The calendar of works artak. Garden Works Calendar
In order to become a successful gardener, you need to have an idea about the various seasonal work at the dacha. The key to the success of any business is a clear and understandable plan for the work ahead.
If you are only taking the first steps as a gardener and a gardener, it is not necessary to immediately follow all the recommendations and grow most of the garden and vegetable crops on your plot. Decide where you would like to start, and stick to the seasonal work schedule. Well, as you gain summer experience, you will be able to expand the range of cultivated vegetables, fruits or flowers and delight your loved ones with a rich and healthy harvest.
All information in my seasonal schedule is divided by months of the year. In each section, the month are useful tips for beginners as well as for experienced gardeners.
January
Plan your future plantings, decide on the crops you need that will grow better in your area;
Buy in specialized stores seeds, fertilizers, film for greenhouses and greenhouses (I advise you not to buy seeds and equipment from random individuals - there is no guarantee that they will not sell a fake);
Take care of fruit trees and shrubs in your garden - use the fallen snow for their shelter and insulation. Tear off any dried, curled leaves - many caterpillars and pests overwinter in them.
February
Continue work to protect fruit and berry crops from frost and rodents. If hares, voles, and mice have got into your area, tie a tree stump of fruit trees or wormwood. You can also use roofing felt, frequent metal mesh or plastic film (3-4 layers);
It is already time to take care of the manure harvesting, it should be stored in compacted piles, adding superphosphate (2-2.5 kg of fertilizer for 1 kg of manure);
The end of February is a good time for harvesting cuttings of fruit trees for grafting. Cuttings should be done only from well-developed and healthy trees. Store cuttings best in the basement in a box with wet sand or sawdust;
It is time to prepare the sowing boxes, repair or renew gardening equipment, repair greenhouse frames;
In the first half of February, start growing seedlings of pepper.
March
After the snow melt, remove the strapping and treat the tree trunks with sunscreen whitewash. You can use the finished products, and you can make a whitewash with your own hands from the chalk with the addition of clay;
Treated in winter trees treat garden pitch;
Remaining fallen leaves from the autumn lay in compost heaps, covered with a layer of earth;
Untie the bushes, pick up the raspberry shoots curved up for the winter, thin out the neglected bushes of currants, gooseberries;
Consider how to properly place the vegetables on your site. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the compatibility of crops with each other and previous cultures. I offer you a classic scheme of vegetable crops: the area allotted for vegetables, divided into 4 parts. On one plant cucumbers, cabbage, zucchini, which need abundant organic fertilizer. On the second place onions, tomatoes, radishes, garlic and green vegetables. All of these crops, as a rule, do not require a lot of fertilizer. The third part of the vegetable plot is intended for beets, carrots, root parsley, radish, parsnips, turnips, as these vegetables are grown on mineral fertilizer. Plant early potatoes in the last section. The soil under it is enriched with mineral and organic fertilizers. In the second year of culture, occupying the second part of the garden, will move to the first, which will significantly reduce fertilizer consumption. Potatoes will take the place of root crops, and pumpkin vegetables and cabbage will be moved to the plot of potatoes;
If you plan to grow vegetables in a greenhouse - it's time to start building a greenhouse. How to do it - the task is simple, there would be a set of necessary building materials, film and desire;
In the first half of March, sow seeds of tomato, eggplant, physalis, black onion, early varieties of white, red, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower and savoy cabbage, as well as broccoli and kohlrabi for seedlings;
Not later than the third decade of March, plant healthy potato tubers for sprouting;
You can sow carrots prepared from the fall of the ridge.
April
The main work in the garden is pruning the orchard and forming the crowns of young fruit plantations;
Loosen the soil in the garden and apply organic and mineral nitrogen fertilizers for shrubs and trees;
The optimum time for planting and transplanting trees and shrubs has arrived. Start planting as soon as the soil permits;
In the first half of April, plant sprouted tubers of early potatoes;
In the middle of the month, sow radishes, carrots, turnips, radishes, onions, lettuce, parsley, spinach, dill, peas and other cold-resistant crops.
During the flowering of gardens it is necessary to protect the trees from night frosts. The tested method of protection is smoke, which raises the air temperature by 1-2 degrees;
The first decade of May is the best time for planting strawberries and strawberries. Beds with already growing strawberry bushes need to be loosened in between rows and weed until it blooms;
Proceed to the main planting of potatoes, spring planting of table beets. May is also the time of the mass planting of cucumbers and tomatoes. Continue sowing root crops, green crops, radish; from the end of May, it is possible to sow cucumbers, zucchini, squash, pumpkin in open ground;
Harvest young perennial greens - onions, sorrel, rhubarb.
June
Provide trees and shrubs with nutrition and moisture, loosen the soil in the garden;
Start collecting the first ripe strawberries and strawberries;
Loosen the row spacing in the beds to a small depth (up to 5-6 cm). Such loosening is especially necessary after watering: the crust and cracks in the soil are unacceptable;
At the end of June, make the first removal of the stepsons on the tomato plants;
Sprinkle cucumbers and cabbage infusion of potato tops against aphids and spider mites;
Start picking fresh lettuce, dill, onion and radish.
July
Pay attention to the growth of the garden, often and abundantly water the trees and shrubs;
If you expect a large harvest of fruit - put a prop under the branches;
Harvest currants, gooseberries and raspberries. After the final harvest of strawberries, feed the bushes;
From mid-July, start harvesting cherries and early summer varieties of apples;
Weeds need weeding, loosening and watering; Spud potatoes last time and process for phytophtoras and Colorado beetles.
August
Start collecting apples and pears of summer varieties, sea-buckthorn berries, black chokeberry, wild rose;
Start harvesting on vegetable beds, in the first half of August remove onions and garlic (always in dry weather);
Spray tomato bushes from phytophtoras, pick ripe tomatoes from the bushes in a timely manner.
September
In dry weather, harvest apples and pears for winter storage;
If necessary, conduct an autumn planting of seedlings of fruit trees and shrubs;
Try to harvest the vegetables until frost, in the last decade of September, dig up the potatoes, dry well and reassemble it before laying in the cellar;
Plant winter garlic until mid-September.
October
Finish picking up late varieties of apples;
Acquire and plant fruit tree seedlings;
Spend the autumn dressing of the garden with fertilizers, treat the trunks with whitewash and cover it from frost and rodents;
After the final harvest, dig the soil with fertilizer (do not forget about the alternation of crops);
After the first autumn frosts, make podzimnye crops of carrots, beets, parsley, lettuce, onions, dill.
November
Continue digging the soil, take care of the soil for the next year;
Prepare the harvest for storage for the winter;
Drain the water from the water pipes, remove the hoses from the area to the utility rooms;
Collect, clean and dry all gardening equipment.
December
All work on the site is completed, now focus on storing the resulting crop, the acquisition of the necessary equipment, seeds and fertilizers.
So, having familiarized with the details of seasonal work at the dacha, you can make your individual work plan for the year. Have a good harvest!
The last month of summer is invariably identified in our understanding with full-scale harvesting, with preparation of fruits for storage, with the first conservation and winter harvesting - so, work in the garden and in the garden in August, as you can see, is abundant. In addition to harvesting this month, enterprising summer residents complete the sowing of green and vegetable crops, bring greenhouses and greenhouses into a proper form. What else events require the attention of summer residents in the garden, garden and flower garden in August?
Works in the garden and garden in July
 Midsummer is the hottest time in every sense of the word for summer residents, primarily because the main work in the garden and garden in July implies not only enhanced care for plantings and crops, but also the implementation of measures to protect plants from the scorching sun, droughts and pests. It is now beginning and very pleasant trouble associated with the collection of the first crops and the preparation of blanks for the winter. What else provides for the calendar of summer works in July and what needs to be done in the garden, in the garden and in the flower garden in July?
Midsummer is the hottest time in every sense of the word for summer residents, primarily because the main work in the garden and garden in July implies not only enhanced care for plantings and crops, but also the implementation of measures to protect plants from the scorching sun, droughts and pests. It is now beginning and very pleasant trouble associated with the collection of the first crops and the preparation of blanks for the winter. What else provides for the calendar of summer works in July and what needs to be done in the garden, in the garden and in the flower garden in July?
Works in the garden and in the garden in June
 Much of the work in the garden and in the garden in June is focused on sowing vegetable and flower seeds, planting seedlings and caring for existing plantings, which in the beginning of summer intensively form shoots and ovaries. Also, with the onset of June, work continues in the dacha connected with the prevention of plant diseases; pests and weeds are being controlled; after the spring rains, they struggle to flood the entire site. However, the detailed calendar of works in the garden and in the garden in June is not limited to these events. What else should summer residents do in the first month of summer?
Much of the work in the garden and in the garden in June is focused on sowing vegetable and flower seeds, planting seedlings and caring for existing plantings, which in the beginning of summer intensively form shoots and ovaries. Also, with the onset of June, work continues in the dacha connected with the prevention of plant diseases; pests and weeds are being controlled; after the spring rains, they struggle to flood the entire site. However, the detailed calendar of works in the garden and in the garden in June is not limited to these events. What else should summer residents do in the first month of summer?
Works in the garden and garden in May
 The rapidly increasing amount of work in the garden and in the garden in May is largely due to the approaching warmth and the changes that occur in nature during this period. This month it is important to have time to finish all the major plantings, to provide comfortable conditions for the growth and fruiting of plants, and, of course, take care of your plot. Due to the fact that the May weather is almost always characterized by the sudden return of frosts - work at the dacha in May also provides for the provision of all sorts of measures to protect the garden plantings from the cold weather. What else should be done by summer residents with the arrival of sunny and at the same time - dangerous May days?
The rapidly increasing amount of work in the garden and in the garden in May is largely due to the approaching warmth and the changes that occur in nature during this period. This month it is important to have time to finish all the major plantings, to provide comfortable conditions for the growth and fruiting of plants, and, of course, take care of your plot. Due to the fact that the May weather is almost always characterized by the sudden return of frosts - work at the dacha in May also provides for the provision of all sorts of measures to protect the garden plantings from the cold weather. What else should be done by summer residents with the arrival of sunny and at the same time - dangerous May days?
Works in the garden and in the garden in April
 The second month of spring is considered to be the most time-consuming for summer residents, since the plan for working in the garden and in the garden in April becomes much wider and more complicated. This month, it is important to finalize the list of future plantings, determine the places on the site for the planned crops, and, of course, take care of your beloved summer house. What activities does the calendar of work at the country house provide in April and what needs to be started to implement now?
The second month of spring is considered to be the most time-consuming for summer residents, since the plan for working in the garden and in the garden in April becomes much wider and more complicated. This month, it is important to finalize the list of future plantings, determine the places on the site for the planned crops, and, of course, take care of your beloved summer house. What activities does the calendar of work at the country house provide in April and what needs to be started to implement now?
Works in the garden and garden in March
 The arrival of spring marks the opening of a new tense pore for summer residents, since work in the garden and in the garden is significantly increased in March. This month it is important to have time to do something that was not implemented in February, and at the same time - to carry out all those things that the plan should be implemented with the onset of sunny March days. So, what should the summer residents have to do in March and what does the detailed calendar of March works in the garden, in the garden and in the flower garden look like?
The arrival of spring marks the opening of a new tense pore for summer residents, since work in the garden and in the garden is significantly increased in March. This month it is important to have time to do something that was not implemented in February, and at the same time - to carry out all those things that the plan should be implemented with the onset of sunny March days. So, what should the summer residents have to do in March and what does the detailed calendar of March works in the garden, in the garden and in the flower garden look like?
Works in the garden and garden in February
 With the arrival of the last winter month, summer residents get more trouble, because work in the garden and in the garden in February provides for preparations for the coming spring season, which is about to come. This means that it is already possible to start planting seedlings of some vegetable and flower crops, while not forgetting about the activities traditionally carried out in winter.
With the arrival of the last winter month, summer residents get more trouble, because work in the garden and in the garden in February provides for preparations for the coming spring season, which is about to come. This means that it is already possible to start planting seedlings of some vegetable and flower crops, while not forgetting about the activities traditionally carried out in winter.
Works in the garden and in the garden in January
 Immediately after the end of the New Year and Christmas holidays, experienced gardeners start implementing a work plan in the garden and in the garden in January, because it is precisely this month that pleasant troubles come in preparing for the upcoming summer season. What activities need to be carried out in the stern January days and what work in the country - in the garden, garden and flower garden - should be done during this period?
Immediately after the end of the New Year and Christmas holidays, experienced gardeners start implementing a work plan in the garden and in the garden in January, because it is precisely this month that pleasant troubles come in preparing for the upcoming summer season. What activities need to be carried out in the stern January days and what work in the country - in the garden, garden and flower garden - should be done during this period?
January:
1. Planning: take a sheet of paper, write on it a list of important purchases for the garden this year, immediately divide the list into chapters (for example: "seeds", "fertilizers", "tools"). Such a list will help bring "order in the head", do not forget anything, plan the approximate budget for the summer season in advance. On the same sheet, draw an approximate pattern of placement of new plants. Well, if you have the same list from last year, it will be much easier to plan this year. Do not forget to leave a new plan until next year.
2. On the site: shake the snow from trees, greenhouses and roofs of buildings; throw snow to the trunks of fruit trees; take care of bird feeders.
February:
1. It's time to start buying seeds. In order not to get lost in a huge assortment of shops and not to buy something that you will have nowhere to plant, act according to the plan, use the list. Do not forget about the purchase of soil, fertilizers and other necessary goods.
2. At the end of February, time to plant annual plants with small seeds for seedlings: marigold, petunia, aster one-year, begonia, balsam, etc.
3. Sow celery, peppers, eggplants on seedlings
4. Review the tubers and bulbs of begonias, dahlias, gladioli, montbretias, cann. Discard the sick.
March:
1. In early March, sow early varieties of tomatoes, eggplants and peppers on the seedlings (feed in time, provide light, and spray the soil with copper solution before picking the tomatoes)
2. Blanch the tree trunks
3. Go through the bulbs of gladioli, tubers of dahlias
4. Clean the beds of snow
5. In late March, sow the seeds of asters and marigolds on the seedlings.
6. Cut and trim the crowns of apples, pears, hedges
April:
1. As soon as the snow melts, remove the spruce branches from the beds.
2. In early April, cut off all dry branches from the trees, disinfect and cover wounds.
3. Feed nitrogen fertilizer shrubs
4. In late April, sow the early varieties of greens: parsley, watercress, cilantro, etc.
5. Open the roses, covered for the winter. Trim and feed them.
6. At the end of April, sow the seeds of frost-resistant annual flowers (cornflowers, forget-me-nots, etc.) into the ground
7. Plant raspberry seedlings, fertilize them with peat. Untied the raspberry shoots folded from the fall, remove the frozen and broken, cut the good ones to the first bud.
 May:
May:
1. At the beginning of May, it is already possible to plant seeds of cucumbers, zucchini and pumpkins in greenhouses;
2. Do not forget to feed the seedlings
3. Tomato seedlings can already be planted in the greenhouse
4. Buy up seedlings of annual flowers, dill, parsley
5. Spray the plants with nitrogen fertilizer at the time of unfolding the leaves.
6. In the middle of May transplant seedlings of tomatoes, eggplants, peppers; cover them
8. At the end of May, plant cauliflower seedlings, pumpkins and squashes in open ground.
9. Prepare smoke heaps to protect the flowers of fruit trees from possible night frost.
10. Spray peonies with anti-rot agents.
11. As soon as the earth is warm enough to plant potatoes
12. Planted in the autumn saplings of gooseberry and currant gnaw, feed manure or peat
13. Sow radishes
June:
1. Plant cucumbers, white cabbage in open ground
2. Sow turnip and radish
3. Destroy young weeds, mow the grass
4. Trim the ends of the young raspberry shoots as soon as it reaches 1 m in height.
5. Feed peonies, phloxes, roses, raspberries, pumpkins, zucchini, cucumbers, etc.
6. Cut the arrows off the garlic.
7. Feed nitrogen fertilizer bushes, fruit trees, strawberries.
8. At the end of June, remove and burn the ripening berries of black currant and gooseberry (to kill the larvae of the sawfly)
9. Cut the faded brushes of lilacs, daffodils and tulips. Dig out the tulips. Sow Pansies, Daisies
10. Spend hilling potatoes
July:
1. Do not forget about the timely destruction of pests of fruit and vegetable crops.
2. Feed your cucumbers and tomatoes well.
3. At the beginning of the month, save the gooseberry and red currant from the caterpillar, and in the end the pepper from the rot and raspberries from the purple spot of the stems
4. Do not forget about the destruction of weeds.
5. At the end of July, process strawberries.
August:
1. In early August, after harvesting, feed and treat currants and gooseberries
2. Cut out the seedlings and weak raspberry shoots, pinch the tops of the annual shoots
3. At the end of the month, plant garlic and strawberries.
4. During the summer, remove root shoots from bushes and fruit trees.
September:
1. In early September, remove the potatoes, for a week, mowing the tops
2. After the first frost cut the tops of the dahlia
3. Harvest and plant the cuttings of shrubs (2-4 years old shoots)
4. At the end of September, cut off the aerial part of phloxes and peonies.
5. Remove carrots, onions, tomatoes.
6. Harvest beets
7. Until the middle of the month, divide and transplant perennial flowers.
8. At the end of the month wind the trunks of trees.
9. Dig the beds and pristvolny circles.
10. Plant bulbs of daffodils, tulips, lilies and hyacinths, dig and dry the bulbs of gladioli.
October:
1. Feed trees and shrubs with organic fertilizer.
2. Rake fallen leaves
3. Dig and fertilize the land.
4. Prepare the roses for the winter: cut, lay the lash on the ground, cover it with spruce branches
5. Cut the cabbage and Brussels sprouts.
November:
1. Shake the remaining leaves from the trees, scoop all the leaves in the garden
2. In early November, spray trees from wintering pests.
3. Blanch the tree trunks
4. Install supports under the branches of bushes to prevent them from breaking under the weight of snow.
December:
1. Read the literature for gardeners, gardeners.
Other posts on the topic:
Self-pollinated and cross-pollinated plants.
In the springtime boiling flowering, in the lush greenery in the summer, weighed down with fruits in the autumn or covered with snow in the winter - the garden lives in any season of the year and constantly requires care and care. Any work must be timed to its date: to hurry or be late means to waste time and energy, to lose in the harvest, and even to harm the land and the plants. The approximate monthly calendar should promptly remind gardeners of the approaching dates for carrying out the main works, so that they can be prepared in advance. Terms of work are indicated approximately in relation to the regions of central Russia, but it should be borne in mind that, depending on the climatic and weather conditions, the timing of flowering, fruiting, etc. can shift by 10 - 12 days in one direction or another, and the need to use different agricultural methods - to change. For example, during hot, arid weather, watering plants becomes paramount, and with top dressing one should wait until a more favorable period, since with a lack of moisture in the soil, excessive concentrations of nutrients can negatively affect the root system.
January
The first, usually the coldest month of the year. In winter, gardeners are free from large works in the garden, but this does not mean that you can forget about it. It is necessary to purchase tools for pruning and caring for trees in advance, prepare garden wares, seeds, check the temperature in the storage (cellar) and sort out the fruits.
The main concern of gardeners in January is to protect fruit trees from frost and rodents. If the soil temperature at a depth of 20 cm drops to -12 ...- 18 ° C, then the roots can freeze. A high snow cover serves as a reliable protection for them, so if frost is expected to be -30 ...- 35 ° С, then all fruit trees of any age should be spud. With snow they cover not only the shtamb, but also the bases of the skeletal branches. In especially severe winters, when it happens, the whole above-ground part of the tree freezes over, its most vital organs (the shtamb and the base of the skeletal branches), covered with snow, remain intact, and it is always easier to recover the tree from them.
When hilling trees with snow, gardeners often make a dangerous mistake. Inspired by the work, they rake so much snow to the tree that the soil around it becomes bare and it turns out: “the head is in the house, and the legs are on the street”. The soil not protected by snow quickly and deeply freezes through and often to such an extent that the entire root system of a tree dies. Therefore, snow should be raked shallowly between trees and berry bushes, and a somewhat larger layer from the tracks and from the ditches, unless there are adult fruit trees near (no closer than 2 m from the trunk) - otherwise the soil is exposed above the roots.
If the trees are spudding in the days of thawing, then the snow is well compacted around the trunk, only you need to take it a little bit so as not to damage the branches. On a frosty day, the snow is friable, and it must be compacted around the edge of the rolled up cone.
Another, no less important job in January is the fight against rodents: hares and mice eat the bark, especially in young trees. If in the fall in a young garden, the stumps were not carefully tied, then on the days of thaws, which are often in January, it is necessary to clear the snow around the trunk: the dense snow cylinder that encircles the stem, serves as an obstacle for mice. This work is repeated several times a month, gradually crushing the snow with their feet. Begin the treatment at a distance of 30 - 50 cm from the trunk, then gradually approach it. To protect against rodents, the strands are also tied with fir branches, wormwood, tar, roofing felt or plastic wrap.
It is necessary to shake snow off the trees, gathering on the branches after heavy snowfalls and thaws, as the branches may break off from its head. In addition, carefully examine all fruit trees and destroy winter nests of pests. Be sure to remove the remaining mummified fruits on the branches.
We must not forget about the birds that help plants get rid of many dangerous pests. Feeding troughs are arranged for them and fed regularly.
February
Last month of winter, the time of sudden changes in temperature. The time of the most dangerous frosts has passed, but in February the lowest temperature of the soil is observed at the depth of the roots, therefore it is necessary to constantly monitor that the soil around the trees, the trunks and the bases of the skeletal branches are constantly under snow cover. Work started in January on accumulating snow in the garden and protecting the branches from breaking.
It is in February that particular care should be taken to preserve the fruit trees from the invasion of mice, which begins in the middle of the month and lasts until March, until the snow gets very wet. In the days of thaws, snow continues to be otpatyvat around young trees, not tied with spruce branches or other materials. Check and correct the strapping around the protected trunks and the condition of prikatannyh seedlings.
At the end of the month, care should be taken to protect the trees from sunburn (whiten the trunks and bases of the skeletal branches, shade the trunks). At this time, you can check the condition of the fruit buds after overwintering, for which branches are selectively cut from the trees and put them in water for growing. It is necessary to carefully consider the features of crowns, outline the plan for pruning. It is equally important to do the repair and preparation for the work of tools and equipment: sharpen saws, pruners, knives, shovels, hoes, etc.
In February, you can perform a winter vaccination. Carry it out in a warm room, preferably with an improved copulation method. Periodically aerate the reservoir and inspect the apples.
March
This month is considered the morning of the year. Do gardeners added work. The first step is to bypass the site and carefully examine all the fruit trees. Around shtambov young trees densely trampling drifts, destroying mouse passages and not allowing rodents to get to the bark. In pristvolny circles with a shovel or pitchfork carefully destroy the crust and free from it branches, so that they do not break when the snow melts. At the beginning of the month, stick wet snow is shaken off the branches to prevent them from breaking.
Begins to melt snow. If it is necessary to speed up the descent of snow and thawing of the soil, blackening substances are scattered: earth, peat, ash, soot. In the gardens located on higher ground, the meltwater is retained, and in the lowlands or on heavy soils they are drained to avoid stagnation, for which special grooves are dug. At first, they try not to walk around the site until the ground dries out, so as not to disturb the soil structure.
After the snow has melted, they check whether the branches of young apple trees and the seedlings dug in the winter are not damaged by rodents. Damaged branches cut pruning shears on the kidney or on the side branch. Small focal superficial wounds can be not treated, they will heal thanks to the preserved cambium.
If significant pieces of bark are damaged on shtamba and skeletal branches, they are immediately wrapped in black film without cleaning them with a knife. Transparent film can also be used, but from above it must be covered with dark paper - this is how wounds heal faster. Hollows in the trees are cleaned of decay, disinfected with 3–5% solution of copper or iron sulphate (30–50 g per 1 l of water) and cemented.
At the end of the month, in cloudy weather, the trees are free from protective strapping against rodents. In March, fruit trees often suffer from sunburn, especially the trunk and fork of skeletal branches. Trees that lack winter-hardy varieties and frozen in previous severe winters also need protection. A sharp change in day and night temperatures causes damage to the cambium. Therefore, after the snow melts, the stumps and the bases of the skeletal branches are treated with whitewash materials or emulsion paint.
If there are breaks between the branches, they are fastened with iron straps or wire, the cracks are treated with a solution of ferrous sulfate.
When the snow melts and the soil at the site dries out a bit, once again carefully examine the trees. If damage is found again, they are treated the same way as recommended above. In case of significant damage, it is impossible to do without re-grafting by the bridge. Then, from a tree known for its good compatibility with many varieties, several strong annual gains are cut, wrapped in a wet cloth, then tape and stored in the basement or on the ground under the house or shed from the north. The graft is dosed during active sap flow in a damaged tree.
In March, they begin to harvest annual growths for spring grafting of fruit crops. Their wood should be light green. If it is brownish, then the shoots are frozen slightly and are unsuitable for inoculation. As soon as the daytime temperature rises above 0 ° C, they start pruning fruit trees.
After the snow has completely melted down, the fallen leaves that have not been cleaned in the fall are collected and put them in a pile to produce valuable organic fertilizer - compost. At a temperature of 5 ° C, it is possible to start the treatment of fruit trees from pests (chemical preparations or ash solution).
To attract useful birds to the site, it is necessary to prepare nesting houses for them and install them before the snow melts.
April
This month, the spring takes effect. Visibly warmer, frosty nights less often. There is a lot of work in the garden.
In those places where the snow has not yet melted, it quickly melts, and therefore it is important to keep melt water on the site. To do this, make various grooves and rolls across the slope. In low-lying areas, the drainage grooves are free of snow. Before bud break, pruning of fruit trees not affected during the winter-spring period is continued (young trees are pruned in the spring after planting or the next spring).
Conduct spring inspection plantings. In mature trees, it is necessary to periodically scrape off the old bark, so that pests do not accumulate under it. If this has not been done before, be sure to clean, disinfect, and cover with garden pitch or ocher all wounds and bites on the bark. The trunks and skeletal branches are washed with a piece of burlap dipped in copper or iron vitriol, paying particular attention to the fork between the branches. If the bark around the trunk is heavily damaged by rodents, in the sap flow movement they are vaccinated with a bridge. In dry weather, they begin grafting and re-grafting of fruit trees: before sap flow, with improved copulation, with sap flow, in other ways. From the middle of the month, low-value varieties can be grafted more promising.
When the soil dries enough, it is harrowed with a rake. Strongly compacted soil digging. The pristvolnye circles of fruit-bearing trees are broken up with a pitchfork in order for the soil to warm up rather and “work” the roots. At the same time, fallen leaves and plant residues are raked into a compost pile.
As soon as the soil permits (usually in the second half of April), they start planting fruit seedlings in the pits prepared since autumn. At the same time, young trees are transplanted. It should be noted that in central Russia, fruit crops can be planted in spring and autumn. But the autumn planting is dangerous because during winter the weak roots and the above-ground part can freeze. Therefore, it is best to plant seedlings in the spring before bud break. At this time, they also check whether the root necks of young trees are buried and, if necessary, raise them. In early spring, they also plant winter vaccinations stored in cold conditions.
In April, stratified apple seeds are sown in beds. In order to get friendly shoots, it is necessary to sow sprouted seeds, their further care comes down to keeping the soil moist, loose and clean from weeds.
With the onset of warm days, pests awaken and diseases begin to develop. To combat them requires a set of preventive measures. Cutting dried and damaged branches, which must then be removed from the site and burned, is very effective against a wintering stock of pests and diseases. At a temperature not higher than 10 ° С, apple trees and other pests are shaken off the fruit bearing trees on the litter. On shtampy impose trap belts for collecting weevils, tsvetoedov and other pests. For disinfection from fungal diseases and wintering eggs of pests, fruit plants are treated with Bordeaux mixture, a suspension of colloidal sulfur, lime broth or infusions and decoctions made from plants.
In case of spring frosts prepare piles of garbage and combustible materials for smoking.
May
Under the warm sunshine the garden comes to life, it is time for flowering.
Work continued in April. Complete planting and sowing plants. Graft trees of low value varieties.
In May begins the rapid growth of leaves and shoots. But if in the previous winter the trees were frozen, their vegetation is delayed. Such trees are pruned at a later date, that is, in May. This work must be completed before flowering. All sections, even small ones, are painted with oil paint (ocher or iron red lead). Garden pitch in this case is unsuitable, because under the action of strong juicing lags behind cuts. Pruning heavily frozen trees should be postponed for a year. Root and shtambovoy shoots cut out on the ring.
Flowering is a crucial period for fruit crops. Late spring frosts (mornings) are possible at this time. They are especially dangerous for pestles and stamens (the critical air temperature for them is -1.7 ° C), so they should be protected as much as possible. It is necessary to carefully monitor the possibility of frost (air temperature, atmospheric pressure, etc.) in order to prevent danger in time. The tested method of protecting plants from spring frosts is smoking, which increases the air temperature by 1 ... 2 ° С. If the air temperature drops to 2 ° C and continues to decrease, harvested manure, peat, wood rot and other materials are lit on the leeward side in order to get more smoke.
Often in May, set the hot and dry weather. In such conditions, it is necessary to regularly water and loosen the soil in tree trunks of young plantings and fruit-bearing trees. It must also be mulched with peat or humus. Fruit plants can be fertilized with manure. After flowering, trees are watered to preserve the ovary.
Of all garden works, the most laborious is, perhaps, the fight against rhizomatous weeds, especially wheat grass. These weeds appear in May. Shovel or pitchfork need to dig up the area and carefully remove the rhizomes.
June
The first month of summer. Nevertheless, frosts are still possible in its first decade in the middle lane, and if necessary, plants continue to protect against them. During this period, the apple tree ends flowering and forms the ovary.
One of the main concerns in June is pest control of fruit crops. On the stumps of fruit trees impose trap belts that prevent pests from rising into the crown or going down to the ground for pupation. They are especially effective against caterpillars of the codling moth. Belts are inspected every 10 to 15 days; pests are found to be destroyed.
Not less important work in June - cleaning shtamb and thick skeletal branches of adult fruit trees from dead bark. Purified places are washed with a solution of iron or copper sulphate (40-50 or 20-30 g per 1 l of water, respectively) or a solution of pale pink manganic acid potassium. After drying, small wounds are covered with garden pitch, and large wounds are painted with ocher or iron red lead.
In fruit trees, grafted in spring, shoots that appear below the grafting site are removed. Cutting strapping on branches with a diameter of less than 2 cm is completely removed. If you used the method of grafting behind the bark, then the plant is tied to a support so that it does not break off. Incorrectly growing shoots pinch, cut out the shoots on the ring.
Sometimes at the very beginning of summer, the above-ground part of the trees begins to die off: the branches dry up, the bark lags behind, etc. This is due to winter damage. Such trees can be restored by pruning to reverse growth, if the intact part remains above the grafting site.
In trees with a heavily frozen aboveground part, a strong growth of root growth begins in June. It must be removed, otherwise the trees will die.
This month there is an inevitable and natural physiological process of the fall of the ovaries - the so-called June fall. In the first place fall ovary, damaged by pests and diseases, underdeveloped, but sometimes it happens with healthy ones. The whole windfall is collected and destroyed. In years with high yields, mature apples can be fed after the June shedding of the ovaries.
Pristvolny circles continue to maintain a loose and clean from weeds condition. Weed weeds laid in a compost pile. In dry weather, plants are watered by soaking a layer of soil in the zone of active roots to a depth of 50 cm. After watering, the soil is immediately mulched with a thin layer of peat or humus.
June is the month of intensive growth of shoots and ovaries. At this particular time, both young and adult trees should be provided with the best possible nutrition and moisture. Seedlings, as well as plants with winter and spring vaccinations, after abundant watering, are fed with a solution of slurry or bird droppings.
When the fruits on apples and pears reach the size of a walnut, vertical backwaters are placed under the most loaded skeletal branches. Their upper end is made in the form of a dovetail and is wrapped around a strip of rubber. On such a backwater, the branch does not slide and the crust is not damaged. The supports are left under the trees until harvest.
July
The hottest month in central Russia. The growth of shoots and ovaries continues, the basis of the future harvest is being formed - new fruit buds. During this period, trees need watering, loose soil and weed-free soil. At the end of July, the shoots complete growth, wood, apical buds are laid. If the summer is dry, the garden is watered. The number and timing of irrigation depends on the amount of precipitation, the type of soil and its humidity. Another important job in July is fertilizing fruit crops. After it, the soil is loosened and mulched. Proceed also to its preparation for the autumn planting.
They check the binding on spring vaccinations and, if necessary, weaken it in order to prevent the formation of hauling. In the first half of the month, pinch strong shoots to turn them into semi-skeletal and overgrown branches in the future. In fruit trees with a flat crown, shoots are bent down, which by this time reach a considerable length (as they grow, the work is repeated in the following months). This technique weakens the growth of shoots and accelerates fruiting. The required position of the shoot attached with the help of tied twine. In the second half of the month proceed to budding.
Carrion regularly collected under the canopy of trees. Do it better in the evening. The collected dropas is destroyed, otherwise the moth will have time to leave the fallen fruits. Check trap belts and destroy the pests caught in them. Spraying trees against pests and diseases continues. Under the most loaded branches, the previously established supports are corrected: this improves the supply of air and light to them.
In the fruit-bearing garden after the ovaries fall off, the expected yield is determined by the fruits remaining on the branches. Begin collecting the fruits of the cherry.
August
The final month of summer. The main work in the garden is harvesting. They start to eat apples of many summer varieties (July Chernenko, Cowberry, Candy, Mantet, Melba, etc.) and pears of summer varieties. If the fruits ripen at the same time, they are removed in several stages, removing first the largest, characteristically colored. Fruits of summer varieties, shot slightly immature, can be stored up to 2 months.
Apples and pears of autumn and winter varieties are picked regularly. Tree branches of summer varieties are free from backwaters.
Inspect trap belts, destroy the pests caught in them. Well-fruiting plums, apples and pears of later varieties are fed with a solution of mullein, slurry or bird droppings. Fertilizer consumption for plums, apples and pears on low-growing rootstocks is one bucket, for apple and pears on high-growth rootstocks there are two buckets (per 1 m2 of crown projection area).
In pristvolnyh circles weed weed. Systematically remove wild root shoots, which take away moisture and nutrients from trees.
In August, complete budding. To halt the growth of strongly growing shoots, accelerate the ripening of wood and laying at the ends of the branches of the apical buds, shoots are shortened or pulled down. To this end, you can also braid branches with each other.
Begin to prepare the trees for the winter. Wet weather can cause secondary shoots, which is undesirable. To stop this process, do not mow the grass, remove the mulch, young plants pinch the tops of highly growing shoots.
Dry weather causes premature leaf fall. To prevent this, the soil must be kept loose and wet, mowing the grass. In dry weather, the compost pile is periodically watered for better overheating of the plant mass.
Despite the fact that before the winter is still far away, you need to take care of feed for birds. For this purpose, seeds of irgi, elderberry, hawthorn, mountain ash, watermelon are harvested.
September
The month of golden autumn and Indian summer. There comes a painful time. The main work in the garden - harvesting and preparing plants for the winter.
By the end of the collection of fruits removed trap belts and burned. On trees that have already been harvested, you can make sanitary pruning. Cut out on the ring all the dried and diseased branches (they are clearly visible against the background of fallen leaves). Also dropping to the ground, damaged by pests, thickened and old branches are also removed. All sections are covered with garden pitch. The fork of the branches is cleaned and washed with a solution of copper sulphate. It is advisable not to water the trees for a month in order to prevent a new wave of growth.
At the end of the month, in young and fruit-bearing gardens, mineral fertilizers are applied and the soil is dug up. The best term for this work is the beginning of yellowing of the leaves, that is, before the active growth of the roots begins in the autumn. The depth of digging under an apple and pear tree is 10–20 cm, between rows 15 cm.
If an autumn planting of seedlings is planned, then two or three weeks before it is dug pits and fill them with fertilizers. Prepare stakes, inventory, mulch materials, water for irrigation.
October
Lose the leaves of trees, wither grass. In the garden, it's time to pick up late varieties of apples. Fruits are best collected in dry weather, as wet apples are quickly damaged by various microorganisms during storage. If you still have to remove the fruit in the rain, then before laying in the storage they need to be dried in a purged place. After harvesting, the trap belts are removed from these trees, they destroy the detected pests.
Branches that have broken off due to overloading with fruits are cut out, and large-diameter branches are cut down. Sections cover with garden pitch. Strands and thick skeletal branches are cleaned of dead particles of bark, pre-spreading a film under the trees. Purification is collected and burned. Close up of the discovered hollows. Young trees are removed from dwarf trees.
Before mass leaf fall, water recharge irrigation of fruit crops is carried out. It is especially needed after high yields and in dry autumn.
After the leaves are fallen, the fallen leaves, weeds, etc. are carefully picked and composted. If the ground was not dug over in September in the tree circles, this is done in October.
In the first half of the month, planting is completed. If the tree is planted instead of the deceased, then the landing site is shifted, retreating from the former by not less than 1.5 m in order to reduce the effects of soil fatigue.
If trees grow on dwarf rootstocks on the site, the soil beneath them is mulched with peat, humus or sawdust in a layer of 5-6 cm. Due to low frost resistance and surface placement, their root system can freeze with the onset of early cold weather, especially in the absence of sufficient snow cover.
The mouse holes lay out poisoned bait.
November
Late fall. Gardeners have a lot of work to prepare the site for the winter, by the middle of the month the main work should be completed.
In the garden, remove all plant debris. Compost pile covered with old plastic wrap, tar or roofing material. Particular attention is paid to areas with excessive moisture, thoroughly cleaning the ditches for land reclamation. In the gardens on the slopes, where spring waters wash off the fertile soil layer, fascines are put across the runoff (fence from twigs). In areas with flat terrain, soils that are light in texture and insufficient moisture, it is advisable to embank it around the perimeter: in the spring, the shafts will trap a large amount of moisture.
As noted, a very common winter damage to fruit trees is sunburn. Mature trees protect against burns in the spring and autumn. To this end, a creamy mixture of clay and mullein is applied with brush on the stumps and bases of the skeletal branches. Whitewashing with a solution of lime and copper sulfate (2.5 and 0.5 kg per 10 liters of water respectively) has proven itself well. It helps and thin paper, such as newsprint. It is applied in two or three layers at the end of autumn.
Great harm to trees (up to 15 - 17 years) cause the mouse. Therefore, with the onset of resistant frosts, young trees are tied with reeds, spruce and pine branches (tops down) or toly. The lower part of the shtamp of trees grafted onto dwarf rootstocks or vigorous with a dwarf insert should be especially carefully protected, since the thick and juicy bark of dwarf rootstocks very much attracts rodents. Continue to lay out and poisoned bait.
After the first frosts (-5 ...- 10 ° C), annual shoots of fruit crops for grafting are harvested and stored until spring in damp sand in basements or cellars.
In the fruit storage systematically monitor the temperature and humidity. Periodically inspect the fruit, discarding rotten. Before the onset of this winter, bird houses are hung in the garden.
December
The beginning of winter, the first drifts. But at this time there is work in the garden.
With the falling out of sleet, they watch that there are no breakages of the branches, they carefully shake it off and trample it down. In the days of thaws, leaves that are not fallen down are removed and the nests of wintering caterpillars of the hawthorn, the golden-eyed bird, and the eggs of the ringed silkworm are removed. On young trees check the status of the strapping.
Periodically inspect and, if necessary, sort out the fruits laid down for storage. Monitor the temperature of the air in the basement (it should be 2 ... 4 ° C), air the room.
Harvested manure for making fruit crops. With the formation of a stable snow cover, birds are fed. Clean and grease garden tools.
- Online Store Articles Login
Garden Works Calendar
Gardeners and gardeners who have been busy with their own summer cottage or plot for a long time and regularly gather a rich harvest cannot but agree that success in this difficult endeavor depends largely on natural rhythms. After all, plants are an integral part of wildlife and, of course, grow, develop and bear fruit according to its laws. And the use of competent agricultural technology, which takes into account all the features and timing of planting and maturation of plants, can give a repeated positive impact in the form of an excellent harvest.
When carrying out garden and gardening works, it is desirable to take into account the dates of the lunar sowing calendar, do not underestimate this ancient knowledge. Quite a lot is known about the influence of the lunar phases on all biological processes occurring on Earth, and the proper use of the lunar calendar can save many plants from premature death and significantly increase growth and productivity.
January
January - the time of rest, work this month is much less than usual. And at the same time - this is one of the most alarming periods for summer residents. After all, not every fruit tree can endure the January frosts, and even winter pests - hares and mice are particularly active during this period.
The trunks and branches of fruit trees can withstand quite severe frosts (up to 42 degrees), but the root system of trees is very vulnerable during this period. In some trees, the freezing of the roots occurs already at 10-12 degrees of frost. The most frost-resistant fruit trees that can withstand temperatures down to 45 degrees include:
- Cherries (Siberian selection) - Altai large, Blizzard, Subbotinskaya, Ob.
- Apple trees - Antonovka ordinary, dawn of Alatau, Anis gray.
- Plums - Timiryazevskaya, Moscow Hungarian, Pineapple, Ussuriyskaya.
Protection against frost and winter pests
What to do if the trees in your garden do not belong to frost-resistant varieties? Snow is the simplest and most affordable means for insulating the root system. It is necessary to rake around trees and spud stumps (parts of trunks without branches) of trees with them, in the same way shrubs are protected. You can also trample down solid circular boulders around the trees, bringing in an extra amount of snow. In addition to natural insulation, they play the role of protection from pests. The snow drifts located around the trees do not allow hares and mice to reach the shtambov fruit trees. Do not forget also in time to shake off excess snow from the branches, because under its weight, they break very easily. Especially often it occurs during heavy wet snowfalls.
Sowing on seedlings
January is a good time for planting and planting plants for seedlings. This month you can plant onions (in the greenhouse or on the windowsill), celery, parsley and dill, cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, watercress, radishes and small strawberries. You can also engage in the preparation of soil for further planting and germinating citrus seeds.
If you want to see an early blooming klubma in your garden, then you can plant seeds of primrose garden, sabo carnation, Turkish carnation, love, eustoma on seedlings.
February
Preparation time for spring. In February, you can plan future work in the garden, design flower beds and flower gardens, make plans for future crops. At this time, there are no queues at specialty stores, and therefore, it is possible without haste to stock up on film for greenhouses and greenhouses, mineral fertilizers, and missing tools.
Protection against burns and frost
The intensity of light emission in February increases significantly, which can lead to burns of the trunks of many dark-stem trees and the formation of frost cracks on them. To avoid this, the trunks must be protected with a reflective material, such as whitewash. It is also possible to cover the trunks with whitened roofing felt or glass roofing.

Preparation of cuttings for vaccinations
In February, you can cut fruit trees and shrubs and harvest cuttings for spring grafting of such trees as apricot, plum, apple, cherry, pear and fruit and berry crops - gooseberries, grapes, raspberries, currants. A start to improve in grafting fruit trees can be in early February.
Sowing on seedlings
Until February 10, it is advisable to sow tomatoes, cucumbers, radishes, eggplants, peppers, and leeks for seedlings.
From the 10th to the 20th of February you can sow watermelon, pumpkin, cabbage, celery and lettuce (parsley and dill), this is also a very good time for sowing legumes.
In February, it's time to engage in stratification of the seeds of various plants, especially for aromatic plants such as lavender, wild garlic, and stevia. At the same time, it is necessary to sow flower plants for seedlings - zinnias, nasturtiums, marigolds, chrysanthemums, petunias, godecia. You can also do the germination of rhizomatous plants, such as dahlias.
March
With the onset of March, gardens and cottages begin to revive. This is quite a busy period when preparations are being made for the “hot” summer season. Frosts are declining, there is a thaw.
Snow removal
It's time to clean up the snow in your garden. Be sure to remove the snow from the crowns and branches of trees, because heavy and wet snow can easily break or deform the branches. It is also necessary to remove the snow in the root zone of trees, around the shtambov. Otherwise, during the melting of the snow, an excessive amount of water may lead to the heating of the bark.
The very first whitewashing and spraying
The next stage of gardening work this month will be checking the condition of the plants. Make sure that the trees and shrubs have normal wintering and their bark is not damaged by rodents. Primary protection from rodents in March can be removed. At the same time, the very first treatment of fruit and berry crops from pests and diseases is carried out - spraying and whitewashing.

Damage treatment
If the bark of the boles is damaged by rodents, you should proceed as follows: I apply a layer of sawdust or moss up to 5 cm thick to the damaged areas and wrap it with film material, as a result of which evaporation of the liquid decreases. If the bole is not very damaged and the damage is not circular, then until July, sawdust or moss under the film is impregnated with some kind of growth stimulator. Repeat this procedure several times so that the contents of the dressing are always wet. Remove the film in July, after which the tree goes through the usual procedure of preparing for winter. It is impossible to cover the places of damage with any compositions. In the event that the shtamb is damaged quite badly and there is no cambia left on the damaged area, then the tree is prepared for grafting with a bridge. They do this as soon as the danger of frost has passed.

Frost-damaged tree bark
It is also worth checking out how the trees suffered frosts. For this, it is necessary to grow indoors two-year branches with buds, or annual shoots. In that case, if the wood is badly affected by frost, the tops of the branches will turn pretty brown, and the intact wood will remain light. Be sure to pay attention to the cut branches. If you notice a dark layer between the bark and wood, this means that the cambium of the tree is seriously damaged by frost. Such a tree can be considered dead.
Pruning and harvesting cuttings
In March, they are engaged in pruning trees and shrubs, removing dry, diseased or thickening branches. The shortening of branches is made to enhance their growth. And berry bushes after thinning and pruning give larger fruits. Also in March, it is possible to prepare cuttings for subsequent vaccination, if this has not been done previously. The cuttings are wrapped with film and stored in any cool place - in the cellar, basement, or even under the snow.
What is planted in March
In March, you can sow turnips, radishes, turnips, radishes, mustard, parsley, cilantro, carrots, beets, leeks, hops, bulbous flowers and leguminous plants. Also at this time, it is advisable to do the sowing of pumpkin crops and corn, colored, white cabbage, red cabbage and Brussels sprouts on the seedlings.
It’s also time to plant early potatoes, strawberry mustache, horseradish rhizomes. In March, potatoes should be laid for vernalization.
Sowing seeds of sunflower, poppy, lemon balm, calendula, borage, daisy, cornflower violet, forget-me-nots. March is the time of gathering flowers and leaves of coltsfoot.
As for flowers, you can grow begonias, dahlias and gladioli. At the end of March, asters, marigolds, campies, sweet tobacco, nasturtiums and petunia are usually sown on seedlings.
April
Soil preparation
April - the time of preparing the garden and vegetable garden for planting and sowing and the beginning of planting. In order not to waste time in vain, you can dig and fertilize the soil for planting and planting crops in open ground. In early spring, it is best to fertilize the soil with ashes, compost, humus or manure.

Frost protection. Garden fumigation
Do not forget that in April frosts are still possible. Unblown flower buds die at -4 °, and blossomed do not withstand temperatures of -1 ° ... -2 °, ovaries can also die at -1 ° ... -2 °. It is possible to fight frost during the flowering of trees by burning smoke heaps. In order to create a smoke pile, put a cross on the cross two stakes, between them set the third. It is necessary to lay dry combustible material on stakes - firewood, straw, brushwood. On top of the dry is usually laid wet combustible material - manure, sawdust, leaves, shavings. From above everything is sprinkled with a thin layer of soil. A layer of soil gives a specific effect of smoking, thanks to her a lot does not burn, but smokes, fumigating the garden. Such heaps are located at a distance of 1.5-2 m from trees and set on fire if a sharp drop in temperature to 1-2 ° is observed. Burning a pile, get a third stake out of it, air will flow into it through the hole. Finishing the fumigation of the garden should be no earlier than 2 hours after sunrise, this will help avoid rapid thawing of blooming flowers.
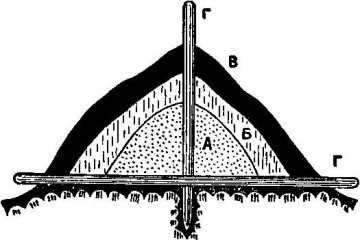
Smoke heap: A) dry combustible material; B) wet combustible material; B) soil layer; D) construction of stakes.
Pest control
Another important April exercise in preparing your garden for the fruiting period is pest control. After all, with the awakening of the garden, his enemies also wake up. Before the start of the active extermination of pests, be sure to feed all plants with nitrogen.
After the temperature reaches 4-5 °, you can proceed to the next stage of work. First of all, clean the tree bark from the dead bark, wash them with a solution of copper sulphate and be sure to put traps on them that will fight the apple beetle beetles, because it is at this time that they begin to crawl out of their winter shelters. To combat other insects, spraying will help.
The very first spraying is done before the buds have blossomed (30-40 g of copper oxychloride per 10 liters of water). If you are late, then the procedure is better to postpone until the end of flowering, because plants can get burned. The second spraying is carried out after flowering and dropping flowers with the same preparation. In some cases, it is recommended to do a third spraying, 2-3 weeks after the second. Repeating this procedure ensures a significant reduction in the number of pests such as flower beetles, parslippers, listobloshki, caterpillars, aphids, scab, powdery mildew, ringed silkworms and haws. It is necessary to spray not only trees, but also shrubs.
After the third spraying, you can hang out the cans with kvass or decoction of dried fruits to determine the emergence of the codling moth and begin to fight with its larvae.
What is planted in April
In April, shrubs and fruit trees are planted, and this is also an opportune time for replanting trees. At the end of April, there is a planting of turnip seeds, swede, lettuce, onions and circular radish in open ground. Also in open ground planting seedlings of cabbage, pepper, eggplant, zucchini, pumpkin crops, tomatoes. This month begin planting spring garlic and potatoes. You can also sow herbs, cereals and lawn grasses.
Broccoli, cucumbers, melons and gourds, remontant strawberries, as well as flowers and climbing plants are sown for seedlings in April. In the same month, sprouting of the seedlings is made and ready cuttings of fruit bushes are planted.
At the beginning of May, during the first decade, complete all the tasks in your garden that you did not have time to finish in April: complete pruning of trees, eliminate all dead and damaged branches of shrubs. Please note that weeds are starting to appear at this time, so additional tillage is required from you.

Readiness to return to frost
Frosts can be returned this month, it is likely that the temperature will drop to 0 °, so continue to form smoke heaps. The height of the smoke heap is on average 80cm, its diameter is 1.5 meters. One such pile is designed for 5-6 trees and can serve you during 2-3 possible frosts. The burning of wet piles should be slow, with a large amount of smoke and water vapor. The most preferable option is collective smoke, because in this case a very dense smoke screen is formed, which reliably protects the earth from overcooling, and on sunny days it prevents aggressive radiation and protects trees from burns.
Plant nutrition
If you did not manage to feed plants with fertilizers in April, you can do it in the May period. Top dressing of fruit trees is as follows: according to the projection of the crown of the trees, small grooves are dug (10-15 cm deep), a solution from the slurry is introduced into these grooves (1 bucket of manure per 10 liters of water) or a solution of bird droppings (15-20 water buckets - 1 litter bucket). The solution should flow into the grooves when it reaches a state of light fermentation. After making the solution, the grooves are covered with earth. If you do not have manure, the use of ammonium nitrate or urea is allowed.
Gooseberry and currant shrubs, as well as strawberries, are fed with special mixtures: garden-fertilizer, or fruit-berry (50 g of mixture per bush or row). After feeding, the soil is loosened and mulched with peat, compost or humus.
Pest control
Do not forget about pest control. To protect seed trees (apple, quince, pear, etc.), they must be treated with a suspension of colloidal sulfur (100 g per 10 liters of water) or 1% solution of copper sulfate in lime milk (Bordeaux liquid). Karbofos used against cherry weevil or apple sawfly.
Gooseberries are also treated with karbofos, fighting fire. The mealy dew on the gooseberry also causes a lot of trouble. Effective remedies against it - infusion of mullein (1 part of fermented manure to 3 parts of water), ammonium nitrate, as well as a solution of soda ash (50 g) and washing powder "Lotus" (2 tablespoons) per 10 liters of water.
Black currant can hurt with terry: a set of thin branches, each with 3 pointed lobules on narrow leaves (instead of the put 5). Sick bushes should be destroyed, and the treatment of colloidal sulfur will help (100 g per 10 liters of water) to get rid of the tick. Raspberries should also be processed by cutting out sticking shoots affected by a raspberry fly.
What is planted in May
When planting plants in open ground this month, you should focus on the actual temperature rather than on the calendar. If the soil warms up enough (up to 10 degrees), then you can plant potatoes. In the open ground this month, you can sow sunflower, corn, beans, parsley, onions, radishes, lettuce, carrots and beets. Squashes, watermelons and pumpkin crops can be sown in greenhouses.
Also planted in open ground seedlings of tomatoes, cucumbers, leeks, peppers and eggplant. You can also plant spring garlic.
As for flowers, then in the open ground you can plant seedlings of daisies, carnations, forget-me-nots, and sow - alissum and asters.
June
Spring is over! In the summer, worries will be more than enough. First of all, remove the unused smoke heaps, then apply additional feeding and watering of plants and pest control. Not superfluous will be katarovka (pruning of surface roots) of shrubby plants. If you do not make it in time, the plants can gradually go to the surface roots, a deep root system simply does not form, which can lead to a weakening of the bushes and their early death.
Plant nutrition
June is the time of the second feeding of berry bushes and fruit trees. Dilute mineral fertilizer (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water) or potassium nitrate in water and spray the trees with this mixture. It is very important that the underside of the leaves be moistened. After about 20 days, when the ovaries begin to form, you can arrange a third dressing.
Top dressing of plants is perfectly combined with their watering. Raspberries can be fed with slurry or mineral fertilizers, approximately 1 tablespoon of saltpeter, 2 tablespoons of superphosphate and 1 spoon of potassium sulphate per 10 liters of water, strawberries with urea. For fertilizing trees and other berry bushes, in addition to raspberries, also slurry and bird droppings are suitable in low concentrations. In the absence of manure or bird droppings, the soil can be fertilized with urea, ammonium nitrate, superphosphate, and potassium chloride and sulphate, as well as various combinations of these fertilizers. If you do not have the opportunity to feed the plants, still water them and loosen the soil after watering.

Top dressing of a young tree
Pest control
Pest control is a common summer occupation for a gardener. It is often necessary to observe that the apple trees in the garden are badly damaged, and the leaves are eaten together. The reason for this may be the apple moth - a small butterfly with snow-white wings with black dots, the reverse side of the wings is gray. The pests are not the butterflies themselves, but their caterpillars that appear in the autumn on the bark of apple trees. In the spring, they begin to gnaw open leaves. They breed colonially, forming spider nests, and in each of them there can be up to 100 caterpillars. To avoid serious damage to the trees for the next year, you need to deprive the mole of the opportunity to multiply. This goal is achieved by burning spider nests. In addition to the apple moth, you will also have to fight with the ringed and unpaired silkworm, codling moth and apple aphid. Catcher belts and kvass banks hung on trees will provide you with invaluable help.

Apple Mole
Grapes and strawberries
Also in June, you can take up the garter of green shoots of grapes and spraying the vineyard, and if you plan to get a good harvest of strawberries in August, then in June you need to separate sufficiently developed sockets, to destroy berries affected by gray rot.
What is planted in June
Until mid-June, you can plant late seedlings of cucumbers, eggplants, peppers, and tomatoes in open ground. In the second half of June, you can sow cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, turnip, cucumbers, and radish for the autumn harvest. You can also re-sow radishes, dill, kohlrabi and lettuce. At the same time, thin the previously planted carrots, beets and other vegetable crops.
You can sow cornflower, flaxseed, iberis, kosmeyu, calendula, levkoy. In this case, you will extend the flowering of your flower bed until autumn.
July
Tillage
In the first half of July, special attention should be paid to the state of the soil, especially its air and water regime. It is necessary to loosen it, remove weeds, water. Loosening it, it is possible to provide the roots of plants with an additional inflow of air, and as for the leaves, it will not prevent their hydration.

Plant nutrition
Also, the first half of July is the time of intensive feeding of plants. It is during this period that it is very important to feed the plants, because starting from the second half of the summer, nitrogenous feeding of perennials, berry bushes and fruit trees is undesirable because it will lead to the formation of new shoots that will not have time to mature and the plants will not be able to prepare for the winter naturally. in a way.
Plants can develop and bear fruit only if the necessary nutrients are sufficient in the soil on which they grow. Plants need phosphorus, nitrogen, iron, copper, zinc, boron, manganese, potassium. The lack of these elements in the soil can be filled with fertilizers, as well as foliar top dressing (spraying).
With insufficient nitrogen nutrition, plant leaves take on a yellowish tint, due to the insufficient formation of chlorophyll. Falling of the ovaries and flowers may also occur. Urea, ammonia water, ammonium sulfate, calcium and ammonium nitrate help to cope with these problems. During periods of flowering, the formation of fruit ovaries and preparation for the cold season, fruit plants are particularly in need of nitrogen nutrition.
Phosphorus is of great importance for the formation of seeds in fruits, formation of fruit ovaries, important for fertilization and vegetation. In order for the needs of plants in phosphorus to be satisfied, phosphoric flour, superphosphate (regular or double) is introduced into the soil. The ability of a plant to absorb phosphorus depends on how satisfied its nitrogen needs are. The better the availability of nitrogen in the soil, the better the plants will absorb phosphorus.
Plants need potassium very much. It contributes to the formation of immunity against fungal diseases, improves the taste and color of fruits, prevents the fall of flowers and ovaries. To potassium fertilizers include ash, salvinit, sulphate and potassium chloride, potassium salt. Sulfur, which is a part of sulphate salts, also has a beneficial effect on the growth and development of plants, but chlorine does not always have a positive effect on their formation. Therefore, the use of sulphate salts for soil fertilization is always preferable to the use of chloride fertilizers. Grapes, raspberries and currants are very sensitive to chlorine. Clay soils are saturated with potassium salts, so the need for potash fertilizers on such soils is small.
Also, plants need enzymes that regulate metabolism and promote growth. For the formation of enzymes need microfertilizers, these include copper, iron, manganese, zinc, boron, and many others. By the end of July, shoots of pears and apples complete their growth and the formation of the final bud occurs. If by this time the shoots have not completed the annual growth cycle, then they should be pinned. However, the exact time of completion of the growth of shoots should be clarified, since it very much depends on the region of growth.
Wild strawberry
July - time to do strawberries. Mowing leaves in time, this increases the number of reproductive organs of strawberries, and as a result, yields increase. Cut the leaves starting at the age of 3 years.

Also at this time you can spray strawberries with karbofos, this will help get rid of many pests, such as weevil, spiderweeds and strawberry mites. A strawberry struck by a nematode, you need to immediately dig and burn. The soil where the affected plants grew should be treated with nitrophene and dig up. Visually, the nematode can be determined by the short stature of the plants, they are characterized by shriveled leaves and disfigured inflorescences, flower stalks are thickened.
If you plant strawberries at the end of July, then next year, it will undoubtedly please you with large and juicy fruits.
In July, the crop of white cabbage and cauliflower, kohlrabi ripens. After harvesting, if you have seedlings of cabbage of the second sowing, you can plant it on the vacant place.

Also, potatoes, carrots, cucumbers, peppers, early tomatoes, radishes, beets, celery, dill, onions and garlic ripen by this time. Of the berries you can enjoy the early harvest of strawberries and strawberries, gooseberries, raspberries, currants.
What is planted in July
You can sow salad vegetables, beans, dill and parsley, black and green radish, plant daikon. In the second round, you can plant potatoes, cucumbers and sow many crops, the vegetative period which will allow you to harvest a second time in the autumn. Salad vegetables, including sorrel, are quite cold-resistant, so that you can sow them almost the entire season, because you can harvest such a crop at almost any stage of its ripening.
August
Tillage
This is the time when you need to take care of plants twice as intensively as usual. In August, fruits and berries are saturated with juices, and also the formation of buds for the harvest of the next year. Loosen and moisten the soil more often, remove weeds, and also do not forget about top dressing.

August harvest
Check the condition of the trees
Make backups for those trees, which ripen a rich harvest. Indeed, under the weight of the fruits of the branches can break off and the tree will be permanently disfigured. Also do not forget to pinch the shoots of young trees, so that by the fall they have time to mature.
Budding
In the event that there is a need to make a budding (grafting eye) - you can do it in August. This is the most favorable time for this procedure. The expediency of budding depends entirely on the situation: for example, the fruits of a young apple were not very tasty, or the purchased seedling turned out to be a tree of a completely different sort from which you were counting. There are more complicated cases. For example, if in winter there was a partial freezing of the root system of an apple tree, and later a wild growth formed around the trunk. You can uproot a tree and start over. But if the years of waiting do not suit you, then it is possible to plant the desired variety in the wild. The best period for such actions is the third decade of July and the beginning of August.
Pest control
Pest and disease control is also part of the August concerns. If the currant is damaged by a stem gallfly or a glass case, then carefully clean the bush from unhealthy branches and burn them. Gooseberries can suffer from moth. If this happens, pick up the affected berries and destroy them. Powdery soda solution effectively fights with powdery mildew (you can add Lotus washing powder to the solution). Just remember that the use of toxic chemicals should be stopped for 20-25 days before harvest. In the event that an outbreak of any disease occurs just before the harvest, modern bio-preparations, which are developed by modern technologists for just such cases, can help.
Preparation of planting material
In August, you can engage in stratification of seeds of fruit trees and their planting. You can also prepare pits for autumn tree planting. Harvesting seeds for future plantings can also begin this month.
Preparing for the winter
Also this month, it's time to start preparing for the winter. It is to accelerate the ripening of the shoots and stop their growth. Besides the fact that some of them should be pinned, it is advisable to take the following measures: at the end of August, stop feeding and watering the trees, stop destroying the weeds. Now they will take away excess moisture from trees, as a result of which new shoots will cease to form, and the aging of wood will significantly accelerate.
August is the time of harvesting apples, plums, pears, cherries, black currants, strawberries, late gooseberries. Also stops this month to bear raspberry.
Vegetables in August can be harvested onions, zucchini, carrots and beets, many types of cabbage, including cauliflower and broccoli, medium-early varieties of potatoes, beans and green peas.
What is planted in August
Radishes and daikon are planted in August. However, for the most part this is a month of perennial plant care. You can engage in the division of phlox, primrose, delphinium and primrose.
September
Harvesting
The most pleasant September concerns include collecting and sorting the harvest. Apple harvest should begin after the first healthy fruits begin to fall on the ground. Collect them in baskets, the bottom of which is sprinkled with chips. Best of all, fruits are stored at a temperature of 0-2 ° C and at a very high humidity of 80-90%. Such conditions can be achieved by digging a hole in the basement and filling it with sand, which can be moistened periodically. Also in September, harvested vegetables - beets, potatoes, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers.

Feeding trees
Approximately two weeks after you collect the fruits from the trees, you can begin feeding them with mineral and organic fertilizers. It is at this time that the trees grow intensively absorbing roots, and during this period additional feeding will be most effective. If the tree is 6 years old or less, then it should be enough of those fertilizers that you applied to the planting pit. If the trees are older, then fertilize follows the following scheme (for pears and apple trees): age from 7 to 12 years - superphosphate (2/3 takana), potassium chloride (1/3 cup) and about 4-5 kg of any organic fertilizer; The age of the tree is 15–20 years — superphosphate (one cup), potassium chloride (half a cup) and 7–8 kg of organic fertilizer. If trees are older than 20 years, then the amount of fertilizer will be, respectively, more. Organics contribute no more than once every 4 years. Of course, these are approximate norms. More accurate indicators can be found only if you conduct a laboratory analysis of the soil of your site. Spraying urea solution will help eliminate the scab damage of your trees. To carry it to the beginning of the leaf fall. It has also been observed that trees treated with urea tolerate winter much more easily.
At a later date should not be engaged in digging, watering the soil or fertilizer. This can stimulate growth processes and prevent the preparation of plants for winter rest.
Compost pit
Preparation of the compost pit - this can be done all year round. Collect grass, tops, flower stalks, sawdust, organic garbage in a hole. As a result, you get a great tank with valuable organic fertilizer. Do not dump into the compost pit branches and leaves of diseased trees that remain after sanitary and preventive pruning. Viruses and various pests may not be useful to your garden as fertilizer. From unhealthy pruned branches you can make the most valuable wood ash, which you will always find use in your garden.
Cuttings
September is the right time for cutting currants.
What is planted in September
In the second half of September, they sow winter vegetables and plant winter onions and garlic. It is not too late to plant strawberries to harvest next year. Also at this time you can plant raspberries and strawberries.
September is the month of flower care. At this time, plant all the onion flowers, such as daffodils and hyacinths, and plant peonies and primroses in flower beds.
October
Planting seedlings
October is the time to prepare the garden for winter and various planting works, especially for tree saplings. In the pit for planting seedlings make the following mixture: one kilogram of ash, 200g. superphosphate and one bucket of soil from the top layer. This mixture is poured to the bottom of the pit. Having placed the root system of the seedling in the pit, it must be filled with soil and a light seal around the perimeter should be carried out. Around the perimeter produce stronger pressure, closer to the young shtambu press a little weaker.
For the next few years, it is necessary to loosen the soil around the periphery of the seedling roots, 30-40 cm deep and fill the groove with organic residues and debris, adding a little potassium and phosphates. After that, the soil can be tightly tamped.

Preparing for the winter
Preparing the garden for the winter is perhaps the most important event of October. The decrease in the number of light clocks and cooling causes the trees to stop all growth processes, this applies not only to the land part of the plants, but also to the roots. If at a distance of one meter from the tree and at a depth of 25-30 cm the soil temperature is above 5 degrees, and the humidity is 70-80%, then, most likely, the tree continues to grow the root system. The presence of light roots and processes on the root lobe is a sign confirming growth processes. Those trees that continue to grow roots until mid-October, as a rule, do not develop frost resistance. Their root system can freeze even at -7 ° ... -10 °. In order to slow down the freezing of the soil and enable the trees to quench, about two weeks before the onset of frost, watering the trees should be done, moistening the soil to a depth of 80-90 cm. For irrigation of adult fruit-bearing trees, about forty buckets of water are needed, saplings, of course, much less is required - about 20 buckets.
Winter pest protection
In order to protect saplings from winter frosts, it is desirable to tie them with spruce branches and roofing felt. It will also provide additional protection for them from rodents and hares. Rodents and pests can inhabit autumn leaves, but they should not be burned. You will deprive your garden of additional organic fertilizer. Pests will not be able to harm your trees if you whiten them with a special compound: about 3 kg of freshly shed lime and 100g. copper sulfate on a bucket of water. Blanch not only the stumps, but also the large skeletal branches. Try to do it on a sunny day so that the whitewash is not washed away by the rain. It is desirable to whiten not only trees, but also fruit bushes.

What is planted in October
This month they plant onions and garlic, bulbous plants and some winter crops.
November December
Already in November, real frosts can occur. Well, if the snow falls. After all, even 3-5 cm of loose snow raise the temperature of the soil by 10-12 degrees. To protect the root system of seedlings, you can create around them small circular rollers that will insulate the soil. With the onset of December, scatter the rodent poison in the garden and check the condition of the tree strapping.
Also in winter, you can prepare the cuttings for grafting and cutting branches of shrubs that will become your planting material in the spring. Do not forget to bring bread crumbs or seeds for birds to the garden!