Datura Indian - encyclopedia of medicinal plants - dictionaries and encyclopedias. Medicinal plant dope indian.
(harmless dope) -Datura innoxia Mill.
The nightshade family.
Grayish, velvety-pubescent, perennial (in the annual culture) herb plant, height 60-150 cm. The root is pied, thick, yellowish, with a short thickened root neck bearing a kidney. Stem erect, 3-4 cm in diameter at the base, hollow, forked-branched, greenish or reddish-purple, densely covered with soft hairs. The leaves are alternate, petiolate, upper pairwise approximated in pairs, because of which they appear opposite. Leaf blades are ovoid or oblong-ovate, pointed with a truncated or heart-shaped, unequal base, whole or shallow, grayish-green, pubescent on both sides, like petioles. Flowers are large, single, located in the ruins of the stem. Pedicels erect, curving after flowering. Calyx densely pubescent, long tubular, swollen, 9-10 cm long, usually with 5 teeth, less often with 2-3. The corolla is white, tubular-funnel-shaped, with a folded, five-pronged limb, 17–20 cm long and 6–8.5 cm in diameter. Stamens 5. A pestle with an upper ovary, a long filamentous column and a bilobed stigma. The fruit is a spherical, drooping, multi-seeded, grayish-green or brown capsule, 4-5 cm in diameter, with an overgrown, bent-out base of the calyx. The box below is four-necked, above - two-cemented, densely seated with thin needle-shaped thorns up to 1 cm long; when ripe, it improperly cracks or remains closed. Seeds are ocher-yellow or brownish-brown, kosopochkovidnye, dented in the middle, with a wavy roller on the back, 4-5 mm long and 3.5-4 mm wide.
Blossoms in July and October, fruits from August.
Within the species of Indian dope, 4 morphological forms are distinguished:
1) ordinary form (f. vulgaris) withscopolamine yield over 7 kg / ha;
2) small-fruited form (f. microcarpa) withscopolamine yield 5.75 kg / ha;
3) powerful form (f. robust a)with the release of scopolamine 6.28 kg / ha;
4) long-legged form (f. longipediculata)with the release of scopolamine 6.44 kg / ha.
The most valuable in practical terms is the ordinary form - Datura innoxia Mill vulgarus, which has non-opening boxes when ripe and has the highest yield of scopolamine.
Other types of dope:
1) the dope is snowy,differs from the Indian dope with smaller leaves and boxes, larger flowers. It grows in South America, Mexico, in the southwestern United States. The yield and content of scopolamine is inferior to the Indian indian;
2) the dope is snowy,has many varieties, differing in color and terry color of flowers. The most common violet and white flowering species. Differs late maturity. The yield of fruits is inferior to the Indian dope, but with a higher content of scopolamine;
3) tree dope -tree 1-3 m tall with very large drooping flowers. Homeland - Peruvian Andes. Due to the high decorativeness of flowers, it is cultivated in many tropical and subtropical countries. In Russia in open ground does not winter even in the area of humid subtropics of Transcaucasia. As a source of scopolamine practical interest is not.
Homeland Datura - Central and South America. As an invasive and weedy plant found in Central Asia and the Caucasus. Cultivated in the Krasnodar Territory, Crimea, Moldova. The plant is warm and light-loving, demanding on soil fertility. Sowing is carried out in spring with dry seeds, 70 cm between rows. The plant grows and blooms until autumn frosts. Frosts below 2-3 ° C are detrimental to seedlings and adult plants. From germination to ripening of the first fruits, 110-130 days pass. Due to the fact that the content of scopolamine sharply decreases as fruits ripen, they are harvested at the beginning of ripening (yellowing) of them on the branches of the first order. Harvested fruits are threshed or crushed and divided into 2 fractions: seeds and crushed boxes, which are then dried.
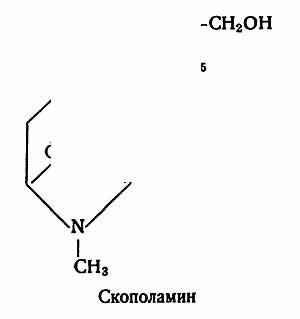
Are used unripe fruits (seeds and boxes separately from seeds) from which the alkaloid scopolamine is extracted.In all organsdatura contains alkaloids: leaves -0,23-0,39%, in stems -0.15-0.24 in roots -0.21-0.46, in colors -0.2-2.89, in fruits -0.76-0.83, in seeds -0.83%. The main one is scopolamine, the content of which varies: in leaves -0.005-0.16%, in stems -0.04-0.122, in roots -0.08 in colors -0.34 in fruits -0.38-0.41, in seeds -0.77%. In addition to scopolamine, hyoscyamine, nigoscyamine, tigloidin, meteloidin, atropine, tropin, pseudotropin, and others were isolated.
Leaves,also contain:
macronutrients (mg / g) - K - 52.7, Ca - 38.0, Mg - 9.9, Fe - 0.8;
microelements (µg / g) - Mn - 0.44, Cu - 1.57, Zn - 2.4, Co- 0.18, May 4.0, Cr- 0.2, Al- 0.48, Ba - 17.77, V - 0.26, Se - 1.33, Ni - 0.45, Sr - 2.17, Cd - 22.4, Pb - 0.16, Li - 240.0, B - 91 , 6; concentrates Fe, Cu, Zn, Mo, Sr, Ba, Cd, Li, especially Zn, Mo, Li, Cd, Sr.
- - one-year plant. up to 1 m high. The stalk is thick, developed; leaves are large, ovate. Flowers are large, white; fruit-boxes, spit-studded, D. has a nasty smell, and therefore livestock does not touch him ...
Agricultural dictionary reference
- - English thorn apple, escape it. Weißer Stechapfel french ...
Phytopathological dictionary reference
- - a genus of grasses, less often shrubs or trees. slopes. St. 10 species, prev. in the tropics and subtropics. D. ordinary, common in temperate and warm belts of Eurasia, - poisonous drugs. district ...
Natural science. encyclopedic Dictionary
- - genus of plants of this. slopes. Grasses, less often shrubs and trees. The flowers are large, long. sometimes sv. 25 cm, with a tube-funnel-shaped corolla. More than 10 species, in the tropics and subtropics ...
Biological Encyclopedic Dictionary
- - Datura stramonium -. Herbaceous plant of the family Solanaceae, contains various alkaloids
; D. - a classic genetic object used to analyze the manifestation of polysomy ... Molecular biology and genetics. Explanatory dictionary
- - genus of plants from the family of nightshade; large grasses, rarely treelike plants. Flowers large, corolla funnel-shaped. The ovary is 2 nesting, and the nests are often still divided into 2 semi-nests each ...
Encyclopedic dictionary of Brockhaus and Euphron
- - genus of plants of the bouillon family. Grass, rarely shrubs and trees. The flowers are large, 5-membered; corolla tubular-funnel-shaped. More than 10 species, mainly in tropical and subtropical areas ...
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- - a genus of grasses, less often shrubs or trees of the nightshade family. St. 10 species, mainly in the tropics and subtropics ...
Datura Indian(harmless dope) -Datura innoxia Mill.
The nightshade family.
Grayish, velvety-pubescent, perennial (annual crop) herb 60–150 cm tall. Taproot, thick, yellowish, with a short thickened root neck bearing a kidney. Stem erect, 3-4 cm in diameter at the base, hollow, forked-branched, greenish or reddish-purple, densely covered with soft hairs. The leaves are alternate, petiolate, upper pairwise approximated in pairs, because of which they appear opposite. Leaf blades are ovoid or oblong-ovate, pointed with a truncated or heart-shaped, unequal base, whole or shallow, grayish-green, pubescent on both sides, like petioles. Flowers are large, single, located in the ruins of the stem. Pedicels erect, curving after flowering. Calyx densely pubescent, long tubular, swollen, 9-10 cm long, usually with 5 teeth, less often with 2-3. The corolla is white, tubular-funnel-shaped, with a folded, five-pronged limb, 17–20 cm long and 6–8.5 cm in diameter. Stamens 5. A pestle with an upper ovary, a long filamentous column and a bilobed stigma. The fruit is a spherical, drooping, multi-seeded, grayish-green or brown capsule, 4-5 cm in diameter, with an overgrown, bent-out base of the calyx. The box below is four-necked, above - two-cemented, densely seated with thin needle-shaped thorns up to 1 cm long; when ripe, it improperly cracks or remains closed. Seeds are ocher-yellow or brownish-brown, kosopochkovidnye, dented in the middle, with a wavy roller on the back, 4-5 mm long and 3.5-4 mm wide.
Blossoms in July and October, fruits from August.
Within the species of Indian dope, 4 morphological forms are distinguished:
1) ordinary form (f. vulgaris) withscopolamine yield over 7 kg / ha;
2) small-fruited form (f. microcarpa) withscopolamine yield 5.75 kg / ha;
3) powerful form (f. robust a)with the release of scopolamine 6.28 kg / ha;
4) long-legged form (f. longipediculata)with the release of scopolamine 6.44 kg / ha.
The most valuable in practical terms is the ordinary form - Datura innoxia Mill vulgarus, which has non-opening boxes when ripe and has the highest yield of scopolamine.
Other types of dope:
1) the dope is snowy,differs from the Indian dope with smaller leaves and boxes, larger flowers. It grows in South America, Mexico, in the southwestern United States. The yield and content of scopolamine is inferior to the Indian indian;
2) the dope is snowy,has many varieties, differing in color and terry color of flowers. The most common violet and white flowering species. Differs late maturity. The yield of fruits is inferior to the Indian dope, but with a higher content of scopolamine;
3) tree dope -tree 1-3 m tall with very large drooping flowers. Homeland - Peruvian Andes. Due to the high decorativeness of flowers, it is cultivated in many tropical and subtropical countries. In Russia, in the open ground does not winter even in the area of the humid subtropics of Transcaucasia. As a source of scopolamine practical interest is not.
Homeland Datura - Central and South America. As an invasive and weedy plant found in Central Asia and the Caucasus. Cultivated in the Krasnodar Territory, Crimea, Moldova. The plant is warm and light-loving, demanding on soil fertility. Sowing is carried out in spring with dry seeds, 70 cm between rows. The plant grows and blooms until autumn frosts. Frosts below 2-3 ° C are detrimental to seedlings and adult plants. From germination to ripening of the first fruits, 110-130 days pass. Due to the fact that the content of scopolamine sharply decreases as fruits ripen, they are harvested at the beginning of ripening (yellowing) of them on the branches of the first order. Harvested fruits are threshed or crushed and divided into 2 fractions: seeds and crushed boxes, which are then dried.
Are used unripe fruits (seeds and boxes separately from seeds) from which the alkaloid scopolamine is extracted.In all organsdatura contains alkaloids: leaves -0,23-0,39%, in stems -0.15-0.24 in roots -0.21-0.46, in colors -0.2-2.89, in fruits -0.76-0.83, in seeds -0.83%. The main one is scopolamine, the content of which varies: in leaves -0.005-0.16%, in stems -0.04-0.122, in roots -0.08 in colors -0.34 in fruits -0.38-0.41, in seeds -0.77%. In addition to scopolamine, hyoscyamine, nigoscyamine, tigloidin, meteloidin, atropine, tropin, pseudotropin, and others were isolated.
Leaves,also contain:
macronutrients (mg / g) - K - 52.7, Ca - 38.0, Mg - 9.9, Fe - 0.8;
microelements (µg / g) - Mn - 0.44, Cu - 1.57, Zn - 2.4, Co- 0.18, May 4.0, Cr- 0.2, Al- 0.48, Ba - 17.77, V - 0.26, Se - 1.33, Ni - 0.45, Sr - 2.17, Cd - 22.4, Pb - 0.16, Li - 240.0, B - 91 , 6; concentrates Fe, Cu, Zn, Mo, Sr, Ba, Cd, Li, especially Zn, Mo, Li, Cd, Sr.
Datura causes a temporary clouding of consciousness and deep sleep, and therefore has always been used by not very honest people. Indian prostitutes used a dope to their clients for a long time did not regain consciousness. Indian women gave their husbands a dope and after that, directly in front of them, they made love to Europeans, while husbands with a clouded mind and open eyes did not understand anything. The impact of the dope is so great that the Indians from Colombia gave dope to the slaves and wives of the leaders before they were burned alive on the fire along with the dead.
Description.
Grayish - fluffy annual medicinal herb 0.6 - 1.5 m in height. Belonged to the family Solanaceae. The stem of the plant is branched, with ovate, long-petaled, alternate leaves grayish-green. Datura flowers are large, solitary, up to 20 cm long, white in color, located in the ruins of the stem. The fruit of the dope is a box that looks like a ball, brown or grayish-green in color, about 4 - 5 cm long, which is densely studded with spikes. Seeds are greyish, kosopochkovidnye, ripen from August. Medicinal plant dope Indian blooms from July to October.
Spread.
The homeland of the medicinal plant is South and Central America. Industrial advisable on chernozem structural soils with a sufficient content of humus.
Stocking
Preparations from a medicinal plant Datura Indian cooked from its leaves. To do this, they stock up from the beginning of flowering until late autumn. When collecting use gloves. The collected leaves are immediately dried in the shade or in ventilated rooms at 45 ° C. Dried leaves are stored - 24 months in an airtight container.
Chemical composition.
All parts of the Indian dope contain alkaloids. The plant contains nigoscyamine, hyoscyamine, meteloidin, tigloidin, tropin, atropine and pseudotropin.
Pharmacological properties.
Scopolamine has a sedative and sedative effect. It removes cramps and tremor caused by arecoline. Scopolamine reduces the secretion of sweat, salivary and bronchial glands, relaxes the muscles of the bronchi and intestines and speeds up heart contractions.
Application.
Drugs of Indian medicinal plants are used in Parkinson's disease, in diseases with muscular hyperkinesis, as a means that can soothe the excitement of a maniacal nature, as an antiemetic during their stay at sea on a ship. Dry leaves of Datura Native American smoke with mental illness, rheumatism and shortness of breath.
Treatment of medicinal plants dope Indian.
Decoction.
250 ml of boiling water pour 2 tbsp. l leaves of Indian dope, then put in a water bath for 5 minutes, remove the container and inhale the vapor for 20 minutes through the nose.
Contraindications.
Indian dope is poisonous, so you can use it after consulting a doctor.
3. The leading group of biologically active substances
4. Botanical characteristics
Datura native - a perennial herb with a forked red-violet thick stem. The leaves are alternate, broadly ovate, shallowly grooved, densely pubescent, on long petioles, with a strong stupefying smell. Flowers solitary, regular, five-membered, with double perianth, calyx tubular, green, corolla tubular-funnel-shaped, white. The fruit is a drooping, almost spherical box, densely seated with soft thorns, with remains of a calyx at the base and numerous seeds of a bright yellow color.
Within the species Datura innoxia Mill, four morphological forms were identified:
A) ordinary form (f. Vulgaris) - sprawling plants with an obtuse angle of branching of the stem, expressed only for the branches of the first and second order, with large, solid or shallowly notched leaves and oblate-spherical, when ripe, drying out, but not opening the box. The yield of marketable products is 18 kg / ha (in the air-dry condition); Scopolamine yield over 7 kg / ha;
B) small-fruited form (f. Microcarpa) - has smaller, strongly notched leaves and smaller, ovate, with ripening remaining succulent, opening boxes. The harvest of marketable products is over 14 centners per hectare; scopolamine yield - 5.75 kg / ha;
C) a powerful form (f. Robusta) is a large plant with an acute angle of branching of the stem and a large, spherical, fleshy, drop-down box when ripe. The harvest of marketable products is 17.73 centners per hectare; scopolamine yield - 6.28 kg / ha;
D) the long-legged form (f. Longipedunculata) is similar to the previous one, but has long (up to 6 cm) sharply curved peduncles. Harvest of marketable products 18.56 c / ha; scopolamine yield - 6.44 kg / ha.
The most valuable in practical terms is the ordinary form-Datura innoxia Mill. f. vulgaris, which has fruits that do not open when ripening and the highest yield of scopolamine.
Other species. Datura meteloid (Datura meteloides DC.). In systematic terms, very close to the Indian dope. Differs from the latter in smaller ones, with a wedge-shaped base, leaves, larger, with a blue limb, flowers and more small boxes, seated with sharp, short spikes. It is found in the northern regions of South America, in Mexico and in the southwestern United States. The yield of fruit and the content of scopolamine is inferior to the Indian dope.
Datura snowstorm (Datura metel L.) is a perennial herb of Indian origin. Grows in tropical and subtropical areas of Asia and America. There are numerous varieties, differing mainly in the color and terry of flowers. The most common of them: violet, terry (var.fastuosa = D. fastuosa L.) and white flowered non-terry (var. Metel D. alba Nees) varieties. In our climate, this species is disadvantageously different from the Indian dope by its late maturity. The yield of fruit is significantly inferior, and the content of scopolamine is slightly higher than the Indian dope.
Tree Datura (Datura arborea L.) is a tree 1-3 m tall, with very large drooping flowers. Homeland - Peruvian Andes. Because of the high decorativeness of its flowers is cultivated in many tropical and subtropical countries, as well as in greenhouses. In the CIS, it does not winter in the open ground even in the region of humid subtropics of the Transcaucasus, therefore, it is of no practical interest as a source of scopolamine.
Cultivation techniques. The plant is demanding to heat, light and high soil fertility. Cultivated as an annual. The best predecessors - black steam or winter, sown on the fertilized pair; a good predecessor should also be considered tilled (except for plants of the family of nightshade). Very responsive to manure and mineral fertilizers. Under the autumn plowing they bring on 1 hectare 20-30 centners of humus in a mixture with 2 centners of ammonium sulfate and 3 centners of superphosphate. Sowing is done in spring, dry seeds, ordinary or square-nested method. Seeds close up in depth
5. Distribution
Homeland Datura Indian - Mexico. In the CIS, it is cultivated as an annual crop in the Krasnodar Territory (Russia), Crimea (Ukraine), Moldova and the Chimkent Region (Kazakhstan).
6. Habitat
Tropical, subtropical and moderately warm countries of both hemispheres.
7. Procurement
Cleaning boxes made by hand. Gather juicy immature fruits in two or more terms as they develop.
8. Security measures
No need, the plant is cultivated.
9. Drying
The boxes are cut on straw cutters and dried either in the sun or in dryers at a temperature of 40-50 ° C. After drying, the seeds are separated from the bolls on the screens, since the technological processes of extracting alkaloids from them are different (the seeds require preliminary degreasing).
10. Raw materials
Semina Daturae innoxiae - seeds of Datura Indian,
Fructus Daturae innoxiae - fruits of Datura Indian.
11. Definition
Collected during the ripening period of the lower bolls and dried seeds collected in the fruiting phase, dried and ground fruits of the cultivated perennial (in the annual crop) Indian Datura (Datura innoxia Mill.) Plants from this. solanaceae (Solanaceae).
12. Standardization
The quality of raw fruit is regulated by FS 42-612-72.
The quality of raw materials of the seeds of the Indian dope is regulated by FS 42-1005-90.
13. External signs of raw materials
FRUIT.
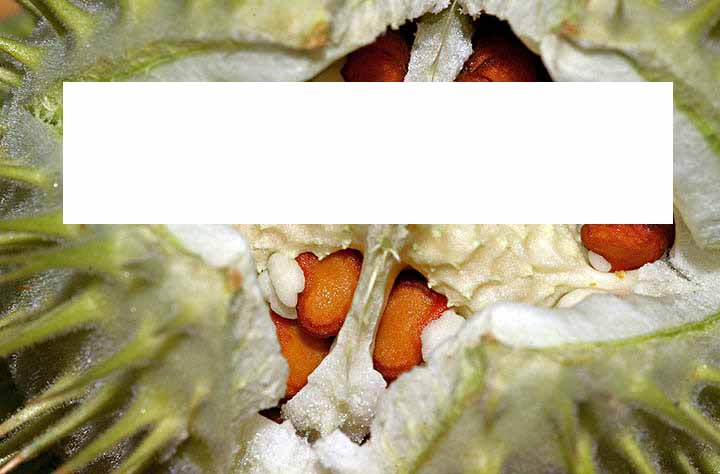
The raw material consists of a mixture of pieces of boxes of various shapes and sizes, seated with thick, sharp, thin, strongly pubescent spikes up to 1 cm long, parts of seedlings with papillae. The smell is weak, peculiar. The taste is not determined (!).
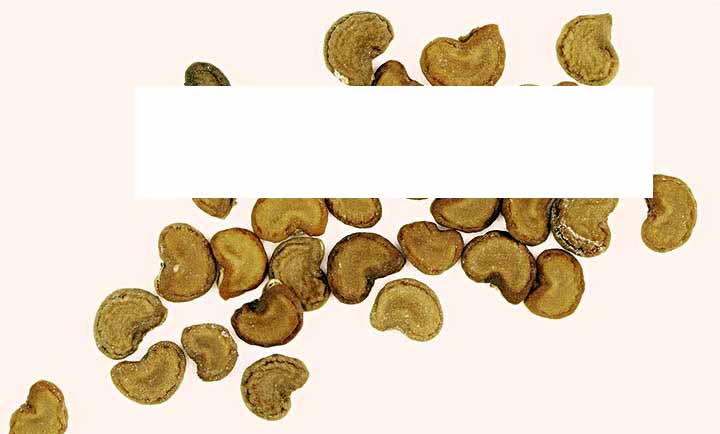
SEEDS.
Seeds 4–5 mm long, 3–4 mm wide, kidney-shaped, flattened, with a dimple on the ventral side and a tuberous cushion on the dorsal side. The surface of the seeds is finely cambered. Color from grayish-brown to yellowish-brown, matte. The smell is weak, peculiar. Taste does not define (!).

14. Qualitative reactions
Common methods for the detection of alkaloids in herbal drugs:
When conducting qualitative reactions, alkaloids are extracted from the raw materials usually
With the filtrate, qualitative reactions with general alkaloid reagents are carried out. These reactions make it possible to establish the presence of alkaloids even with their minor content. They are based on the fact that alkaloids, when interacting with reagents, form
All these reactions are not very specific and allow only tentatively to draw conclusions about the presence of alkaloids.
Group and specific reactions are carried out if it is necessary to establish the presence of a certain
Recently, for the discovery and study of alkaloids are used
A common component of solvent systems for TLC is a mixture of chloroform with lower alcohols, for example.
On the chromatograms alkaloids are detected by fluorescence in UV light and after treatment with a reagent.
15. Microscopy
FRUIT.
The epidermal cells of the boxes are polygonal straight-walled with numerous.
SEEDS.
In a cross section through the central part of the seed visible

A. Mature fruits, x 0.5; B: X 38; C: X 60; D: x 96.; E - Cross-section of seeds x96; F - Details of the internal epidermis with developed vascular components (shown by arrows); x 240
16. Chemical composition
All parts of the plant contain tropane alkaloids - scopolamine and hyoscyamine. The highest content of alkaloids is noted in fruits and seeds. The content of scopolamine in immature boxes is 0.55%, in seeds - 0.31%. Raw material concentrates Fe, Сu, Zn, Mo, Se, Sr, Ba, Cd, Li.
17. Numerical indicators
FRUIT.
The content of scopolamine, determined by the gravimetric method, is not less than 0.2%; humidity not more than 14%; total ash not more than 25%; organic impurity not more than 1%, mineral - not more than 2%.
SEEDS.
The content of scopolamine base, determined by the gravimetric method, is not less than 0.2%; humidity not more than 12%; total ash not more than 5%; organic impurity not more than 1.5%, mineral - not more than 1%.
18. Quantitative determination
General methods for the quantitative determination of alkaloids in herbal drugs:
The whole process of quantitative determination of alkaloids in plant materials can be divided into three main stages:
Extraction of alkaloids and their purification are based on the fact that almost all alkaloid bases
Extraction of alkaloids from plants can be carried out in the form of salts and in the form of bases. Most commonly used methods for the extraction of alkaloids from raw materials are
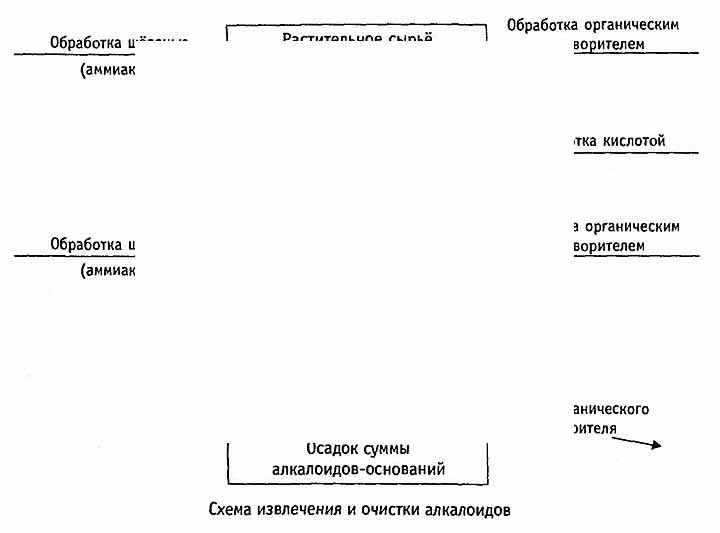
Quantitative determination of unknown alkaloids carried out by the gravimetric method. If the alkaloids are known, titrimetric methods (direct or reverse titration), photocolorimetric, nephelometric, densitometric, spectrophotometric, etc. can be used.
Practically for each type of medicinal plant material containing alkaloids, individual methods for the quantitative determination of alkaloids have been developed, described in the relevant regulatory documents.
Methods for the quantitative determination of alkaloids in the LES of Datura Indian:
The analytical sample of the raw material is ground to a particle size passing through a sieve with 1 mm diameter holes. About 10 g of crushed raw materials are placed in a 250 ml flask, 150 ml of ether, 7 ml of ammonia solution are poured in and the mixture is stirred for
Alkaloids are maximally extracted from ether extraction with 1% hydrochloric acid solution in portions of
Acid extraction is made alkaline with ammonia solution until alkaline via phenolphthalein, and alkaloids are extracted successively with 20, 15, 10 ml of chloroform, stirring for 3 minutes. Chloroform extraction filter in the flask for distillation capacity
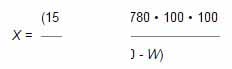
where 0,005780 - the number of alkaloids in terms of hyoscyamine, corresponding to 1 ml of hydrochloric acid solution (0.02 mol / l), in grams;
V is the volume of caustic soda solution (0.02 mol / l) consumed for titration, in milliliters;
m is the mass of raw material corresponding to the measured volume of ether extraction, in grams;
W is the mass loss during the drying of raw materials in percent.
19. Pharmacological properties
20. Packaging, Storage, Shelf Life.
Fruits and seeds are stored according to the list B. The shelf life of the fruit is 1 year, the seeds are 3 years.
21. Drugs and use
Medicines. Drug "Aeron"
Application. Fruits and seeds are used to produce alkaloid
Datura innoxia Mill.
Description of the plant. Datura is an Indian-large perennial (annual crop) herbaceous plant of the family Solanaceae, reaching a height of 60-150 cm. The stem is hollow, fork-branched, greenish or reddish-purple, densely covered with soft hairs. Leaves alternate, petiolate; leaf plates ovate or oblong-ovate, grayish-green, pubescent on both sides. The flowers are large, solitary, light purple or white. Fruit-spherical, grayish-green or brown box with thin needle-shaped spines.
Blossoms in July and October, fruits from August.
Habitat. Spread. Homeland Datura Native American-Central and South America. In our country it is very rare to be found as a wild plant in Central Asia and the Caucasus. Datura Indian heat-loving, medium dry-resistant and light-loving plant. For a friendly emergence of shoots requires a combination of relatively high temperature and sufficient soil moisture.
Unripe fruits are used as raw materials for the production of scopolamine and atropine.
The main cultivation area of Indian-South Datura is Kazakhstan. The most favorable for its cultivation are fertile, well-cultivated soils with a high content of humus.
Procurement and quality of raw materials. The fruits of Indian dope are harvested immature in August. The younger the fruit, the more they contain scopolamine. Selective harvesting 2-3 times per summer as the fruit grows increases the yield. All plant organs are poisonous, so when working with dope you must take precautions.
Immediately after harvest, fresh fruits are cut on a straw cutter and sorted on sieves with 5-6 mm holes for seeds and parts of bolls devoid of seeds. Both fractions are dried separately in dryers at 40-50 ° C, na sun under canopies. Seeds are cleaned on sorting and packaged in bags; crushed boxes are pressed into bales.
The seeds have a color from gray-brown to ocher-yellow, the content of scopolamine must be at least 0.2%. Another type of raw material is pieces of crushed capsules in the mass of brownish-green, the content of scopolamine is not less than 0.3%. Shelf life of raw materials 1 year.
Chemical composition. In all the organs of the Indian dope contain alkaloids: in leaves 0,23-0,39; stems 0.15-0.24%; the roots of 0.21-0.46%; flowers 0.20-2.89%; fruits 0.76-0.83%, in the seeds of 0.83%. The main alkaloid is scopolamine. In addition to scopolamine, hyoscyamine, atropine, tropin, pseudotropin, tigloidin, matheloidin, tigloyl-meteloidin, ditigloyl dioxitropane, tigloyl-oxytropane, norigioscyamine, kusggrin, nicotine were isolated. The content of scopolamine in the fruits of the Indian dope depends on the vegetation phase and the degree of seed ripening.
Use in medicine. Datura Indian used in combination with leaves and henbane bellow in the form of anti-asthma cigarettes. Scopolamine and hyoscyamine are included in the preparation aeron, which is used for the prevention and treatment of sea and air sickness, as well as for the prevention and cessation of attacks of Meniere's disease. Scopolamine hydrobromide is prescribed to treat parkinsonism and muscle hyperkinesis; in psychiatry, it is used as a sedative for manic states.
Contraindications to the use of scopolamine and aeron are the same as in the appointment of atropine. One should take into account individual sensitivity to drugs and avoid overdosing them due to the possibility of strong arousal, hallucinations, thirst, and other side effects.