What to plant after the melon next year. Then planted zucchini in the open ground
Popular with gardeners zucchini takes priority in planting gardens and garden plots. This is easily explained by the nutritional properties and simple agrotechnics of growing vegetables. After harvesting, experienced gardeners, realizing the effectiveness of sticking to the right crop rotation, think about what can be planted after squash on next year in a sunny, well-fertilized place where the zucchini grew?
Zucchini - a vegetable that after harvest does not leave negative consequences for the soil. Therefore, the range of plants that are planted in the used area after the harvest of this vegetable is quite wide. Experienced gardeners have long tested various plants for the annual circuit in their garden beds.
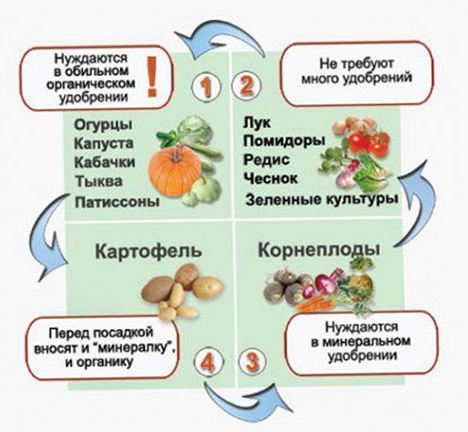
If you do not know how to properly plan the planting of vegetables on your site, then study the information from a special table.
The most popular plants that are actively developing and bearing fruit on the site where zucchini was previously grown include:
Onions and garlic, which due to their properties disinfect the soil;
various types of legumes, in particular peas: they not only produce high yields in these areas, but also enrich the soil with nitrogen;
vegetables from the family of nightshade, in particular tomatoes, including the most demanding on soil indicators - cherry tomatoes;
root vegetables: radishes, beets, carrots.
The success of each owner is a well-thought-out crop rotation. A good harvest will delight the gardener and reward him for hard work if he uses the experience and technology he has gained over the decades.
Traditionally, before the start of the season, it is necessary to refresh the main principles of crop alternation on the site and strictly adhere to them. Usually the plant is planted in the place where it grew, no earlier than four years later, and at this time the plot is planted with other types of vegetables. This rule applies to zucchini. Experienced gardeners often plant potatoes or tomatoes after squash, i.e. vegetables that are susceptible to contamination from infected land. Since zucchini is resistant to pests, after them the soil remains “clean” and contains a lot of nutrients to obtain good harvest other cultures.
It should avoid planting cabbage after squash. Plants will be weak and the harvest will not justify the effort. Themselves zucchini fruit perfectly in areas where cabbage was grown. Of course, a high yield will be only subject to the rules and timing of planting, watering and the necessary agrotechnical work: weeding, loosening the soil, easy hilling up of the stems.
Competently using experience and knowledge, planning a place for planting in advance, an experienced gardener can count on success - a good harvest will surely please him!
The vegetable marrow popular among gardeners takes priority in disembarking on kitchen gardens and garden sites. This is easily explained by the nutritional properties and simple agrotechnics of growing vegetables. After harvesting, experienced gardeners, realizing the effectiveness of sticking to the right crop rotation, think about what can be planted after squash for the next year in a sunny, well-fertilized place where the squash grew?
Zucchini - a vegetable that after harvest does not leave negative consequences for the soil. Therefore, the range of plants that are planted in the used area after the harvest of this vegetable is quite wide. Experienced gardeners have long tested various plants for the annual circuit in their garden beds.
If you do not know how to properly plan the planting of vegetables on your site, then study the information from a special table.
The most popular plants that are actively developing and bearing fruit on the site where zucchini was previously grown include:
Onions and garlic, which due to their properties disinfect the soil;
various types of legumes, in particular peas: they not only produce high yields in these areas, but also enrich the soil with nitrogen;
vegetables from the family of nightshade, in particular tomatoes, including the most demanding on soil indicators - cherry tomatoes;
root vegetables: radishes, beets, carrots.
The success of each owner is a well-thought-out crop rotation. A good harvest will delight the gardener and reward him for hard work if he uses the experience and technology he has gained over the decades.
Traditionally, before the start of the season, it is necessary to refresh the main principles of crop alternation on the site and strictly adhere to them. Usually the plant is planted in the place where it grew, no earlier than four years later, and at this time the plot is planted with other types of vegetables. This rule applies to zucchini. Experienced gardeners often plant potatoes or tomatoes after squash, i.e. vegetables that are susceptible to contamination from infected land. Since zucchini is resistant to pests, after them the soil remains “clean” and contains enough nutrients to get a good harvest of other crops.
Zucchini - one of the most common crops in any garden. Unpretentious, productive, frost-resistant. Constant planting of zucchini on the same garden bed weakens the plants, increases the risk of possible diseases. After the recommended predecessors, the land is guaranteed to yield abundant harvests for the next year.
Crop rotation
In the process of growth, any plant releases into the soil enzymes - spent substances. The alternation of cultures will protect the site from depletion, as well as enrich it with essential trace elements. Crop rotation is needed for:
- reduce the number of dangerous earth viruses;
- increase in the content of beneficial bacteria;
- reduce the negative impact of drugs and fertilizers.
Main principles of crop rotation:
- After crops with a shallow root system, plants are planted with deep roots.
- After late - do not land early.
- Plants suffering from the same pests do not alternate.

Planting zucchini
Some cultures can be kept up to 5 years in one place, but it is better to change every 1-2 years. Also of great importance is the "neighborhood" of vegetables. The roots of the plants should be in different layers of the soil.
Next to squash planted onions, or winter garlic. When the bushes will actively grow, early ripe greens are removed. So well saved space in small areas. Legumes saturate the earth with nitrogen. Beans and peas will have time to grow until zucchini grow lush foliage. Tall plants such as trellis beans, corn, sunflower will not compete with squash for a place in the sun. Also, they will be a good natural protection from the wind. From sawflies, moths and aphids, melons will protect tomatoes, and black radish from the invasion of spider mites.
Tip! Squashes are easily pereopilyatsya with other related cultures, so plant them in the distance.
Squashes return to their place once in 3-4 years.
Predecessors for courgettes
The best option - this culture siderats. Deep branched roots penetrating into the soil, saturate it with oxygen. It creates a favorable environment for the functioning of beneficial bacteria. For example, phacelia. The plant is sown after harvesting zucchini. In winter, tops of siderata will hold back the snow and will not allow accumulation of excess moisture. In early spring, the plot is plowed over and sown again with phacelia. Before planting zucchini in June, phacelia will bloom. The field is again plowed and planted seedlings.
Tip! As sideratov sown winter cereals, cruciferous, clover, lupine.
Zucchini grow well after any solanaceous. It should be borne in mind that the potato absorbs a large amount of phosphate and potash substances, therefore making min. fertilizer needed. After tomatoes, the ground also needs support with phosphorus and potassium.

Siderata
From eggplant, usually, there are very fertilized beds, as this crop likes nutritious soil. Squashes in such a place will bear more fruit.
Do not deplete the bed for zucchini tuberous: carrots, turnips, beets. These cultures feed in deeper layers. Legumes saturate the soil with nitrogen, which is so necessary zucchini to build green mass. Therefore, beans, beans, green peas, lentils, vetch and other cultures - will create the necessary environment in the ground for the growth and development of zucchini.
Gourds are not suitable as predecessors. Not everyone knows that cucumbers also belong to this family. Very often, the cucumber plant is affected by powdery mildew, and zucchini is susceptible to this disease.
Useful properties of zucchini
Squashes come in different shapes and colors. Recently, gardeners prefer a more delicate zucchini. All zucchini contains vitamins from groups B, A, C, PP, K. Microelements: potassium, magnesium, copper, cobalt, vanadium, zinc, selenium, phosphorus, iron and others.
![]()
Zucchini is very useful fresh
At the same time zucchini is absolutely dietary product. It is part of many diets and a balanced diet. Zucchini lowers cholesterol naturally, stimulating the liver to produce the necessary enzymes to break down fat. The risk of atherosclerosis and vascular occlusion decreases by an order of magnitude. Vitamins contained in zucchini, remove dangerous carcinogens from the body, preventing oncology.
Culture almost does not require care for the season. The exception is the dry period, when the bushes are abundantly watered. Weeds do not suppress the planting, as the plant has wide, large leaves. On a well-fertilized and “rested” garden bed, the harvest of zucchini is removed until the cold weather.