Secrets of growing garlic in Siberia. Growing garlic garlic care. Spring Garlic Care
There are very few people who would not like the flavor and sharp taste of garlic. About the healing properties of this plant has long been known and so far they have not been neglected.
In addition, garlic benefits not only people, but plants. If you plant it next to potatoes, cucumbers, currants, gooseberries, black currants and raspberries, these plants will be protected from pests and diseases. Therefore, there is no doubt - you need to plant garlic on your site. It remains only to decide what is growing and its secrets, and what kind of care is needed here.
Here in the northeast, we often think that there is a short growing season. In other regions, many people sit down as if there is a beginning and an end. But gardening, wherever you do it, is circular. There may be slow times, but planning ahead is crucial for what is around the corner. Right now we are thinking about garlic next year. Here we are, another turn of the season. Cool days and nights will begin soon. Although it is too early to pull out sweaters, prepare warm soup and plant in the garden, it is not too early to think about the golden age of the year, to fall.
Types of garlic and the differences between them
Garlic (Allium sativum) is a perennial plant belonging to the onion family. The homeland of this culture is Central Asia. It was also cultivated in ancient Egypt, Rome and ancient Greece. At that time it was used mainly for medicinal purposes. In ancient China, the plant was attributed to the property of scaring evil spirits.
In addition to the annual cleaning and refueling, autumn is the best time of the year to take notes, reflect on mistakes and successes, and enjoy the last sighs of heat and sun. So it is really wonderful that one of the last tasks of planting in a garden is getting garlic in the ground. On the other hand, the very act of planting, looking forward to spring, summer and harvesting, brings a cycle of seasons together quite well, proving that the garden never starts or does not end, only changes. How much you plant depends on what you want from the crop.
Over time, garlic began to be used in cooking as a seasoning for meat and mushroom dishes, as well as to pickles. Now it is very widely used in kitchens, so its cultivation in large quantities is justified.
There are winter and spring varieties. Winter, according to the name, is planted closer to winter, from the end of September to the end of October. For this variety is characterized by an arrow with an air bulb, which is used for breeding. The bulb of winter garlic contains up to 10 large teeth, which are arranged in a row, around the central stem. Cultivation of winter varieties gives a good harvest, which is cold resistant. This variety of garlic can withstand the temperature of the soil to -20 ° C, so it can be planted in Siberia. But at the same time he is picky in storage, and care here is minimal.
If you want to create your own seed supply and your own food supply, plan to reserve 30% of the crop for planting. As we follow the rotation of vegetables, we know where our garlic will be much better than planting. This gives us a lot of time to make sure the beds are well crafted, weeded, fixed and prepared.
Terms of planting garlic in the spring
Here is what you need to consider. Plan ahead a few weeks before the landing date. First select your site. Garlic prefers rich, well-drained soil, weed-free soil and full sun. Ideally, choose a spot that is in full sun from winter to spring. It is difficult to grow crops in the most miserable beds, so think about it when you do reconnaissance during the summer.
Unlike winter, the cultivation of spring garlic occurs in the spring. Its yield is lower than that of winter varieties, but the bulbs are stored an order of magnitude longer. The head of spring garlic consists of 20-30 teeth, which are arranged in a spiral. With the approach to the center the teeth are reduced.
Spring garlic is believed to be more beneficial than winter because it accumulates more nutrients. Growing spring garlic is a painstaking task, but worth it.
Consider your mulching options. Compost, older manure and junk hay or straw mulch are good choices. Give yourself enough time to figure it out - do not leave it for later, so that you do not forget! A few days before landing, prepare your site. Visit our bed post for tips on how to get a good, even garden bed.
Try to leave enough time before the earth freezes for the garlic to set roots. Start by placing the garlic heads in a clove. Each stud will be planted at a distance of 6 inches, in rows of 12 inches. Weed and work in enough garden space. After cultivating the space, mark the lines. Vegetable carnations root side down, 2 deep, at least 6 apart, in rows 12 inches. Your garlic will need to weigh as soon as the earth heats up and it starts to grow.
How to plant spring garlic
In order for this vegetable to give a good harvest, you need proper care and fulfillment of the following requirements so that the cultivation will pass without problems:
- Sandy or loamy soil rich in humus, with neutral acidity.
- Garlic is extremely demanding on soil fertility, as it has a shallow root system. Therefore, the site on which potatoes, tomatoes or bulbous plants previously grew is not suitable.
- The place where legumes grew before was more than favorable for growing garlic.
- When planting the teeth in the acidic soil, growth and development will noticeably slow down.
Some gardeners begin to prepare the bed for the cultivation of this culture in the autumn. They dig, compost and complex mineral fertilizer. A day or two before planting should be treated the ground - well dig, remove weeds, loosen and level.
Spring growing conditions and care: garlic begins to poke through the ground as soon as the soil heats up. If you put your garlic with a thick layer of mulch, thunder it to warm the soil faster. Garlic prefers rich weed-free soil and sufficient water. Starting in the spring, pull out the weeds when they are small, and try not to damage the garlic when you pull them out. Fried varieties produce garlic slices in spring. As soon as clusters appear, immediately cut them off to direct the plants “energy to the production of bulbs”.
The onions themselves also need preprocessing:
- for landing the best fit large and elastic teeth;
- after calibration, disinfection should be carried out in the ash liquor. To do this, the ash is mixed with water in a ratio of 1: 5, and the teeth are kept in this solution for about 2 hours;
- at night they should be soaked in warm water. To activate the plant processes can be added to the water a little nitroammofoski.
The best time to grow spring garlic is April-May, when the snow melts and the soil temperature reaches 10 ° C. The teeth are planted at a distance of about 10 cm from each other and 20 cm between the rows. It is not recommended to plant deep garlic. The optimal depth of planting will be 4-7 cm. Teeth are not pressed in, but simply put in the prepared hole.
Shovels - edible spring delicacy. Fruitfulness: it is strongly recommended to give garlic under the action of nutrients in early spring. Garlic goes well with the addition of nitrogen in the form of alpha food or a light side dress of compost. They prefer chefs for exceptional flavor and large, easy-to-clean cloves. All bulbs have the same taste, taste and large cloves. However, smaller bulbs have a longer shelf life.
Gourmet varieties Fried garlic varieties are more dramatic with a smaller amount of cloves larger. They have less outer shell of the bulb. Braces can be harvested and used for creative cooking before the garlic itself is actually harvested. We grow 20 varieties of 7 hardheck garlic groups.
Spring Garlic Care
Spring garlic needs more moisture than its winter equivalent. Abundant watering should be carried out until July. At this time there is an active growth of the leaves of the plant. After watering is to loosen the ground to give access to the air.
Care is watering. When growing occurs at the stage of bulb formation, watering frequency should be reduced. In early August, the plant can practically not be watered. Water during this period will adversely affect the ripening of the bulb.
Their bulb wrappers are usually very thick, fluffy and parchment and cover several of them densely, but large carnations. They are the densest of all garlic. Named for their white skin wrappers, but may have, depending on environmental conditions, light shades of pink, purple or brown. Porcelain is known for its high allicin content. Allicin attributes their hot sulphurous aroma. Allicin helps lower cholesterol, increases circulation and boosts the immune system.
They are distinguished by a belt with free and somewhat random coils before straightening. The plants are bright and strong in the garden. The bulbs are usually large with smooth white hides and contain from 4 to 6 carnations. This feature is great for cooks. Lamps are stored for 5-7 months.
From the moment the first leaves appear, you can begin to feed the plant. This is a very helpful care. Fertilizers should be predominantly nitrogenous. Perfect bird droppings, herbal tinctures, mullein solution and mineral fertilizers. But fresh manure will not be the most successful option - it significantly reduces shelf life and can also lead to plant diseases. Top dressing needs to be combined with watering.
Usually works well in cold climates. One of the most popular hard cards. It is easy to grow at a cold pace and very hardy. It has a very high Allicin content. The plants are tall, run out late and produce large bulbs containing from 4 to 5 huge carnations. Clove wraps have an attractive purple color. Dense, full and rich with an average temperature.
Spicy raw, but gives the meat a balanced garlic aroma when cooking. Rich strong bright white late porcelain with a little heat, but not too hot with a strong strong aroma. Uniformity in appearance and taste. Hardy and productive plants, an average of 4 to 6 very large carnations.
To speed up the ripening process, towards the end of August, you can prune part of the roots or slightly pull the onion out of the ground. In this case, all the energy of the plant goes to the ripening of the root, and not to grow. Harvesting garlic should be started when its leaves turn yellow and fall down. This is done carefully, first undermining, and then shaking off a clod of earth. Sharply pulling bulbs out of the ground is not recommended. If the care was correct, then the harvest will be canceled.
Loved and called "porcelain of a working horse." Romanian Red - Originally from Romania. Romanian adds a long hot and spicy bite to any dish. Emit a large amount of allicin. Despite the sharp character, it has an excellent aroma. Great secret ingredient for barbecue sauces. Hot strong porcelain that is well stored. Beautiful large bulbs vary in color from white to red-white. The bulbs contain 2-6 round carnations. Ripens late with a strong smell of garlic.
Georgia Fire - Originally from Russia, Georgia Fire organic hardy garlic has an exceptionally hot aroma when it is eaten raw, which makes it an excellent choice for salsa. Like most porcelain, it is a large and beautiful garlic with a rich, strong taste, which is strong and has a lingering aftertaste. Medium 4-6 large carnations per bulb.
During the growing season, the plant may be affected by diseases. For example, white and bacterial rot, neck rot, peronosporozom and black mold. The main precautions - planting healthy teeth, this is the main care, which is the prevention of infection.
In addition, garlic can attack insect pests. These include:
Georgia Crystal is pure, fresh garlic garlic with excellent aroma. Georgia Crystal adds the perfect crunchy flavor to frying, vegetables, chicken and fish. Light tastes go well with root vegetables, cabbage, chicken, seafood and fish. The soft, raw taste is great for raw dips and salsa. Their bulbs contain an average of 4-7 very large cloves. This garlic has a very pure flavor without naturalism.
Storage of spring garlic
Yugoslav red - this garlic has a spicy garlic aroma and a strong, hot spicy taste that disappears to the sweet in the mouth. It withstands long cooking times well. The thick, hard reddish wrapper makes it excellent for storage.
- onion fly;
- onion stem nematode;
- onion moth;
- onion thrips;
- root mites.
A solution of tobacco or salt can help cope with these pests.
To protect against pests, we advise you to plant calendula or chicory next to it. Despite the fact that spring garlic has good self-defense against pests, it is still worth controlling the condition of your plant. Regular soil loosening will also help to increase plant resistance to pests and diseases.
A very attractive white thinking light bulb with lots of purple, brown and red layers on a white background. The bulbs are usually fairly uniform and very large in size. The taste is mild, but richly complex with a bit of a hat, which is a long, but rarely harsh tasting. This garlic is well suited for use both raw and soggy. It provides not too hot taste with a pleasant non-sulfonic aftertaste. Due to its high sugar content, it caramelizes well.
Creole group - Creole harlik has from 8 to 12 carnations per bulb, located ideally symmetrically around the central stem. They are unique in appearance, configurations of pinks and colors. They are great to look with taste, full, but pleasantly warm. Creole harliks have a beautiful deep pink color that becomes more beautiful than the more layers you take off, opening the caps of the carnations, which are almost red with delicate burgundy vertical stripes. They are much more tolerant of adverse weather conditions.
Storage of spring garlic
 Crop maintenance is also not difficult. The optimal storage temperature for this type of garlic is 15 ° C. At this temperature, spring garlic is stored for six months. Then the temperature should be reduced to 3-5 ° C. This will help minimize the consumption of nutrients, preserve the turgor of the teeth and prevent various diseases. It is important to care for the bulb, it must be protected from mechanical damage, which can serve as an "invitation" for microorganisms.
Crop maintenance is also not difficult. The optimal storage temperature for this type of garlic is 15 ° C. At this temperature, spring garlic is stored for six months. Then the temperature should be reduced to 3-5 ° C. This will help minimize the consumption of nutrients, preserve the turgor of the teeth and prevent various diseases. It is important to care for the bulb, it must be protected from mechanical damage, which can serve as an "invitation" for microorganisms.
They can be large hardy garlics and grow where other species cannot. It gets hotter the longer it is stored. It has a rather rich, musky, earthy aroma and a noticeable bite, but it is still on the bright side most of the year.
It keeps a lying stone and grows well in most parts of the country. A typical lamp has from 4 to 7 studs. These plants are very energetic in cold climates. Bogatyr - originated in the former East Germany. A fascinating purple stripe that lasts longer than some other hard-tech. Best described as a true garlic flavor without heat. This is another culinary favorite. Great flavor perfect for Italian dishes and garlic bread. Gorgeous dark purple brown bulbs that are energetic and grow easily.
Garlic in Western Siberia
The value and distribution of garlic - the second culture after onion. It is exceptionally rich in valuable organic substances, mineral salts - for example, iron in it is as much as in apples. Essential oils that determine the taste and smell of garlic, contain volatile, suppressing the development of pathogens.
It develops well in cool, wet weather. Approximately 6 to 8 studs. Metekhi - they say that they come from the Republic of Georgia. Not the largest bulbs, but beautiful purple and white striped. Very homogeneous bulbs are squat and plump in appearance with purple strips of wraps on average from 5 to 7 carnations that are easy to clean. The plants are short shoots with narrow, almost horizontal leaves at maturity. It has been described as "Fire of fires." Deliciously sharp at first and quite fiery when they are eaten raw, but it has a nice finish.
The content of ascorbic acid is especially high in green young leaves. Medicinal properties of garlic have been known for a long time; for example, Avicenna advised using garlic for all diseases. Antibiotic allicin, isolated from garlic, even in insignificant concentrations can suppress pathogenic bacteria. In folk medicine, garlic is used to improve digestion, to expand blood vessels, urolithiasis, rheumatism, gout. There are garlic-derived pharmacological preparations allipsad.
The aroma lingers in cooking and is well stored. Siberian - Excellent for cooking, with its aroma and a characteristic, lingering taste. The bulbs are large with purple striped wrappers and contain from 8 to 10 large carnations.
Lamp wrappers are resistant and very colored: wide purple stripes merge into areas of solid purple. The carnation is thick, semi-glossy and has a pink aura with tiny pink veins. Korean Red - Korean Red is usually an energetic producer with large foliage, which is dark green and leads to a good bulb size. Its aroma is very strong, about and spicy and the sticks are around for a long prong.
There are varieties winter and spring garlicMoreover, winter garlic can be shooting and non-shooting, and spring garbage is only non-shooting. Garlic is a cold-resistant plant. The roots begin to grow at +2 - + 3 ° С, leaves at +5 - + 7 ° С, the optimum temperature for leaf growth is +10 - + 15 ° С, during the ripening of the bulbs +20 + 25 ° С.
Climatic conditions in Western Siberia are generally favorable for the cultivation of garlic when planting before winter; Difficult periods, due to an insufficient amount of moisture, are only May June, and frosts in November in snowless winters are also dangerous.
In the conditions of Western Siberia, two new varieties of garlic showed themselves best of all: Siberian - shooter, and Novosibirsk - non-shot, and also CIR-10 - highly resistant with large aerial bulbs.
Siberian it is distinguished by increased winter-hardiness; its yield is 40-50 kg per hundred, although 122 kg per hundred was obtained during state trials. The bulb contains 4-5 cloves, the taste is sharp and semi-sharp.
Novosibirskgives a bulb of 13-15 cloves, the average yield is 57 kg per hundred, and 104 thousand per hundred is obtained during state trials.
Both varieties easily adapt to different climatic conditions and produce good yields not only in Siberia.
Garlic is propagated by teeth or aerial onions, which, when planted in autumn, produce single-toothed bulbs next year, and then real bulbs grow from them. The best areas for the placement of garlic - smooth, preventing the accumulation of spring moisture. Good predecessors are legumes, cucumber, early cabbage, green cultures. Not suitable as a precursor of onions and early potatoes. The soil should have a neutral reaction. Garlic is responsive to organic fertilizers, organic matter should be added to the soil: about a bucket of humus per 1 m, as well as mineral fertilizers - (phosphate 30 g, potash 20 g, nitrogen 20 g per 1 mz), and part of the fertilizer can be applied in the fall under digging, and part of the grooves during planting and dressing.
The garden plots mainly produce winter garlic, which gives a good harvest in any year. Its bulbs are large with a small number of cloves, but it is stored worse than spring ones (which can be stored for up to two years). Spring garlic is very picky about growing conditions - the slightest deviation from the right agricultural technology reduces the harvest or even leads to its death.
Growing garlic
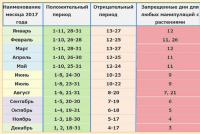
The scheme of planting garlic can be different, but in any case, a sufficient distance between plants is necessary so that it is convenient to loosen during the growing season. In the row, the distance between plants should be at least 4 cm. In the fall, large teeth and a single-tooth are planted at a depth of 8-10 cm, in the spring by 6 cm. The optimum planting time in autumn is the end of September - beginning of October, in this case the teeth will root, but the leaves will grow will not start. In the spring you need to plant as early as possible, in early May.
Before planting, the bulbs of winter garlic are dried and divided into teeth. In nonstarting varieties for planting take larger external teeth. Planting material should be etched in a 1% solution of copper sulphate or potassium permanganate for 12 hours. You can soak in 0.1-0.5% solution of trace elements for a day.
Immediately after the snow melts, winter garlic must be fed with nitrogen fertilizers and bury. Garlic should be loosened often, but not deeply, since its roots are located close to the surface. If aerial onions are not needed, then after the arrow leaves, pinch it at a distance of 5-10 cm from the inflorescence. Removing arrows increases yield by 20–25%. Often, watering garlic should not be enough for the growing season 2-3 good watering. A month before cleaning watering is recommended to stop.

The onset of shedding aerial onions is a signal that the garlic is ready for harvest. If all the onions are removed, then the readiness of garlic is judged by the mass yellowing of the leaves. You can not be late with the cleaning - the bulb can fall apart into individual teeth. Dug out plants folded under a canopy for airing and drying. Leaves should not be immediately cut: due to the outflow of nutrients from them, the quality of the bulbs is improved. After drying, the leaves and arrows are cut and folded garlic for storage in boxes or tied in braids. Before storing the bulbs, it is useful to hold them in the sun to disinfect them from fungi and bacteria, and gently clean them from the ground without damaging the covering scales. The roots are cut short, and the neck is left more genuine 3-4 cm, which protects the bulb from infection. Then once again dry the garlic in the room. It is not recommended to store garlic together with potatoes, beetroot, cabbage in the storage, as these vegetables emit a lot of moisture undesirable for garlic bulbs. All varieties of garlic are well kept.
at a temperature of about 0 ° C. Garlic needs to be sorted out no later than November, while removing sick, damaged or frost-frozen fruits.
In the last decade, planting of garlic has been promoted not by teeth, but. bulb onions. This applies to shooting marks. Aerial onions are formed on the floral arrow at the base of the underdeveloped buds. They can be considered as an analogue of seeds and therefore the offspring obtained from them is more viable than with vegetative propagation, and, of course, this method is much more economical. Cultivate garlic from aerial onions in three ways.
The first - growing seedlings. Bulbs sown in autumn or early spring. By the end of July, the beginning of August, single-teeth bulbs are formed. It is removed, dried and planted in the fall for the production of bulbs for the next year. Planting sevka garlic (unlike onions) should be in the fall.
Second way - direct culture: plants obtained from aerial onions are not dug out in the autumn, but left for the winter. The next year, the harvest will be multi-jagged bulbs and single-teeth.
Third way - cultivation of ozimi, in which by the fall a well-developed root system and a thick false stem are formed. In this case, the best landing period is the beginning of June. Usually it rains at this time, aerial bulbs germinate quickly.
In crops there are half-matured plants, fully matured and winter, remaining in a vegetative state until the autumn cold weather. These plants are hardened and winter well. In the spring, winter grows very early. In her harvest there are commodity bulbs, and sevok. This method differs from direct culture by the fact that vegetative plants go to winter; for this it is necessary that they do not stop their growth in August, which is expressed outwardly in the yellowing of the leaves and the death of the roots. If necessary, in August you need to spend watering.
Air bulbs should be stored first at room temperature, and two months before sowing, i.e. in early March, they should be placed in a refrigerator at + 2 ° C, and it is better to store in unmilled form - this reduces drying. Completely cold storage is undesirable. This adversely affects the yield.