How to arrange a living fence in the country and what is better to plant as a hedge? The fastest growing hedge: we choose plants.
Gone are the days when neighbors tried to separate the plots from each other with high fences. Now hedges are used for these purposes - they look attractive, and are protected from the winds reliably enough. True, from unwanted penetration hedge in the country will help hardly, since its main purpose is the aesthetic function and zoning of the site.
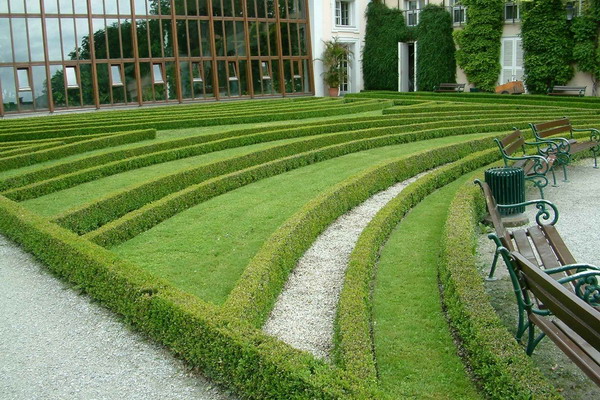
How to plant a multi-row hedge
Long monotonous conifer hedges are also as boring as a long fence, but they can be diversified, as one of the options is the creation of multi-row hedges. In the first row planted low-growing shrubs, and in the second and third - higher (for example, turf, hazel, linden, hairy lilac). Some levels can be cut, some can be allowed to grow freely, it will be a good contrast.
Here is an example of such a hedge of conifers and perennial shrubs:

1st row - shorn low spirea hedge with a gray height of 1 m;

2nd row - freely growing Chubushniki variety "Mont Blanc" height of 2 m, blooming in mid-May for three weeks; as an alternative, you can use a collection of green leaf mite trees, different varieties will bloom at different times, the total duration of flowering of this series will increase to a month;
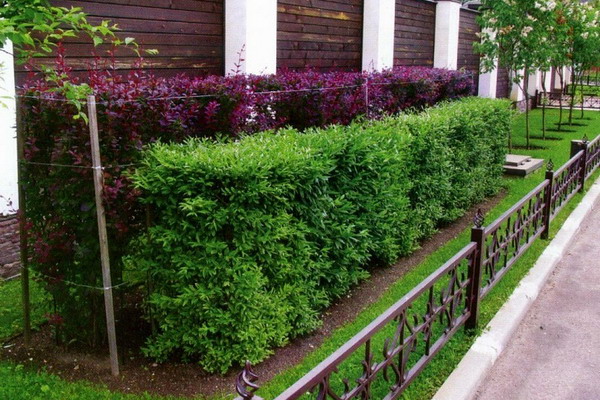

3rd row - light lilac and dark lilac lilacs 4-5 m high, blooming in mid-May.
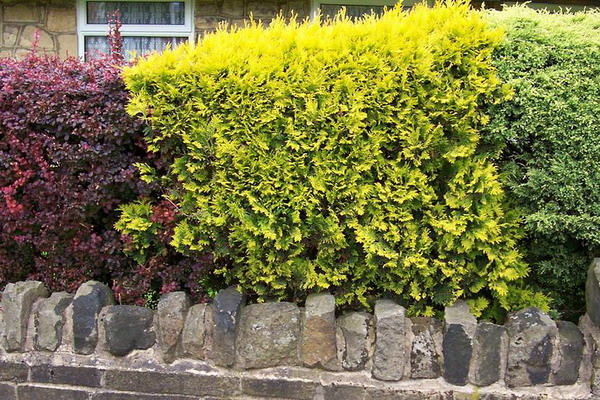

In multi-row perennial hedgerows, the combination of contrastingly colored plants looks spectacular (for example, the combination of light green and dark purple foliage looks interesting, the yellow shrubs brightly play against the background of dark needles).
As seen in the photo, the combination of deciduous and coniferous species in hedgerows looks just great and very unusual:
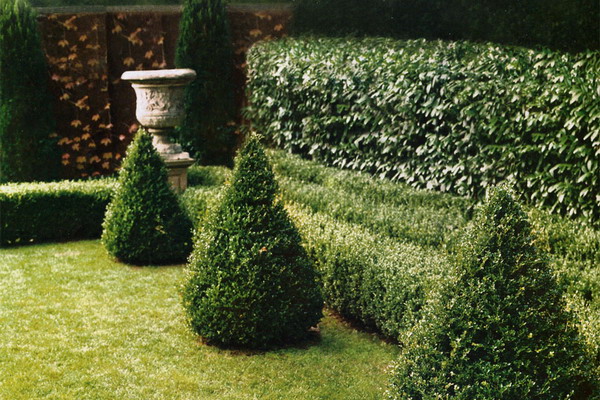



And how to plant a hedge in several rows? If you plant in one row different varieties of the same plant in color, for example, varieties of the western arborvitaire, Califolia leafa tree, barberry are suitable for this variant, you will get the so-called marble shorn fence.
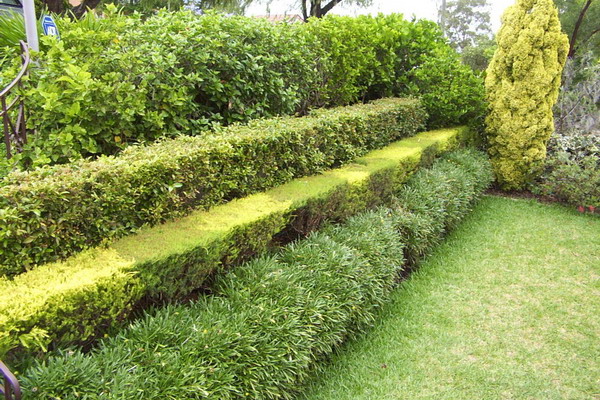

The best hedge is one in which plants are combined not only from an aesthetic point of view, but also have similar biological features - growth rate, relation to light, moisture, soil composition.
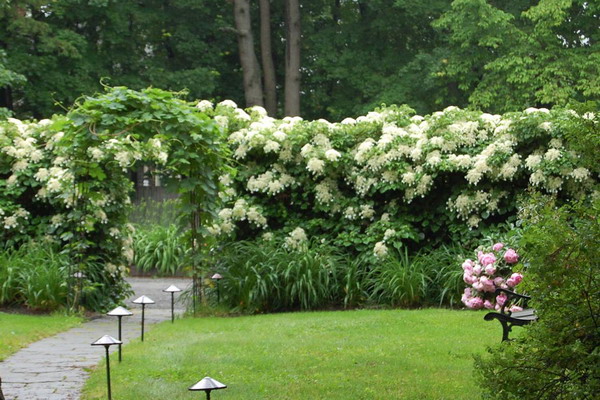

The hedge with inserts from lianas, which does not occupy much space, looks originally.
![]()
If the hedges intersect at right angles, one of them may be with dark green glossy leaves, for example, from a shiny cotoneaster, and the other with frosted light green leaves, for example, from spirea and argutus.
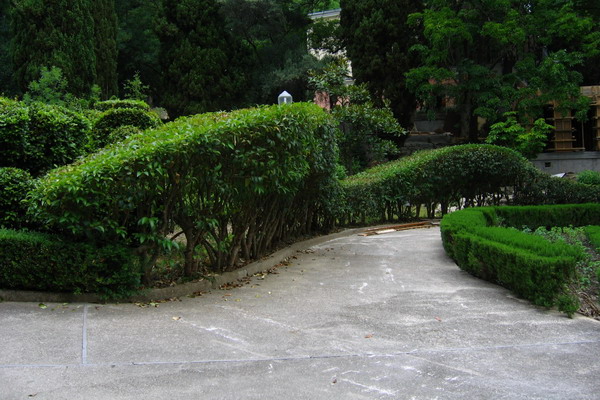

It is not necessary that the top line of the hedge be parallel to the ground.
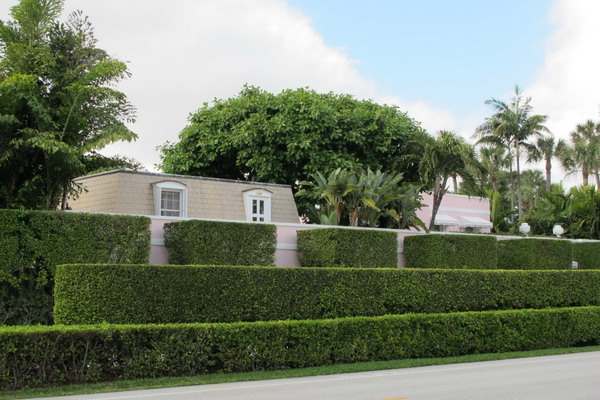

Shiny cotoneaster, tall varieties and barberry species, as well as spring-flowering species of spirea, Van Gutta spirea, gray, argutus oak-leaved, will create a medium-sized green wall.

Well, low green hedges-borders can be made from Kuril tea (Potentilla), Thunberg barberry and low species of spirea - Japanese and Boumald spireas, as well as low and medium varieties of western and peach varieties, including its yellow-colored form.

Border fences are especially often used when creating parterres, they are also good as a fringing trimmed row of the composition, making it more spectacular and neat.
What Tui better suited for hedge
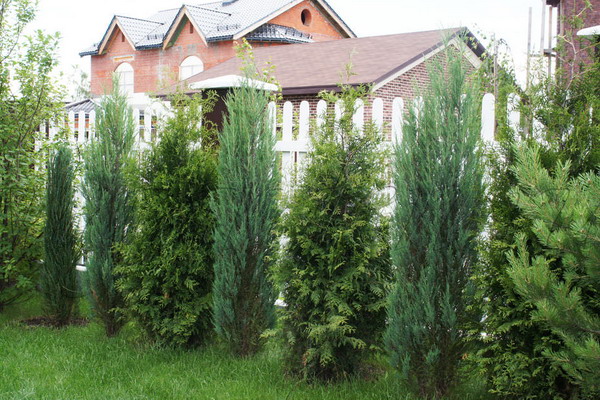

AT middle lane Russia to create a hedge with their own hands the best plants are pyramidal and columnar varieties of western and juniper thuja, as well as varieties and species of spruce.

Thuis western shade-tolerant, frost-resistant, not demanding to the soil - will grow on clay and sand, on dry and watery places, but, of course, the most beautiful will be on good garden soil with sufficient moisture.
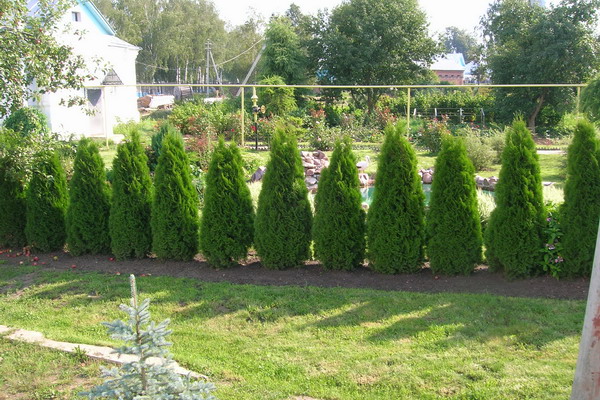

Species plants grown from seeds are relatively cheap, but, of course, not as elegant as varietal. The material for a hedgehog can be grown not only from seeds, but also from cuttings, recently, thuja 50-60 cm high sell cheap and hypermarkets. A hedge is planted at a distance of 50 cm, in the first year they are not sheared.
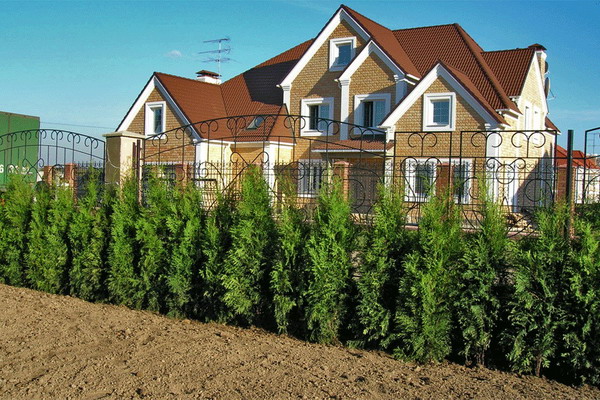

In the second or even third year they cut the tops for better tillering. In the third year, in addition to the top, the side shoots are sheared. Tui grow continuously throughout the season, they can be cut 2-3 times per season.
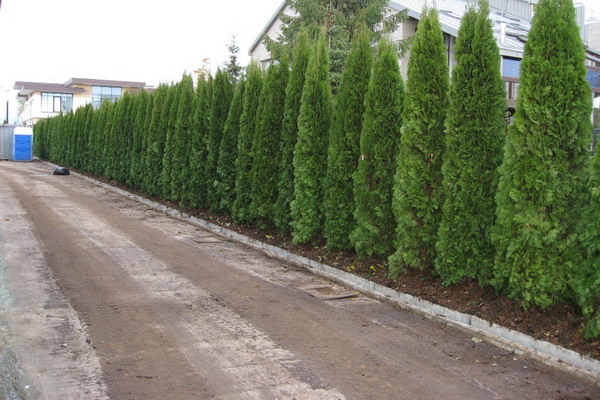

The crowns of tui are inherently thick and dense, because the formation of a hedge is quite easy. It is best to cut them in late June after the completion of active spring growth of shoots. The profile of the fence is desirable to make trapezoid.
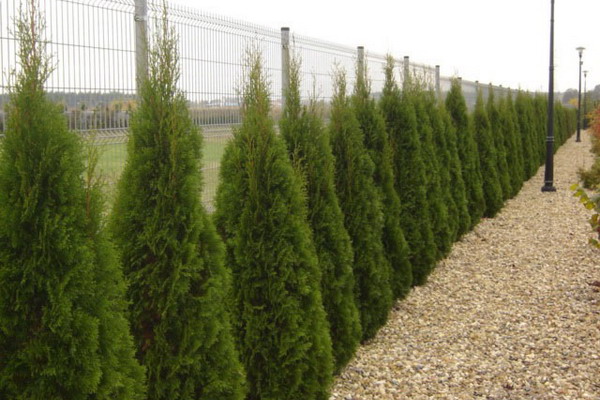

What Tui best for hedges in the middle lane? The most chic variety is the column-shaped Smaragd thuja. Its needles do not turn red or brown either in autumn or in winter, retaining their juicy emerald color throughout the year, but it grows more slowly than other varieties. This grade of a thuja does not transfer a hairstyle, keep it in a free form.
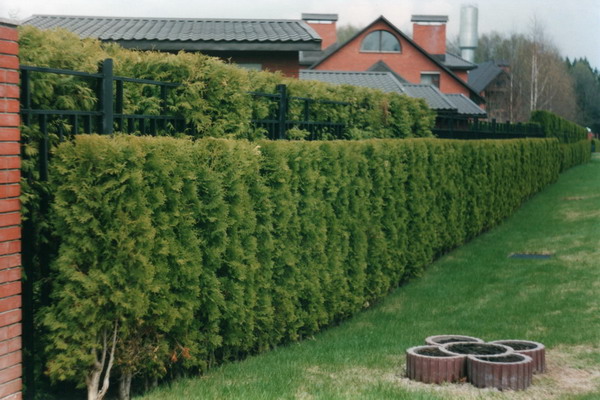

And which Tui are suitable for clipped hedges in our conditions? Thuja "Braband" tolerates even a radical haircut, but is prone to abundant fruiting, which looks sloppy.
What is a hedge and at what distance to plant it
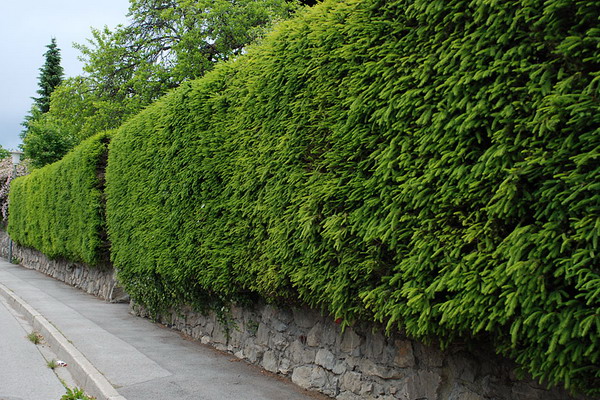

What plants can a hedge be planted from, if thuja do not attract you? The hedge of spruce looks wonderful, once such were popular in Russian estates. To create it, take a seedling with a height of 50 cm and land at a distance of about 1 m from each other.
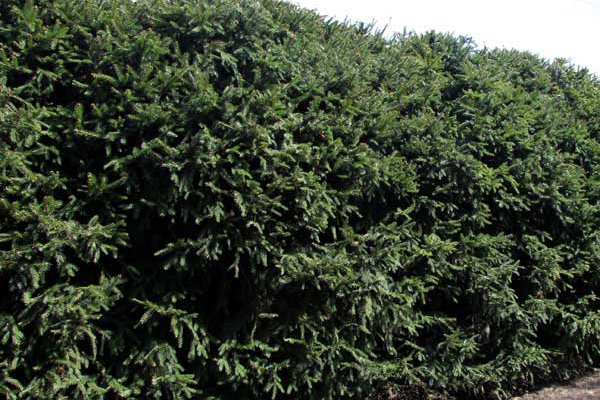

In the year of planting pruning do not spend. Starting from the second year, shear in May-June, shortening the side shoots with a secateurs by about two thirds of the length, the apical shoot - by one third. Such pruning will give a good branching for the next year.
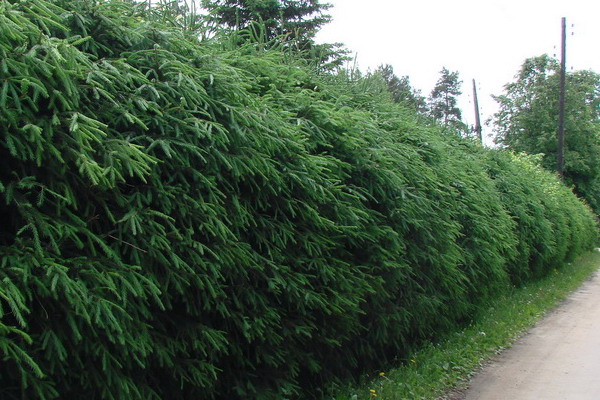

It is important to cut the fence regularly, because for spruce timber pruning over 3 years old is undesirable, that is, it is impossible to fix a running or damaged fence. Cutting is carried out to obtain a given height of the fence, forming a trapezoidal or rectangular profile.
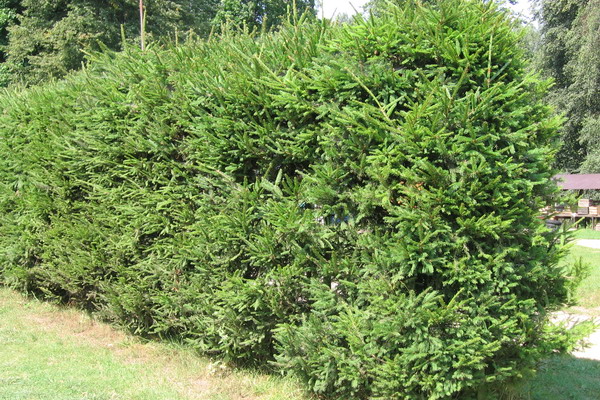

When the desired height is reached, the spruce hedge is supported by trimming with garden shears in late March - early April. The operation is repeated all subsequent years. Due to this, young Christmas trees are actively branching and do not expose from below, creating an impassable green fence. If you plant in a hedge not specific plants, but compact varieties, then they will not require cutting, sorry, they are expensive and grow slowly.
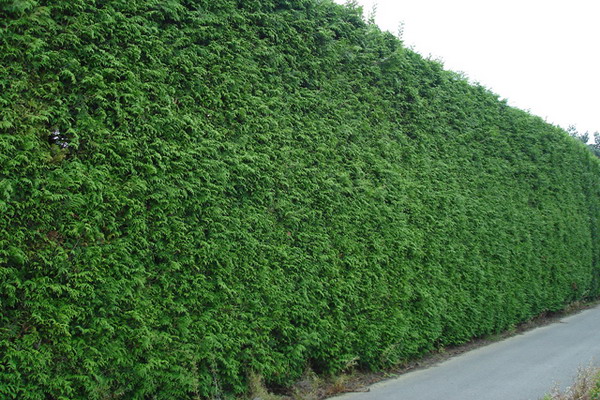

What else is a hedge, easy to maintain and aesthetically appealing? Junipers love the sun, tolerate drought, are resistant to frost, but can not live on heavy clay soil and flooded areas.
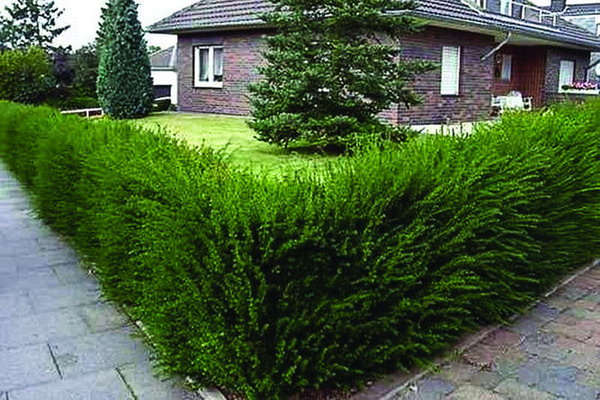

Species plants take root poorly, so they are not suitable for creating a hedge, you have to buy planting material with a closed root system in the nursery. At what distance to plant a hedge of their juniper? The optimal distance is 50-80 cm from each other, in one row.
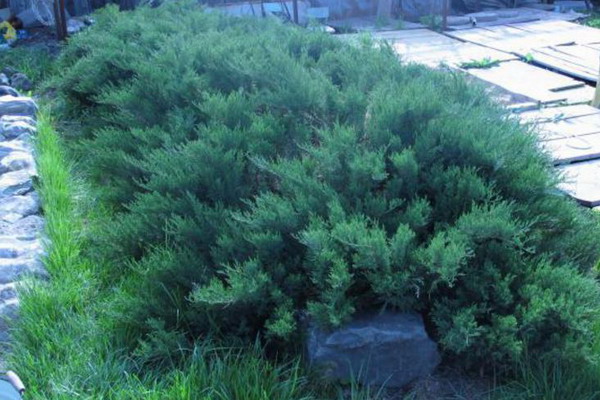

The size of the juniper in the container can be any, the optimum age of the seedling is 3-4 years. Juniper shrubs with scissors for cutting shrubs 1-2 times a year.

All kinds of hedges help to zone the garden, protect from prying eyes, emphasize the beauty of floral and shrub compositions, cover from noise, dust and wind. They are created for many years, so it is better to design, plant and grow them according to the rules.
In the next section of the article, you will learn which bushes can be used for a hedge in central Russia.
What shrubs can be used for hedge
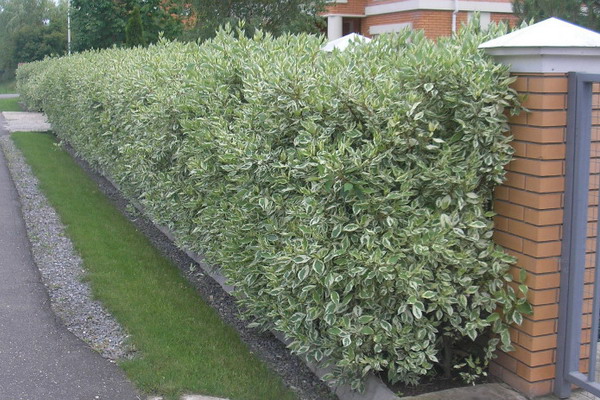
Hedges can be very different: short-haired or free-growing, coniferous or deciduous, made from a single breed of shrubs or combined, single or multi-row, prickly or soft.

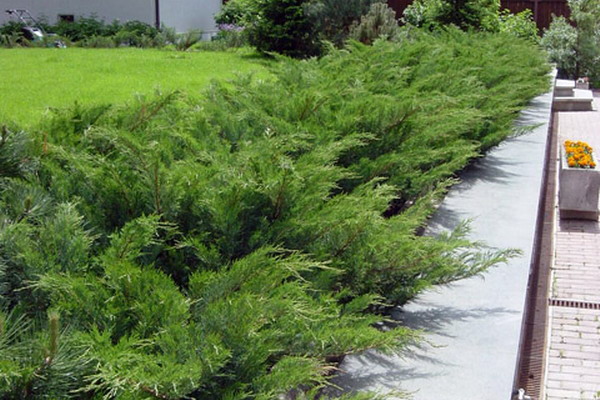
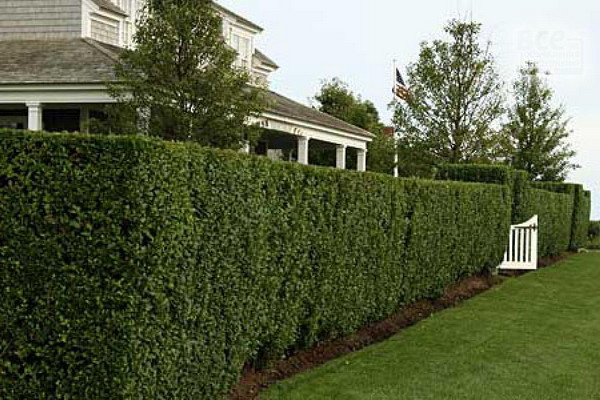
All hedges, both deciduous and coniferous, are created from densely leafy trees and shrubs that can be trimmed well. The main thing is that the plants from which you can make a hedge have a dense crown and relatively slow growth.

Freely growing hedges look less formal than the sheared ones, but require considerable space, their width is from 1 to 3 m. Most often such hedges are created from rocks that have natural compact crowns.
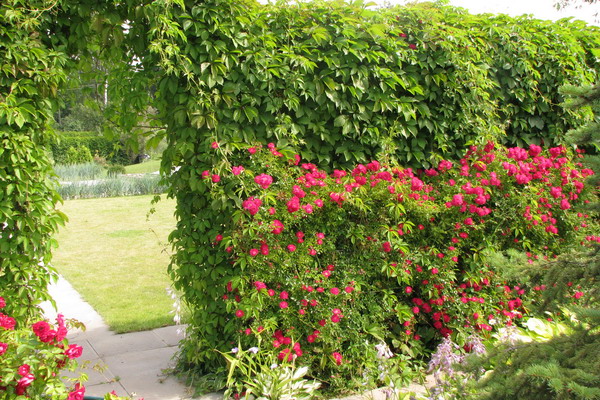

What shrubs use for free-growing hedge? These fences should include beautifully flowering and spectacularly fruiting plants that can transform the monotonous appearance of the "green wall" (dogrose, euonymus, various types of spirals, Hungarian and Amur lilac, Chubushnik).
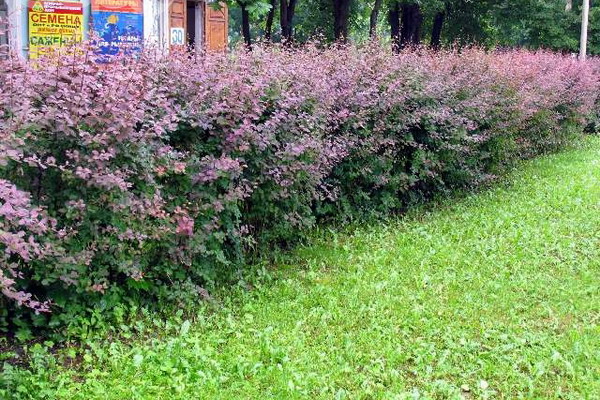

In central Russia, you can also use different types of hawthorn, elderberry, Maac honeysuckle and Tatar. Of what other shrubs there is a hedge, so it is from the viburnum of Gordian (common viburnum often suffers from leaf beetles), blister and deren.
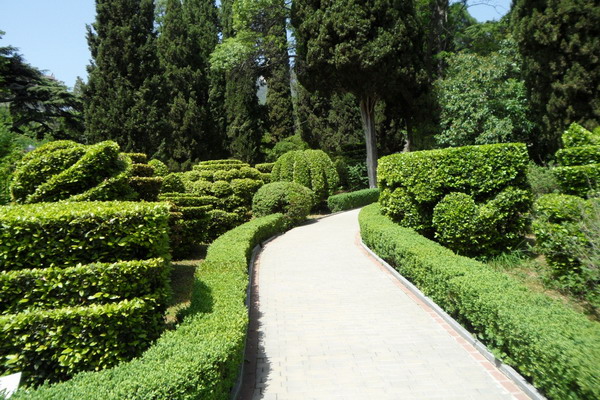
Evergreen shorn hedge
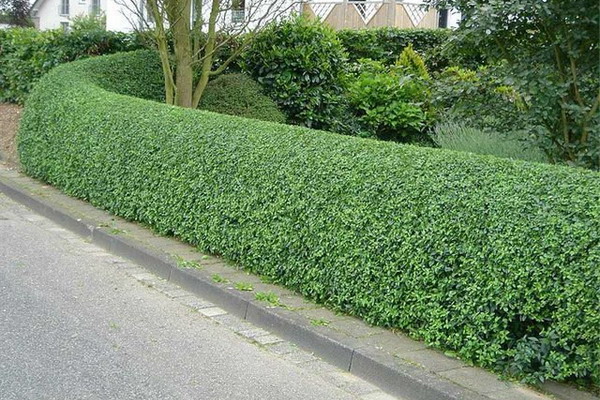

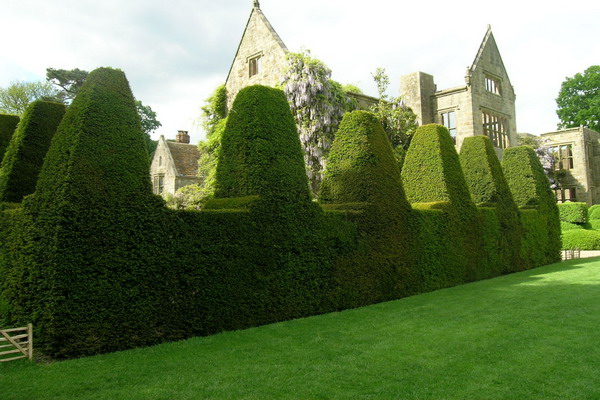
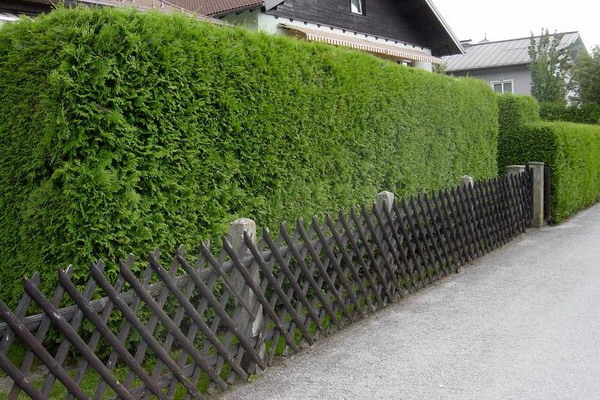
Shorn evergreen hedge is compact in width and therefore most suitable for small gardens. Creating and maintaining a trimmed hedge in good condition will require material, time and physical costs, this work is not limited to planting. If you decide to grow a clipped, or formal, hedge in your garden, you will have to work on it all your life.
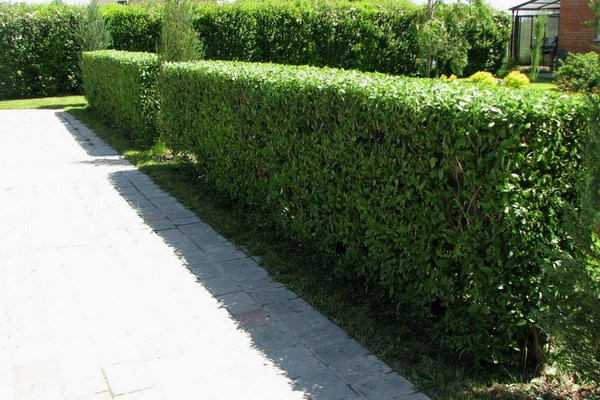

Comply with the technology of trimming plants is extremely important, as the blunders made are almost not subject to correction. In addition to regular hedge trimming, it must be provided with sufficient moisture and nutrients so that plants can compensate for what they lost during pruning.
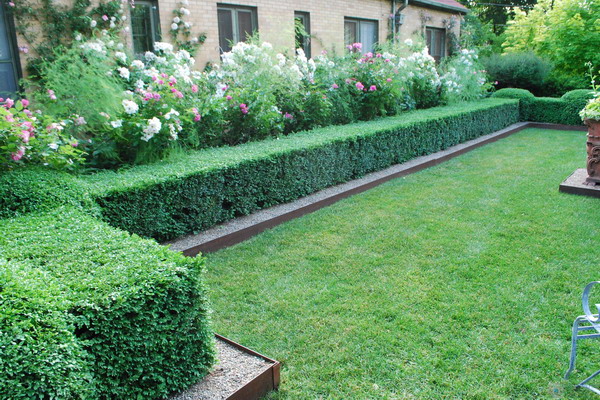

Freely growing shrubs for some time can be disregarded, but often planted and regularly shrubs in molded hedges need to be fed and watered annually, making organic and mineral fertilizers. If the soil is very fertile, they can be applied once every 3-4 years, the poor need additional feeding every year. In addition to watering and fertilizing will need weeding, loosening, mulching, as well as spraying from pests and diseases.
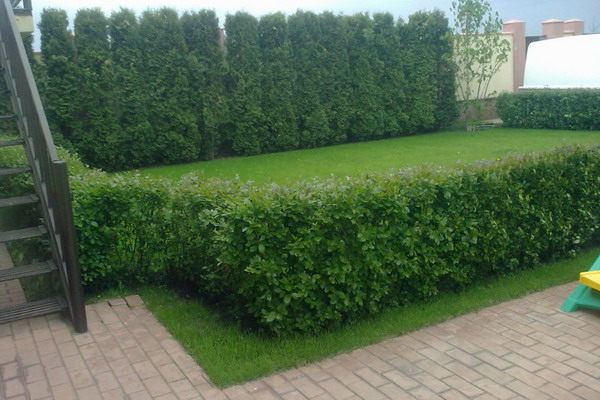

Neglecting the needs of plants affects the appearance of the hedge. Do not allow soil sodding around the plants in the hedge, timely cut the lawn, the ground at a distance of 50 cm on both sides of the hedge should be mulched.
Fences can be classified by height. High fences are called above 2 m, medium ones - 1.5-2 m high, low ones - 1-1.5 m, curbstones - 30-50 cm high.
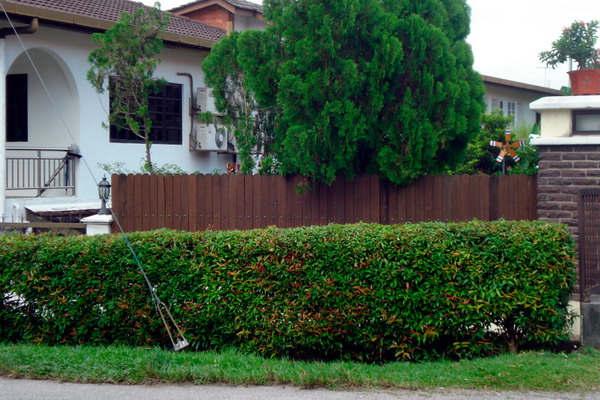

With age, tall hedges become impassable and impenetrable for views, that is, they successfully play the role of a fence, protect from pollution and dust, as well as the wind, create a special microclimate, serve as an excellent backdrop for ornamental plants. They bring clear lines into the structure of the garden, they can be used to divide the garden into separate functional areas, disguise utility structures or the garden area.
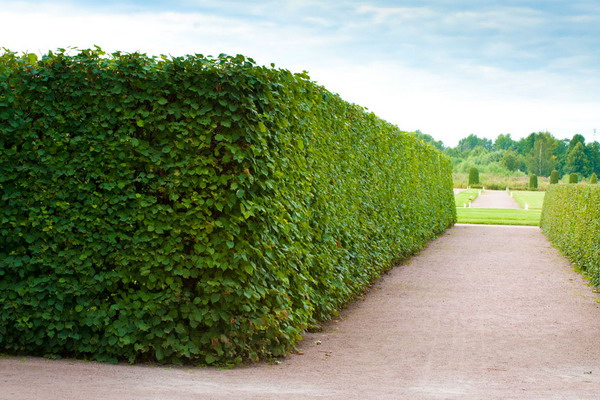

In central Russia, high deciduous trimmed hedges can be made from such trees as small-leaved linden, alpine currant, shiny cotoneaster, spring bloom spiraeus, hawthorn (prickly, blood-red and slinoist), Ginnnal maple and Tatar.
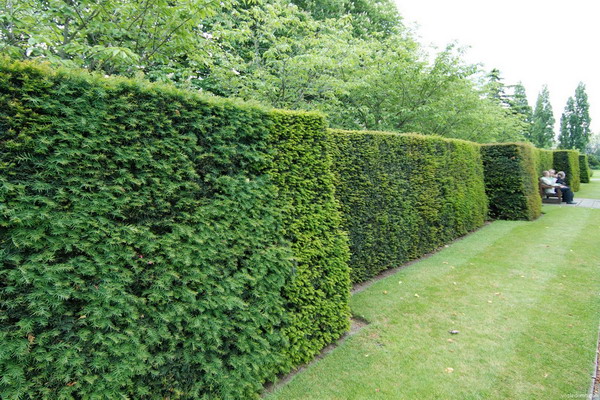

“Construct” excellent coniferous high clipped fences can be made of ordinary and prickly firs, from western thujas and junipers.
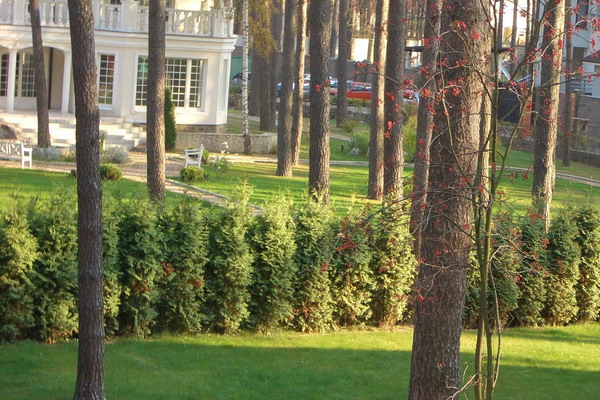
Hedge of coniferous plants (with photos)
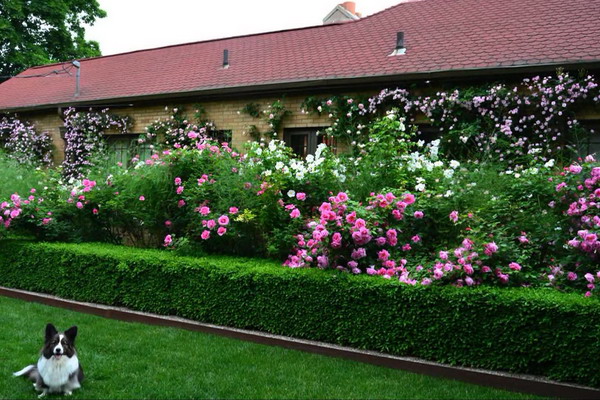

Coniferous plant fence looks strictly and is an excellent background for flower or decorative leafy plants. Evergreen "fence" will reliably protect the garden from prying eyes, even in winter.

The severity, monotony, the ability to cut oneself well make a coniferous fence a desirable decoration of the garden, it always looks respectable.
![]()
The range of suitable coniferous plants capable of growing in the climate of central Russia is small - this is western thuja, spruce and common juniper. Conifers grow slowly, and are expensive.
As seen in the photo, a conifer hedge can be shorn and free-growing:
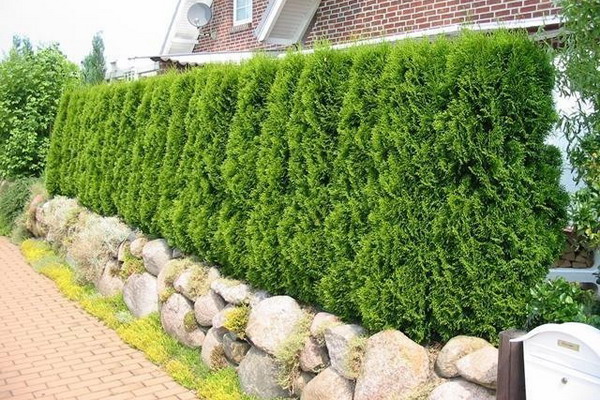
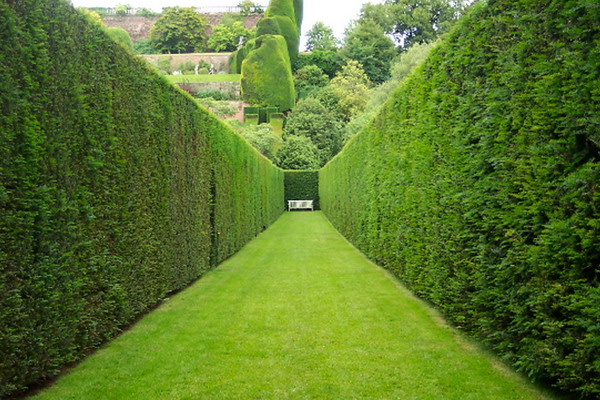



Unwanted plants for perennial hedges

If one or several plants freeze out in your “green fence” during some severe winter, it will lose its appearance immediately and forever, therefore yew, privet and boxwood, so spectacular in warm Europe, we have bad candidates for “building” live hedges. But not all frost-resistant shrubs should be planted in a hedge. With age, the lower part of the bush varietal lilac bare.

It must either be covered with plants planted in front of it, or used wild species lilac, wilted, Hungarian and Amur, which are quite suitable for creating a green wall, as they grow quickly, form a dense volume, are unpretentious and resistant to pests.




Real summer residents spend a lot of time on their plots, from early spring to late autumn. Someone removes dachas only for the summer period, and some in general live all their life in country private houses. Regardless of who does what on his land plots, he rests, simply lives or plants vegetable beds and grows orchards - everyone wants it to be cozy, beautiful and comfortable. Recently in landscape design elements such as hedges became fashionable. Fast-growing, perennial, evergreen - after all, we really want those. Is not it? To grow quickly, always pleased with its greenery and did not need to plant it every year for a new one.
To satisfy all these wishes, what kind of plants should be planted as a living fence? Let's talk about this in more detail.
For the creation of hedges landscape design experts recommend the use of climbing plants, shrubs and even trees.
If you competently pick up planting material, plant by all the rules and provide the plants with the necessary care, your green fence will delight for many years with its magnificent flowering, berry harvest, and at the same time preserve all its decorative qualities.
As a rule, one plant is chosen for creating hedges. After all, we want to see a natural fence with a uniform density and the same height, and different types of greenery can grow unevenly - one will be pulled up, the other will begin to grow in breadth. Even if you decide to use several types of vegetation in hedges, be prepared for complex care.

In order not to turn to specialists in landscape design and not to spend extra money, let's try to figure out for ourselves which plants are best suited for arranging living fences.
Fast growing fence
That shrubs are the best planting material to create natural fences, as they have several advantages over trees and climbers:
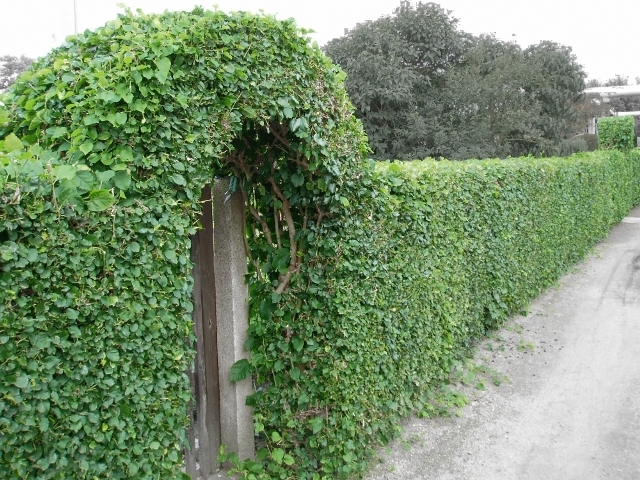

If you plant fast-growing perennial shrubs, then a full-fledged hedge with a height of 2 m will be formed within two years.
Consider the most popular bushes that do not deliver much difficulty in the care, and their beauty will delight from early spring until late autumn.
A very compact plant, it reaches a height of up to 3 m. It is so undemanding and unpretentious that it doesn’t even need a careful pruning. In the spring during flowering such a fence will be just gorgeous. The shrub covered with white delicate flowers, like a bride, attracts attention not only with its decoration, but also with its almond fragrance.
With the help of it, it is possible to create a thick impassable living fence.
The turnip is edible and is harvested after the first frost.
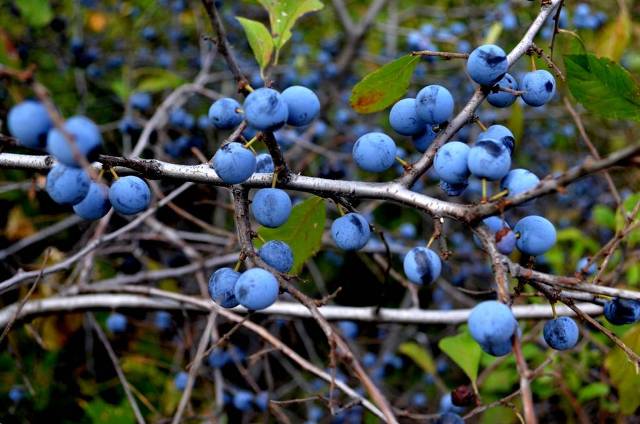

Berries are widely used in cooking and medicine, due to their beneficial healing properties.
Privet primrose
Gardeners love this shrub the most, and landscape design experts recommend it. After all, an ordinary quite unpretentious, grows on any soil, in sunny places and in the shade. The hedge can turn out from it quite high (up to 3 m).
The plant belongs to the fast-growing, thick fence from it turns out to be dense, so you need to cut such a living fence twice a year. If the shrub has been launched and has an unkempt appearance, you can use a cardinal haircut, and in general privet is an excellent material for the formation of all sorts of figures (cubes, balls, cones, trapezoids).
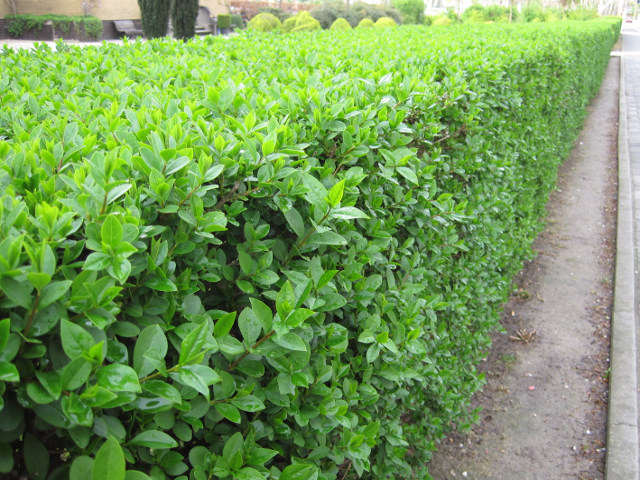

Privet berries are poisonous to humans, and birds go to feed. Therefore, be prepared for the fact that in the thickets of shrubs (closer to subsistence), birds will build nests and hatch chicks.
In winter, privet does not preserve foliage.
Barberry
The barberry of Thunberg is considered to be especially popular for creating hedges. This shrub does not grow as fast as, for example, privet, but it acquires a beautiful spherical shape. Fences are obtained up to 1.5 m in height. The bush has thorns, therefore it will protect your site from uninvited guests and animals.
Very beautiful shades of leaves in the barberry Thunberg - from green and yellow to purple.
In the fall, the shrub is covered with purple foliage and coral fruits that can be harvested before the first frost.
Bladder
it unpretentious plant possesses excellent decorative qualities. He has a rounded lush crown. He prefers more sunny places, although it can grow in the shade, but at the same time the color of the leaves will not be as saturated.
Treats frost-resistant bushes, it is not required to be covered for the winter. If the frosts are very strong, the tips of the shoots may freeze a little.
And a few more tips on shrubs:

Evergreen hedge
Evergreen shrubs for hedges are, of course, very beautiful and comfortable, all year round pleases the eye fresh greens and density. But be prepared for the fact that if the frosts are very strong, the plants will have to cover with some material.
And then, not everyone likes this green monotony. After all, the fences of deciduous plants will change throughout the season - first tender young foliage will appear, then a period of violent flowering with different shades, then the fruits will ripen and, finally, in the autumn the bushes will be covered with yellow-purple-purple decoration.
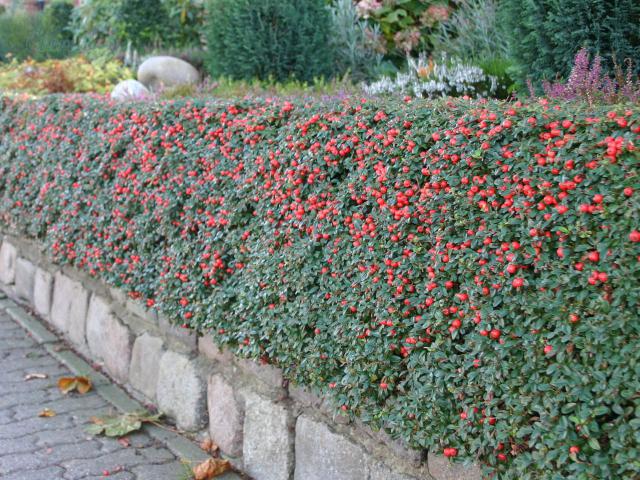

Evergreen hedge such a game of colors will not please. Therefore, for a start, weigh all the pros and cons, decide how you see the landscape design of your site - variegated or monotonous. And then go to choose shrub saplings.
Boxwood
This shrub easily takes root in central Russia, tolerates frost well. Still, the plant belongs to the heat-loving, so in the northern regions is unlikely to be able to grow such a hedge. And in areas with cold winters will have to carefully cover the bushes boxwood for the winter.
The box is literally littered with small shiny green leaves, which densely cover the branches of the shrub. Any soil is suitable for it, the place for landing can be chosen both sunny and shady.

Perfectly tolerates haircuts, as well as it can be transplanted at any age.
Lavrovishnya
Evergreen shrub got its name because its leaves resemble laurel, and the berries are similar to cherries. The leaves are quite large and hard, glossy on the upper side. The fruits of this plant are widely used in medicine, all other parts are poisonous.
Laurel cherry blossoms at the end of April or at the beginning of May, the inflorescences somehow vaguely resemble a bird cherry tree. Flowers of white or cream color are incredibly fragrant.
Thinking through the design of your site, you should pay attention to such a bush as holly. It has very beautiful leathery shiny leaves and attractive bright berries (they are red and orange, black and white, yellow shades). Ripening of berries occurs in autumn, and they are perfectly preserved on the shrub throughout the winter.
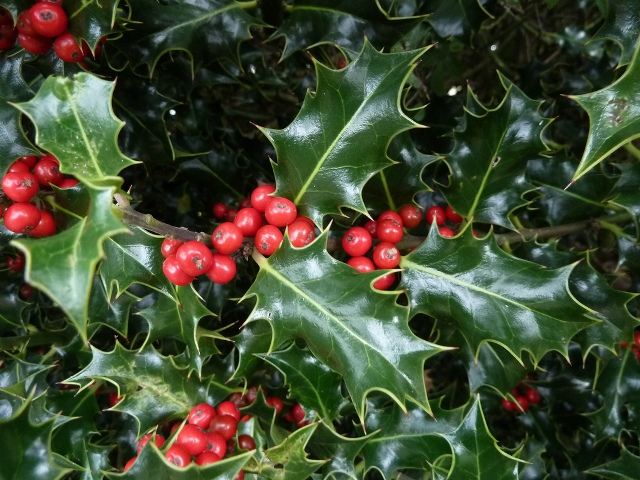

The shrub gets on well on clay and sandy soils. The most common species - holly gold-leaved - can grow even in semi-shady places.
Climbing Hedge
The fence, twined with bright greens, looks very beautiful. Agree, to admire ornamental climbers, but if they still bloom at the same time, no doubt more pleasant than contemplating a concrete or brick wall. And if on the contrary, your fence has long been worn out, and there is no time to repair it, then you can disguise it with plants.
Wild grapes
In the design of many suburban areas used wild grapes.
This is so convenient option in terms of low cost financial, labor and time. The plant is unpretentious, it propagates easily, and the whole care consists of summer watering and garter lashes, which can be up to 20 m long.
The wild grapes have very beautiful leaves - dense and large, as if collected from five small pointed leaves. In the summer, your fence will be saturated with green color, and with the onset of autumn it will be covered with an indescribable beauty of purple.
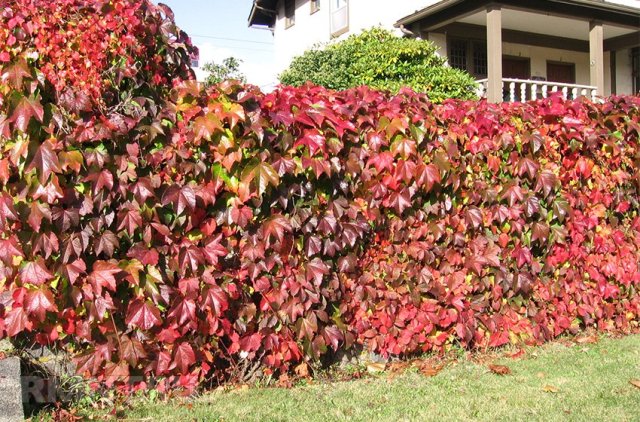

If you plant wild grapes at the beginning of spring, by the end of this fall season, its whips will already reach 2 m, and a year later it will braid the entire area allocated to it.
Both the sun and the shade are suitable for him; it bears normal winter frosts (-35-40 degrees).
Climbing Rose
Bright colors and abundant flowering will give your fence a truly fabulous look. The rose, of course, is more demanding to care than wild grapes. It must be periodically watered, fed and trimmed, but worth it. Especially if you plant a variety that blooms throughout the summer. Roses love the sun, and in the winter they must be covered with spruce or polyethylene.
Campsis
You will get a very beautiful fencing of a plot with such an ornamental plant. Campsis loves light, heat and watering. But with its stunning tubular flowers of bright orange, red or crimson color, it will delight from June to September.
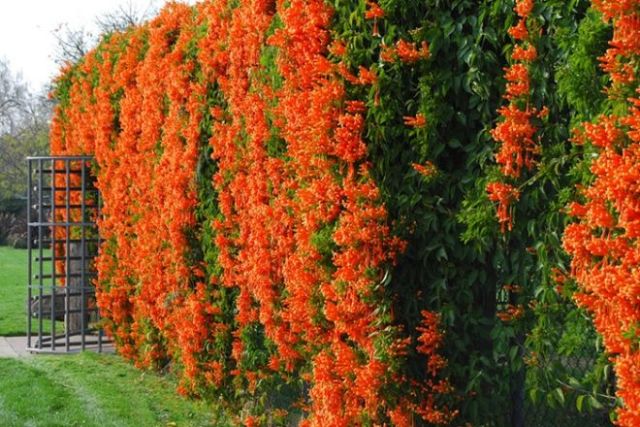

It is necessary to trim it in time, because the lashes can grow to a length of 15 m. In winter, you need to properly cover.
Plants for hedges should be selected in such a way that they fence off your territory, but do not penetrate and grow in the neighboring areas.
To protect your dacha territory from the outside, choose options for shrubs with prickles. Let some people scare, someone already and not crawl through. The fence will turn out impassable and will protect a site from vagrants and animals.
If you plant not only ornamental shrub, but also fructifying, you will get, in addition to the beautiful appearance of the fence, a generous harvest of berries from which you can make preparations for the winter.
Since I am engaged in landscape design and participate in the creation of a generic ecovillage, the main purpose of my trip to the seminar was the opportunity to learn how to create living bodies of water with a sustainable ecosystem. Clean, living water on the site - a very hot topic today, I will say without exaggeration, for all. Right, my goal was not achieved, but I got a lot useful informationto fill in the gaps in the question of interest to me. Frankly, the informativeness of the current seminar surpassed the trip to Holzer in 2008.
It is understood that before starting to create a reservoir, you need to know the location and depth of groundwater in the area. And, as shown by the practice of 2 workshops (Kherson and Kiev), due to the peculiarities of the relief, not all areas are favorable for the creation of reservoirs. Fortunately, Holzer collapsed as an all-powerful wizard-mage capable of creating lakes in any terrain. He remembered his wise words, which he very often and with humor repeats: “You can’t stupidly copy anyone, even me, think with your head, for this God gave it to us, you need to find solutions yourself and try to do everything, only in this way you will get your own experience ". Personally, I have such an attitude of respect, although many at the seminar, as well as I, waited for ready-made solutions. Holzer’s ability to find a way out of seemingly hopeless situations also amazed me.
But back to the seminar. Initially, the task was to examine two sites of eco settlers in a village. Bugivka is great, to assess the possibilities of their further development and, if conditions of the terrain permit, to create lakes.
The survey of the first Boris site showed the result of many years of intensive plowing of the earth: soil depletion, practically no humus layer, oversaturation with mineral fertilizers, the prevailing presence of wheat grass in the soil cover. According to the owner, about 1,500 trees were planted on the site, of which only a few survived, and they do not give an increase due to the fact that every spring they are eaten by hordes of weevils and May beetles. Generally, a complete imbalance.
Then, Boris showed us an attempt to create a reservoir that was 1/3 full, but the water was gone, and this cooled the enthusiasm of the creators to take further steps. Holzer asked the site owner in great detail how he made this lake, how deep the groundwater was, what its capacity was, how he planned to fill the lake with water and maintain the required level. Boris explained that the water was poured with a normal hose from a well, which is located near the house. The flow capacity was obviously not enough, and Holzer advised to use the already existing pit, modify it a bit and make a separate well for more intensive water filling.
The landlord had the idea to fill his own lake, making a water intake from the common stock in the village using a pump pump that Holzer uses in his farm. And we went to watch this rate, and at the same time, to explore the surrounding area. The distance from the lake to the lake turned out to be rather big, according to my calculations, at least 500 meters, besides, the slope is down and the water would have to be pumped up. Plus, plumbing would have to pull through someone else's site. On the road, near the rate, we found a local landfill. Holzer’s summary, taking into account all these factors, in my opinion, was logical: it was not rational to use this method of filling in all respects, and most importantly, the likelihood of contamination of the water of a public reservoir with pathogens and toxic substances from the landfill. Holzer said that it is always more profitable to have all his own, autonomous, Boris agreed and accepted the option of filling the lake from a new well.
To create a sustainable living lake, Holzer named several mandatory parameters: the amount of precipitation should be not less than 600 mm per year, the depth of the lake - 10–12 m, the filling of the lake from an external source - 2 l / sec. And one more interesting nuance. For me personally, it was news that not all the water reservoirs created by Holzer he shake the whole bowl of the lake with the help of an excavator. As I understood, he pre-fills the bowl with water and watches if there is a leak, pour 1 l of milk into the water at the place of the alleged leak. Since milk does not immediately dissolve in water, the place of the fistula can be determined from its flow. And it is precisely this place that he carefully stamps.
Then Holzer talked with the landlord about his vision of the development of the territory. Boris explained where he planned, said that he did not need many fruit trees. To which Holzer replied that it was necessary to think ahead and about everyone. If you feed the soil animals, insects, small animals, birds, in the end, people passing by, this harmonious ecosystem will emerge, where there is no need for constant human intervention. That's why our little cottages suffer and household plots from the invasion of diseases and the so-called pests that we conquer their native lands from them, we think about meeting only our own needs, we grow a monoculture, and we forget about other inhabitants of our planet. Holzer thinks about all.
He suggested that the landlord should plant not just a hedge around the estate, but create an edible forest - an integral ecosystem that will help stabilize the situation throughout the territory.
Since there were a lot of ants and aphids in the surveyed area, then, of course, Holzer had many questions about this. Muravyov Holzer is very respectful and considers nature sanitation, they, like any living creature in nature, have their own mission, which they conscientiously carry out. It is very often possible to observe how countless ant colonies are found on depleted lands. It would seem that what are they doing there? It turns out that with their waste products, they prepare the soil for plants that master degraded soil after wheat grass. Well, they love sweets, so they breed aphids.
So, so that they do not attack our seedlings of fruit trees, pampered in nurseries alone, planted among the wheatgrass, you need to plant a more vigorous elder tree over them and plant a lot of blooming siderats so that the ant can taste the sweet nectar. Good here is mustard, which successfully suppresses wheat grass, and oilseed radish, and turtle-dove, and vetch, and sainfoin, and phacelia, and clover, goatling, alfalfa, lupins, on the sands is good clover.
If you can’t manage to make friends with ants, there are natural products in the Organic Farming Club that can contain their populations. Well, Holzer, as a true entrepreneur, does a good business on ant eggs. To do this, he takes the stems of the Hogweed plant (they are hollow inside), one end tightly closes, the other greases from the inside with honey and spreads it on the ground. After some time, the ants begin to colonize these "houses", and, of course, lay eggs. Then Holzer periodically shakes the eggs from the trunks and sells them to pet stores.
According to Holzer, the aphid is also not a pest, but an assistant plant. He believes that at certain moments in plants there is an excessive pressure of juices, and aphid contributes to the fact that, by opening the pores of the leaves, it lowers this pressure (just like leeches for humans at the time of hypertensive crisis). And in order that it does not hit our lonely landing, you need to create biodiversity in the areas. In this regard, supporters of the idea of creating Family Houses in a more advantageous position, since the size of the area of 1 hectare already allows you to place a sufficiently large number of plants on such an area and create a sustainable ecosystem.
By the way, Holzer himself has a great respect for the enthusiasts of creating Family estates and Family eco-settlements, said he is ready to help with all the means available to him. According to him, what he saw in Ukraine, the former breadbasket of Europe, struck him unpleasantly. Only in one settlement near Zhytomyr, he saw a decent layer of chernozem, into which no one will stick, will grow. In the rest of the places there are often degraded soils overgrown with wheat grass. He said that the creators of ancestral estates, thus, doing a very important thing for the restoration of nature.
There is another important point. When an ecovillage is created in areas with depleted soils, the creation of its own lake in each estate is of great importance in the matter of restoring the land and, especially, restoring the water balance. As Holzer explained, the degraded land is a sponge. Rain is not enough to sate this sponge. And when each hectare has its own stable source of moisture, the earth begins to absorb it very intensively, and at a considerable distance from the reservoir. At some point, the saturation of the soil comes and, in parallel with the process of restoring and structuring the soil surface, water balance is restored, which is very important for the ecosystem as a whole.
Further, Holzer suggested that the workshop participants apply their knowledge in permaculture in practice and create projects for the sites under consideration. It was interesting to me, although time, of course, is not enough for such a global task. In my free time I investigated additionally the site of Boris and the adjacent territory and discovered interesting things. If weevils and May beetles were literally naked around the young leaves of oak and birch trees planted by the owner of fruit trees, then they absolutely did not touch the ash, birch bark, silvery loch and pine growing on the adjacent territory.
I thought that the restoration of the ecosystem and need to start with the planting of these plants. The elder tree is also well suited for this purpose (it is unpretentious, it grows quickly, a good soil conditioner, protects other trees from ants and aphids, attracting them, scares off mice, you can get a lot of mulch and firewood, breaking off old branches, it only grows better) . Elderberry can be used to make hedges, in my opinion, this is the first and unique assistant in the process of restoring degraded lands. Also good svidina (white drayne, unpretentious shrub, it is widely used in gardening and strengthening of ravines), an euonymus, which foresters everywhere used to plant along with young saplings of trees on clearings. He is also a good advocate for plants, taking on invasions of the spider moth. These are frame plants, with the rest you can improvise, creating diversity on the site. I checked all this on personal experiencein his estate. Even in windy open areas, it’s good to leeward on the leeward side, north and west to fruit trees as a “nurse”, the same elder bushes.
Because of the lack of time, I did not manage to put these recommendations in writing, but I drew a rough draft, I hope that he got to the landlord.
Then there was a view of the second section. It turned out to be more difficult, but also more interesting. It seems that they did not plow it for a long time, and the soil cover has already recovered quite well. Pyrey grew only along the upper border, from the middle of the plot to the end of the lower boundary, a variety of meadow herbs began: thyme, mother, sage, clover, St. John's wort, asparagus, mullein, wormwood, bells, tar, cereals and many other plants. When we approached the lower boundary of the plot, we saw a large number of rather deep ravines. Holzer somehow became wary, and then was delighted with what he saw. He admitted that this is the most interesting thing he saw in this area, and we went beyond the territory of the site to explore the ravines.
It was an educational trip. Holzer, accustomed to running through his mountains, showed here an example of endurance. We had to overcome rather steep slopes. And the ravines were in some places up to 50 meters deep. Some of them were stabilized by vegetation, some are prone to growth. Some were classic heat traps, and it was clear that the plants feel very comfortable in them. In general, the finished permaculture in the spirit of Holzer. I was struck by the healthy appearance of apple-wilderness, the mulberry, the crown of which rose above the edge of the ravine, come up and pick fruits from the top of the tree, very convenient.
The site owners Peter and Elena with children told that this year a stream had formed at the bottom of the ravines. And we went to see him. It turned out that this is already a small river, which began to form a lake at the bottom of the ravines. Holzer was satisfied with the inspection, said that this was a ready-made permacultural restoration project, you need to make only a minimum of effort and cost to stabilize the growth of some ravines.
Someone asked how these ravines were formed. Holzer replied that they were the work of man. Total deforestation, long-term plowing of vast areas, the cultivation of monoculture lead to the disappearance of soil cover, loss of humus. Winds dry up the soil and become as porous as a sponge. There are no trees - there is no one to pump water from the lower horizons, the groundwater goes lower and lower. Rainwater flows to the lowest place, taking with it particles of humus to underground rivers. In such places, the soil becomes loose, like a colander, and in the next rain it starts to simply fall through. This is the beginning of the ravine. With each successive rain, it becomes wider and deeper.
Holzer gave advice on stabilizing the edges of the ravines. All trees that have a deep root system are suitable for this: oak, elm, pear, cherry, ash, bird cherry, cedar elfin wood, juniper, hazel. They need to plant in the walls of ravines at an angle of 45o. If a willow or bird cherry grows in ravines, then you can use this method of strengthening the walls: we pre-prepare the rasp, press the branches of the growing tree (bush) to the ground and fix them with the rattles. Thus rooted branches of all types of willows, except goat, bird cherry. If the willow in the place of interest does not grow, you can do the following: cut the cuttings of the desired type of willow at the end of the vegetative period (November, December, beginning of January) on a decreasing moon. We transfer to the places where we will carry out the landing, and fold right on the ground. To land in the month of April on the growing moon.
Also, to stabilize the ravines, you can use all climbing and creeping plants: ivy, grapes, hops, kiwi, actinidia, blackberries, dereza.
Returning to the site of Peter and Helen, they began to discuss the plans and vision of their family for the development of the territory. Regarding the possibility of creating a reservoir, Holzer expressed his doubts and advised Peter to find a geodesic specialist who would make him a detailed map of soils and groundwater. To which Peter replied that he just had such a specialist recently and made such a map. Having examined the map, Holzer confirmed the danger of creating a lake, since there was a tendency to instability of the ground and the growth of ravines.
When the needs of the family were identified, the decision arose to create a protective shaft around the site from the side of the road, and Holzer and Peter went to direct the work of the excavator. The practice finally began and it was very interesting. Our Soviet uncle still began to be stunned by the task assigned to him, but we give him his due, he did not refuse to work, and with diligence and a stream of untranslatable expressions he took to remove the first layer of Pyreyevoi turf. When it turned out that the shaft should be in the form of a miyandra, i.e. a bent, accustomed to thinking straightforwardly a representative of socialist reality, gave a new batch of untranslatable verbal flow. It turned out that, nevertheless, the capitalist principles of the present reality are a good stimulus for the development of thinking, and the excavator operator successfully began to master the new process of work. The case went, and Holzer at the end even expressed his gratitude to the excavator operator for his diligence.
In fact, according to the technology, it was necessary to remove the turf with layers and turn it upside down in order to block the grain and air from accessing air and light. But the soil turned out to be too dry, so it was crumbly and the technology was not fully observed. In some places of the shaft, wheatgrass bundles stuck out and it had to be finished manually. Despite this, the result of the work turned out to be impressive - the shaft was almost 100 meters long, the base width was from 5 to 6 meters, and the height was 2.5 meters. At a height of 1.0 - 1.5 meters from the ground begins the terrace, the width of the base of which is 2 meters, on the sides of the track, 1 meter wide on each side of the shaft. The height of the upper shaft is 1 meter from the base of the terrace, the width of the shaft apex is 1 meter. The slope of the slopes of the shaft - 65o.
It turned out great noise and windproof barrier. When the group was standing on one side of the shaft, and the excavator was working on the other, there was almost no noise. In addition, heat traps formed in the bends of the shaft from the site. In the future, the shaft will also become an edible forest.
The next stage was to be planting and sowing plants on the shaft (if possible, mulching with straw-hay and fixing it with branches), but the seminar time came to an end, and the owners of the site had to implement this stage independently. Holzer gave his recommendations for planting: at the base of the shaft on the inside — melons, pumpkins, zucchini; on the slope - vegetables, berry bushes at an angle of 450; on the first terrace - apple trees and other trees with a shallow root system; At the very top of the shaft are plants with a deep root system: oak, pear, cherry, etc.
In between the processes of managing the work of the excavator, Holzer’s implemented projects in different countries were reviewed, he presented us with new projects that he dreamed about in a dream. The works of the participants in the workshop on the development of Peter and Boris sites and the possible use of ravines were also presented.
Finally, we persuaded Holzer to hold a master class on colonization of tree stumps with mycelium. A group of enthusiasts brought from the ravine a fresh-minted trunk, in my opinion, willows, 30 centimeters thick (for this case only non-coniferous trees are suitable!). Chainsaws were made cuts along one side of a tree trunk, about 15 cm long, 2 centimeters wide, 5 - 6 centimeters deep, every 30 centimeters. Then from the opposite side in a checkerboard pattern. Mushroom saw cuts fill preferably tightly to failure. If it is not enough, the remaining space is filled with a spike, well tamped so that there are no voids. The filled cuts are sealed, preferably with paper tape, which is additionally secured with a steepler.
Everything, the log is stuffed with mycelium, it remains to bury it in a vertical position, in a shady, damp place as it grew in nature (lower part - down, upper - up), moisturize it regularly and after 2 - 3 months start to reap the fruits claims Holzer, for 8 to 10 years. Sometimes it happens that the mycelium for some reason stops and does not begin to germinate. Holzer discovered an original way of her awakening many years ago: dig the log, put it horizontally and knock it with an ax butt first from one end of the log, then from the other and dip the log into the water for a day and then bury it again in the ground. It turns out that not without humor the meter told us, thus, a thunderstorm with torrential rain is simulated, and this is a signal for mycelium to intensive reproduction. And another advice from Holzer for those who happen to be irregular in their own area, in the dacha mode: in order to keep the log constantly moist, you need to put a plastic container with water and a hole in the bottom on it drip irrigation. Here is an inventive fellow revolutionary agrarian.
And at the end of my story, I will give Holzer's recommendations on the development of dusty areas, because of relevance this was question number 1 throughout the workshop. It all depends on the size and intended use of the plots. If this is a small area, you can remove the prairie turf on both sides of the conditional bed and fold it upwards with an envelope on the bed. It turns out the alternation of raised ridges with spruce-free between rows (say, 1 meter bed, 1 meter between rows). Thus, “civilize” the entire plot and quickly sow it with sideratami. You can on the same principle to make a series of high ridges. You can muffle the growth of wheatgrass powerful plants that are much higher than it and create a good shade. These are sunflowers, Jerusalem artichoke, corn, white clover. If the plots are large, then you need to apply the technique.
I'd add: procut cutting the ground and sowing rye or mustard, for several years in a row. Only after harvesting these crops, it is possible to plant or sow other plants no sooner than three weeks from now, since they release substances into the ground that inhibit the growth of not only wheat grass, but also other plants. An experienced agronomist told us that in this way he cleaned his plot from all unwanted plants and sowed mustard strips around the perimeter of his plot each year to prevent weeds from getting to his neighbors. I personally found another solution - I like stationary hemmed beds, well mixed up. And in the rows between them, there is growing wheat grass, which I greatly respect, other plants, they continue to do their own work of restoring the land, and I periodically mow and polish them the beds, no need to do extra work on planting siderats.
Well, and at the very end, recommendations for those who have ground water close to the surface. One of the participants in the seminar bitterly addressed this problem to Holzer. His reaction was, of course, interesting. He, as always, saw this as an advantage, not a problem. He said that the big problem is when the water is very deep. And ... with great joy, I advised this woman to create a water garden. With the help, again, of an excavator, to make high ridges, and between the rows where the ground will be taken out, channels are formed, filled with water. A garden, a vegetable garden are planted on the ridge, ornamental plants. Aquatic plants, fish, crayfish, and waterfowl are grown in the canals. As always, the permacultural approach - everything grows by itself, artificial watering is not needed, just sit down and pick it up.
That was such an informative seminar. Of course, something else could miss, not to hear, not to glimpse, not to understand. I hope that other participants will also provide their feedback, and then the picture will become more complete.
If you decide to make such a decoration in your yard, then you need to determine the goals of the fence, its location relative to the sun and other factors, as well as its shape. After all, it can be free and grow in all directions. And there is one that needs to be shaped, cut and customized to a certain size. Therefore, it is important to choose the right type of plant that will perfectly cope with all your requirements.
Caliphen bladder
This bush has excellent characteristics for those who want to plant their land as soon as possible. resistant to diseases, tolerates frosty winters and, most importantly, these plants for hedges - fast growing. grows immediately in all directions. Its branches are covered with dense foliage, which looks like maple leaves, as well as currants and viburnum. The leaves have a very beautiful and unusual texture. In late June and early July, the plant blooms. Its inflorescences are umbrellas from a variety of small flowers, which densely fill the already dense branches.
Did you know? In one year, the plant extends its branches by 40 cm.
The shape of the crown can be formed independently or allow it to grow in all directions. Standard bush has round shape. Some landscape designers form fountains or square low fences. The height of the bush and its width - up to 3 meters.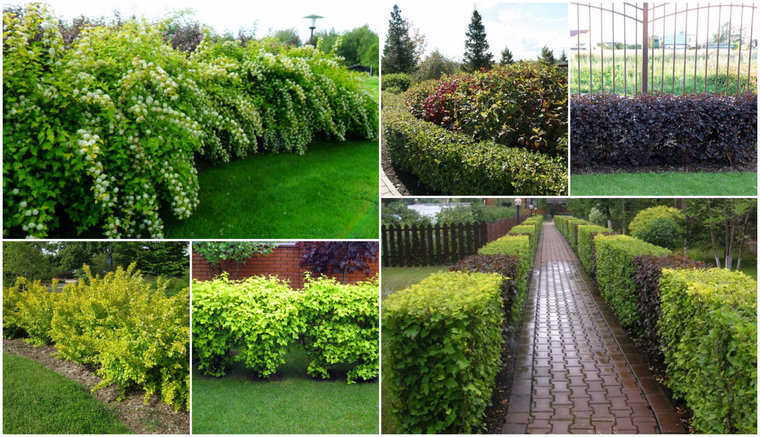  Pruning plants should be carried out regularly, eliminating it from the inside of growing, dry and diseased branches.
Pruning plants should be carried out regularly, eliminating it from the inside of growing, dry and diseased branches.
The best time for this is the end of autumn or the beginning of spring, when the severe frosts were already asleep. It is important to do this at the moment when the juice on the branches has not yet gained their usual speed for the warm season. Then you do not damage your plant. To create the shape of a bush, preferably in spring.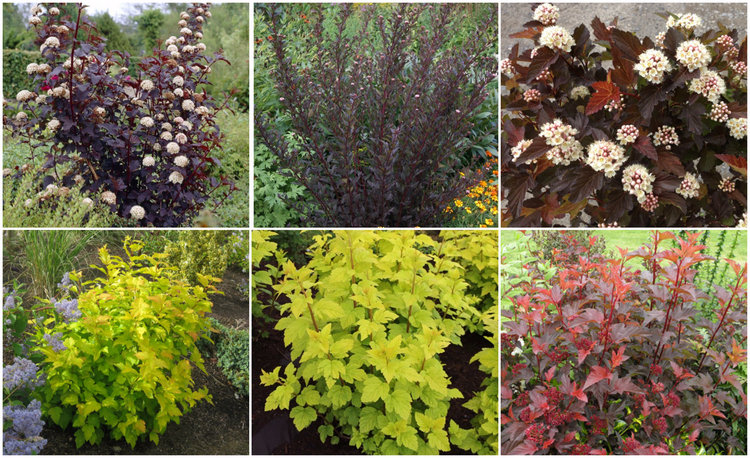  It is worth noting a variety of varieties. They are radically different due to foliage color. She may be:
It is worth noting a variety of varieties. They are radically different due to foliage color. She may be:
- purple color, which may change to red in the autumn period ("Diabolo", "Little Devil", "Coppertina");
- yellow with a golden sheen (Darts Gold, Lutheus);
- the sheet has two colors at once: gold and burgundy ("Center Glow").
There is also a dwarf variety "Nana", which is painted in juicy green color and decorated with bright white flowers.
Thuja
Boxwood
Everybody knows this bush. is he perfect for hedge:
- not bad transfers winter frosts even without warming;
- has numerous branches with small shiny leaves;
- evergreen shrub;
- allows you to create any form.
 When choosing a variety, pay attention to the height of the bushes, because some of them may be. There are varieties that allow you to raise a fence wall of green leaves and a half meters. Some bushes that do not mow, being in a favorable warm area, grow up to 3 m.
When choosing a variety, pay attention to the height of the bushes, because some of them may be. There are varieties that allow you to raise a fence wall of green leaves and a half meters. Some bushes that do not mow, being in a favorable warm area, grow up to 3 m.  Ideally, hedge trimming is a regular procedure that is held every sixth week after the first of May. Then the bushes will look well-groomed and beautiful.
Ideally, hedge trimming is a regular procedure that is held every sixth week after the first of May. Then the bushes will look well-groomed and beautiful. It is important to make the first haircut correctly, on which the subsequent growth of the bushes depends. It is made in the first year after planting the sapling.
Important! The first time pruned immediately half of the bush. This is a real signal for the plant, after which it begins to grow much faster.
 Unfortunately, in a year you will not grow an incredibly large bush. This process is slow. Therefore, in the form of a seedling is better to buy already adult plant three years old and better than eight years old.
Unfortunately, in a year you will not grow an incredibly large bush. This process is slow. Therefore, in the form of a seedling is better to buy already adult plant three years old and better than eight years old.
Cold-resistant varieties have bright green leaves. Variants with other colors are suitable for warm regions.
Hawthorn
This bush is ideal for hedges. He lives about 300 years. It does not have high requirements for care or weather conditions. Some varieties, however, do not tolerate the winter. Therefore, when choosing is worth paying attention to this item.  Most popular options to form a hedge:
Most popular options to form a hedge:
- Ordinary. The average length of the spines is up to 2.5 cm. The height of the bush can reach 8 m. It can grow in the shade, but differs in a rather slow growth process. In August, gives a beautiful red berries.
- Softish It tolerates frosts down to -30 ° С, quite tall bush with long spines gives edible fruits.
- Arnold. This species tolerates not only frost, but also drought. Differs in fast growth and sweet fruits.
- Fan-like. The height of the bush is up to 6 m. It is distinguished by very long spines.
 Did you know? The fanlike form of hawthorn has spines, which are up to 10 cm in length, which is why they are uneven and slightly twisted.
Did you know? The fanlike form of hawthorn has spines, which are up to 10 cm in length, which is why they are uneven and slightly twisted.
From this plant you can make a beautiful, dense and thick the wall.
 Planted better three-year seedlings in a checkerboard pattern. After the first two years of life, the seedlings in your garden should be strongly branches, leaving 20 cm. The bush will give more new branches and thickens. Time for pruning - spring warm days in late April. Then you need to wait a year, after which proceed to the correction of the form, pruning extra branches. Haircut can be done from spring to autumn. Plant growth - 30 cm per year.
Planted better three-year seedlings in a checkerboard pattern. After the first two years of life, the seedlings in your garden should be strongly branches, leaving 20 cm. The bush will give more new branches and thickens. Time for pruning - spring warm days in late April. Then you need to wait a year, after which proceed to the correction of the form, pruning extra branches. Haircut can be done from spring to autumn. Plant growth - 30 cm per year.
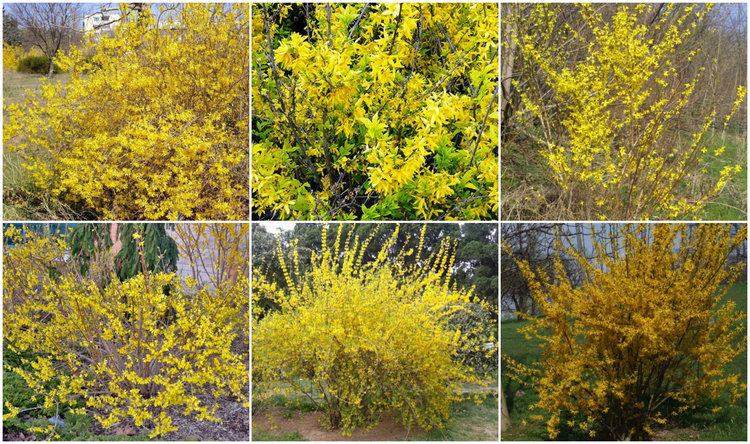
Amazingly beautiful plant, it is desired by every gardener. After all, this is a true herald of heat. This bush is the very first to cover golden inflorescences its branches in early spring, which seem to shimmer in the sun. The time is April, and for the south it is the beginning of March. The plant pleases with its solar beauty for almost a month. The bush also differs in its shape, because each branch is long, thin and elegant.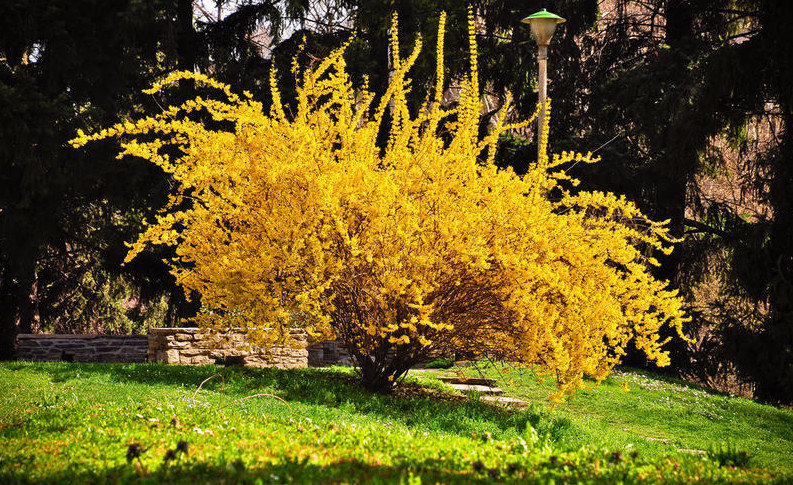  Suitable place for - warm and sunny, without drafts. Shadow will be reflected in weak flowering. Forsythia is variable in terms of resistance to frost: strong frosts can destroy the young twigs, on which flowers form. Therefore, in the winter they need to be closed. But she likes aridity more than strong watering.
Suitable place for - warm and sunny, without drafts. Shadow will be reflected in weak flowering. Forsythia is variable in terms of resistance to frost: strong frosts can destroy the young twigs, on which flowers form. Therefore, in the winter they need to be closed. But she likes aridity more than strong watering.  Haircut should be done carefully, because abundant circumcision will not lead to anything. You simply remove all the young shoots, and you will not see the golden flowering in the spring. It is necessary to make the necessary bush form in June, when the flowering period is completely over.
Haircut should be done carefully, because abundant circumcision will not lead to anything. You simply remove all the young shoots, and you will not see the golden flowering in the spring. It is necessary to make the necessary bush form in June, when the flowering period is completely over.
For hedge design fit these:
- european and Giralda are the most resistant to frost;
- the greenest has the largest flowers, but does not tolerate the winter and is suitable for the southern regions;
- oval leaves;
- drooping
- average winters without loss.
 Important! Fertilizers are important for forcingia: organic fertilizers are applied in autumn, mineral fertilizers are introduced in spring. And also - pruning, which is carried out every year. Without these actions, the bush becomes very weak.
Important! Fertilizers are important for forcingia: organic fertilizers are applied in autumn, mineral fertilizers are introduced in spring. And also - pruning, which is carried out every year. Without these actions, the bush becomes very weak.
Privet
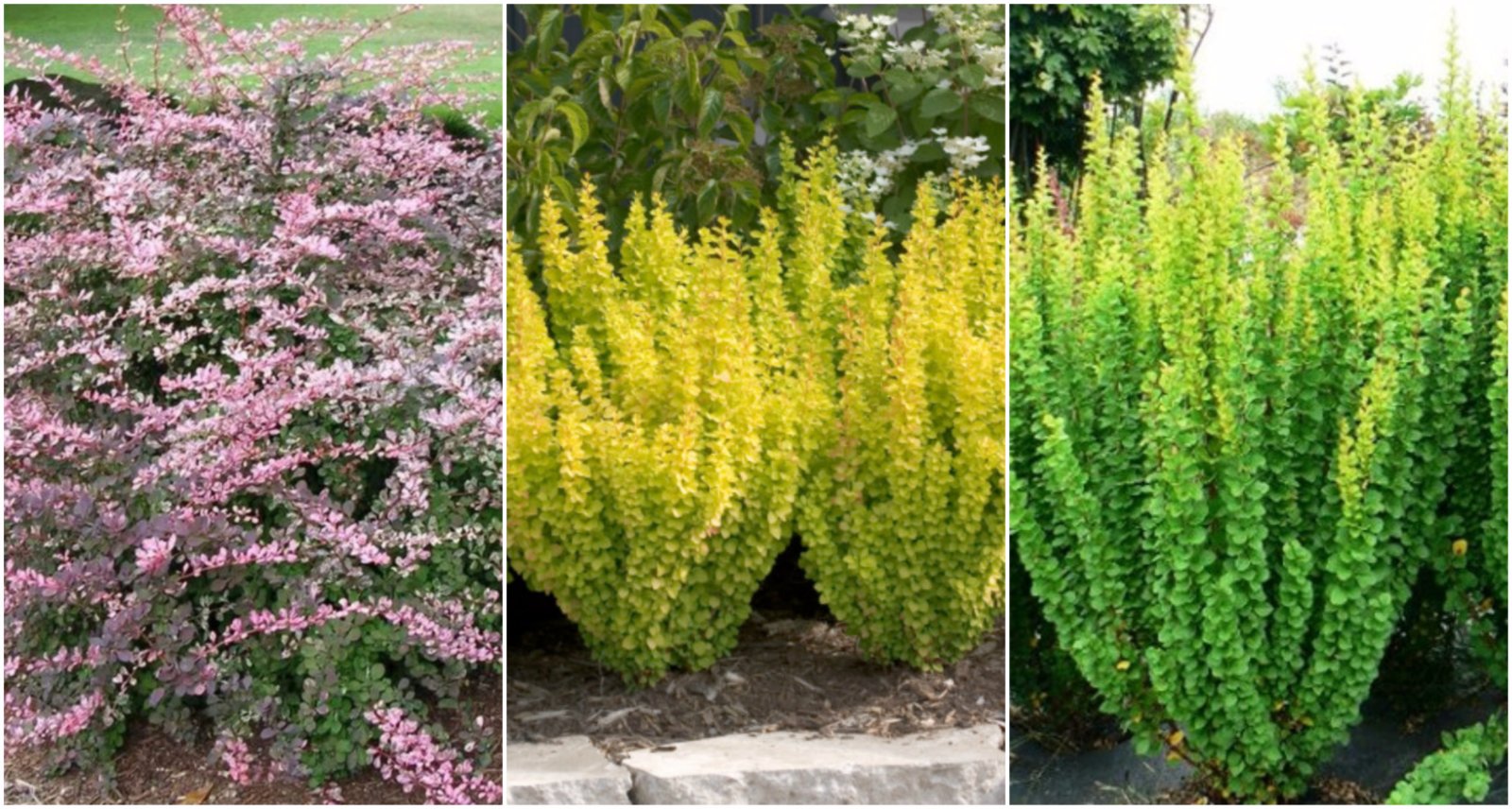
- "Kobold" - a spherical bush not higher than 30 cm with green bright leaves, which become yellow-orange by autumn;
- “Bagetel” - round shape, not higher than 40 cm, has red leaves, which, when growing in the sun, are cast in brown, and in the shade - in green;
- "Admiration" - grows into a ball with a diameter of 50 cm and has a unique foliage, which is purple inside, and at the edges has a bright border;
- "Hastened Gold" is a thick golden crown that turns pink in autumn;
- "Atropurpurea Nana" - a purple-red bush, up to 60 cm high, 1 m wide;
- "Green Carpet" - does not grow above 50 cm and has light green foliage in a rounded crown.
 For high vegetable fence:
For high vegetable fence:
- "Pink Queen" - in the sun leaves turn pink with light and dark strokes;
Was this article helpful?
Well no
Hedges never lose popularity, despite the variety of modern fences. Thanks greenery, the site takes on a very cozy look and special atmosphere. At such a dacha even breathed differently, and all negative emotions disappear without a trace. It is not at all difficult to make a hedge in a country house on your own, the main thing is to choose the right plants and get acquainted with their agricultural techniques.
As the green fences used a variety of plants, differing in height, shape of the bush, colors, density and other criteria. Depending on the height of the plantings, there are three types of hedges:

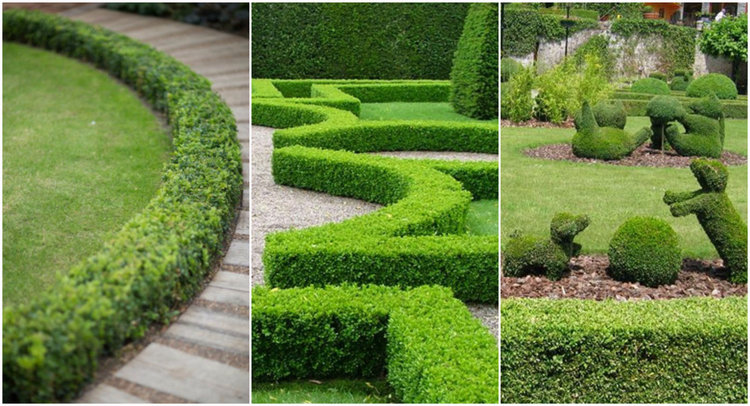
The shape of the bushes, and hence the entire range of plantations, is directly dependent on pruning. Here, too, there are two types of hedges - freely growing and molded. The first view does not require special care and shape correction, bushes grow arbitrarily. This option is best suited for summer residents who prefer natural landscapes. The second type of plantings requires mandatory regular pruning, through which the bushes are given a geometric shape. Such fences look very neat, give the original look of the whole territory.
Another parameter for classification is the rows of plantations. The simplest type of fences is single-row, when all the plants are planted in a row at equal intervals from each other. For small bushes, this interval is 30-40 cm, for bushes with a wide crown - from 50 to 75 cm, for trees - up to 1.5 m, depending on the species.
In the two-row hedges plants are planted in a checkerboard pattern, given the factor of growth. All other multi-row stands are formed according to the same principle, but with one difference: each subsequent row should be higher than the previous one. With such a stepped arrangement, the plants do not block each other, and the whole composition is perfectly visible.
Multi-row hedges require a lot of free space, so they are not suitable for small areas. Also, do not deal with them for beginners, because there will need a lot of experience and skills. It is very important to choose the plants according to the color range and density of the bushes so that the overall composition is as harmonious as possible. In addition, all species should have similar requirements for growing conditions and get along well with each other.
The combination of plants for hedge
By the appearance of plants, hedges are divided into conifers, deciduous and curly, and each of these types has its own characteristics.
Conifer
Coniferous fences remain decorative all year round. They are unpretentious in leaving, easily give in to formation, sate air with pleasant and curative aroma. Due to the diversity of species, conifers can be used as borders, and as living fences along the borders of the site. They have only one drawback - they grow slowly. Although there are certain types of conifers that can grow much faster than their relatives, for example, thuja and juniper.
| Plant type | Description |
|---|---|
| Evergreen, winter-hardy plant-survivor. It has many varieties of various shapes - spherical, pyramidal, columnar, sprawling and others. The color palette is also quite wide - the bushes are bright green, bluish, bluish, yellow, salad. Exquisite carved needles give a special decorative effect to tue. The plant is unpretentious, perfectly tolerates pruning, is widely used in garden design | |
| Evergreen plant tree and shrub type. In landscape design, shrubs are used predominantly, which grow quickly, are easily restored after trimming, and tolerate shade well. Bushes have a pyramidal, spherical, cone-shaped form of all shades of green | |
| Evergreen cold-resistant trees forming impassable living walls. The first 10 years are developing very slowly, but they practically do not require care, they easily tolerate the formation. There are also dwarf varieties for planting borders, different spherical shape. Needle color ranges from dark green to blue. | |
| Slow-growing durable coniferous plant of a kolonovidny form. The yew is suitable both for borders, and for living walls, practically does not require formative trimming, undemanding care | |
| An ideal plant for hedges. It features a large variety of crown shapes and shades of needles. Pruning tolerates easily, well restored, undemanding of soils. The first 5 years develops slowly, then gives a large number of root shoots, which contributes to the rapid reproduction | |
| Frost-resistant unpretentious plant for free-growing hedges. Pruning does not increase the density of the crown and is poorly tolerated. It develops very slowly, but it is resistant to drought, pests and diseases. The greatest decoration is different during flowering. |
Features of plants suitable for creating a hedge
Show on page View full size
Hardwood
Deciduous crops are deciduous and evergreen. They are characterized by rapid growth, a variety of colors and shapes. Many plants bloom beautifully, filling everything around with a pleasant aroma and bright colors. Such plants are well tolerated pruning, easily restored after shearing, form a dense screen that reliably hides the area from prying eyes. These species are quite demanding on the composition of the soil and moisture, react badly to the lack of sun. When thickened plantings decorativeness decreases, some plants can be drowned nearby and dry out.
| Plant type | Description |
|---|---|
| Evergreen, very ornamental shrub, well-shaped. Ideal for creating live borders, it combines perfectly with any garden plants. The box is unpretentious to the soil, but needs regular watering | |
| Evergreen flowering shrub up to 1 m. In cold regions can freeze. Poor drought tolerance, demanding of moisture, but it can grow both in the sun and in thick shade. The plant is decorative not only flowers but also leaves | |
| Very elegant deciduous plant. Appreciated for the long abundant flowering and ornamental forms of the bush. Rarely grows up to 2 m, it is most often used for free-growing hedges. | |
| Decorative deciduous plant forming an impassable thorny fence. Easily tolerates shaping haircut, retains decorative throughout the season, produces a very pleasant smell during the flowering period | |
| Frost-resistant unpretentious shrub. Most hawthorn varieties have sharp thorns, so the hedge of them is a good protection against uninvited guests. The plant is decorative not only flowers, but also leaves, as well as numerous large fruits | |
Cotoneaster black-fruited | Drought-resistant flowering shrub. It is ideal for creating live fences, keeps its shape for a long time after shearing, has a dense neat crown. The plant responds well to transplantation, blooms profusely, has no demanding care |
Curly
For climbing fences strong supports are needed, the functions of which can be performed by a regular fence. Climbing plants they grow very quickly and gradually completely hide the support under them, creating a thick screen of the required height. If you choose flowering varieties, the fence will look just magical, especially when combining varieties of different flowering periods.
| Plant type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Differs in rapid growth, forms a dense solid carpet of leaves. Hop stalks are easy to direct in the right direction, fixing on the trellis. During the flowering period appear very decorative lettuce-colored cones. The disadvantage of a plant is the loss of its ornamentation at the end of summer, when the leaves begin to dry and fall off. | ||
| Amazingly beautiful perennial vines with a pleasant aroma. These plants need competent care and well-prepared soil. They grow quickly enough, forming a thick dark green carpet with elegant flowers | Garden curly perennial with decorative leaves various shapes and colors. It grows well in the sun and in the shade, it is undemanding to the soil, it grows quickly and creates a dense carpet. It is perfectly combined with other plants, acts as an ideal background for flower beds |
Planting rules for hedge
In order for the hedge to have a neat appearance, it is necessary to properly prepare the site. A place for plantings should be chosen taking into account the growth of bushes, especially if you plan to plant along the border of the summer cottage with the neighboring one. Many plants start root growth, and the neighbors are unlikely to like to clean it from their side every year. Avoiding this will help to dig slate or plastic shields into the ground.
Step 1. Determine the location of the fence and stretch along this line twine or rope. They recede 50 cm to both sides of the rope and dig a trench with a depth of 30 to 60 cm, depending on the size of the root system of the seedlings. The top layer of soil together with the grass is laid aside.
Step 2. At the bottom of the trench is laid first layer of sod, which was on top, and slightly tamped it. The earth taken out of the trench is mixed with organic fertilizers and backfilled, smoothing the surface well. Filling the trench to half, the soil is watered abundantly, and then fill up the rest of the earth.
Step 3. In the soft and moist prepared soil prepare grooves for seedlings. In single-row planting, the pits are arranged in a straight line in increments of 30 to 70 cm, depending on the type of plant. If the landing is multi-row, the wells are staggered at appropriate intervals.
Step 4. Water is poured into the pits, allowed to soak in, then seedlings from pots are gently rolled into the holes, leveled and sprinkled with earth. Carefully monitor the density of the backfill - there should be no voids at the roots. Strongly ramming is also not necessary, so you can damage the weak more roots.
Immediately after planting, it is recommended to soil the soil, and the seedlings themselves should be slightly trimmed to facilitate rooting. Then it remains only to periodically water the plants and timely remove weeds. The most best time for landing - this is the second half of September: root system manages to take root quite well, less moisture is required. Formative pruning is recommended in a year or two, when the bush begins to branch well. The first pruning in early spring, then in the middle of summer, and again - before wintering.
First, remove the damaged branches, and then all those that are out of the general form. A simple pruner is suitable for cutting small hedges, but if the plantations are large, it is more convenient to purchase a special electric pruner, which will save time and provide a better result.
Hedgerow do-it-yourselfers