Berry Shrubs. Spray berries. Species diversity of fruit shrubs
The yield of berry crops with proper observance of agrotechnical measures can be very high. Berry plants multiply by vegetative means, bear fruit on the second or third year after planting. Berry crops ripen much earlier than stone fruit and pome fruit.
Shrub berries are rich in various biologically active substances, vitamins, contain pectic substances, sugars, organic acids. Currants, gooseberries, raspberries and strawberries are the most common among berry crops.
April Gardening Calendar
We form and impose the crowns of apple and pear, and in the second half of the peach weaves in the mating phase. We reduce currants and gooseberries. We plant trees and fruit bushes. Systematics herbaceous plants and alpinarium, ornamental plants - in the Department of Greens and in the Palm House. A new object in the garden is the Nature Museum under the open sky. a regional collection of old varieties of trees and shrubs; and a collection of plants. It will also serve as a base for education.
The best nuts for gardening and horticulture
If there are many predicted frosts, we can additionally cover the crown of coniferous plants or frost. Being strong, he begins to bear fruit at a young age. Its nuts are large, long, tasty. This variety is a good pollinator for others. Rarely ill. “Mermaid” is a shrub of both fruit and ornamental, because of its spring cats, young leaves and seed covers.
Berry Shrub
Black currant and raspberry grow better in wet areas of summer cottages. Raspberries are more thermophilic than blackcurrants, but it does not tolerate heat. Red and white currants require sufficient lighting and a drier location.
The most thermophilic gooseberryIt also requires moisture-rich soils. Strawberries suffer from drought due to the superficial location of the root system, and when there is insufficient snow cover and very low temperatures it freezes in winter. All types of berry plants do not tolerate low-water marshlands - depressions and depressions, where water stagnates, as well as areas clogged with rhizomatous weeds, especially couch grass.
How to prepare plants for winter
We currently share a commitment to gardening. And then together we enjoy the effects of collaboration. Trees and shrubs and ornamental plants. Pests: crayfish, pear sorghum, peanuts and grapes. Or perennial bushes conifer shrubs or agrofood. Ornamental or fruit trees.
Frost protection requires a root system of trees rooted with roots, such as magnolia. My garden has been a typical rural garden for generations, in which fruit trees were grown with vegetables and annual flowers. The idea to turn it into a more decorative one, was born after a powerful storm that sprouted fruit trees and ruined the whole area.
Based on the above, on low, moderately humid and warm areas of the garden need to plant strawberries, black currants, raspberries and gooseberries; on more dry, well-lit areas - red and white currants. Berry plants (especially strawberries and raspberries) require reliable protection from winds, and in winter - good shelter with snow. Berry plants in the garden is better to place on a separate area allocated for them. However, planting is allowed (except raspberries) between the rows of fruit trees.
What works should be done in the garden in August?
My garden is reflected in the mirrors, so that it seems richer and more mysterious. We use oil preparations to fight wintering pests before cracking. We cut trees and bushes in the center. This may be a decorative or fruitful heather. Next to these plants, we can plant other species that need acidic soil, so hydrangeas and coniferous trees and trees.
Species diversity of fruit shrubs
Heather creates a climate. The article comes from the October Magnolia, which is already available for purchase at kiosks. We will pay less for diluted juice. Grenadine is much more expensive - pomegranate syrup used for beverages. This fruit gives the correct pomegranate - a thorny shrub 2-4 meters long or a tree from the Mediterranean Sea and lost in the autumn leaves.
Currants, gooseberries and raspberries Most amateur gardeners plant in 1-2 rows along the borders of the cottage plot, along a hedge.
Currants, gooseberries, raspberries and strawberries grow better on a flat soil surface. However, strawberries can be planted in several wet areas on low beds, ridges with a height of no more than 10-12 cm.
The most beautiful fragrant varieties
A sweet sweet bouquet with spicy notes usually consists of flower buds or flowers. White and yellow colors also have refreshing tones of nasturtium or lemon, and orange colors are rich in fruit flavors. The plant has more flowers and in them. Growth regulators can be used for most types of pots, all garden shrubs, perennial plants, as well as fruit trees and shrubs. These preparations are used three to seven times during a season, exclusively in plants that are fully developed in at least one pair of leaves.
Some gardeners make a mistake by planting berry plants very closely, with the result that after a few years the bushes shade each other, the shoots are drawn out, the berries do not ripen well, become shallow and become less sugary, and the plant susceptibility to diseases and pests increases. The density of planting has a particularly negative effect on strawberries, which, under these conditions, is exposed to the disease of gray rot, and the yield of berries is significantly reduced.
Harmful to animal and human health. Willow trees grow so intensely that they often need to be cut in the summer. We run out of gas, and some of us are short, even quite strong. With the chase we can go to the trees and fruit bushes. After collecting the fruit of the cherry tree, we cut a tree that crowns the tree.
Cutting trees - green manor
The tenant as a landlord or as an indefinite use of the property must obtain such permission before the cut. However, no permission is required for the removal of trees and shrubs under the age of 10 years and fruits. Other issues included in the question, namely the rights of members.
Berry Bushes planted as follows: currants and gooseberries - in a row at a distance of 0.5-0.7 m between bushes, between rows - 2 m; raspberries - in a row in the distance between plants 0.5-0.7 m.
Black currant - This is a culture that, according to the content of vitamin C, ranks first among berry plants. Vitamin C is not only in the fruits, but also in the buds, buds, flowers and leaves. Currant berries contain many organic acids and various mineral elements.
In addition, the boundaries are set by groups of trees and shrubs and surrounded by a vegetable garden, which is accompanied by a path supported by plates. The windows under the windows along the western and southern facades of the building were designed for flowering discounts. Bushes viburnum, quince, forsythia and hydrangea.
Beautiful plants are good for tincture
In Poland, there is one species - black-tailed aronia, otherwise known as black or dark red. In schools, you can sometimes find a lot of “Nero” chosen by the famous biologist of Russia Mitsurina, who must “import” a bush to Europe. Hills rise: Clematis blooms early and late, the actual vines, pointed honeysuckle and Pomeranian. Trees and shrubs. The task was to design large, undersized wooden pots. To resist the harmful effects of the sun and rain - they were soaked.
Berry Broth black currant It is widely used to treat various diseases, such as hypertension, anemia and gastric diseases. Also, for therapeutic purposes, it is possible to prepare an infusion from currant leaves, which is used as a diuretic, laxative, in case of metabolic disorders.
Currant is a perennial shrub. Currant bush consists of 12-20 uneven-aged branches. Bushes, depending on the variety, can be compact or spreading.
You will also have the opportunity to buy factories and tools. We invite you to take part in the Gardening Fair. Mushrooms are planted on excretions of aphids, buns and taro, so we fight these pests. Trees and fruit bushes most often. Traction and small trees with dense, spherical crowns, single, deeply carved leaves with smooth or foamy edges growing from thorny stems. Looks beautiful in spring when they bloom white or in different ways. Flowers of some varieties are red.
Something is eating my roses and azaleas
Autumn foliage decorates. You can also spray the soil under the bushes. It is even more efficient to introduce a single nematode into the soil. First of all, flowers, shrubs and small trees, in gardeners - flowers, fruit trees and easily grown vegetables. Increasingly, ridges are also located in large gardens. And this is all because of the fashion for eco-friendly vegetables, he adds. But not everyone has it.
The currant root system is located superficially, the bulk of the roots are in the upper soil layer and can spread to a depth of 80 cm. Skeletal roots first grow obliquely and then go deep into the soil layers, up to 1.5 m.
Currant refers to crops that begin growing very early. Her buds start to grow almost immediately after the snow melts. The most intensive growth of shoots occurs in early May. The currant flowering phase lasts up to 15 days, and sometimes up to 23. The ripening period of the ovary continues until the berries ripen and lasts up to 45 days.
Raspberry, strawberry, cherry, strawberry
They are usually tasty, but they are also a great addition to cakes and desserts. Let's wait for their later, more “attractive” species. Let's also remember that before planting a fruit tree it is important to make sure that it is.
Cut the tree according to the law
The reason and the planned date of removal of the plant, the surface from which it will be removed; - Any expert opinion. There are cases when the administration does not require the removal of trees and shrubs. This applies to fruit species and specimens younger than 10 years.The varietal differences and the instability of air temperature greatly influence the formation of the ovary. Early varieties of this period are 35-40 days, and later - a week later. The ripening period of berries varies greatly, and the difference in terms can be up to 30 days. Have early varieties this period is up to 7 days, and for late days it is up to 11 days. The final stage of the growing season - leaf fall.
Green is life. International Exhibition of Garden Exhibitions
300 exhibitors from Poland, other European countries, South America, Africa and Asia will take part in the exhibition. We will see that the largest plants in Poland and Central Europe show plants for gardens and green areas - trees, shrubs, perennials, fruit and fruit plants. A real exotic breeze awaits.
Properly selected fruit bushes in the garden will be excellent fruits for direct consumption, as well as for canned food from the second decade of May to the first autumn frosts. Most fruit shrubs in home gardens are usually currants, gooseberries, horseradish, raspberries, and tall wrestlers. See which fruit bushes are the easiest to grow, and how to direct fruit bushes to a garden or orchard.
In order to grow berry crops (berry bushes), you need to know what conditions are required for their growth.
Currant is a winter-hardy culture. Under normal conditions of overwintering, currant bushes practically do not freeze slightly. In severe winters with frequent fluctuations in temperature, plants can freeze slightly. A characteristic type of such winter damage is the freezing of perennial branches, as well as the freezing of color buds.
What fruit bushes to choose for the garden
Red currant, white currant and gooseberry are the strongest red. Fruit trees in the garden, it is best developed in the sun, on a soil rich in nutrients, moderately moist during the growing season, with a high proportion of humus and slightly acidic. Only high levels of bolettes, large fruit cranberries and swamps have specific pH requirements for the pods on which they are cultivated. For these three varieties, the soil should be very low, i.e. the soil is very acidic. Regular, balanced nutrition of fruit bushes with organic or mineral fertilizers, as well as soil compaction to prevent excessive growth of weeds and pollution, are the main types of treatment that will ensure an abundant annual harvest.
Red currant is a very winter-hardy culture. Many of its varieties, even in the harshest winters do not freeze slightly. The typical types of winter damage are the same as those of the black currant.
Currant refers to moisture-loving cultures. This is largely due to the fact that root system has a superficial arrangement. But it is also necessary to take into account that highly moist soil for currants is undesirable, since at the same time it grows poorly and bears fruit.
Going to the gardening shop, you should get a list of types and varieties of fruit bushes that you want to buy, not to make decisions at the last minute, and not choose what is only for the seller. However, in the store, we pay attention to the condition of the plant - they should all be sprinkled, the roots of the roots and should not have any signs of damage.
It is also worth knowing that there are certain requirements regarding the diameter of the roots and the number of roots. And so the cubes of the first choice should have at least three shoots 5 mm thick in the gooseberry, 7 mm in the white and red currants and 8 mm in the black currants. Some different requirements for raspberries. Fruit bushes in the garden - black currants are less common than gooseberries. or red currant. And it is a shame, because its berries are many nutrients.
Red currant less demanding on moisture conditions. This is due to a more powerful root system compared to the black currant.
Black currant is a shade-tolerant crop, but at the same time, shading does not tolerate well. Red currant for lighting is more demanding, and therefore it is best to plant it in open areas.
Shadow Protector: Elderberry Black
The fruit bushes in the garden are gooseberries. Unfortunately, both of these varieties are very easily deadly for the American gooseberry, the gooseberry, a disease that causes very large fruit shoots. Thanks to this, gooseberry care will save you from less problems and will not require chemical protection of the bushes. They are imported from the Far East.
The fruit of this plant has been used for centuries in Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Tibetan medicine. It was there that information appeared that its promoter, Lee Quing Yen, was 225 years old, eating goji. According to tradition, the fetus was supposed to help with kidney problems, diseases of the lungs and heart, as well as rheumatism and liver diseases, it could improve its vision, muscle and bone strength. As for the botanical data, it is a manor plant, growing in temperate Asia, but also from tropical parts of Thailand.
Currant grows on all types of soil, but is a culture that is very demanding on the nutrient regime. The most favorable soils for it are considered to be sod-podzolic, having a weakly acid reaction.
Less suitable for currants are soddy, strongly podzolic soils. Soils with a heavy texture are of little use for it. Absolutely unsuitable soil for the growth of currants - marshy, carbonate solonets. On such soils in plants, the root system and the aerial part develop very poorly and, besides, the plant becomes ill with chlorosis.
Growing seedlings
Fruits up to 2 cm in length are reddish-orange and ripen from August to October. They appear on leafy shrub irregularly shaped, overlap and height from 1 to 3 meters. The Chinese flowers of the crown are light purple and white spotted. Goji berries are a source of strong antioxidants, calcium, iron, phosphorus, carotene, lutein, thiamine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid and ascorbic acid, about the same as organic lemon.
The glycemic index of dried fruits is only 29. This refers to the definition of well-being and rejuvenation. Often, however, the positive effects of berries are exaggerated by sales and marketing specialists in berries distribution companies. However, this does not change the fact that fruits from a certain source, eaten in reasonable quantities, can be a very healthy diet.
To replace the old low-value bushes, giving a small crop, gardeners themselves can grow seedlings in compliance with certain rules. First you need to choose bushes (shrubs) for reproduction, they must be high-yielding, high-grade, with no signs of disease and, especially, damage by pests.
The easiest way to reproduce currants - lignified cuttings. Harvest and plant cuttings need in early autumn. In the event that this is done during October, the survival rate of the plant will decrease.
The bush is cut mature matured annual shoots from 2-4-year-old branches. From the shoots, it is necessary to immediately remove the leaves and cut them into cuttings up to 15 cm long. It is necessary that each cutting has at least 5-6 buds. The upper cut is made above the kidney, and the lower - under it. The immature part of the escape is not necessary. In order for the cuttings not to dry, they are left for a while in a cool place or placed in water. For good rooting, the cuttings should first be kept in water for 3-4 weeks. The ends of the cuttings are immersed in water for 1/3 of the length or are treated with growth substances.
Planted cuttings need one or two lines. In that case, if the cuttings are planted in two lines, then the distance between them is made 50-60 cm, and if one - then 8-10 cm. The cutting is planted obliquely, at an angle of about 45 °. It is necessary to ensure that there are two buds left on top of the handle, and one of them should be at the level of the soil (Fig. 17).
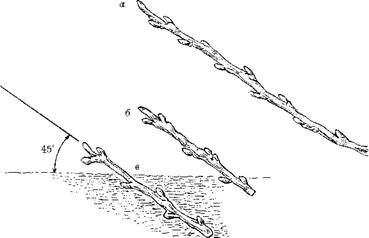
Fig. 17. Planting lignified cuttings of black currant: a - one-year sprout; b - woody cutting; c - planting cutting
In order to avoid the formation of voids, the cuttings tightly squeeze and compact the earth between them. After that, watered and sprinkled with organic fertilizers. After planting the bed should be covered with mulch materials. For better rooting cuttings beds are covered with a dark plastic wrap. The use of the film creates good conditions for the growth of cuttings, as the soil beneath it warms up quickly and is in a moist state.
Planting cuttings
As a rule, currants are planted along fences. The landing site is first dug up to a depth of 22 cm, after making fertilizer in advance. Organics of 3-4 kg should be applied per 1 m2, granulated superphosphate - up to 150 g, potassium sulphate - up to 30 g. Pits are dug 2-3 weeks before planting, up to 40 cm deep and 60 cm wide.
AT landing pit make up to 10 kg of compost (peat or humus), 40 g of potassium sulphate. It is very important that the mineral fertilizers do not come into contact with the roots of the plants during planting in order to avoid burns, as this plant survives worse.
For planting, you need to choose only those seedlings that have a very powerful root system. Such a seedling must have at least three skeletal roots up to 20 cm long. For the above-ground part there should be one or two shoots that go from the base of the seedling.
Most favorable time for planting currants - autumn. The main rule that you need to adhere to in this case is to have time to plant the seedlings 14 days before the onset of frost.
When spring planting is quite possible freezing of the roots of the seedling. In such cases, seedlings should be dripped in the winter in an inclined position to a depth of 40 cm. With the onset of spring, pripednye seedlings cuddle, this is done in order to protect the buds from blooming.
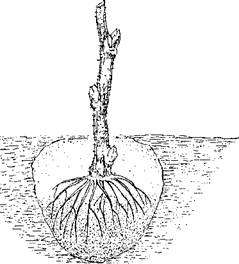
Planted in an inclined position at an angle of 45 ° (Fig. 18). As for the direction of inclination, it does not matter much, as a rule, it is made along a row in any direction. Then the roots are straightened at the seedling, after which they are covered with earth and the soil is thickened.
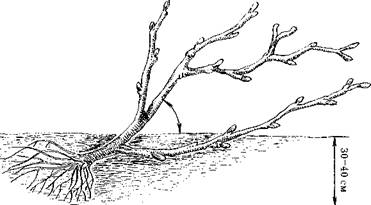
Fig. 18. Planting currant seedlings
When the roots will be covered with earth, but not yet fully, it is necessary to water the seedlings. Then the bush should be covered with peat or sprinkled with dry earth, as this will prevent the formation of a crust after watering. In the event that the seedlings are planted in the spring, the next watering should be done in 3-4 days and then mulch the soil.
Plant Care (shrubs)
Abundant fruiting shrubs is possible only with good growth. Therefore, it is necessary to create all the conditions for their normal growth and fruiting. This is achieved through irrigation, fertilization, systematic pruning, etc.
Currant is a moisture-loving culture, and therefore, in order to maintain a normal water regime, the soil should be kept in a loose, moist condition. Moisture is well preserved if the soil around the bushes is mulched with organic materials.
After planting the bushes, fertilizers, except for those that have already been made, are not needed. The fertilizer area is determined by the placement of a large mass of roots. The bulk of the roots of the currant is located under the crown of the bush. Thus, for adult plants, fertilizers are applied according to the projection of the crown of the bush.
Three years after planting, currants begin to fertilize annually in one or two doses. On loamy soils, organic, phosphate and potash fertilizers can be applied every 3-4 years in autumn or spring. On loamy soils, it is possible to confine ourselves to the basic, spring application of fertilizers.
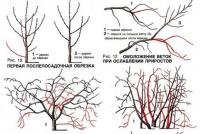
On loamy, sandy, sandy and peaty soils in addition, summer fertilizing with mineral and organic fertilizers should also be carried out. It is desirable to combine such dressings with watering plants. The solution of mullein is diluted 2-4 times, 1 bucket of solution is spent per 1 m2, bird droppings - 8-10 times, 1 / 2-1 bucket of solution is added per 1 m2. Mineral fertilizers dissolve 3-4 g of each element in 10 liters of water per 1 m2. Pruning bushes causes the growth of new root shoots from the underground part of the bush. When pruning, branching of basal shoots increases, thickening of the bush is prevented, the size of the berries increases. Pruning shrubs begin almost immediately after planting. Each shoot should be removed, leaving up to four developed buds.
For the formation of a full-fledged bush every year leave 3-4 annual basal shoots, the rest are removed at the base. The first cut prone to broken, diseased branches and annual basal shoots, except for 2-3 shoots that are evenly spaced.
Formative pruning end at 4-5 year.
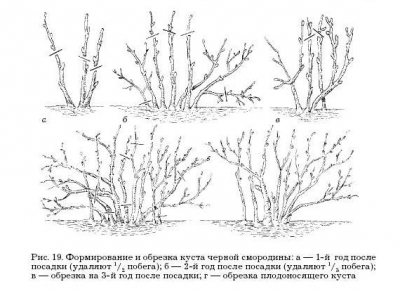
A properly formed adult bush at the end of the growing season has branches of different ages. It is best to leave 10–15 skeletal branches of all ages in the bush, about 2–4 each, with one-year leaves more than 1–2 branches, 4–5-year-olds –– 1–2 less (Fig. 19). By external signs of the shrub, you can determine the age and its productivity. In old branches, the root growth of branches is very weak, less than 15 cm. On old branches, the bark is dark brown, and the older the branch, the darker the bark. More precisely, the age of a branch can be determined by the order of branching. The axis of the root shoot is zero order and corresponds to the 1st year of life. The branch from the axis will be the first order of branching, and the branch will be, respectively, 2-year (Fig. 20).
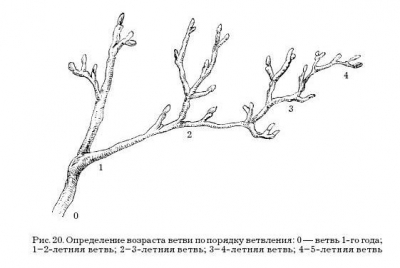
In old branches, pruning is often carried out on perennial wood, i.e., the end parts with weak growth and weak fruit branches are removed to a strong side branching.
In fruit-bearing bushes of red and white currants, after cutting diseased and broken branches, weak root shoots are removed. Perennial branches with weakened fruiting are shortened to strong lateral branching. If not, then the branch is removed completely. When pruning currant bushes remove the branches damaged by the glass. The core of these branches is eaten away and filled with dark secretions. Also cut annual shoots damaged by currant stem gallfly. Such shoots are usually semi-dry and in the lower part have a plot with dark indented spots and cracks. In black-currant bushes and gooseberries damaged by powdery mildew, the tops of diseased shoots are removed. They are twisted and covered with dark spots.
In gardens, thick currant bushes are often found, which have not been pruned for several years. Such bushes thin out, cutting out weak and low-yielding. Also remove the branches lying on the ground and interfering with the treatment of the soil. From the remaining perennial branches, regardless of their age, unproductive branches are cut out, in which annual side shoots have a length of less than 10 cm and few annuli. They are cut near the soil without leaving a stump or shortened to a strongly growing annual shoot that appeared on a branch near the base.

In the old branches left, the drying out ends should be cut to a strong side branch in order to enhance growth on the remaining part of the branch (Fig. 21). In the presence of annual basal shoots and growth shoots on the old branches they are shortened to achieve strong branching.
Pruning berry bushes is a fairly time-consuming process, which requires a lot of time. The best time For pruning, spring is considered, before bud break. But since the currant buds bloom early, it would be better to move part of the pruning work to autumn. In the fall, after harvesting, proceed to the removal of old branches, cutting them at the very base. Such pruning can be carried out throughout the autumn period, before the onset of frost.
Raspberries - semi-shrub of the Rosaceae family, with perennial rhizomes and roots. On the rhizome and adventitious roots are located axillary and adventitious buds. From the axillary buds on the rhizome, shoots develop, called shoots of substitution, and from adventitious buds, shoots. The number of shoots per bush is determined by varietal characteristics and ranges from 5-10 to 25-30.
In the first year after planting, vegetative shoots with a height of 1.5-2.5 m develop. In the second year, they woody, forming lateral branches with loose drooping floral tassels. The leaves are petiolate, consisting of 3-5 ovate leaves. Flowers with double 5-membered perianth, up to 12 mm in diameter. The corolla has a greenish-white color. There are many stamens and pistils in the flower. Blooms after the appearance of the leaves, in the early summer. The main flowering lasts 25-30 days. The flower produces 2-7 mg of nectar and forms a lot of pollen.
Raspberries Best placed on well-lit and sheltered places. If raspberry bushes are placed along the fence, then they are located at least 1 m from the fence. Best time planting raspberries - autumn (late September - first half of October). In spring, the plants should be planted until the seedlings that have been dug in for the winter are just beginning to swell (somewhat germinate) the buds.
When planting seedlings with bare roots in the sun and the wind should not be long. If planting is temporarily delayed or transferred (especially in the spring), seedlings are added dropwise. To do this, dig a groove with a depth of 25-30 cm, plant seedlings into it, cover their roots with soil, water it and compact it a little, and with the onset of frost they pour 15-20 cm of peat from above.
Raspberry seedlings can be planted in holes or furrows 15-25 cm deep. The soil removed from them is folded in one direction and mineral fertilizers are spread on it, then everything is mixed. Saplings are lowered into the furrow (well) by the roots to the same depth as they grew in the nursery, and they are covered with soil (previously mixed with fertilizers). At the same time, the bud, from which the escape shoot develops, must remain on the border with the soil, with a depression of 2-3 cm (Fig. 22). With shallow planting, the root system can suffer with drought and low temperatures, and with an overly deep plant survival rate decreases markedly and plant growth decreases.
In dry areas, raspberries are planted in deep furrows and do not fall asleep completely with soil, which contributes to the greatest accumulation of snow, the preservation of moisture and the development of the root system in more moist soil layers. On overmoistened soils, raspberries are planted in raised ridges, since the root system of this plant does not tolerate flooding; excessive moisture is removed by furrows.
Raspberries are planted in two ways: Ordinary planting with a distance between rows of 1.5-1.8 m and between plants in a row - 0.3-0.5 m; bush planting with a distance between rows and plants from 0.8 to 1 m. Planted plants watered abundantly with water, then cut their stems to a height of 20 cm or at the surface of the soil. The soil is slightly loosened, if necessary, watering the plants is repeated.
Immediately after planting, raspberry seedlings are better to mulch. Peat, dung, straw, dry grass, dry leaves, sawdust, finely chopped wood bark, synthetic films (preferably black) are used as the mulching material.
Peat for mulching is dried, crushed, protected from moisture. The grass is mowed for hay during flowering, dried and stored, periodically drying. Sawdust, on the other hand, is kept accessible by atmospheric precipitation. They are periodically shoveled and used after 2–3 years of storage in the open air.
After irrigation, the soil around the seedlings is covered with a mulching material with a layer of 5-8 cm or covered with a film, making holes with a diameter of 5-10 cm at the stems.
In the event that there are many pests or weeds begin to appear, then in the fall after the disappearance of pests for the wintering, the entire layer of mulching material is loosened and dug along with the soil; In the spring, nitrogen fertilizers are applied to the soil and once again it is loosened to destroy the wintering sites of the pests and a fresh layer of mulching material 15-20 cm thick is poured. In spring, digging is repeated, and the bushes are again filled with mulching material.
Starting from the second year after planting, it is necessary to add manure or compost every spring before digging until the soil becomes loose. If the soil was well prepared for planting raspberries, then it is enough to deposit manure for the 2nd and 3rd year, 2-3 kg per 1 m2.
Then the fertilizer is used in smaller doses, 1 time in 2-3 years manure or other organic fertilizer is applied in pure form or mixed with mineral. In the years when manure is not applied, they give complete mineral fertilizer. If both manure and mineral fertilizers are applied simultaneously, then 2 kg of manure, 3 g of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (the active substance) or 50 g of fruit and berry mixture are taken per m2. At introduction of one manure or only mineral fertilizer of a dose double. Raspberry plots are usually filled with manure in large doses, and there is relatively much potassium in it, therefore mineral potash fertilizers are applied in small quantities. If potassium chloride has to be given a lot, then it must be brought in the fall, so that excess chlorine is washed out with spring melt water and the bushes are not affected. In small doses, potash fertilizer can be applied in the spring.
Forming bushes and pruning raspberries
Raspberry bushes necessarily require support. Tie shoots to the support with twine, polyethylene film tapes, clothespins, etc. The height of the bushes is usually maintained within 1.8 m above the soil surface. With a fan-shaped formation system, the height of the bush is governed by the inclined arrangement of different-sized shoots. Unnecessarily high shoots are tied to the wire, tilting them along the row. The vertical position of the shoot can be saved if the top is bent by an arc and tied to the same wire or cola. Early in the spring (before the kidneys wake up), the raspberry area is carefully inspected, selected from overwintered shoots of 4-6 in a bush or 10-15 on 1 m of a row (possibly one-dimensional), with well-developed buds, without signs of disease and pest damage, and shortened before the first, well-developed and successfully overwintered kidney.
If the freezing of the stems is strong, then if there are 4-6 well-wintered shoots, all the affected shoots are cut out completely. When freezing all the shoots of the bush they are forced to leave and shorten each to the remaining first living buds. If the whole above-ground part of the shoot has died, then it is cut off at the surface of the soil. Selected for fruiting and pruned stalks are tied up, and the rest are cut out at the very base and removed from the plantation.
May-June in raspberry varieties with a high shoot capacity at the base of the bushes, a large number of equal-sized shoots grow, which shade each other very much. At this time, the thinning is necessarily carried out, leaving no more than 10 shoots of the same strength on the bush. In this case, the first cut out shoots affected raspberry fly.
In June and August spend the so-called nip, that is, shorten (cut) by 1-2 cm of the top of young shoots. June pinching leads to branching of the shoots and, accordingly, to an increase in the area of fruiting.
The purpose of the August nipping is to contain the top growth of the shoot, to create conditions for improving the process of preparing the plant for winter. Violation of the timing of nipping can lead to the death of the shoots in the autumn-winter period. June pinching is permissible only in the first 1-2 years after planting and on varieties with extremely low pobegoobrazovatelnuyu ability. In August, immediately after the end of the gathering of berries, they cut out at the base and take out all the seedlings from the raspberry-tree, as well as weak, damaged young offsprings (Fig. 23).
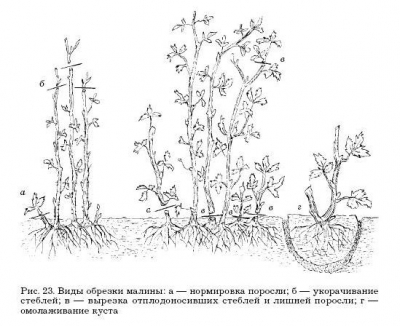
In Octoberwhile the raspberry shoots remain flexible, they are tilted to the ground and connected with the neighboring ones at a height of 30-40 cm. They do this work carefully, taking care not to break the shoots and not to damage the buds. In this case, the shoots of neighboring bushes are tilted towards each other, intertwined with each other and tied with twine. All shoots can be tilted in one direction and tied to the base of a nearby bush. For a more complete preservation of the shoots in the winter, snow retention and shelter of raspberry plantation are regularly carried out with loose snow.
 Gooseberry- shrub of the gooseberry family. Forms spiky shoots up to 1 m in height, leaves alternate, 3-5 lobed, up to 3-4 cm wide, dull, shortly pubescent on both sides. The flowers are small, bisexual, 5-membered, have a bell-shaped calyx and curved petals of a greenish or reddish coloration, located 1-2 each in the axils of the leaves. In the flower of 5 stamens. Like currant, gooseberry bush consists of branches of different ages. Fruiting in gooseberry is reduced to two types. Some varieties have a bushy form with strongly curved, arcuate branches, others have a more condensed form, in which the perennial branches in the center of the bush occupy a vertical and oblique position, and the lateral branches are slightly curved.
Gooseberry- shrub of the gooseberry family. Forms spiky shoots up to 1 m in height, leaves alternate, 3-5 lobed, up to 3-4 cm wide, dull, shortly pubescent on both sides. The flowers are small, bisexual, 5-membered, have a bell-shaped calyx and curved petals of a greenish or reddish coloration, located 1-2 each in the axils of the leaves. In the flower of 5 stamens. Like currant, gooseberry bush consists of branches of different ages. Fruiting in gooseberry is reduced to two types. Some varieties have a bushy form with strongly curved, arcuate branches, others have a more condensed form, in which the perennial branches in the center of the bush occupy a vertical and oblique position, and the lateral branches are slightly curved.
Gooseberry retains the properties of this variety only during vegetative propagation, which is based on the ability to develop additional roots on the branches covered with soil.
If reproduction takes place in the fall, when the leaves fall, the soil around the bush should be well processed and organic and mineral fertilizers should be made in it, procure hooks from any tree 20-30 cm long and, making a small hole at the attachment point, select the desired branch, tilt it to the ground and in the prepared hole to press well. The free end of the branch, pressed against the board or other object, align vertically. In the spring, this branch will start a good, normal growth.
It is necessary to finish the work with cuttings by watering and dusting the soil several times before a small soil mound forms above the hook. If the snow falls on the thawed ground or if the soil freezes slightly, then by the spring on the branch, in the place of its attachment with a hook, small roots can be found. Abundant soil moisture and increased spring temperatures will lead to the formation of significant roots and intensive growth of the young gooseberry bush.
The easiest way to breed - horizontal layering. They are obtained from the majority of shoots of a young 3-5-year-old bush. In early spring, soil is loosened under uterine bushes, then shrubs are fertilized with organic fertilizers. After that, the grooves are made up to 12 cm, 1-2-year-old developed shoots are stacked in them, pinned down and the middle part of the shoot is sprinkled with earth, while leaving the upper end above the soil surface (Fig. 24).
With regrowth of vertical shoots up to 10 cm, they are spud friable soil, then after three weeks the hilling is repeated. Throughout the summer, the soil with cuttings is abundantly watered and mulched with organic materials.
In the autumn rooted shoots are separated from the uterine bush, while well-rooted are divided into layers that can be planted on permanent place. In the event that the layering is poorly rooted, they are left near the bush for the second season or transplanted to the garden for growing.
To the soil gooseberry is not picky. But it grows poorly on marshy, very acidic soils. Loose fertile soils are most favorable for gooseberries. On sandy and sandy soils, it can produce high yields only with annual application of organic fertilizers, irrigation and mulching. On heavy clay soils, the gooseberry aisles need frequent loosening, which ensures free access of air to the roots of plants.
Gooseberry bushes are recommended to plant no closer than 5-6 m from each other. If you plant bushes at a distance of 2-3 m between them, then this will lead to the disease of the plants by the sphere library, from which the yield drops sharply. Usually, gooseberry bushes are planted at the border of the garden, but in such a way that the gooseberry is not located on the adjacent plot at the same border.
Gooseberries are planted in the fall, as even a slight delay in transplanting in the spring has a very negative effect on the growth of the bush in the spring-summer period. When planting, the root collar is lowered into the pit deep enough.
A deep planting with moderate watering leads to the formation of a strong root system both due to the development of the existing and additional ones, which positively affects a steady and abundant crop for several years. Planted in well-prepared pits, with careful care, gooseberry bushes begin to bear fruit on next year and give good harvest for 6-10 years.
Pruning gooseberry bushes
In the formation of gooseberry bushes based on the duration of its growth, the time of entry into full fruiting, the completion of the plant's life, and hence the end of fruiting. Gooseberry bushes form within 6-8 years. By the specified date, each individual bush should have up to 25 strong shoots with a bush diameter at the base of up to 50-60 cm. Due to the fact that the gooseberry fruit formations are located on the tops of the shoots, shorten the shoots due to the possible large yield loss should not be.
To pruning gooseberry need to be approached carefully and carefully. At the same time, it is always necessary to know which branches bear fruit well and which ones bear bad. Before the start of pruning, they clarify the force of growth of the branches of the bush, the presence of dry, sick and spoiled among the fruit-bearing branches, as well as the degree of thickening. If the bush is thickened, then pruning begins with the elimination of this deficiency, for which the older branches are removed at the base of the bush, creating conditions for normal growth and fruiting of the young branches.
Then cut out dry branches of the first and another order, as well as weak-growing young ones, when there are many of them. As a result of pruning, the gooseberry bush should have rare, but strong and young branches, with good illumination during the summer growing season. Hanging branches, especially hanging down to the ground, in the mass of the bush after pruning should not be.
Beautiful, convenient and practical - it is quite difficult to combine such properties in one object, especially if this object is a plant. And it is especially difficult to choose such plants for small garden, for example, six hundredth. But they are! Ornamental shrubs with edible, tasty and healthy fruits unpretentious, do not require special attention, grow well and bear fruit in central Russia, and some of them - and in more northern areas. Choose who likes what!
Most unpretentious
Irga is often used in ornamental gardening. As a fruit plant, this is a real find for busy gardeners who do not have the ability to care for capricious crops, but still want fresh fruit. Even with minimal care, irga will provide you with sweet berries that can be eaten fresh, frozen, dried or made into jam or stewed fruit. In addition, they are useful: they contain about the same amount of vitamin C as there is plum, as well as significant doses of vitamins of group B. Fruits contain substances that contribute to the prevention of myocardial infarction and vascular diseases. In addition, fresh rye works as a mild sedative.
What does it look like?
Irga round-leaved is a thick, tall shrub up to 4-6 m high. If it is grafted onto a red mountain ash, you will get a tree on a trunk. The leaves are oval or rounded, in autumn they acquire a reddish-yellow color. The flowers are small, white or slightly cream, collected in brushes like bird-cherry, bloom in May. Small (diameter 8-10 mm) apples-fruits in ripe form become almost black with a bluish bloom. Ripen in July.
Agrotechnology
Irga is so unpretentious that it can grow without problems on its own. It is cold and drought resistant, undemanding to soil conditions, but prefers fertile, neutral or slightly alkaline soils. It grows well both in the sun and in partial shade. Practically does not require maintenance and specific trimming. Pests and diseases are very rarely damaged - sometimes shepherd and hawthorn attack her.
Fruiting plants respond well to fertilizing (early spring or autumn) with organic fertilizers: manure with the addition of superphosphate or ash, infusion of bird droppings, etc. Adult bushes thin out from time to time, leaving no more than 10-15 trunks in each.
Irga is most conveniently grown from root suckers. They are dug in the spring and immediately planted in a permanent place. After planting, the above-ground part is cut, leaving only hemp no more than 5 cm. As a result, the plant directs all forces to rooting, which has a positive effect on survival.
Sorta
In our country, there are selected forms of irgi with large fruits of very good taste, which are slightly inferior to imported varieties of a related species - Canadian irgi, as well as Krasnoyarskaya cultivar (winter hardy and fruitful, late ripening, fruits above average size, bush height - up to 4 m).
In the wild, irga grows in North America, East China, Korea and Japan, North Africa, Central and Southern Europe. Of its 25 species, most are located in North America, and only one is common here — the round-leaf irga (Amelanchier rotundifolia). Irga culture was introduced in the XVI century in Europe. And the first industrial plantations appeared in the second half of the XIX century in the United States. These were the most large-fruited forms selected from wild plants. Nowadays, irgu also fell in love with the Russians, who grow it almost throughout the territory of Russia,- true, mostly in amateur gardens.
The most golden
Golden currant is very beautiful during flowering - because its flowers are much larger than those of black or red relatives, and brightly colored in golden-yellow color. In the fall, her foliage first becomes orange-red, and then purple-carmine color. This currant is no less valuable as a berry crop. Its aromatic fruits are distinguished by a high content of biologically active substances (vitamins C, E, P, carotene, pectins, organic acids). They also contain iodine and other trace elements. Berries are sweeter than those of black currant. They are suitable for fresh consumption and for processing into jam, jams, compotes, wine, for drying and freezing.
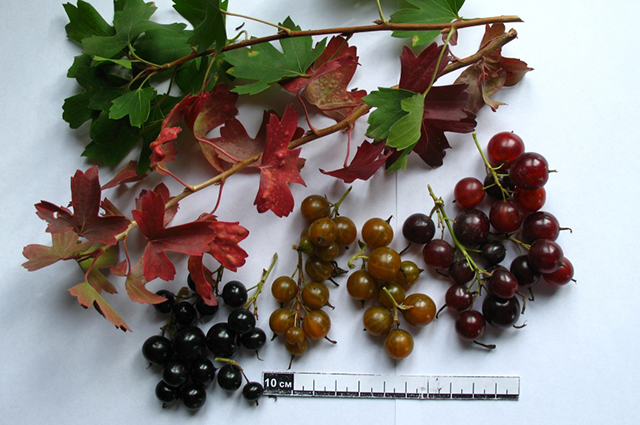

Golden currant. Photo: Anna Solovyova
What does it look like?
Currant golden - deciduous shrub up to 2-2.5 m. Leaves resemble gooseberry leaves. The flowers are golden, fragrant, gathered in brushes 3-7 cm long. The berries are black or purple-brown with a diameter of 6-8 mm. Currant blossoms golden in May for 15-20 days, fruits in July.
Agrotechnology
Golden currant has a high ability to withstand many vicissitudes of the environment. She endures winter troubles, drought and heat. Leaves can withstand temperatures up to 40 ° C without burns, and later flowering prevents damage to flowers and ovaries by returning spring frosts. Golden currant is resistant to pests and diseases and has a good yield. This currant practically does not require care, except for pruning, which is done on the same principle as that of black currant. It is advisable to have a few in the garden different varieties - single plants are samobesplodny and can be left without berries.
Sorta
The best known are Venus (black berries), Laysan (yellowish berries), Shafak (dark red berries), as well as new varieties of golden currant, created in the Siberian Institute of Horticulture named after M.A. Lisavenko (Barnaul): Present to Ariadne, Siberian sun, Barnaul, Levushka, Valentina, Ida, Dar Altai. It is possible to propagate the golden currant with green and lignified cuttings, dividing the bush, root shoots and even seeds (not varietal).
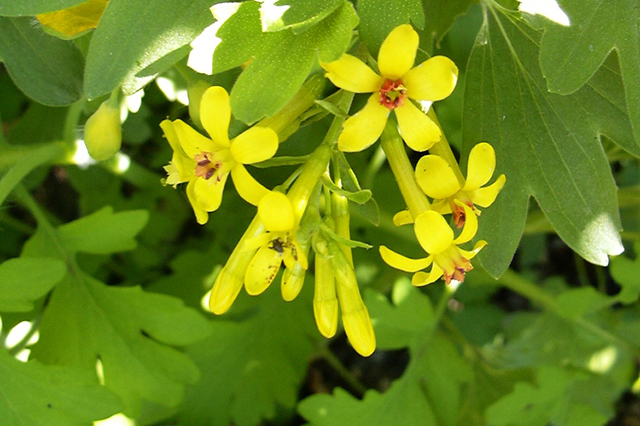

This culture originates from the wild currant golden (Ribes aureum), which grows in the western part of North America. In culture since the beginning of the nineteenth century. In Russia, I. V. Michurin was the first to pay attention to her. He sowed seeds of the American variety Crandal and brought out several varieties, including the seedling of Krandal, which became one of the pioneers of modern varieties. In the years 1930–1940, the golden currant as a low-tolerant to soil conditions and a drought-resistant plant began to be included in the list of crops for forest shelter belts in the steppe regions of the USSR. Then it spread to the southern regions of Russia as a berry plant.
Most versatile
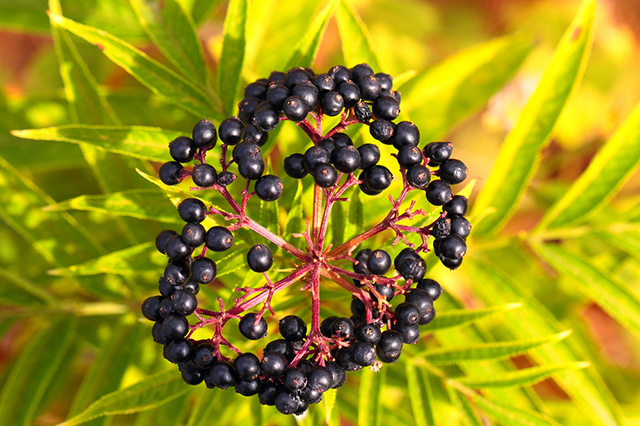
Black elderberry is used as an ornamental, medicinal, melliferous and fruit plant. In ancient times it was believed that it heals a person and prolongs his life, and for this it was called a sacred tree. The ripe black elderberry fruits are palatable, contain vitamins C and E, carotene, tannins, glycosides, anthocyanins, essential oil and other biologically valuable substances. It is consumed in both fresh and processed form. Of them prepare the jam, jam, marmalade and various drinks. Juice is used to color food and wine, and flowers are used in medicine. By mixing one part of the dried flowers of the black elderberry with three parts of ordinary tea, they get fragrant medicinal tea.

Elder. Photo: Shutterstock.com / Rashid Valitov
What does it look like?
Elderberry is a deciduous shrub or a small tree up to 7 m high. With leaves it looks like a well-known red elderberry. Yellowish white small flowers collected in lush inflorescences, "clouds", located at the ends of annual branches. They have a pleasant aroma. Fruits are up to 7 mm in diameter, usually round, shiny, juicy, fragrant, edible. The elder blossoms in May - June, the fruits ripen in August - September.
Agrotechnology
Elderberry is one of the most unpretentious plants, but it grows better and develops on fertile and moderately moist soils. Growing fast. Shade-tolerant, heat-loving - to the north of the forest-steppe zone does not occur in nature, but it tolerates dry air well and is almost not affected by diseases and pests (sometimes the tips of the shoots can be infested with aphids, less often with spider mites). It is easily propagated by seeds (they need to be sown immediately after harvest due to the rapid loss of germination), root suckers, layering and cuttings. You can plant an elderberry both in spring and in autumn.
Sorta
From the decorative black elderberry, varieties with an interesting crown shape are known: Pyramidalis (column-like), Pendula (weeping), Nana (in the form of a ball). There are varieties with unusual leaves - golden (Aureo-variegata, Aurea) or very openwork (Laciniata). Known varieties of black elderberry, created in the US and in Western Europe: Hidden Springs, Johns, Kent, Nova, Scotia, Victoria, York and others.
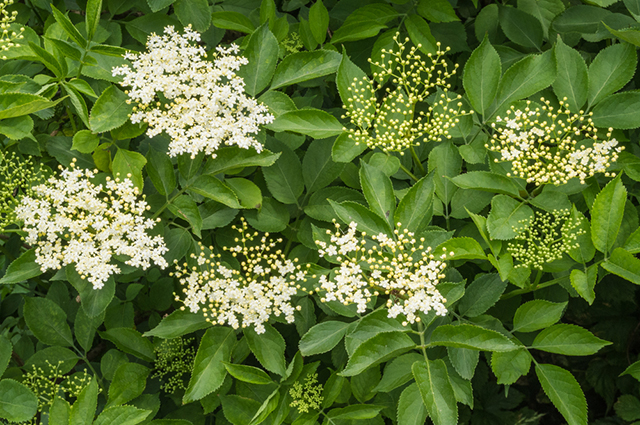

Photo: Shutterstock.com / Ralf Neumann
Black elderberry (Sambucus nigra) as a fruit crop was introduced to the culture 100 years ago in the USA, and then in Western Europe, especially in Germany, Austria, Holland. In Russia, it is known more as an ornamental and medicinal plant.
The brightest
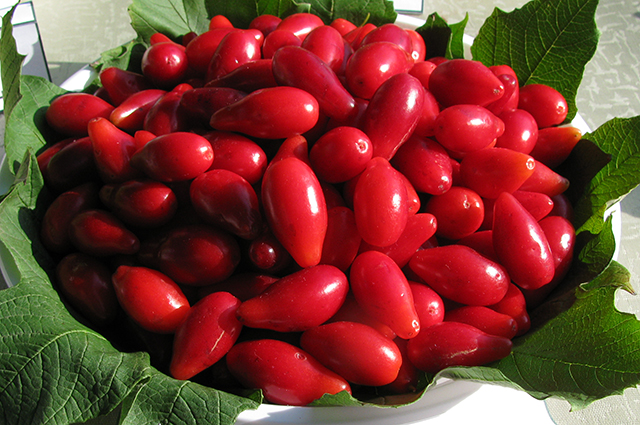
The bright fruits of dogwood are tasty and healthy. Biologically active components included in their composition, normalize blood pressure, prevent sclerosis. Cornel is useful as a tonic and anti-inflammatory agent, it is useful for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. AT traditional medicine It is used for metabolic disorders, joint pain, skin diseases, anemia. Cornel fruits are used raw, for making jam, stewed fruit, marmalade, juices and sauces. how ornamental plant Cornel is particularly effective during flowering and fruiting.

Dogwood. Photo: Dmitry Bryksin
What does it look like?
Common cornel, or male lard, is a shrub or small tree up to 5 m high. It blooms early, before leafing (in April). The flowers are small, yellow, collected in umbellate inflorescences. Fruits oval or pear-shaped, juicy, 1-3 cm long, with an oblong bone, ripen in August - September. They taste sweet-sour, slightly astringent. By the way, the color of the dogwood is not always red - there are forms with pink, yellow and black berries.
Agrotechnology
Cornel is a drought-resistant, shade-tolerant and fairly frost-resistant plant (many samples grow normally in the Central Region). To soils undemanding, but reaches the best development on fertile clay, moderately moist, containing lime to the earth. Forms a powerful, but not deeply rooted root system.
On household plot it is necessary to plant at least two cornel plants of different varieties - only in this case, you can count on a harvest. Cornel is extremely sensitive to fertilization. Therefore, when planting, neither manure, nor humus, nor mineral fertilizers are brought into the pit. In this culture loves calcium, therefore, add lime. The pits are made small, no deeper than two spade bayonets, and the roots are filled with fertile earth. Cornels do not need special pruning, while leaving only broken, interlacing and thickening branches are removed. For pests and diseases, the plant is quite stable. The soil under the cornel can not be deeply loosened - it is processed no deeper than 2-5 cm.
In country conditions, dogwood is most rational to propagate with green cuttings or grafting.
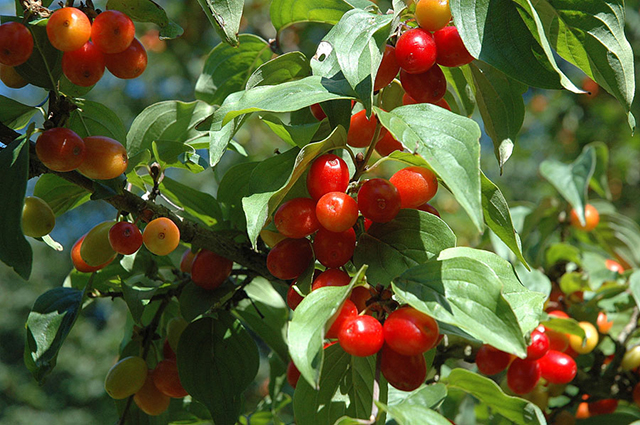

Photo: Dmitry Bryksin
Sorta
For the southern regions there are many fruit varieties of this crop. In Central Russia, the Bulgarian pear-shaped and Coral varieties feel well. Their fruits are large, tasty and numerous. Of the decorative forms, Aurea cornels are the most well-known - with yellow leaves, Macrocarpa - with large fruits, Flava - with yellow fruits, Pyramidalis - with a pyramidal crown, and many others.
The bright red fruits of the dogwood, tasty and healthy, are well known to the residents of the southern regions of our country, the Crimea and the Caucasus, Southern Europe and Asia Minor, where this remarkable plant grows, one of the most ancient, used by man for food. The ancient legend says that Romulus, the founder of Rome, outlined the boundaries of the future city with his spear, and then thrust it into the ground - and the pole of the spear took root and blossomed. So the first cornel tree appeared. In fact, the dogwood is much older - even in the Stone Age, primitive people appreciated its fruits and actively collected them. Interestingly, the correct, botanical, name of the plant is male (Cornus mas). This is the only species of the Dören genus that has edible fruits.
The most healing
Chinese lemongrass is widely used in ornamental horticulture for vertical gardening and decorating walls, gazebos and other structures, as well as a berry crop and a medicinal plant. Fruit juice is added to compotes, jelly and syrups. Dry ground fruits or lemongrass seeds are consumed with fatigue and stress, but only as prescribed by a doctor. A fragrant tea is brewed from the leaves and bark; it has a tonic effect that can easily replace natural coffee.
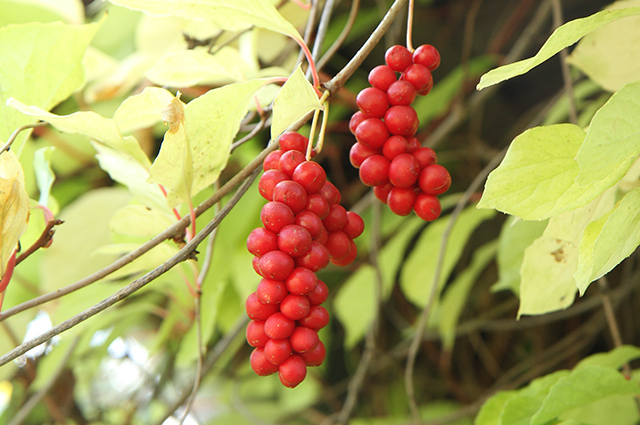

Lemongrass Photo: Elena Kozhina
What does it look like?
Lemongrass is a climbing deciduous vine. The plant is very powerful - it can climb to a height of 4-5 and even 10 m. In autumn, leaves turn ochristo yellow or yellowish orange. The flowers are white, waxy, up to 2 cm in diameter, fragrant, located in the axil of the leaf in 3-5 pieces. A single “brush”, sometimes up to 10 cm long, consisting of round red double seed berries, is obtained from a single flower. Pulp berries juicy, very sour, with the smell of lemon, edible, but not for everybody.
Agrotechnology
Lemongrass grows best on rich, moderately moist and well-drained soils, in partial shade and in places protected from the wind. 2-3-year-old seedlings are suitable for planting. An important feature of lemongrass - the need for support, on which it rises up. Without a support, the plants will produce a lot of root growth and creep along the ground, and it is impossible to speak of flowering and fruiting in such cases. Caring for lemongrass is reduced to the removal of old branches and shortening or pinching too long shoots to 10-12 buds, irrigation and mineral fertilization (spring and autumn) and organic (after flowering) fertilizers.
In country conditions it is easiest to propagate lemongrass root suckers.
Sorta
There are several selected varieties of Chinese magnolia. In the State Registry there are 4 varieties of lemongrass: Volgar, Debut, Myth, Firstborn.

This extraordinarily beautiful and useful vine has come to the gardens. middle band Russia from the forests of the Far East. Chinese Schizandra (Schizandra chinensis) - such is its botanical name - in its significance is in second place after the famous root of life - ginseng. Even in ancient oriental medicine, it was valued as a valuable medicinal plant, giving a person vivacity and prolonging youth. And lemongrass is also called the fruit of five tastes, because the flesh of the fruit is sour, the skin is sweet, when you chew the fruit, you feel a bitter and acrid taste, and the infusion of seeds is salty. Lemongrass plant is called because of the pleasant lemon flavor, which is fragrant with many of its parts - bark, leaves, flowers and fruits. The genus Lemongrass has 14 species, common in Japan and China. On the territory of our country only one of them grows - Chinese lemongrass.
Most vitamin
Actinidia kolomikta - a relative of a tropical plant, known to us from the fruits of kiwi, which are sold in stores. But if kiwi can grow only in conditions of tropics and subtropics, then actinidia kolomikta is a true northerner who withstands temperatures down to -40 ° C in winter. It is suitable for vertical gardening and at the same time serves as a berry plant.
What does it look like?
This plant is considered both decorative and at the same time berry, and its fruits are very tasty and healthy. Actinidia kolomikta (Actinidia kolomikta) - one of the 36 species of the genus. All actinidia are perennial tree lianas that can climb up to a height of 15 m. Stems and branches are thin, smooth, dark brown in color. The leaves are large, wrinkled, changing color: at the beginning of growth they are bronze, then green, before flowering (in open places) bright white color appears at the ends of the leaves, when flowering pink or crimson-red, and then they turn green again. In autumn, the leaves turn yellow. Flowers solitary, white, with a diameter of 1.5 cm, collected on 3-5, fragrant. Fruits are oval or cylindrical in shape, up to 3.5 cm long, green, unlike kiwi smooth, not hairy, fragrant, with a delicate sweet taste. Fruits ripen at the same time and fall off easily.
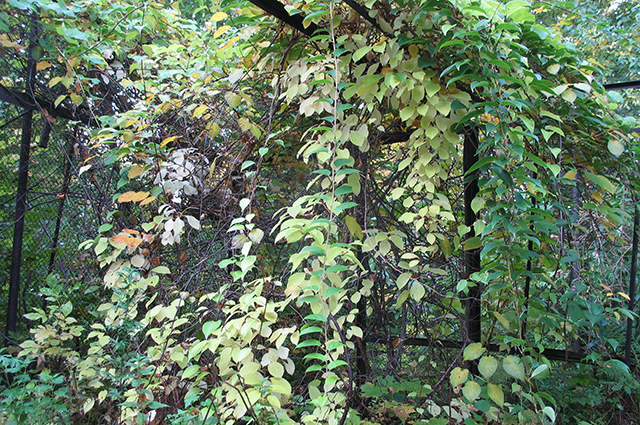

Actinidia. Photo: Elena Popleva
Agrotechnology
Actinidia Kolomikta - dioecious plant: it exists in the form of female and male copies. To get the fruit, you need to plant those and others: for 3-4 women's just one "gentleman". Actinidia kolomikta winter-hardy and shade-tolerant, almost not damaged by pests and diseases, prefers rich, moist, well-drained soil, suffers from soil and air drought, as well as from late spring frosts. It needs a solid vertical support. In favorable conditions, lives up to 100 years. Propagated by cuttings (green and lignified).
Actinidia kolomikta cultivated since the mid XIX century. On its basis, a lot of winter-hardy and high-yielding varietiesincluding domestic ones. Now the number of actinidia varieties zoned in Russia is approaching four dozen. Most of them are derived in the conditions of the Moscow region. The most famous varieties: the Queen of the garden, Gourmet, marmalade, ella and others.