvesting;
✓ reducing the frequency of diseases and the number of insect pests;
✓ creation of conditions for the physiological balance between growth and fruiting in different periods of plant life; an increase in nutrient supply to the remaining tree tissues;
✓ rejuvenation and increase the life of the tree.
If you do not adjust the height of the trees, they will be very high, and the fruits are crushed. Their winter hardiness will also decrease.
Pruning trees and shrubs is carried out in two ways:
1) thinning, or cutting (Fig. 1). With this method, pruning removes competitive, interlocking branches, as well as very close and contiguous ones. Thinning is performed by the method of "ring" or transfer to the side branch. When cutting "on the ring," a cut is made at the base of the branch along a circular influx. Stump at the same time do not leave. It is not necessary to make a cut deeper than the annular influx, since this results in a large wound surface that heals longer.
When removing large branches using the method of "three propyl". First, the branch file off the bottom of a quarter of its thickness. Propyl make at a distance of 20-30 cm from the trunk. Then they cut down the branch from above. At the same time, the third cut should be 5 cm farther from the barrel than the lower one. Then cut down the remaining stump. Such a phased cutting prevents the peeling and splitting of the bark, leaving a minimal wound that heals well;

Figure 1. Thinning
2) shortening (Fig. 2). With this pruning method, the end portion of the branch is removed. After pruning, the nutrition and moisture supply of the remaining part of the branch and, accordingly, the buds on it are improved. Therefore, shortening has a stimulating effect on the ability of the tree to grow. It reduces the size of the crown and makes the tree eventually more branched. Shortening is carried out by the “kidney” method. Branch cut obliquely above the kidney. In this case, the cut should not be very oblique, otherwise the kidney may dry out or give a weak shoot. To shorten the branches resorted in the event that in a timely manner they were not nipped.
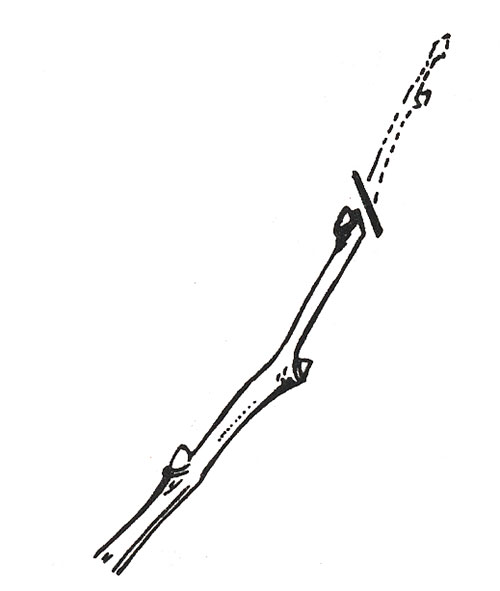
Figure 2. Shortening
The following rules must be observed during trimming.
1. When cutting large, long and heavy branches must be supported by hand.
2. The cut should not be done flush with the surface of the trunk or main branch.
3. On the branches can not be left big spikes.
4. The branches are cut at a small angle relative to the line parallel to the main branch.
5. When cutting large and heavy branches, they are pre-facilitated (remove smaller branches). It is advisable to remove them in parts.
6. Heavy pruning branches after cutting should be lowered with ropes. This will prevent damage to the tree and neighboring plants. Preliminarily, the upper end of the rope is fixed above the branch to be cut, and the lower end - on the branch to be cut closer to the trunk.
7. The edges of the cuts, whose diameter is more than 2 cm, should be cleaned, treated with disinfectants and covered with an insulating layer.
8. On sections there should be no grooves, as they accumulate moisture and possibly rotting wood.
9. Do not leave large hemp after pruning. They do not grow as full-fledged branches and gradually die off. As a result, in their place formed branches.
10. It is impossible to immediately remove a large number of large branches, as this will delay the growth of the tree or lead to its death. They are removed by 1-2 per year.
11. When pruning from slow-growing trees (apples, lindens, elms, norway maple) remove 20-50% increase in the last year. Trees that grow quickly (poplar, ash green, ash-leaved maple) remove 60-70% growth.
The pinching of plants, or pinching, is the removal of the top of a growing shoot (Fig. 3). It causes the branch to stop growing for 2–3 weeks.
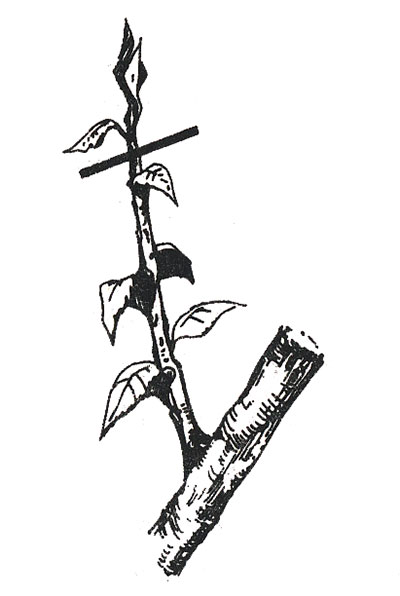

Figure 3. Pinching escape
Pinching is done by hand or pruner. It is carried out mainly for the formation of the crown of young trees. With the help of pinching, they make branches co-ordinated, prevent the growth of shoots in unsuitable places. Pinching is done before the shoots are woody.
On young trees in the spring of each escape, continuing the skeletal branch, there are competing shoots. They reduce the flow of juices to the main runaway and are identical with it in degree of development. Competitor shoots pinch or break when they reach 10-12 cm. After pinching, growth shoots become fruitful for 1-2 years - they begin to bear fruit. This is due to the fact that after the manipulation on the shoots, the development of the lower buds increases. When a place of pinching several strong shoots appears below, the branch is cut over the strongest of them. That escape, which remained, pinch over the 3-5th leaf. When a long shoot is formed, it is cut off above the 3-5th leaf. With the formation of several short shoots leave everything. Also remove unwanted shoots and tops. In the future, they will unnecessarily shade the crown, so do not leave them. If at the end of summer the shoots did not complete their growth, then the tree’s resistance to frost decreases. Therefore, the tops of the shoots pinch and then the lignification of the annual shoots occurs.
Who works in the country from a young age, the technology of spring pruning knows by heart. However, it is useful to remind you that there are three main techniques.
Kidney slice used to shorten the annual increase. To do this, near the base of the branch, choose a well-developed kidney, which is directed from the trunk to the outer side of the crown. Cut the branch above the base of the bud by 2 cm with a slope of 45 °. If done higher, then the extra tissue of the tree will not let the wound heal quickly. And if lower, then the bud will dry up or the shoot will develop too weak.

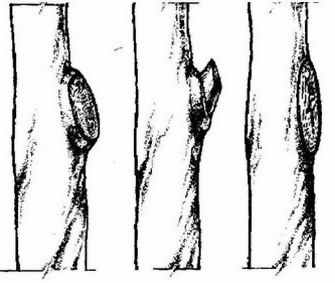 Cut into a ring spend in adult trees when you need to remove a branch or reduce its length. Branch cut to the desired length at an angle of 90 °. When removing completely cut at the base, leaving a stump with a length of 0.5-0.7 mm. To cut a very thick branch, first cut it from the bottom at a distance of 25 cm from the trunk, then from the top 5 mm closer to the base. Remove the rest of the branch, supporting it with your hand. The figure shows that at number 1 the cut is correct, in the second case the stump interferes with the overgrowth of the cut, and in the third cut it is made very deep.
Cut into a ring spend in adult trees when you need to remove a branch or reduce its length. Branch cut to the desired length at an angle of 90 °. When removing completely cut at the base, leaving a stump with a length of 0.5-0.7 mm. To cut a very thick branch, first cut it from the bottom at a distance of 25 cm from the trunk, then from the top 5 mm closer to the base. Remove the rest of the branch, supporting it with your hand. The figure shows that at number 1 the cut is correct, in the second case the stump interferes with the overgrowth of the cut, and in the third cut it is made very deep.
Pruning to translate used to change the direction of growth of the branch. The cut is made with a slope of 30 ° in the direction required for growth.

Pruning fruit trees
With fruit bearing trees, two important procedures should be remembered: the branches should be shortened and thinned. The first accelerates the growth of shoots, and therefore increases yield. The second improves the crown illumination and increases the number of ovaries, as the flowers receive more light and heat.
Depending on the age of the tree and how it bears fruit, the branches should be cut strongly (slightly more than half the length) or weakly (by a third). With a strong shortening is formed up to 3-4 new shoots. Annual branches should be cut above the bud, perennial branches above one of the branches. Old trees should be pruned necessarily. As soon as the tree begins to produce fewer fruits, it is necessary to form a new crown in the spring. Young trees should be pruned to form a crown and consistently high yield.
Which form to choose?
When pruning trees can follow several forms of crowns. All of them have their pros and cons.
Bush shape different high spreading. The first branches depart to the sides at a height of 50-70 cm from the ground. Large branches in the crown 4-6 pieces, and it is impossible to determine which of them is the most powerful. Such a crown is almost not damaged by frost, but the fruits inside the thick “cap” do not have enough solar heat, so the crop is reduced. It is suitable for heat-loving plants (apricots, peaches, plums) and low varieties of apple and pear trees. The tall ones will occupy too much space.
Pyramid shape crowns suitable for winter-hardy apple trees, pears, cherries. The plant remains a powerful central trunk, and the branches are further pruned by “herringbone” - the higher, the shorter. For the winter, these trees need additional shelter, but in summer the fruits receive maximum heat and sunlight.
Standard crown it is formed in the same way as a bushy one, but the distance to the first branches from the ground is 1–1.5 m. This is done on lands with high groundwater so that the lower branches do not rot and spoil. A boom can form a pear, which generally does not tolerate excessive moisture.
Free form suggests that the tree can be allowed to grow without formative pruning (but you should not forget about sanitary!). It can be a quince and the fact that it is grafted on it (apricots, pears, although pears are grafted on mountain ash).
Remember that spring pruning is only an addition to the necessary shortening and thinning of the branches. It is necessary to remove them in the spring, so as not to overload the tree with flowering and fruiting. And the optimum form of the crown chosen by you will help you get a good harvest.
Spring pruning shrubs
Berry and ornamental shrubs with their thick crowns and tenacious twigs bring a lot of trouble during the spring pruning. It is necessary to allocate a couple of days to bring them in order.
Berry bushes are pruned in the usual way: remove all old, diseased and pest-damaged branches under the root. Places pruning smear garden pitch.
Blackberries and raspberries form in the form of a bundle, cutting out weak shoots at ground level. When the branches reach a height of 90 cm, pinch the tops. Begins a powerful growth of lateral shoots (they should grow by 30-60 cm), on which the main crop is formed.
All old branches are removed from the currant. The lateral branches that are removed from the branches are also cut out, leaving 2 cm of hemp.
If in the front garden you have maple, juniper and bubble trees. In the spring, they must also be cut, giving a spherical shape. Once every 3-4 years rejuvenate shrubs, cutting out most of each branch, leaving 4-5 buds on them. But flowering shrubs in spring can be cut only after flowering.
 Raspberry Crop
Raspberry Crop
To raspberry gave more harvest, it is cut twice.
The first pruning is done in spring. Secateurs slightly shorten the young shoots, cutting off the top. In length, the shoots remain at 0.5-1 m. Due to this, the lateral processes are formed throughout the season.
The second pruning is carried out on the same shoots, but in the spring of the next year, when the raspberry buds are fully blossomed. At this time, and shorten the top of last year's shoots, and cut off all lateral processes.
For twice-cut raspberries look almost the same as for the usual. The only difference: all young shoots, as soon as it appears, are immediately removed. Otherwise, all the forces of the bush will be spent on it.
With this pruning raspberry every year will be better and better. spend at the end of September.
Harvest and tidy crown - action plan
Cutting is done only at air temperature not lower than -5 °.
Use a sharply sharpened pruner, for large branches - a hacksaw.
Cut dry and old unproductive branches.
Remove the branches directed downwards, the harvest from them is low.
Cut the fat shoots (tops) and old branches, directed strictly up, they give less fruit than horizontal ones. Yes, and harvest them harder. Cut young inner shoots that hinder the development of other branches.
Cut the slices immediately with a garden pitch.
Observing these easy-to-remember features of pruning in the spring, you will always have a good harvest and a well-formed plant.
The main methods of grafting apples
How to rejuvenate an old tree
All types of copulation, how to immunize with cuttings
The main tasks of pruning fruit plants are to form a strong skeleton of the crown, regulate the growth and intensity of fruiting, improve the quality of the fruit and timely replace the aging branches.
In central Russia, pruning of fruit trees is carried out from the end of February to the end of April, that is, before the start of active sap flow. In the summer, if necessary, they do sanitary pruning, i.e. remove dry, broken and diseased branches.
Consider the basic rules of pruning on the example of the most common pome crops: apples and pears.
All branches according to the strength of growth and location in the crown are divided into:
Skeletal - large branches of the first and second order of branching;
Semi-skeletal - smaller branches of the second and subsequent orders;
Fouling - fruits are formed on them, therefore they are also called fruitful, generative.
The main carriers of the harvest are overgrown perennial branches, so the main goal for pruning is to create the most favorable conditions for them.
Basic trimming methods
1. Cutting (thinning)It consists in the removal of unnecessary branches in the crown, resulting in improved light mode. The crown volume does not change much, but the branches are placed more freely. This leads to an increase in the durability of the overgrowing branches on which fruiting takes place, since in such conditions they live 2-3 times longer than in poor lighting. As a result, the inner part of the crown will have a greater number of them, that is, the unproductive zone will decrease.
2. ShorteningThis method increases the budding of the buds and the sparing ability of the plant; as a result, the number of side branches per unit length of the remaining branch increases. If you do not shorten, then most of the lateral buds do not germinate, and only strong shoots from the upper buds begin to form.
The degree of shortening is determined by the length of the annual growth, that is, the length of the shoots grown during the year. If the increments are less than 40 cm, then they are usually not shortened, if 40-60 cm, then they do a slight shortening (by 1/4 of the annual increment), if more than 60 cm, then they are shortened by 1/3.
The stronger the shortening rate, the denser the strong side branches are placed, and the zone with non-awakened lateral buds becomes minimal. Skeletal branches during shortening better thicken, their strength and stability increases.
This also increases the length of increments, but this increase does not compensate for the part that was removed, that is, the shortened branch weakens the stronger, the longer the shortening was. Strong shortening during the formation of a young tree weakens it and delays the entry into fruiting, so thinning and weak shortening are often used during formation (strong only if necessary on individual branches).
If you regularly prune all the branches, the tree becomes more compact, the crown volume decreases, but the thickening increases and the light regime inside it deteriorates, which should not be forgotten. This method of pruning is more like for ornamental plants.
When forming a crown with a sturdy skeleton (selection of skeletal branches), it is necessary to take into account the angles that are formed between the branches in the crown.
Angle of discharge - the angle at which the side branch moves away from the trunk.
Angle of divergence - the angle formed by two adjacent branches in the horizontal projection. It must be at least 90 °, so the number of branches in the longline is limited, otherwise crown thickening will occur.
Formation and pruning can not be patterned: for each tree, methods and degree of pruning are selected individually depending on the type of plant, age, location of branches, etc. So, for some plants, thinning is necessary, for others shortening.
The response of plants to pruning changes with age as growth activity fades out.
In an adult tree, the number of overgrowing branches increases and reaches a certain maximum, but due to the weakening of growth processes, the length of growths decreases and the provision of flower buds, flowers and fruits with assimilation products sharply weakens, excessive flowering occurs, the fruit are set, which then fall off, which is useless. large amount of nutrients. In such cases, in order to restore the balance between generative and vegetative activity in adult trees, it is necessary to reduce the number of fruiting points (fouling branches). This is achieved by rejuvenating or detailed pruning.
Anti-aging pruning - strong shortening of the branches, which allows you to restore growth processes. Such pruning is carried out in the zone of last year's growths, the length of which is not less than fifty centimeters (branches older than three years).
Detailed trimming - shortening and thinning of old fouling branches.
Types of cuts
1. On kidney (garden knife, pruner)
The cut line must begin at the base level and end at the top of the bud. When shortening, make a cut on the outer kidney.
| Figure 4 | Figure 5 | Figure 6 | Figure 7 | Figure 8 |
| Too sloping (heals for a long time, the escape may break later) | Too high cut (left stump can be a hotbed of infection) | Damaged tissue (may also develop diseases) |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 9 | Figure 10 | Figure 11 |
| 2. (pruner, garden knife, garden saw) It is used to change the direction of growth of branches, to limit the height of trees. The cut line should form an angle of 55 ° -65 ° relative to the bearing branch. It is impossible to cut higher, leaving hemp, and lower, in this case the wound will not grow well. | 3. (garden knife, pruner, garden saw) This type of cut is used when necessary to completely remove a branch. The cut line should run parallel to the outer folds of the annular crustal flow. | |
Trees with a compact, pyramidal crown are cut to a bud or to a side branch directed outwardly (Figure 4, Figure 9), in order to expand the crown and improve the light mode inside it, and trees with a spreading crown are cut to a kidney, or to the side branch in such a way that the crown becomes more compact.
Work with garden tools
Garden tools (garden knife, pruner, garden saw) should be sharp and sharp and maintained in good working condition. During cutting, the pruner cannot be rotated to the sides, since the bark is damaged, the wound edges are uneven and the resultant overgrowth of the cut. If the branches are cut with an acute angle of discharge, then the instrument is placed at the bottom, and if it is blunt, then a cut can be made from above. In any case, the edge of the pruner should be on the side of the branch that is left, and the supporting blade on the side of the branch that is being removed. To facilitate the cutting effort, the branch to be cut can be slightly deflected.
The procedure for pruning a tree1. Inspect the wood.
2. Cut sick, broken, injured, dry branches.
3. Cut branches with sharp angles of discharge
4. Remove strong upright branches-competitors to the main shoot (Figure 12)
5. Branches growing inside the crown (Figure 13)
6. Remove parallel branches, closely spaced one above the other, intersecting (Figure 14, Figure 15)
When pruning, they are guided by the rule of subordination: the main (carrier) branch must be twenty centimeters longer than the lateral branches in each branching order. In this case, the branches thicken well.
An example of pruning a three-year sapling:
Figure 16

Branch 3 is cut on the ring, because it is weak, thickens the crown and, if left, then after a while it will cross with branch 2.
Branch 6 forms a too sharp angle of discharge with the trunk and over time there may be faults in this place, so it is also cut out on the ring.
Branches 1, 2, 4, 5, 7 and 8 are shortened in accordance with the rule of subordination.
Cutting large branches of an adult tree is recommended to be done together to avoid breaking the branch. First, 5–10 cm recede from the intended line of cut and make a sawn half-diameter below, then the branch is removed from the top, and the left stump is cut along the desired line.
Features pruning berry bushes
RaspberriesShrub, the above-ground part of which is formed by one- and two-year-old shoots, the underground part is a perennial rhizome, on which buds-renewals are formed, from which new shoots-renewals grow annually. In the first year these shoots grow intensively, flower buds are laid in the leaf axils, the next year they bear fruit and die.
Most varieties of raspberry fruit during the growing season once, they are called once fruit-bearing. Pruning such varieties includes:
- removal of two year old branches that are carved at the base. This can be done either immediately after harvest, or in spring.
- rationing the number of annual shoots
- removal of underdeveloped shoots
- sometimes they shorten the tips of annual shoots if they do not have time to mature
There are varieties that can bear fruit several times per season - remontant. In these varieties, the upper buds on the annual shoots of renewal are early maturing and therefore are able to bloom and bear fruit in the same year in the autumn. This part of the shoot dies off after fruiting, and the next year in the usual time the remaining two-year branch bears fruit. Pruning of such varieties can be done either as in the case of single-fruiting ones, or the first fruiting on two-year-old shoots can be discarded and the entire above-ground part can be removed in autumn. This avoids the appearance of most pests and diseases.
Black currantA shrub whose aboveground part consists of zero-order branches of different ages. The productivity of one branch is maintained up to five years. In this regard, pruning black currants includes the following:
- the number of shoots of each year should be the same, usually 3-5 branches, and the same number of new leaves will be left to replace the cut ones
- branches are cut after 5 years of fruiting
- branches should not be closely spaced, cross, lie on the ground
A shrub whose aboveground part consists of zero-order branches of different ages. The longevity of individual branches can be up to ten years. Fruiting prevails on bouquet branches, which are more durable than black currant. Therefore, the ratio of branches in age may not be the same.
When pruning should prevent thickening, remove broken, old, unproductive shoots.
GooseberryGooseberries are more prone to thickening than currants, and therefore need regular thinning. When pruning, it is possible to form various combinations of uneven-aged branches, but, as a rule, it is the same as that of currants - 3-5 shoots each.
Features pruning cherryThe difference between bush and tree forms of cherries lies in the nature of their fruiting.
In tree varieties, the main amount of flower buds is formed on the bouquet branches, which live up to five years.
In varieties belonging to the bush type, fruiting occurs mainly on the elongated growths of the last year, and the bouquet twigs are almost absent.
The flower buds of both forms are simple, that is, only flowers are formed from them, then fruits, and no shoots are formed.
Trees and bushes of cherries, as a rule, are shaped and cut according to the basic general rules.
The purpose of pruning at a young age is to prevent the thickening of the crown, the formation of a solid tree structure. Cut low-lying shoots, weak, parallel or too close to each other. Shortening is used to equalize and subordinate the branches, giving a good direction of growth, but the degree of shortening should be the smallest (more often it is necessary for bushy varieties).
With age, when growth begins to decrease, it is necessary to carry out a rejuvenating pruning on the side branch, as a rule, on 2-3 year old wood, waking up sleeping buds on the bare part and the emergence of new shoots that begin to bear fruit. It should cut out all thickening branches growing inside the crown. Thus, over time, the crown acquires a funnel-shaped shape, and the tops begin to grow inside it, they are left, and the end of the old, bare, unproductive branch is cut off above the exit-branch exit (top), on which the crop will now be formed.
Pruning plants - the necessary annual work in the garden. When the procedure is systematic, trees and shrubs develop in the way the owner needs; they bloom and bear fruit abundantly. Proper pruning is the most important event on the list of garden works.
Basic principles of pruning fruit trees
Competent approach using a variety of techniques and proper processing of slices, the use of a good tool in the work, regularity and deadlines - these are the basic principles of cutting trees and shrubs.
Trimming techniques
The operation is carried out in two ways:
- Shortening is the removal of a part of a branch in order to awaken dormant buds and the emergence of new shoots or to activate the growth of weak ones. The branch is pruned to a definitely located kidney, as a rule, a crown growing outward, or to a branch in the right direction. Pinching of young shoots will be attributed to shortening, if, instead of a fruit-tree, for example, a branch has grown. Hold without a tool, thumb and forefinger, repeatedly.
- Branch removal - performed with the purpose of thinning the crown to increase the amount of light falling on the foliage, or to remove old or drying branches. The branch is cut "on the ring", i.e. in front of the roller on the barrel.
Terms of pruning fruit trees and shrubs
During the growing season, one or another type of pruning is carried out in the garden:
- sanitary - carried out in the fall and spring, as needed in the summer, in order to remove dried branches, to prevent the spread of the disease, to destroy insects;
- forming - carried out in spring in fruit and ornamental for the correct location of the branches of the crown, ensuring optimal lighting and the possibility of processing and harvesting, the formation of a winning crown;
- rejuvenating - the removal of part of the branches stimulates the awakening of dormant buds and the activation of the growth of weak shoots, as well as flowering and fruiting. Conducted in the spring;
- corrective - after the main pruning during the summer, shorten or pinch the shoots, the growth direction of which is wrong (inward, downward, parallel to the trunk).
The main pruning is spring.
Slice Processing
Pruning plants is carried out before the start of active sap flow or after it ends. Therefore, wounds up to 2 cm in diameter are not required to be treated. Slices of a larger size are first leveled with a knife, bring the surface to smoothness, trying to keep the density of the bark fit. Then these places are covered with garden pitch. It is an industrial paste based on waxes, paraffin wax, rosin and disinfectants. When applied to the cut, it prevents the loss of moisture through the wound, the ingress of fungi and pathogenic bacteria, prevents rotting.
Garden poultry is inexpensive, so making it yourself is possible, but not always advisable. Before applying the paste is kneaded in the hands without gloves - it softens under the action of the heat of the human body, then it is applied to the cut, tightly smear the entire surface and edges.
Julia Petrichenko, expert

How to prune fruit trees and shrubs in spring
Spring pruning begins at the very end of winter or early spring, before sap flow. This time is convenient lack of foliage - all the excesses that require pruning, are clearly visible.
Necessary tool
The best care for garden plants during pruning is to make it a perfect tool. Any "surgical intervention" is, along with the optimization of growth, also the weakening of the plant. A good tool of labor will allow the plant to avoid unnecessary wounds, which means it will provide an opportunity to direct forces to the growing season, and not to heal the cuts.
Trimming tools:
Pruner.
It must be sharp, with close-fitting and well-cutting blades. Acquire a secateur, based on its ergonomics - it should fit well in the hand, not be tight, not tiring when working. Such tools are not cheap, but working with them will bring joy to the gardener, and safety to the plants.
Pruning lopper
View of the pruner on the telescopic handle, which allows you to reach the branches that grow high on the tree. Rarely are impeccable quality, but worth a look.
Hacksaw.
Preferably use a garden rather than a construction file. It is more convenient - it has a smaller size, rounded canvas and specially sharpened teeth. The cuts will be flawless.

How to prune berry bushes
In the spring, not all fruit bushes are subject to shortening of the branches. Many bushes, flowering and fruiting on the shoots of last year, do not require annual pruning. In the spring they spend perhaps sanitary cleaning. These plants themselves form their crown, during life only cutting out the oldest branches: bird cherry, irga, aronia (black chokeberry), mountain ash.
Raspberries
Annual shoots crown - they cut off the upper 5-6 buds, which stimulates the development of young basal shoots. Weak and frozen shoots are removed completely. At this spring pruning raspberry ends.
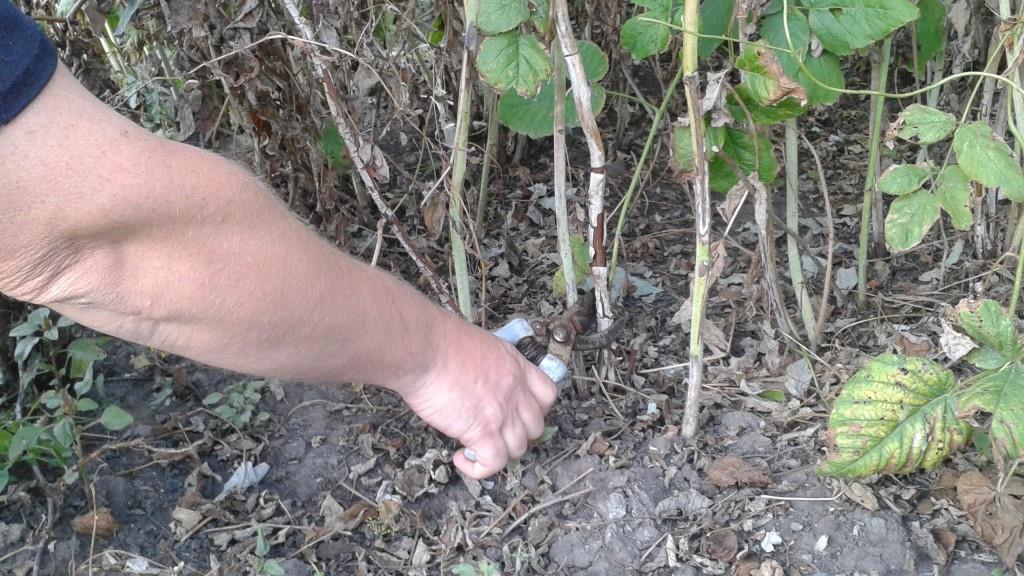

Currant
In the spring, thin the shrub, completely removing the branches older than 7-8 (on the red and white 10) years and the excess root shoots are the weakest shoots. They cut the ends of the branches, perhaps, they froze over in winter, as well as for preventive purposes - pests settle on the periphery. During flowering, parts of branches with flowers damaged by mites are separated - their buds are larger than healthy ones, this is noticeable. Pruning helps to improve fruiting.
Gooseberry
Starting from 3–4 years of age, thinning is carried out to enhance illumination, and later - cutting out old branches and shoots.
Cherry
Kustovidnye varieties of cherries in the spring pruned carefully, because it blooms on the shoots of last year and precisely on the periphery of the crown. Shorten after fruiting to grow new shoots. In spring, thickening and weak branches are cut out, thinning or sifting out root growth.
How to prune fruit trees
Formation is carried out every spring in young trees, and in adults - maintaining a general habit. For fruit, it is important to achieve uniform insolation of all branches and leaves on them. Therefore, since the landing proceed to the creation of the crown. By systematically pruning and removing extra branches at the beginning of fruiting, a tree is formed in the desired shape. Any molding is to determine the direction of growth of skeletal branches, maintain them in the foliage state and shortening the shoots on them for laying fruit buds.
Stone seeds
Plum is grown with a standard tree, since when bushy form very quickly thickens and ceases to bear fruit.
The formation of plums and cherries in the standard form is carried out from a very young age. Bouquet branches that bloom and bear fruit, live up to 5 years, so by the time of fruiting the tree should be fully formed.
Thick branches at the plum and cherry can not be cut on the ring, it can cause the formation of a hollow on the trunk and the death of the plant. They are shortened to escape, changing the direction and nature of growth. In spring, root shoots are cut or removed.

Dwarf trees
Own-rooted or grafted dwarfs come into fruition early, so they are not recommended to delay the crown formation. They select the position of the skeletal branches and cut them every year, pinching the shoots. The upper conductor grows freely before fruiting. With age, fruiting decreases, but it can be activated by moderate pruning, as well as by bending the upper part of the trunk and some branches of substitution.
Formation of the crown of fruit trees
When forming fruit trees give the following forms:
- Long-sparse. For its creation, each year, lay 1 tier of 2 - 3 branches growing in the right direction. The branches of the next tier are chosen so that they do not interfere with the lighting of the underlying. Unnecessary, non-skeletal branches in the first years are cut out completely.
- Horizontal (saucer). As the tree grows, one tier of branches is left in a flat-rounded shape, which ensures uniform insolation. Over time, the central conductor is cut out, all other branches on the trunk are removed as they appear.
- Vertical (palmettes). The trees are shaped in the form of a plane so that the sun illuminates both sides during the day. The orientation of the branches is preserved by trimming the shoots growing on the trunk and stem.

The formation of any crown is a long-term process. It is carried out each spring, continued in the summer and controlled in the fall. As the form is consolidated, only excess shoots are cut off and the main branches are shortened.
Spring garden work begins with an early pruning of trees and shrubs even in the snow. This operation marks the beginning of a new season in the life of the garden, its awakening from winter dormancy.
We hope to continue the conversation about spring pruning. What kind of crown do you prefer? Tell us about your garden!