Features of the development phases of fruits and vegetables. Accelerated ripening of vegetables. How to accelerate the ripening of white cabbage
Fruits and vegetables, as well as any biological objects, are characterized by periods of growth and development of ripening or ripening, dormancy, germination, aging and withering away.
There is a difference in the periods of vital activity of vegetables and fruits.
Vegetables are characterized by growth, ripening, post-harvest ripening, deep rest, emergence from rest, germination, fruits - growth, ripening, ripening and over-ripening.
In the case of potatoes, as with other plants, the harvest time depends on the variety. Early varieties can be collected in June, but late in the fall. Ripe potatoes can be found on the above ground. According to the old rules of horticulture, potatoes ripen when three weeks have passed since the death of above-ground shoots.
Now you can dig up the vegetables with a potato scoop or a regular fork. Work will be much easier if you pre-wash the soil with a hoe. After successful harvesting, potatoes are stored in dark and cool rooms. Although the vegetables are usually ground, do not wash them before putting them in the drawers, but wipe them gently.
Growth. From the moment of fertilization of the ovary to the removal of vegetables and fruits, their mass and volume continuously increase. In the early stages of growth occurs due to the growth of the ovary, and then due to the development of the endosperm.
If we consider the example of apples, then within the first ten days the ovary grows almost 10 times and in 2-3 weeks after the petals fall, the fruit reaches the size
Proper collection of other fruits and vegetables.
If you think that the above rules are too vague and uncertain, you can do a test: take the potatoes that you dug and beat. If the skin does not fall, it means that the vegetable is ripe, and you can dig the rest. If vegetables grow on the ground, it is easier to know whether you can start cleaning or not. In the case of tomatoes, color is a clear indicator of whether a vegetable is ripening. Tomatoes often have fruit when the outdoor temperature is already lower. In this situation, you can pick green tomatoes - they do not ripen on the trees, but in the warmest room, as far as possible.
walnut. In the following months, the size of the cells increases, the volume increases by 2-3 times, and then growth slows down and significant qualitative changes occur in the tissues that distinguish the mature fruit from the immature, i.e. ripening is in progress.
Maturation. When ripe, the mass and volume of fruits and vegetables increases, albeit at a more moderate pace than during the period of growth.
Many varieties of vegetables, such as cucumbers, kohlrabi and zucchini, are best suited when they are young. You do not need to break the whole salad if you only need a few leaves. Cut them only with scissors and enjoy their freshness. The same applies to broccoli: if the roses are cut off under the roots, new, smaller ones will grow in this place. For other species and varieties it is difficult to give general rules for appropriate harvest time. This can be useful, however, according to the following principle: unlike fruits, vegetables do not improve in the morning.
Many varieties, such as lettuce or spinach, accumulate nitrates, which can be harmful to humans. Light breaks down nitrogen, which means that picking up these vegetables can begin during the day. If you want to collect fruits and vegetables correctly, check the individual requirements of each variety. Right time Harvesting also depends on the weather in the last weeks or months before harvest. You will enjoy long collections if you collect them in dry weather, because moisture favors the growth of mold and mildew.
There are processes of synthesis aimed at the formation of spare nutrients.
When ripe, the starch hydrolysis occurs, which leads to the accumulation of sugars and taste improvement, the hydrolysis of protopectin - the consistency becomes softer, the coloring, aromatic substances accumulate, consumer properties improve, the hardness and tartness inherent in immature fruits and vegetables disappear.
If you carefully pick fruits and vegetables, you will enjoy a bountiful harvest. In the edible parts of the vegetables, even after the harvest process occurs, therefore the provision of appropriate storage conditions in this case is very important. Storage temperature affects the intensity of respiration, transpiration, chemical transformation and activity of rotting microorganisms. However, onions, garlic and leeks can be stored at a constant negative temperature.
Thawing should be gradual so as not to damage the tissue. The intensity of transpiration affects the intensity of moisture. The easiest way to increase humidity is to pour water on a concrete floor or in the ventilation ducts. It is also possible to insert boxes or cover whole stacks with polyethylene.
Depending on the ability to ripen during storage, fruits and vegetables are divided into ripening and under ripening.
To ripening include: apples and pears of winter and autumn varieties, quince, mountain ash, some varieties of plums, cranberries, lingonberries, black currants, citrus fruits, bananas, pineapples, persimmons, pumpkins, melons, tomatoes, cucumbers, peas, beans, corn, unripened include figs, pomegranates, eggplants.
Storing vegetables in a controlled atmosphere brings the following benefits. Reduces the intensity of respiration and the rate of biochemical changes, inhibits maturation and aging, reduces sensitivity to damage to cold and ethylene, reduces the incidence of diseases.
Among the dangers caused by inadequate selection of the gas composition of the atmosphere are listed. Ethylene accelerates the processes of respiration and aging, reducing the shelf life of vegetables. The main source of this gas in the storage is apples and pears. It is also produced by rotting vegetables and while using some storage facilities. It may enter refrigeration chambers, so do not store fruits and vegetables in the same chamber or even in the chambers where you previously stored these products.
Maturation is a continuation of the same processes as during maturation, but in this case, the synthesis of substances slows down, and hydrolytic processes predominate: hydrolysis of starch, pectin substances.
When ripening, consumer properties are improved, a more attractive color appears (tomatoes from brown become red), flavor, texture, with the exception of cucumbers, zucchini, legumes, when ripe, the texture becomes coarse, voids appear, taste and smell deteriorate.
During storage it is extremely important to ensure proper hygienic conditions. At the end of each storage period, warehouses should be thoroughly cleaned and ventilated. A good method of disinfecting rooms is chalking of walls and ceilings and burning sulfur. Harvested vegetables should be placed at a different location each year. If this is not possible, the area should be disinfected by lime.
Cabbage vegetables, with the exception of cabbage, are medium or long-lasting or intermittent species, characterized by high respiration and rapid decomposition of chlorophyll. It is important to correctly determine the cumulative maturity. The harvest should be carried out when the vegetables are dry, but not dried. Vegetables harvested during heavy rains are characterized by lower storage values and are often infected with pathogens.
During maturation, dye synthesis occurs, chlorophyll is destroyed. Phenolic compounds, phytoncides, proteins, wax, ethylene are formed from the decomposition products of carbohydrates, organic acids.
The ripening of fruits and vegetables can be accelerated by ethylene. A small amount of ethylene (1: 1,000,000) is sufficient for this.
For vegetables, there is a dormant period.
Delaying nitrogen fertilizer or using too much of this ingredient leads to delayed ripening and reduced resistance to diseases and pests. In turn, magnesium deficiency, especially in heavier soils, causes chlorine-tissue between the main nerves, while too little potassium causes inhibition of plant growth. Therefore, it is important to follow the principles of rational fertilization and avoid over-spraying.
Most often, this disease manifests itself immediately before harvest and during storage. The low temperature in the storage chambers does not prevent the decay of infected tissues. Bacterial wet rot can occur at all stages of brass development. Only unprocessed vegetables should be used for storage and be sufficiently ripened. There are currently no chemicals in Poland to protect themselves from this infection.
The resting period is the physiological state of vegetables in which the vital processes do not stop, but slow down and there is no visible germination.
The resting state of vegetables is divided:
♦ in deep rest - even under favorable conditions, germination does not come;
♦ forced rest - educational tissues can germinate, but this does not happen due to the lack of favorable conditions.
Rotten grapes are especially dangerous for storing vegetables. There is the presence of brown spots that quickly overlap with a white rash, and over time there is black sclerosis. Vegetables quickly decompose. Symptoms of black rot brass on vegetables that made the head or roses are not visible to the naked eye. Only black discoloration of the fabric is visible in the section, which during storage can have very negative consequences.
Downy mildew from brassica during storage is transferred from the affected leaves to healthy, cauliflower and broccoli darkens the interior of roses and nests. The pathogen responsible for dry rot of brassica in infected plants also grows in storage conditions, and the symptoms of the disease are dark brown spots with black conidia at the base of the leaf at the back of the leaf.
One of the important goals of storage is the lengthening of the rest period; this requires the use of low temperatures, as well as the use of substances (phytohormones), treatment with y-rays that suppress germination.
The rest period depends on the species, variety, growing conditions, storage.
Potato tubers are the longest dormant period.
Density of pepper is manifested during long-term storage at inadequate temperature, which is lower than recommended and accompanied by high temperatures during the growing season, with nutrient deficiencies. Internal cabbage heads are physiological diseases of cabbage heads and roses, the development of which is inhibited during storage, but if this occurs during the attachment of heads or roses, the symptoms are visible only after the organs are cut off.
To grow vegetables from brass, note that. Plant tissue cannot be damaged, as it reduces their shelf life, it is important to follow the rules of proper rotation, weed destruction, removal of residues of remaining infected plants, preventive health, preventive storage diseases - important hygiene, appropriate storage conditions for them. These functions, combined with the proper farming practices and maintaining a healthy plantation, guarantee long-term returns.
A short deep rest is characterized by cabbage, root vegetables. Deep peace is absent in onions, garlic. Cold rainy summer lengthens the rest period, dry - shortens.
Aging. After the ripening process, the fruits begin to age, in which individual cells first die, and then their number increases.
In the case of wet rot, they appear after harvest and during storage. The pathogen develops inside the plant, so the symptoms appear only after some time, which can cause large losses during storage. Some of them are still visible on the field, among others. humus rot.
During storage, infected vegetables are susceptible to secondary infections. Fusarium root crops are visible immediately after harvest and are exposed to lenticular spots. For longer-lived stems, spots grow, forming large subcutaneous areas. In the case of root rot, vegetables show distinct resistance to mycelium growth. However, after a few months, its symptoms become more apparent.
Dying off is caused by gradual destruction of cellular structures, tissue maceration begins, the contents of vacuoles are mixed with cytoplasm.
All these processes lead to irreversible changes in tissues: the formation of dark-colored compounds, the appearance of a bitter taste.
Visible signs of aging and dying off of fruits and vegetables are manifested in the form of physiological diseases - plumpness, sunburn, wet burn.
A common onion disease is onion neck rot. Its symptoms are not visible during growth and harvest. Lamp storage is observed only during storage. Onion fussy decay is already visible during the growth phase, although in case of infection of older plants, symptoms can be observed only during storage.
Excess nitrogen in fertilization reduces storage. The potassium content also affects the quality of stored vegetables. In the case of onions, its deficiency contributes to the tops of the onions and the youngest leaves. Calcium limits the occurrence of memory disorders and strengthens the epidermis, and in combination with boron, it affects the effective synthesis of sugars and assimilates.
Aging and death of a living organism is an inevitable phenomenon caused by the gradual destruction of cellular structures and dysfunction.
Currently, up to 100 species of various crops are cultivated in home gardens. They are extremely diverse in their biological characteristics and economic affiliation, have different properties, and each of them requires compliance with certain conditions of planting, care, etc. But all cultures are usually grown for the purpose of obtaining a crop, and from this point of view are combined into several groups.
Prevention of diseases of the root canal and onions is of great importance: proper displacement, prevention of cultivation in monoculture, as well as in the case of onions, also on wet stands, care for high-quality seeds, removal of crop residues, prevention of mechanical damage to the roots and onions, correct distance between plants B field, right choice raw materials for storage, care for proper storage conditions, including proper hygiene of storage facilities and equipment, rational fertilization, plant protection from diseases and pests.
All classifications of vegetables, fruits and berries, including the one that is given in this book, are quite arbitrary and are offered solely for the convenience of their consideration.
Thus, vegetable crops in most classifications are divided into groups based on a combination of biological traits, characteristics of use in the economy and similarity of growing methods. Depending on this, there are 7 groups. vegetable crops.
Protecting fruits from storage diseases is as important as infections arising during the growing season. Among post-harvest diseases of fruit of fungal origin, the most dangerous and difficult to master are hidden, which appear only during storage. They are bitter rot, the first symptoms of aseptic spots appear only on the fruits of maturity, that is, after several months of storage. Spores do not infect other fruits, only those that were contaminated during the pre-harvest period.
Growing on the shoots of these trees. The most severe infections occur 1, 5-1 months before harvest. The development of bitter rot in the cold stimulates: too late fruit harvest, slow cooling of the fruit after harvest, low calcium content in fruits and too high storage temperature. The first dark brown decaying spots are usually found on a cup of apple or pear during storage. A characteristic feature of this disease is the appearance in the fetus of a nest with several or more rotting fetuses bound by mycelium.
To vegetables cabbage groups include white, red, Brussels sprouts, Savoy, cauliflower, kohlrabi, leafy and Peking cabbage. In our country, gardeners give undoubted preference to white cabbage, and red-colored and colored are also quite widespread in summer cottages; other species are less popular. Cabbage is valuable primarily because it has high yields, excellent nutritional and taste qualities, has good keeping quality and is not too demanding on the conditions of storage and transportation.



Vegetables of the cabbage group: a - white cabbage; b - cauliflower; in - kohlrabi; Mr. Brussels sprouts; d - Chinese cabbage
Fruit group Includes all vegetables of the family Solanaceae, except potatoes (tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, Physalis), pumpkin (cucumbers, zucchini, squash, pumpkin, melon, watermelon, lagenaria), legumes (beans, peas, beans), and also sugar. Practically on everyone household plot grow tomatoes and cucumbers - these vegetables are most common among all the crops in this group. It should be noted that sometimes in the agronomic literature such vegetables as pumpkin, melon and watermelon, stand out in a special group and belong to the melon crops.


Vegetables of the family of nightshade: a - tomato; b - eggplant; in - pepper


Pumpkin family vegetables: a - pumpkin; b - zucchini; in - squash; d - cucumber
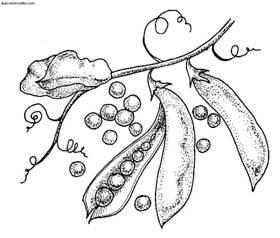
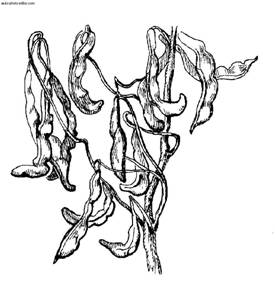
Vegetables of the pea family: a - pea; b - beans
A separate group of vegetables are roots. This includes some crops of the umbrella family (carrot, parsley, celery, parsnip), cabbage (turnip, rutabaga, radish, radish), and also beetroot belonging to the family of swan. The main value of all these cultures is concentrated in rich nutritious roots, due to which they got their name. Among the root vegetables grown in our summer cottages, the most common are beets, carrots, radishes, celery, parsley, etc.
Root vegetables are among the vegetables that are most easily stored for a long time at home.
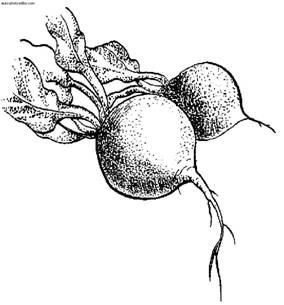
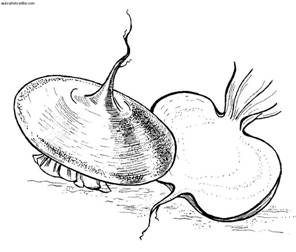

Root vegetables: a - radish; b - turnip; in - radish; g - beets; d - carrots
TO bulb group belong to the plants of the lily family, among which should be mentioned first of all the various types of onions (onions, leeks, batun, shallots, shnitt, slizun, multi-tiered), as well as garlic.
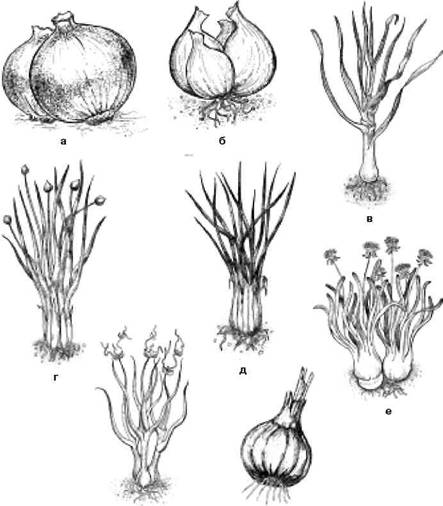
Onion vegetables: a - bulb; b - shallot; in - leek; d - batun; d - Schnitt; e - slizun; W - multi-tiered; h - garlic
In a special group agronomists distinguish tuberous fruitsvegetables, among which potatoes are in the first place - one of the most valuable and useful agricultural crops of our country. At the same time, it is customary to attribute only early potatoes to vegetable crops, while late or mid-season potatoes belong to field crops.
An important role in modern home gardens also play green and perennial vegetables. The first of these groups includes plants of various families — such as the syllocene (leaf lettuce and cabbage), quinoa (spinach and beetroot, or chard), umbrella plants (dill, coriander, parsley and celery), cabbage (cress, salad mustard, Chinese cabbage) and others. Perennial vegetables are considered to be sorrel and rhubarb from the buckwheat family, horseradish from the cabbage family, asparagus from the lily family and some other cultures.
Green and perennial vegetables: a - dill; b - parsley; in - horseradish
In addition to vegetables, the owners of summer cottages also grow fruit trees and berries. Among all their numerous species, pome fruits, stone fruits, nuts and berries are distinguished.
For pome breeds characterized by fleshy fruit with a developed pulp, within which are located special seed chambers with seeds. The brightest representatives of this group fruit trees - apple and pear; they also include the less common mountain ash, hawthorn, shadberry and quince.

Seed seeds: a - an apple; b - pear; in - hawthorn; d - quince
Among the fruits and berries the fruits of the pome group are kept the longest: apples, pears, etc.
Fruit stone fruit cultures represent the drupes, surrounded by dense and juicy pulp. The most popular among most gardeners are cherry, sweet cherry, plum, sloe, and apricot in the southern regions of Russia. In addition, this group includes sea buckthorn, viburnum, bird cherry, barberry and some other crops.

Stone fruit cultures: a - cherry; b - sweet cherry; in - drain
Walnut crops not very popular with domestic amateur gardeners. Sometimes, however, owners of private plots cultivate common hazel or hazel, and grow in the south of our country. walnut. Widespread various berry crops - strawberries, strawberries, raspberries, gooseberries, all types of currants (red, black, white and golden), etc. Most of these crops are characterized by early ripeness and high yields, thanks to which they are so popular with almost all gardeners.



Berry crops: a - strawberries; b - raspberry; in - gooseberry; d - black currant
Varieties of crops
In order to ensure timely collection and proper storage harvest, you must have an accurate idea of the varieties grown on your site fruit and vegetable crops. The fact is that for any particular variety certain indicators of early maturity, yield, keeping quality, etc. are characteristic, therefore each of them requires compliance with special conditions of collection and storage.
Depending on the period of cultivation, which lasts from the moment the first shoots appear before the harvest begins (and this period is also different for each variety), agronomic science divides the varieties of all fruit and vegetable crops into early maturity (early), mid-ripening (medium) and late ripening (late).Naturally, this indicator largely determines the timing of the harvest and the basic requirements for the transportation and storage of certain fruits and vegetables.
However, gardeners and amateur gardeners should take into account the fact that this division is rather arbitrary, since within each group of varieties there may be deviations in the direction of increasing or, on the contrary, shortening the period of cultivation. Thus, if, for example, two varieties of cucumbers are classified as early ripening, this does not mean that the crop should be harvested strictly at the same time.
Characteristic varietiesThe difference in the timing of ripening early, mid-ripening or late-ripening varieties of a particular crop can vary from a few days to 1 month.
Currently, there are 4 groups of varieties. white cabbage: in addition to the main ones, breeders managed to bring out the early-ripening varieties Early and June. However, for long storage they are unsuitable, and therefore are intended for use in the summer. Mid-season varieties - Slava Gribovskaya 231, Slava 1305, Belorusskaya 455, Nadezhda, Tayninskaya, Podarok, etc. - are stored much better. All of them have high yields and are used for fresh consumption in autumn and winter, for salting and long-term storage. The late ripening varieties of white cabbage are the longest: Moscow Late 15, Winter Gribovskaya, Zimovka 1474, Amager 611, etc. As for cauliflower then of all its varieties are best used for storage of domestic and Moscow canning.
Among early ripening varieties tomatoes the highest keeping quality is provided by the Soil Gribovsky 1180, Alpatyev 905a and Dwarf 1185. Another early variety, Gone 13, is also able to be stored for a long time and is resistant to transportation. Tomatoes early ripe varieties Muscovites are recommended to collect green because they ripen very well.
When choosing a particular variety, it is necessary to be guided by various criteria: taste, ripening speed, keeping quality, etc.
All listed varieties of tomatoes are zoned, and their seeds are always commercially available. But many gardeners prefer varieties bred by amateurs, spreading their seeds among themselves. Of these varieties, Persimmon and Mikado have the best indicators of keeping quality: taken from the bushes with green, they ripen perfectly in the room.
Best grades eggplant considered to be Donskoy 14, Long Purple 239 and Jubilee. They belong to the category of mid-season and are characterized by high yields. However, regardless of the variety, eggplants cannot be stored for long, and therefore are intended for direct consumption or processing.
The same can be said for peppers. The most popular varieties of sweet pepper are Novocherkassky 35 and Bulgarian 79, spicy - Astrakhan 147. All of them, as a rule, are used immediately after the harvest.
Cucumbersin general, they do not tolerate long-term storage, but individual varieties of this vegetable crop can lie in the refrigerator for quite a long time, without turning yellow and not losing their taste. Among these varieties are primarily early ripening Altai early 166, Elegant, mid-ripening Non-Rush 40; all are salad destination. Other varieties, such as Vyaznikovsky 37, Shchedry 118, Universal, are used primarily for pickling and pickling.
Among the varieties courgettes Gribovsky 37 is most common in the central regions of our country, 37 as well as the Nemchinovsky hybrid. Both of them belong to the category of early ripening and have high yields. However, just like the squash (the best variety is White 13), it is advisable to use them immediately after harvesting so that they do not lose their taste. Squashes are most often marinated.
A sufficiently high keeping quality is characterized by most varieties. pumpkin. For climate zone middle band The Gribovskoye winter variety perfectly suits Russia; with proper observance of temperature and humidity, it can be stored until the next harvest.
Other gourds can be stored for a long time - watermelons and melons. Of all the varieties of watermelons, the most widely distributed are Stokes 647/649, Ogonyok, Lyubimets farms of Pyatigorsk 286. However, all of them are early, and therefore not suitable for long-term storage, as they are susceptible to various diseases and quickly change their structure. To this end, it is customary to use late-ripening varieties, which are characterized by the best indicators of keeping quality. As for the melons, the most popular varieties Soil Fungovskaya, Kharkovskaya early and Kolkhoznitsa 593 are considered. Collected immature, like winter varieties, they are successfully stored until the end of winter.
Legumes (vegetable peas, vegetable beans, vegetable beans) are known to be excellent for storage regardless of variety. Among top grades Pea should be called Zhegalov 112, Inexhaustible 195, Early 301, Winner G-33, Late-ripening cerebral superior. All of them are used for storage in dried form, and for preservation. The most well-known varieties of beans are Russian black, Windsor, Belarusian, beans - Kustovaya without fiber 85, Moscow white green-manual 556 and some others.
Storage conditions potato also largely dependent on the variety. The bediness of this vegetable crop can be different and is determined by such factors as the ability to enter a state of rest after harvesting, resistance to various diseases, etc. One of the best potato varieties from this point of view is the Ural Early; if all technological parameters are observed, Lorch, Spark, Dream, Friendly and many other varieties are also kept well.
Potatoes variety: a - Ural early; b - Spark
Early Varieties carrots - Nantes 4 and Nantes 14 - differ in tasty and juicy root crops, but due to early ripening are very poorly stored, and therefore are intended for use immediately after harvest. Mid-season high high-yielding varieties - such as Losinoostrovskaya and Vitamin 6, in contrast to them, they have rather good keeping quality. But it is best to use for winter storage Shantere 2461 and Moscow winter A-515.
Sorta beets Gribovskaya flat A-473, Egyptian flat, Polar flat K-249 and Pushkin flat K-18 ripen earlier than others, but their keeping quality is not high enough. Much better suited for long-term storage of Bordeaux 237 and the Incomparable A-463. Mid-season fruit variety Camouoli is recommended for pickling.
All other types of root crops, when the necessary conditions are met, are also capable of long storage. The best and most deadly varieties of radish are Winter Round White, Winter Round Black and Grayvoronskaya; early Odessa 5 is intended for consumption in the summer months. Among the varieties radish the most resistant to long-term storage is characterized by medium late Pink-red with a white tip and Red Giant, turnips- Petrovskaya 1, rutabagas- Krasnoselskaya, parsley- Sugar, Yield, Bordovik, celery- Apple and Root Gribovsky, parsnip- Student and Best of all.
Many varieties of onion are well kept in winter. onions and garlic. The most deadly fruitful varieties of onions are the sharp Vishensky, Mstersky, Arzamas, Rostov bulb, Spassky, Skopinsky, Strigunovsky and Timiryazevsky, as well as the peninsular Skvirsky, Danilovsky 301, Karataly and Oktyabrsky; Myachkovsky local stored much worse. As for garlic, such varieties as Gribovsky 60, Dungansky local, Danilovsky local, Marinsky and others are most suitable for winter storage.
Many fans grow green and perennial vegetables of various varieties in their gardens. The most valuable varieties lettuce considered Moscow greenhouse, Berlin yellow, Stone head, Bettner, spinach- Leafy, dill- Gribovsky and Armenian, rhubarb- Moskovsky 42, Krupnozhereshkovy, sorrel- Belleville, Broadleaf, asparagus- Arzhenteylskaya and others. However, they are not designed for long-term autumn and winter storage and are used, as a rule, in the first days after collection. However, in some cases it is possible to extend the shelf life of green and perennial vegetables up to 1 month, and to a greater extent this applies to the above varieties.
Of course, this is not a complete list of varieties of vegetable crops grown on the summer cottages; nevertheless, the most common of them have found their place.
It is known that in winter, not only vegetables are well stored, but also the fruits of pome crops (mainly apples and pears). The keeping quality of stone fruits and berries is, of course, much lower, but some of their varieties can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 2 months..
Numerous varieties apples traditionally divided into summer (early ripening), autumn (middle ripening) and winter (late ripening). The first group includes Grushovka Moscow, Papirovka, Melba, Suislepskoe and Youth; they all ripen in August and are stored, as a rule, no more than 12–15 days. The group of autumn varieties is represented by the Autumn striped, Cinnamon striped, Borovinka, Bessemyanka Michurinskaya, Anis Alyny and some others; they usually ripen in late August or early September and are stored for 2 to 3 months. Winter varieties of apples are intended for long-term storage: Antonovka, Pepin saffron, Anis striped, Welsey, Slavyanka, Skryzhapel large, Northern synapse, Lighthouse, Babushkino, Rennet bergamotny. The removable ripeness of the fruits occurs around the end of September; apples of these varieties are stored until January-May.
Among all varieties pears Amateur gardeners prefer Bergamot red, Bessemyanka and Tonkovetke. These varieties have a relatively low (even for this type of fruit) longevity and lose their quality after 15-20 days. Pears of Bere winter Michurina are preserved longer than others: under good conditions they can lie until February.
Most suitable for storing varieties plums - Anna Shpet, Renklod Altana, Victoria, Hungarian Azhanskaya, Hungarian Ordinary, Edinburgh, etc. In a suitable environment, they can last for 2, 3, and sometimes 4 months.
Concerning cherries then the highest keeping quality is characteristic of fruits with dense flesh and dark color (Lyubskaya, Fetalnaya Michurina, Shubinka, Consumer black, etc.). Such fruits can be stored from 1 to 1.5 months.
Varieties of cherries: a - Lyubskaya; b - Fur coat; в - Consumer black
A similar shelf life is characteristic of berries. black currant. The quality of these fruits also depends on the variety. So, the best kept dove, Semirechenskaya, Jubilee, Goliath, Luxton, Neapolitan.
Maturity of fruits and vegetables
One of the most important moments of the harvest is the correct determination of the degree of maturity of the fruit. Premature or, on the contrary, too late collection can significantly impair product quality and reduce its resistance to storage conditions.
In agronomic literature it is customary to distinguish biological(physiological) and removable (technical, harvesting, household, consumer) fruit maturity. If the plant has reached biological maturity, this means that it has completely completed the cycle of its development and is capable of reproducing a new generation of individuals. Thus, for example, the biological maturity of potatoes, cabbage, onions and some other perennial vegetable crops implies a final cessation of growth, a transition to a state of rest and the ability to continue the life of their wintering food organs (in this case, tubers, bulbs, roots, etc.). In this state, they can be stored for a long time.
The concept of “removable maturity” has a slightly different meaning. It occurs when fruits and vegetables begin to meet the standards of GOST (which, of course, does not matter much for gardeners, gardeners, amateurs and owners of private household farms), becomes suitable for consumption, processing, transportation and storage.
There are fruit and vegetable crops in which both removable and biological maturity occurs at about the same time (all types of melons). But in most cases, the fruits reach removable maturity earlier than biological.
Of course, when the harvest of the same crop is intended for different purposes, then removable maturity occurs at different times (for example, if dill is grown for greenery, it is removed until the inflorescence appears, if it is used for pickling, removable maturity almost coincides with biological).
In determining the timing of harvest, gardeners and gardeners should be guided by the onset of a removable, rather than biological, maturity.
Not all cultures come to a state of removable maturity at the same time. So, the harvest of onions, garlic, potatoes, root crops and late cabbage, as a rule, is harvested once, but there are also so-called multi-harvest cultures ripening gradually (tomato, cucumber, pepper, eggplant, melon, etc.). In some cases, the number of fees can reach 10-15; however, as a rule, there is a chance to get a higher quality crop, but, of course, this process is extremely time consuming and requires large physical costs.
Lezhkost fruit and vegetable products
The ability of fruits and vegetables for a certain (long enough) time to maintain their commercial quality, without being subjected to various diseases and without losing weight, is called keeping Indicator keeping quality plays a decisive role in the storage of fruits and vegetables. It has a quantitative designation and, for convenience, is expressed in weeks or months (that is, the maximum possible storage period under ideal conditions).
There is also a concept persistence vegetables and fruits, meaning their keeping quality in certain specific conditions. As you know, depending on the last storage period of products can vary, and keeping quality is affected by a variety of external factors such as the season and growing area, storage technology, temperature, humidity and many others.
Naturally, different types of keeping quality are peculiar to different types of fruit and vegetable crops. From this point of view, they are usually divided into 3 groups. The first includes potatoes and biennial vegetables (roots, onions, cabbage). The peculiarity of these crops is that there are buds on their tubers, heads, bulbs and root crops - the so-called growth points. During storage, these buds are slowly prepared for the subsequent reproductive development, which should occur during the vegetation period (as is known, new plants will later be formed from them). Thus, since the onset of biological maturity until the beginning of the growing season (that is, just during storage), vegetables of this group are at rest. This period may be different for different cultures. So, onions and potatoes enter a state of deep dormancy and do not germinate over time even in cases where the environment is ideal for growth. Root crops and cabbage are characterized by a less deep rest: under favorable conditions, they are able to give shoots. However, by lowering the storage temperature, the quiescent period of these vegetables can be extended for a while.
The process of reducing the air temperature should be carried out gradually. Sudden jumps can adversely affect the yield and lead to the development of physiological diseases.
The shelf life of potatoes and biennial vegetables is determined by the duration of the rest period: the longer and deeper it is, the higher their keeping quality and persistence. The fact is that during growth, the storage organs (tubers, bulbs, roots, etc.) give all the nutrients to the kidneys, as a result of which they are depleted, lose weight, lose resistance to various diseases and, as a result, become unsuitable for consumption. Therefore, in order to increase the shelf life of these vegetables, it is necessary to slow down the growth processes and, accordingly, extend the state of rest, which is carried out, as a rule, by limiting temperatures.
Of course, if the vegetables are not intended for consumption, but for obtaining seeds, the task is just the opposite: in order to provide the necessary preparation of the kidneys, the temperature, on the contrary, increases.
The second group of fruits and vegetables include fruits and fruit vegetables. As a rule, it is customary to collect them immature, and during storage they continue their life cycle. At the same time, the fruits acquire the characteristic appearance, color, consistency of the pulp, taste, and the seeds inside are gradually developing due to the nutrients of the pericarp. When the seeds reach final maturity, the tissues of the fruits begin to age, lose weight, lose their commodity and taste, and are exposed to all sorts of diseases.
Thus, the shelf life of fruits and fruit vegetables directly depend on the length of their post-harvest ripening: the slower it flows, the longer the product quality remains. That is why, for example, summer apples are stored much worse than winter ones, because they ripen completely on a tree, while the latter are usually taken unripe.
The third group includes green vegetables and berries. Their keeping quality is very low, because they have delicate fabrics with a high concentration of moisture and thin skin, which contributes to the rapid evaporation. In addition, more intensive respiration and metabolic processes are characteristic of fruit and vegetable products of this group. As a result of these properties, leafy vegetables and berries quickly lose moisture and fade, and therefore can be stored for very short periods. It is possible to increase their shelf life by lowering the temperature and increasing the relative humidity of the air in the room.
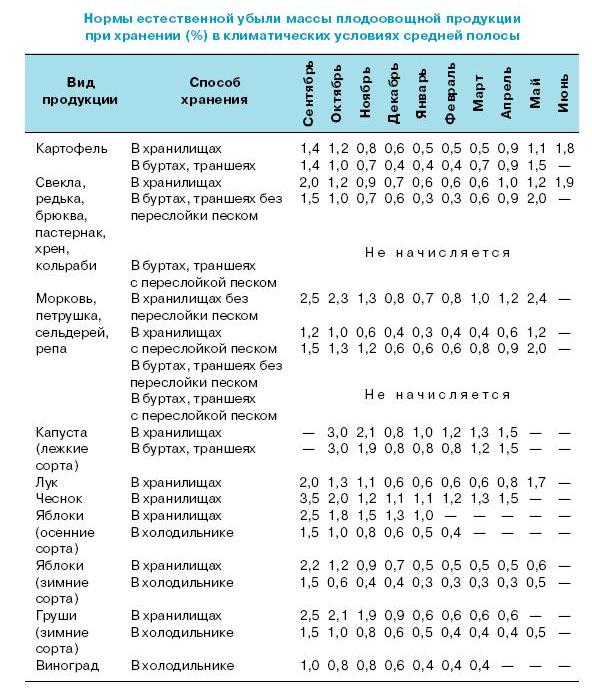
The keeping quality of fruits and vegetables is also affected by the intensity of their breathing, which is the main metabolic process. With intensive respiration in the tissues of fruits and vegetables, energy is released faster and nutrients are lost, which means that product quality deteriorates. Different types of vegetables and fruits have a different degree of respiration rate, therefore their storage time is different.
The intensity of respiration is influenced by many factors, among which the degree of maturity of fruits and vegetables, the presence of mechanical damage, the storage mode, etc. must be mentioned. All these factors should be taken into account during transportation and storage of products.
One of the most important signs determining the keeping quality of vegetables and fruits is their resistance to diseases and mechanical damage. The higher the fiber content in the tissues and the more developed the covering surface, the more resistant to mechanical stress and, therefore, the product is conserved. The high concentration of tannins and dyes determines the resistance of fruits and vegetables to various pathogenic microorganisms that cause diseases. It is known, for example, that red cabbage is stored longer than white cabbage, and painted onion varieties last longer than unpainted ones. It has been proven that it is much more difficult to fight diseases and injuries of vegetables and fruits after harvest than during the period of their cultivation.
Some types of fruits and vegetables have the ability to heal shallow mechanical damage, producing a layer of corky cells that separate the damaged area from healthy tissue and thereby protect the latter. This ability is highest in potato tubers; it is also characteristic of various types of root crops (carrots, radishes, beets), although to a lesser extent. Moreover, in the process of storage, vegetables gradually lose this property.
The fact is that, as is known, during storage they are gradually depleted, losing the ability to resist harmful external influences.
In addition, under conditions of storage or cellar, fruits and vegetables are in close contact with each other, which creates an optimal environment for the development and spread of pathogenic microorganisms.
And finally, during the storage of fruits and vegetables it is impossible to use chemical means of protection, since in this case we are talking about food products. Therefore, perhaps, the only way to combat all types of diseases of fruits and vegetables is to observe the necessary requirements when storing them and constantly maintaining an ideal temperature, humidity, etc.