Curly roses how to seed. Rose climbing
Let's find out more about what a climbing rose is. Planting and care in the open field for this wonderful flower will be discussed in stages in this article. Summer residents and gardeners know that with the help of this type of roses, even the most modest plot can be turned into a beautiful romantic corner.
Climbing rose - a description of the type and features of planting
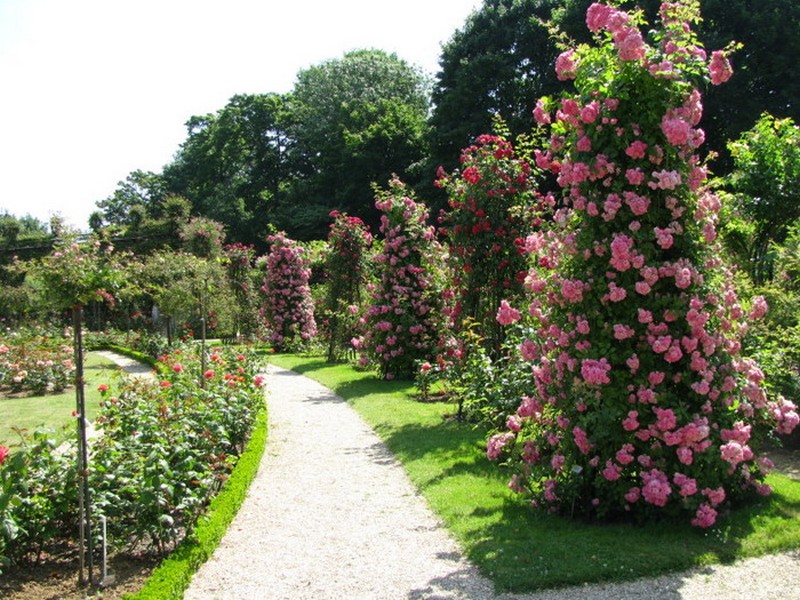
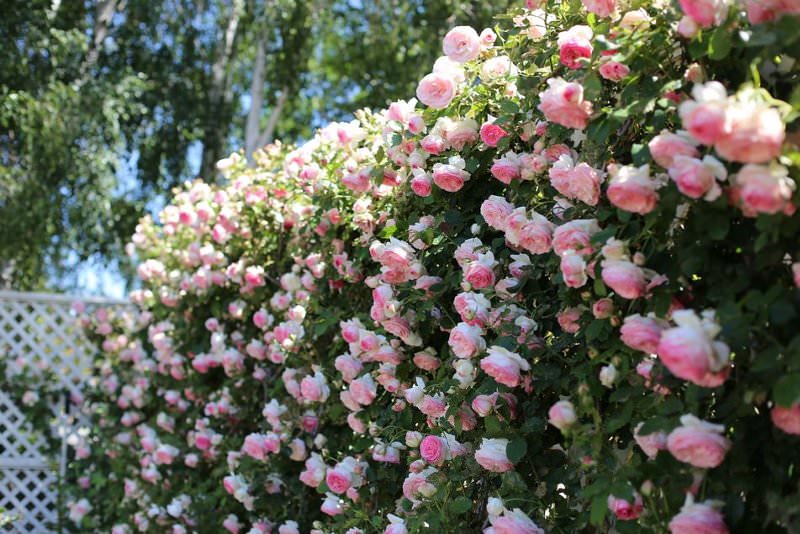
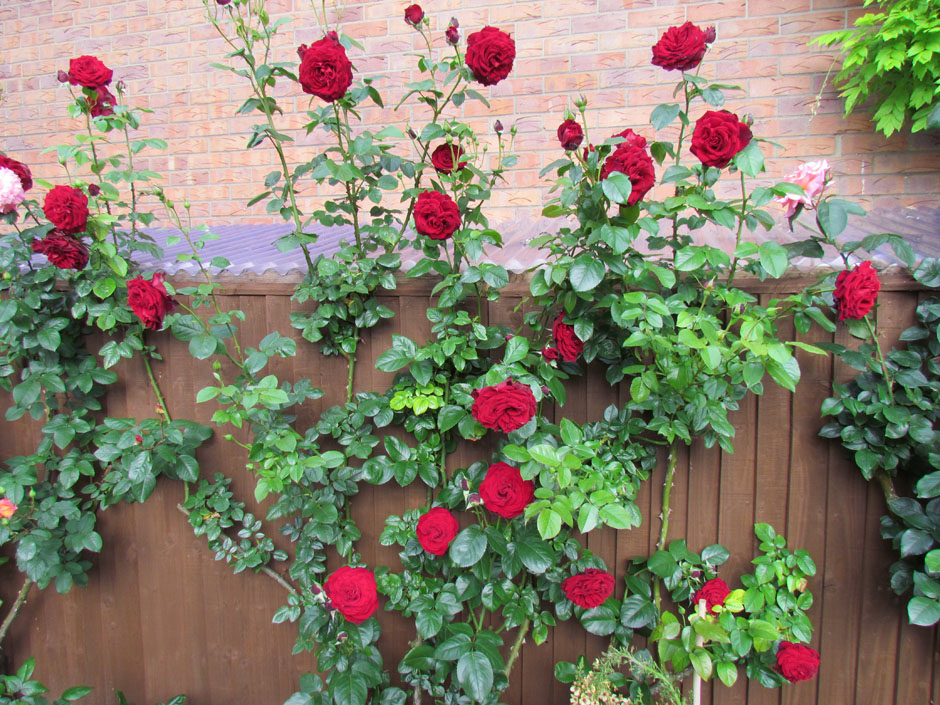
Shoots climbing roses can reach several meters. Any support, located in close proximity to the bush, pretty quickly braided its long and flexible branches. You probably more than once admired the flower arches of amazing beauty. Flower columns, pyramids, lanes, successfully disguised old buildings, part of a wall or roof - a luxurious climbing rose can decorate any garden structure with its presence. This type of plant is ideal for vertical gardening, but in order that everything looks harmonious and attractive, you should know the rules of planting, pruning, care and protection of bushes from pests.
The color range of this type of roses is as diverse as that of their park or ground cover relatives. The size of the buds can be from 2.5 to 12 cm in diameter, varieties of climbing roses bloom in June and continue to bloom as long as the warm season lasts (about 30-170 days, depending on the variety). There are many varieties of climbing roses, but all of them can be divided into groups:
- Polupletistye, whose height reaches 1.5-3 meters.
- Climbing - 3-5 meters.
- Curly - 5-15 meters.
The shoots of these roses are formed continuously, the phases of budding and flowering differ, again, depending on the variety. Among these representatives there is a one-time blooming speciesand re-flowering.
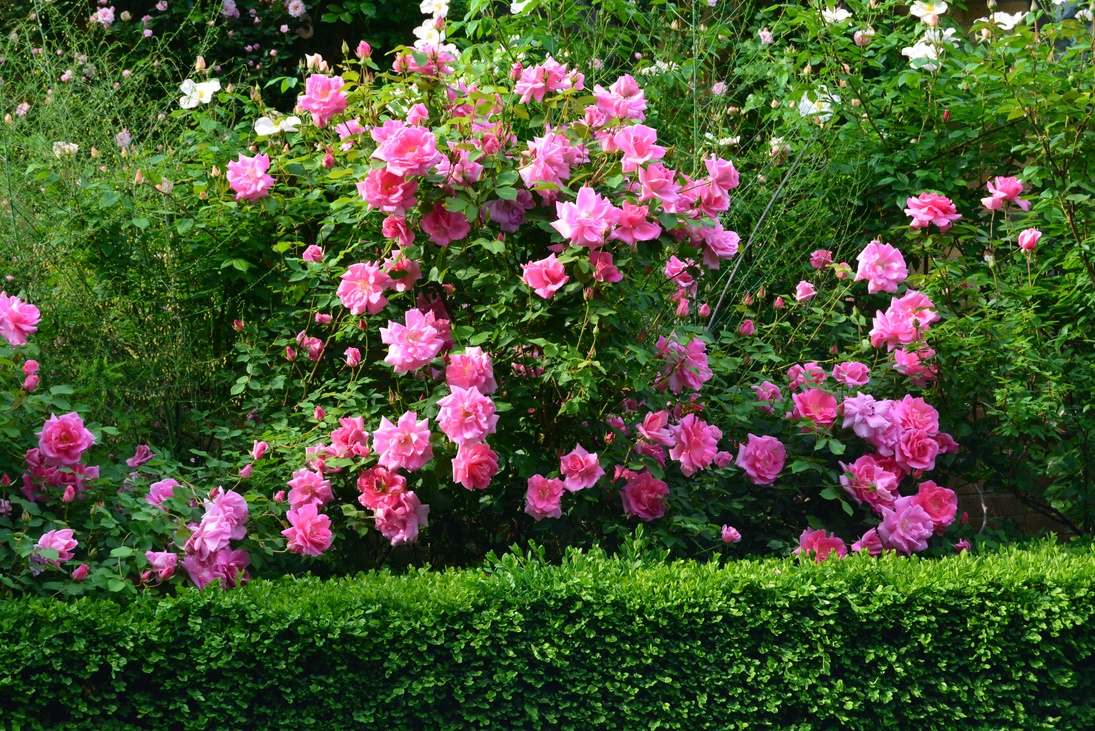
Climbing Rose, a photo:

The buds of individual varieties can exude a pronounced aroma, which is heard from a distance, some fragrant slightly audible, delicate and gentle. This culture will feel great in sunny places with good ventilation. The wetlands are strictly contraindicated, as well as sandstones and heavy clay soil. In general, loose loams or fertile soils with good soil permeability are most suitable for this type of roses. If the soil is not suitable for climbing roses on your site, then be sure to dilute it with a suitable one. Thus, sand is introduced into clay soil, and clay (to a depth of about 30 cm) is introduced into sandy soil; in addition, humus or humus, as well as phosphoric additives should be added.
All land adaptation procedures should be carried out six months before planting roses, or at least 2 months before. Seasoned gardeners recommend planting curly roses where their fellows did not grow up before. If it does not work out differently, then before planting it is necessary to replace the top layer of earth (by 50-70 cm). Ideally, a climbing rose should be planted on a small hill. The root system of these plants goes deep into the ground (up to 2 meters), so you should make sure in advance that the selected groundwater does not pass close to the top layer of soil.
If you decide to “drape” a part of a house wall with a climbing rose, then the distance between the bush and the wall should be at least 60 cm (and at least half a meter from other plants). Most often planting a climbing rose is held in the last weeks of September or in the first half of October. Thus, before the onset of a severe cold snap, the roots will have time to settle down in a new place. With the arrival of spring, all parts of the plant will enter a phase of active development and growth, and by the beginning of summer the rose will bloom in full color. If a climbing rose is planted in the ground in spring, then by this time it should warm up to at least +10 ° C, catch the moment when the buds have not yet dismissed - this is important. The second half of April / the first weeks of May - the most optimal timing for spring planting.
Planting climbing roses in the ground in spring
I will make a reservation right away that the rules of spring planting of seedlings are not much different from those of autumn. All described stages, and also the subsequent leaving, are applied both in the spring, and in the fall. You should be prepared for the fact that the roses planted in spring will lag a little in development, will require you to pay increased attention to your person. Compared with their autumn brethren, they can delay the flowering time by about 10 days.
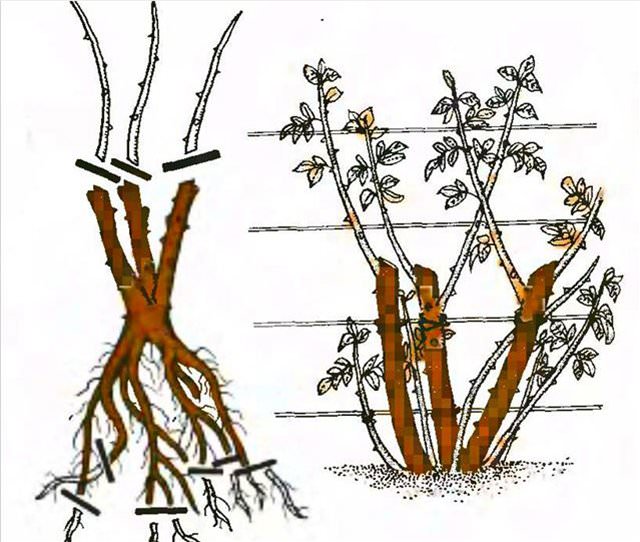
So, before planting the sapling you need to shorten the branches, up to about 20 cm long, the roots - too, up to 30 cm. Dig a spacious hole so that the roots have room to grow. The depth of the pit should be 60-70 cm. If you plant several bushes, the distance between them should be at least 100 cm. When immersing the seedling in the soil, make sure that the root neck is also 12-15 cm deep - this will protect it from frost in the cold season. Roots gently straighten, fall asleep with soil, slightly compacted with his hands. Make sure that all the roots are directed downwards and do not bend upwards!
Planting spring climbing roses involves the introduction of nutrient soil in the hole. About 3-5 kg, for example, a peat compost, will appeal to your rose. After planting, the soil is slightly trampled and watered abundantly. It will be very good if in the water for this first irrigation you add a preparation with beneficial growth-stimulating bacteria, for example, "Phosphobacterin". Phytohormone "Heteroauxin" is also great.
In some cases, gardeners cover just-planted bushes with a polyethylene film - this technique contributes to a better adaptation of plants in a new place. To do this or not to do it is up to you if the weather conditions of your region push you to create greenhouse conditions for climbing roses, then do not forget to lift the film daily and gradually increase the ventilation time every day. After stable, warm weather is established, remove the film and grumble the ground around the bushes with leaf humus, peat, chopped tree bark or straw.
How to plant a climbing rose in the spring, bought in a store?
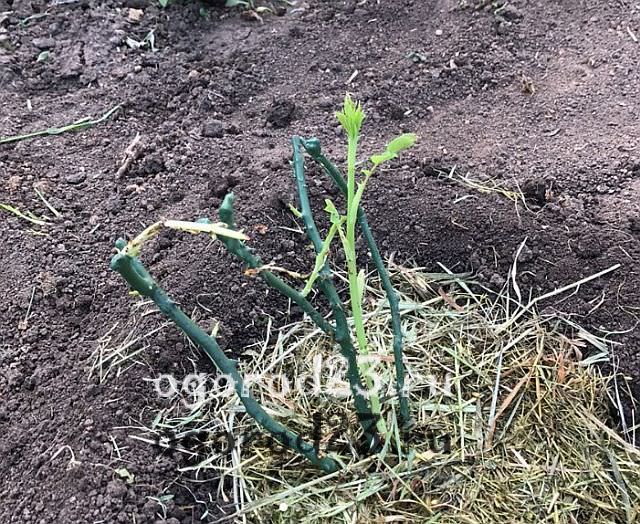

Today in flower shops you can purchase climbing roses with open or closed root system. Representatives with open roots should immediately be planted in the ground. When choosing, pay attention to the presence of lignified shoots - there should be at least two. Such a shoot must be ripe (bend with a crunch), otherwise the rose may not survive the wintering. The bush as a whole should look healthy, have well developed roots, strong, without dried fragments. The length of the shoots must be at least 60-70 cm.
Varieties of climbing roses with a closed root system are sold in pots, so you cannot immediately assess the condition of the roots. Carefully inspect the shoots, they should look healthy, not very elongated, if they have a light green color, then it is better to refrain from buying. The elongation of the shoots and their bright hue signal improper storage of seedlings, either in excessive heat or in low light. Such a rose will be weak, painful, is unlikely to survive the winter. Close attention should also be paid to the sites of inoculations; a properly grafted cutting should have a callus tissue in the place of the “joint” that promotes healing. If the vaccination site peels off and looks unhealthy, then with such a rose you will only have problems.
Planting spring climbing roses from the store, stages:
- A rose with a closed root system is carefully removed from the pot along with an earthy lump, and then planted in the selected location. Representatives with an open root system remove the film from the roots, put them in water. If there are buds or shoots below the graft site, we remove them. If there is a wild growth, we also remove it, too long shoots can be pinched. Do not forget to cut the ground with powdered wood or activated carbon.
- In the water, the roots should be 3-4 hours, so the plant will be saturated with moisture, the transport earth will become soft, it can be easily removed and carefully examined root system. In the water, you can pre-add the stimulator "Kornevin" (according to the instructions).
- We take out the roses from the water, if possible, gently straighten the roots and put the seedling in the excavated hole. What should be a pit and how to mix the soil (if the situation requires it), has already been discussed a little higher. Thoroughly pour a rose water.
- After the water is absorbed, you can pour more earth (spud). When the soil is replenished again, the grafting site can be covered with a layer of soil, but not more than 3 cm.
- If the spring sun shines too brightly, do not be too lazy to cover the young bush with a paper bag or a cloth of light shades - this way it will not burn. Such a protective coating can be left for 5-7 days.
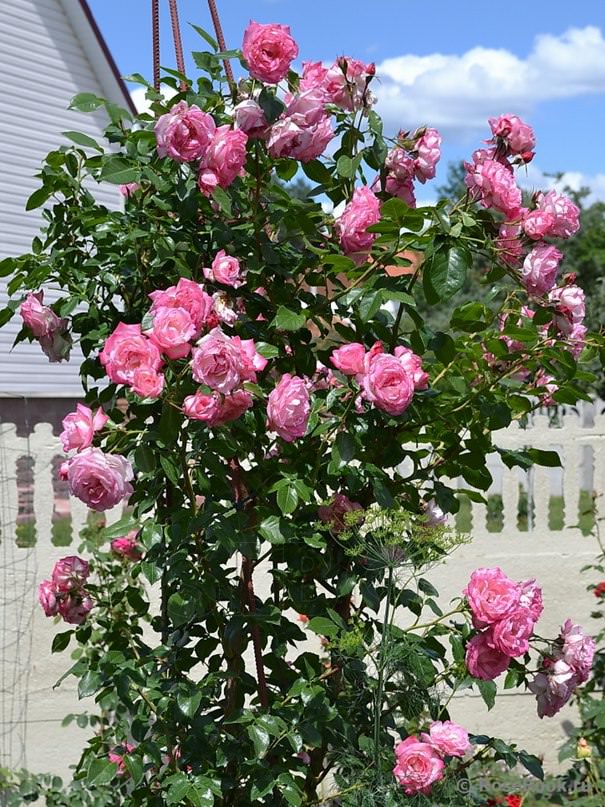
Climbing roses - care and cultivation
In the heat and drought, rose bushes should be watered once every five days. After 20 days after planting, you need to carefully clean the soil from the bush. By the way, roses planted in autumn also open after the winter in the first weeks of April. For this procedure, it is advisable to choose a non-solar day, so that the plant subsequently will not experience stress during the night temperature drop. Ensure that the inoculation area remains approximately 10 cm deep in the soil.
During the growing season, a climbing rose requires generous watering. After the appearance of buds, as well as after the formation of a bush, the plant should be watered every 10 days. At the same time, water should penetrate to the very roots and deeper, 10-12 liters per bush will be quite enough. After a couple of days after rain or watering you need to loosen the soil around the rose. You can also mumble. Over-wetting and lack of moisture are equally harmful for roses, so keep the balance in this matter.
Climbing rose photo:
![]()
How to fertilize climbing roses
Fertilizer is an important step in the care of a climbing rose, because this species is quite demanding to feed. Throughout the summer, nitrogen supplements should alternate with complex fertilizers, they are recommended to be made every 2-3 weeks. With the onset of spring, the plant is fed with a complex mineral fertilizer, for example, Agricola-Rose (according to the instructions). After two or three weeks, you can add organic matter - fertilizer "Ideal" or "Flower". You can also use the old proven method - 10 liters of mullein and 3 kg of wood ash, diluted in 50 liters of water. One liter of this mixture is recommended to be diluted in 10 liters of water, and then pour the plant under the root itself with the resulting composition. From about the second week of July, you can begin to slowly add phosphorus and potassium supplements in order to prepare the bushes for the coming winter. Carefully read the dosage of drugs in the instructions, remember that having fed the rose with chemistry, you can simply ruin it.
Climbing rose care in the first year
How does it differ from standard requirements? Its further development and flowering splendor depend on competent care in the first year of a plant’s life. When new shoots appear, the soil is removed from the bushes (the one used for hilling). If there are sunny days, then at first, light shading by coniferous lapnik will not prevent it. After 10–12 days after the removal of the pile-up soil, the first pruning of the central shoot can be started. It should be shortened over the second or third sheet. A little later, with the lateral branches of the second order, a similar procedure must be done, with the eyes “looking” inside the bush to be removed, and those eyes that are located on the outer side are left for further correct formation of the shrub.
Care of a climbing rose in the first year also implies the removal of the buds, however strange it may sound. From the beginning of flowering and up to the first weeks of August, only two flowers are recommended to be left on each branch. With the arrival of autumn, these flowers will turn into seed boxes (fruits), and after the manipulations, your rose will bloom especially magnificently next year.
Trimming climbing roses or how to trim climbing roses

Is a climbing rose pruned in the fall for the winter? If other types of roses can be simply spud, then it is necessary to cover the climbing line completely - this factor does not depend on your region of residence. You can choose one of the thermal insulation methods, in the first case the ground part of the bush is removed from the support, the foliage is removed, and all weak and old shoots are cut off.
Here you will have to choose 10-12 of the strongest and healthiest branches (left after trimming), combine them into one bundle, rewind with string and gently tilt to the ground. With the help of metal brackets (cut the wire into fragments and bend) the branches are fixed on the ground, and then covered with the appropriate protective material. If there are several shrubs, they are located in close proximity to each other, then they can be covered with one common covering sheet. In the second case, everything happens in a similar way, only in this case the plant is not removed from the support, but securely wrapped with protective material directly on it. The base of the bush spud as described above.
How to trim a climbing rose? This important agrotechnical care event should be given special attention. Pruning helps to properly form the crown of the plant, contributes to the generous and long-term flowering, a positive effect on the health and vitality of climbing roses. Immediately after planting, all shoots are shortened by 20-30 cm, in the summer, faded buds and branches growing inside the crown (thickening it) are cut.
Starting from the second year of the plant's life, pruning is done at the end of the flowering phase.
How to trim climbing roses after flowering? They bloom around the end of August - September (depending on the climate in the region), at this time all diseased and dead branches should be removed. The oldest shoots (choose 1 or 2) are cut off completely, then they will be successfully replaced by the young basal shoots. If these shoots are not present, then the old branches should be measured approximately 40 cm from the base, and the rest should be removed - this procedure is aimed at activating the growth of replacement root branches.
The rest (not very old) shoots are pruned in the place where new powerful shoots began to form, later it will serve as a conductor. Short branches of peduncles are pruned to 2 or 3 buds (approximately 15-17 cm from the base of the branch), weak stems are pruned to 3 buds (also measured from the base). The skeleton (base) of the crown should be formed from the strongest, correctly growing shoots (evenly directed), on which young branches will later be formed.
How to cut a climbing rose in the spring? The pruner should be picked up when the buds begin to swell on the branches below (the last weeks of April / beginning of May), not earlier. If you start pruning too early, then at night frosts the branches may simply freeze, as a result of which the rose will bloom much later than its due time. If you miss the time of pruning, the plant will throw all the forces on the formation of new branches and foliage, and flowering will be scarce.
Pruning climbing roses in the spring has one important moment - the removal, namely - the breaking off (not cutting) of wild shoots that have grown below the graft site. Usually this situation becomes apparent after the spring opening of the bushes. Also at this time, all diseased, dead branches are removed, all affected fragments are clearly visible in spring, when buds swell on the "living" branches.
Transplanting climbing roses to another place
Sometimes due to inexperience, the gardener chooses an unsuccessful place where the plant feels uncomfortable and ill. In such cases, the situation can be corrected by transplanting. The best time to conduct this operation is autumn, September, or the first weeks of October. Transplanting later is not recommended, as the rose needs time to adapt to the new place of residence before the onset of cold weather.
However, if circumstances so require, the transfer of a climbing rose in the spring to another place is also possible. As soon as the earth thaws out after winter frosts, and the buds on the branches of roses have not yet had time to wake up, you can get down to business. For this, the ground part of the plant is removed from the support, the bush itself is carefully digged (moving circularly), about 50-60 cm recede from the base of the plant. Do everything very carefully so as not to damage the root system of the rose, let the pit be better than it is necessary roots will remain safe and sound.
During transplantation, the same rules are followed as in the case of standard planting - the roots are stretched and directed downwards, the empty space in the pit is filled with the appropriate soil mixture, the soil is slightly tamped and generously watered.
After 3-4 days, the land should be filled (it will settle slightly), the spud of your rose.
There is one interesting nuance associated with transplanting roses - their affiliation to groups of climers and ramblers. I will allow myself a small digression: all varieties of climbing roses can be figuratively divided into these two groups:
- climbery;
- ramblers.
Varieties of climbing rose-climers are called climbing, they form coarse and thick branches that can reach 3-5 m in length. Shoots at climber are not very flexible, when transplanted, they must be cut to half the entire length!
Ramblera - it is climbing roses with flexible and soft shoots, whips, whose length can reach 10 meters. Rambler roses are characterized by active growth, when transplanted, they cut off all the shoots that are over two years old. All young branches are left intact, but at the end of the calendar summer they must pinch the tops - this technique speeds up the woody branches.
How to propagate climbing rose?
There are four ways of breeding this rose: seeds, cuttings, cuttings and grafting. The most common and convenient option is grafting. Seed propagation is possible only if you purchase seed in the appropriate store. As you know, self-collected seeds from climbing roses growing in your country house or in the garden do not carry the varietal characteristics of the mother plant.
Growing a climbing rose from seeds
Pre-soak the seeds in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 30 minutes. Such disinfection creates a shield against the appearance of mold in the subsequent stages of plant growth. After removing the seeds from the solution, lay them on a thin layer of cotton wool, again, saturated with hydrogen peroxide, top cover with a similar cotton layer, which is also saturated with peroxide.
The resulting “sandwich” is placed in a plastic bag and hid in a refrigerator in the compartment for greens and vegetables. Periodically inspect the seeds, change the cotton layers to new ones (also soaked in hydrogen peroxide).
After 40-50 days, the already germinated seed can be gently moved to peat tablets or small plastic cups with a corresponding ground mixture. Cartridges for seedlings also fit.
Watering young shoots should be as the soil dries. In order for plants to grow properly, they need to provide daily coverage for 10 hours. If you do everything right, then a couple of months after planting the seeds in tablets or in cassettes, the first buds may appear on young roses. With the arrival of spring, new livestock are planted in open ground.
Reproduction of climbing rose cuttings

This is the easiest way of reproduction, almost always giving a 100% positive result. For cutting the cuttings, the already flowering or still flowering branches will suit you; they take them from the rose in the very middle of summer, on the 10th of July.
There should be at least two internodes on the cut fragment, the place of the lower cut (angle 45º) should be located close under the kidney. The upper cut (flat) is carried out at a considerable distance from the kidney.
Further, all the lower leaves are cut off at the cutting, and the upper ones are cut by half. In the container prepared in advance with sand or with a mixture of sand and soil, a cutting is placed, buried about 1-2 cm, covered with a glass jar and cleaned in a well-lit place.
Now you will need to periodically water the cutting (without removing the jar) and make sure that it does not fall under direct sunlight.
Reproduction of climbing rose by layering
In the spring, from the shoots growing from the bottom, we choose the most attractive and make cuts on it, right under the buds. Next, we draw up a small bed-groove about 10 cm wide, put a thin layer of humus on the bottom of the groove, sprinkle it on top with the same layer of soil. Now gently bend the shoot, put it in the groove and fix it with metal straps. After falling asleep the soil, but leave the top looking outward. Further, as usual, we take care of the bush, but do not forget to water and fertilize the place of the buried escape. After a year, when spring comes, the layering can be cut from the bush and put in a separate place as a full-fledged plant.
Propagation of roses by grafting (budding) on dogrose
Climbing rose can be grafted on wild rose bush - this technique is often used by gardeners and summer residents. Best time for this operation - the last week of July or the first half of August. Before budding dogrose should be generously watered with water.
Right on the root collar of the shrub, an incision is made in the form of the letter “T”, after which the edges of the bark are slightly drawn off. In this kind of "pocket" is placed the eye, cut from a climbing rose. The eye must be separated from the rose along with the bark and a small piece of wood.
Next, firmly press the peephole to the neck of the stock and also tightly wind this place with a special film for budding (freely sold in flower shops). After all the manipulations, the briar bush is knocking out, and so that the soil rises above the graft area by 5 cm (this is the minimum). After two or three weeks, the film can be slightly weakened, and with the advent of the new spring it is removed for good.
Climbing rose does not bloom - why?
This can also happen, at least in the flower forums, gardeners often ask each other a similar question. Experiencedly, 7 factors were found that influence the lack of flowers in climbing roses.

Climbing rose - diseases and pests
 Rose Caterpillar on Rose
Rose Caterpillar on Rose  Rose, affected by spider mite
Rose, affected by spider mite At the initial stage, aphids can be removed from the branches by hand, before wearing garden gloves, but as soon as she feels like a full owner, you will need the help of chemical preparations. Insecticides "Sharpei", "Aktara", "Inta-Vir", as well as good old "Karbofos" will help you to cope with this problem.
If you want to try the so-called folk methods of struggle, then rub the soap (1 tbsp.) On the float and dissolve it in 1 liter of water. Irrigate the rose bushes with this solution for a week, after which remove all the affected fragments - this should help.
Spider mite loves heat and drought, silvery foliage is a sign of the presence of an intruder. Old methods of struggle with the help of thick tobacco infusion or wormwood broth give very good results. Contact necoric "Neoron" is one of the best means of protecting roses from spider mites. One ml of the drug is dissolved in a liter of water, after which the bushes are irrigated. Sometimes it is enough double treatment of roses with this drug, so that the tick surrenders its position. Bio-insecticide "Fitoverm" also proved itself in this case.
According to reviews experienced gardeners, the drug "Aktara" works great against rosilny sawfly. Preparations Actellic and Phosbecid (15 ml per 10 liters of water) also show a good result, which applies not only to the sawfly, but also to the other “lovers” of climbing roses.
In addition to all of the above, I would like to remind you of spring and autumn spraying of roses with Bordeaux liquid - this is important.
Among the diseases of climbing roses, the most dangerous are: bacterial cancer, gray rot, powdery mildew, coniotrium (bark burn).
 Mealy dew
Mealy dew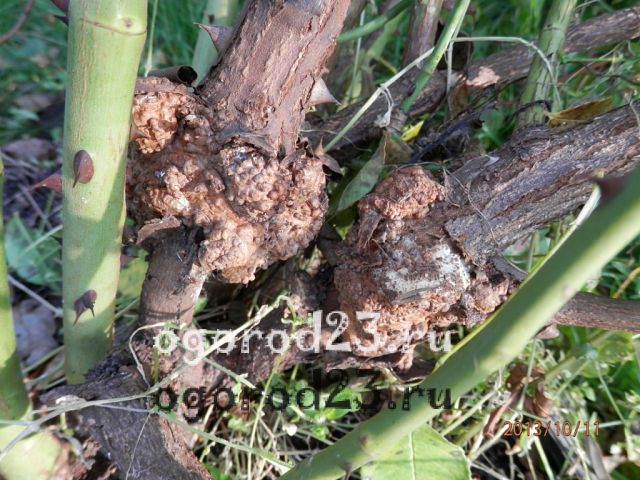  Bacterial cancer
Bacterial cancer There is no cure for some diseases (bacterial cancer), but a serious attitude towards prevention minimizes the risk of the disease.
Disinfection of the root system in a solution of three-percent copper sulfate (before planting), removal of suspicious fragments and rapid irrigation of wound sites with the same copper sulfate are the most often recommended preventive measures.
Coniotirium damage can be detected in the spring, as soon as the protective cover is removed from the roses. In this case, you need to immediately cut off the diseased branches (with the capture of healthy fragments) and burn them. Until the moment when the kidneys awaken, the plant can be treated with a 3% iron sulphate, the ground around the bush should be irrigated too. The same Bordeaux liquid or drug "Abiga-Peak" can also participate in the case, while the kidneys have not yet dissolved.
In principle, the usual pattern works to fight against other diseases of roses - removal of the affected areas and their subsequent burning, abundant irrigation of the plant with a solution of iron sulphate (3%), copper sulfate (2%) or bordeaux fluid (3%). Such spraying is often carried out in three stages (with a weekly interval), but sometimes, especially at an early stage, one treatment may be enough.
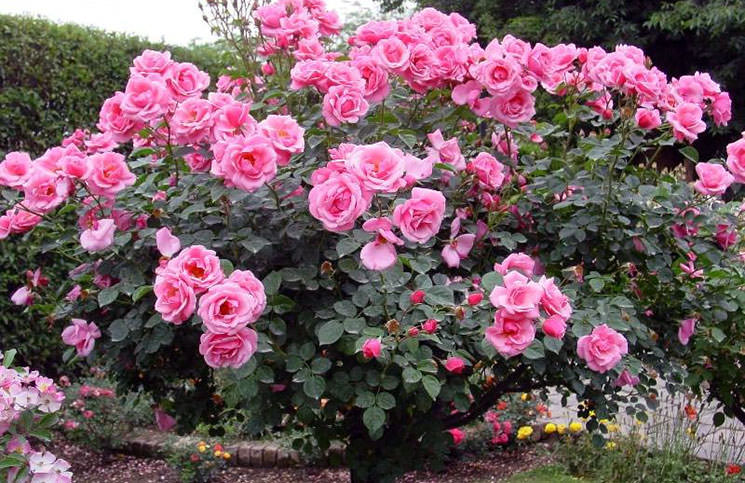
Climbing roses - photos and names of winter-hardy varieties
The dream of any gardener is to make your favorite flowers look lush with buds as long as possible and endure wintering. To mention all winter-hardy and long-flowering varieties of climbing roses is simply unrealistic, but I would like to highlight some of them, briefly describe their main qualities.
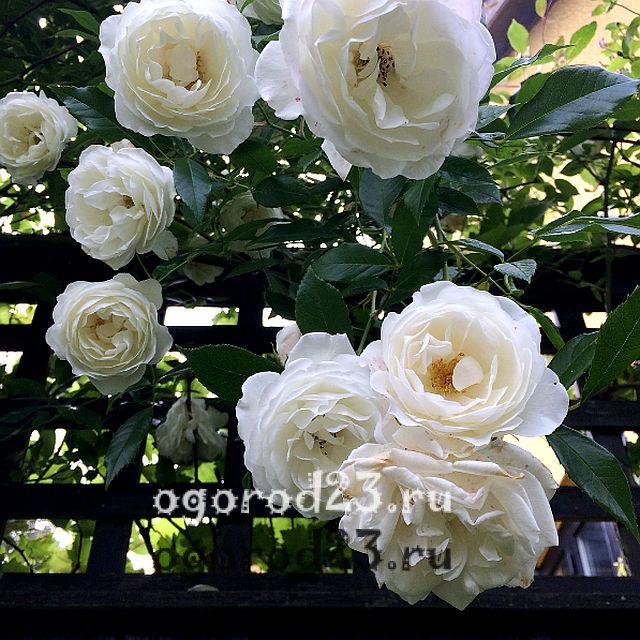
Climbing rose "Iceberg"
It fully justifies its name, its snow-white buds will bloom for a very long time (until the autumn) and abundantly. Re-flowering is a distinctive feature of this rose, it grows quite quickly and in the shortest possible time can braid the arch or wall of a building. The plant is unpretentious, cold-resistant, the aroma is weak.
Variety "Iceberg", photo:

Climbing Rose "Lavinia"
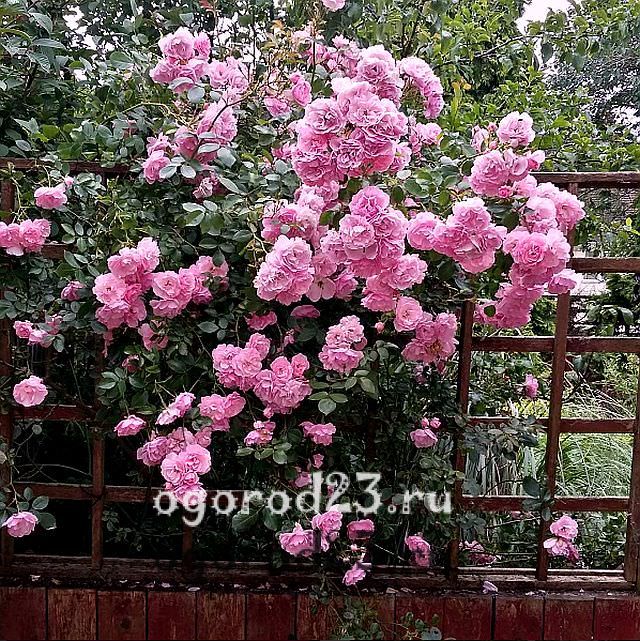
It boasts cup-shaped flowers of rich pink color, careless, re-flowering, aroma with light nutmeg notes. It grows to 3 m in height, has good immunity to most diseases of roses, blooms continuously until the first frost.
Lavinia variety, photo:

Variety "Polka"
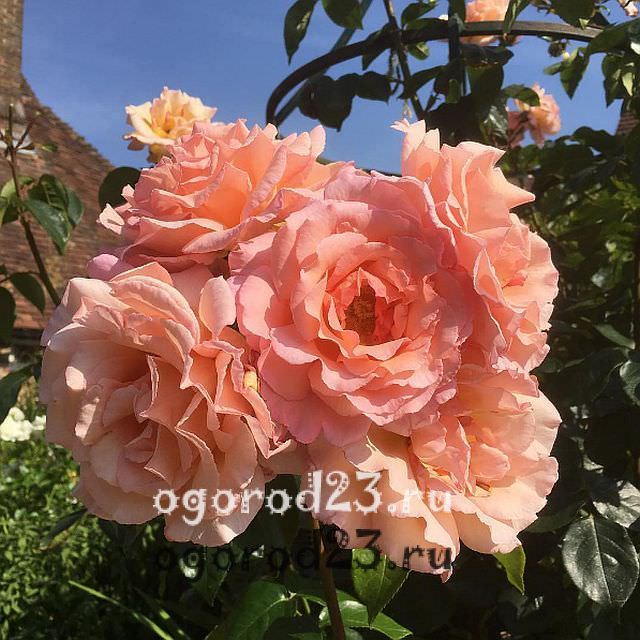
Characterized by a wavy flowering, about five waves per summer. Buds terry, apricot hue, gradually turning into a cream color. Very fond of sunlit places, has good disease resistance, can grow up to 3 m in height. This variety has powerful and spreading shoots with large thorns, the flavor is weak.
Photo of climbing rose varieties "Polka":

Climbing Rose "Don Juan"
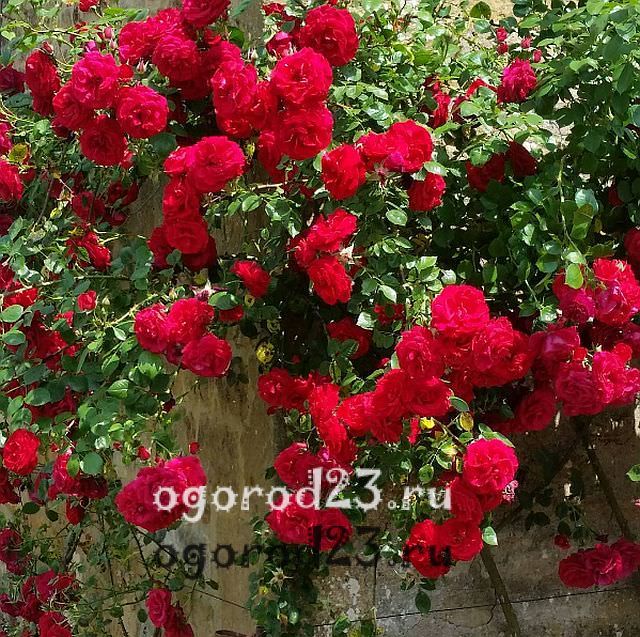
Magnificent terry rose with large (12 cm in diameter) flowers of rich red color. It is a great option for decorating the walls of buildings and any vertical supports. It grows up to 3.5 m in height, loves the sun, but also blooms in the penumbra without problems. These roses can be cut to make bouquets, they are very fragrant and long-lasting fresh.
Variety "Don Juan", photo:

Variety "Flamentants"
This rose is considered one of the most attractive representatives of the red color. Her buds are large (8 cm in diameter), terry, multilobe. It has high frost resistance, powerful bushes can reach 2-3 m in height. With proper care, this variety can grow and bloom in one place for about 20 years. The aroma of a rose is very delicate, but not very pronounced.
Photos of roses "Flamentants":

Climbing Rose "Handel"
The buds of this variety have a very interesting color - white and pink, with bright crimson edges and a slightly yellow center. The buds are large, about 10 cm in diameter, the bush grows up to 2.5-3 m in height. Rose re-flowering, disease resistance average, should beware of black spot and pepelitsy.
Variety "Handel" photo:

Variety "Bobby James"
Small-flowered representative, but the most attractive in its category. It can reach 8 m in height, is disease resistant, semi-double white flowers, with a yellow center (about 4.5 cm in diameter), resemble cherry flowers. It has a pronounced musky aroma, during flowering the branches are simply covered with buds, so that behind them there is almost no foliage. The buds themselves have the peculiarity of slowly opening up within about 10-12 days. Spectacular and incredibly luxurious variety
Photos of Bobby James variety rose:

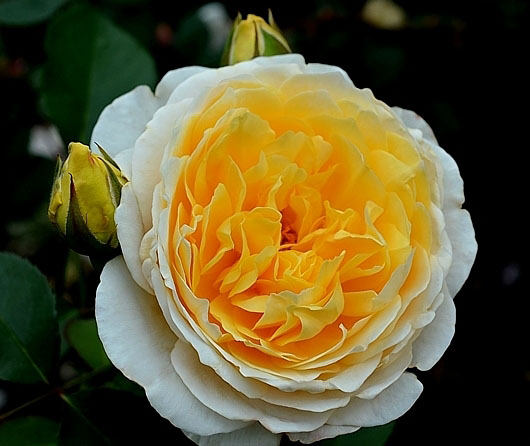
Climbing Rose "Golden Perfume"
Repeated flowering variety, which blooms slowly, to the joy of gardeners. Large buds (up to 10 cm in diameter) of this rose exude a very strong aroma that can be heard even from afar. Flowers rich bright yellow shade will adorn the bush until the arrival of the first frost. Shoots grow up to 2-3 m in height, the foliage also looks very attractive - rich green, thick, creating a beautiful contrast with yellow flowers.
Grade "Golden Perfume" photo:

Variety "Parade"
One of the most winter-fast, repetitive climbing roses, with large (10 cm in diameter) multi-petal buds of a juicy cherry shade or deep pink. Luxurious inflorescences are so large and heavy that the shoots literally bend from their weight. It blooms throughout the summer, blooms slowly, reaches a height of 2-3.5 m, resistant to precipitation.
Roses varieties "Parade", photo:

Climbing Rose "Schwanensee"
One more grade differing in the increased cold-resistance. The multi-petal buds of this rose have a classic shape, medium size (7-9 cm in diameter) and a very delicate color — white, with a cream-pink core. Schwannensee blooms to the frost, slowly dissolving and spreading a delicate subtle scent. A variety of hardy, re-flowering, resistant to precipitation. The bush can reach 3 m in height.
Variety "Schwannensee" photo:

Variety "Casino"
This rose is suitable for cutting in a bouquet, has a bright fruity aroma, lemon-colored buds are the most beautiful in the uncool form. A multi-petal variety, the diameter of a terry flower reaches 9-11 cm, its color is darker inside, the outer petals are paler. The bush grows up to 3-4 m in height, it blooms profusely, magnificently, many times throughout the summer.
Climbing rose varieties "Casino", photo:

Of course, a climbing rose will require time and effort from you, but, you see, its luxurious beauty fully justifies such “sacrifices”. Follow all the above recommendations, be careful in choosing a place of residence for the rose.
Do not plant it near bushes and trees with powerful roots, do not forget to feed them with appropriate fertilizers in time.
Provide her with reliable support, the types of which I will tell you in the next article.
Let a climbing rose be sure to settle in your plot. Planting and care in the open field, the nuances of reproduction and replanting, a rough idea of the individual varieties - you now know all this and can apply my advice in practice.
Successfully complement the article the following video:
Glittering roses look gorgeous on any site and give it a special look.
These are fairly common roses, which are simple when gardening, improving the landscape and are unique in creating a special style.
Usually wicker roses are grown in a warm region, but in any other region it is quite possible. The main thing is to know how to warm the rose and prepare it for the cold.
If you want to get chic buds, you must properly disembark and care.
We will teach you this.
Varieties and groups of climbing roses
There are countless of them, but the most popular ones are:
- Pierre de Ronsard (have a faint fragrance, can be cream or lavender, strong-growth and re-flowering, height reaches up to 300 cm);
- Flamentants (saturated red climbing with double flowers up to 40 petals, able to withstand frost at -30);
- Roster Hutter (buds reach 12 cm and have a bright crimson color, lush with a sweet smell);
- Handel ( white Rose with pink koyma, frost-resistant and ever-flowering, reach up to 400 cm);
- weaving rose Santana (great for, have a rich red color with a faint odor, can reach up to 300 cm);
- Sympathy (purple velvety roses with unforgettable aroma, not afraid of precipitation and frost, can reach up to 400 cm);
- Aloha (large, thick and prickly roses with apricot blossom and pink edges, reaches a height of 300 cm);
- Cordes (weak fruit aroma, maroon buds, bush reaches 200 cm and looks like a liana);
- Golden perfume (bright yellow luxurious flower with an amazing aroma, bush strong and frost-resistant, up to three meters high);
- Klaming pis (delicate creamy-yellow flowers, up to 6 meters high, grow quickly and are resistant to bad weather);
- Lagoon (bright pink flowers with a wonderful aroma, can bloom again and reach up to 250 cm).
Climbing Roses

Allocate:
- large-flowered;
- small-flowered;
- miniature;
- hybrid;
- polupletytye.
Climbing large-flowered roses

Often formed by renal mutation. They have more whip-like branches, and as if climbing up.
In these roses bloom young and perennial shoots. Reach three meters and if you arrange them like a fan, you can achieve a special charm.
Climbing roses have large buds, but they rarely grow. Have a delicious and delicate smell and tea shade.
Not very susceptible to disease, and the degree of resistance to cold is average.
Climbing Roses

These small flowers are very loved in the old days. They were surrounded by arbors, and at home.
They have arched, flexible shoots, which seem to creep and can reach up to 15 meters. Very comfortable in landscaping, because they themselves cling to the surface.
Small flowers can be of different mossiness and have different colors. Do not have a strong smell, it may be absent altogether.
Shrubs bloom once a year, but buds remain strong for up to 40 days at the beginning of summer.
They are highly resistant to cold and can grow back to back.
Polupletistye roses

They have not quite flexible stems and do not grow more than 2 meters. Grow well on props. Excellent for Russia is considered a variety of fireworks.
At the moment they are referred to as shrubs, but this opinion is wrong. People just do not know how to properly shape them.
Climbing miniature roses

They are small and respond well to weaving and creating forms.
Can reach up to 2 meters and have small leaves and buds. Shoots are formed continuously, so you can admire the gorgeous flowers up to 170 days a year.
These climbing roses grow faster and higher than others, so they are suitable for planting large buildings.
To the miniature group include varieties:
- Hi-Ho;
- Red Cascade;
- Flashdance;
- Nice Day;
- Warm Wellcome.
Not particularly successful is the grade Waterfall.
Climbing hybrid roses

Appeared by mutation of some large-flowered with bush.
They have bright big buds. They survive the winter well and are immune to disease.
They bloom very beautifully right until late autumn, but they are distinguished by tough, thorny stems.
These include varieties "Sympathy", "Karlsruh" and "Dortmund".
How to plant climbing roses

Planting climbing roses

Act in this order:
- dig a hole 60 cm deep;
- place the pit at a distance of a meter;
- immerse the root collar in a hole 10 cm. (to protect from the cold);
- arrange the roots loosely, well filling the voids;
- fertilizer to each well (about 5 kg. of the mixture in one well);
- fill the hole and tamp lightly.
Care for homemade climbing roses

Wait for the beautiful flowers for the second year and only then can you facilitate the care of them. You will only need to cut, water and fertilize.
Trimming is necessary to form a weave and give them direction.
Watering should be done once a week.
Fertilizing of roses is carried out when they are planted, and then two years later just to fertilize.
Climbing Climbing Roses
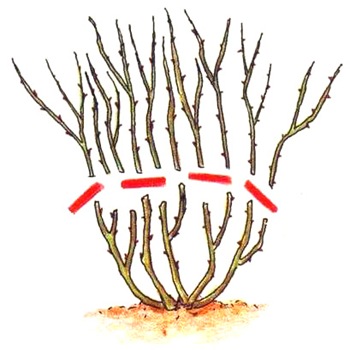
In the spring prune dead and frozen shoots that have not survived the winter.
With a single flowering, cut better so that there is only up to five one-year and five 2-year-old shoots.

If the buds bloom twice a season, the shoots will grow on it for about 3 years.
Pruning done for 4 years, also leaving up to three annual and about 4-5 main shoots.
How to shape climbing roses

Initially, be engaged in giving the necessary position in order not to earn extra problems or a plot in the future.
In order for a lot of flowers to be formed, it is necessary to properly not only care, but also to tie up roses.
It is not always important that the shoots look up, because the flowering can remain only at the top.
To avoid problems, you should shape the branches horizontally, so you will provide pomp. Great for gardening unsightly designs.
To form a bush near the hedge, it is necessary to distribute them in the form of a fan and tie them with a thin wire, but putting a rag under it so as not to cut the bushes or use plastic twine.
To form a climbing rose near the column, simply twist the shoots around it in a spiral.
Climbing Climbing Roses

There are three methods:
- reproduction by layering;
- budding;
- grafting
Reproduction by cutting
Fast and effective method. For its implementation, it is necessary to prepare cuttings in September, cutting shoots of 20 cm into cuttings with at least three buds.
The lower cut should be made obliquely and be located right next to the kidney, the top should be cut straight.
If you decide to propagate a climbing rose in water, then it must be boiled to prevent rotting.
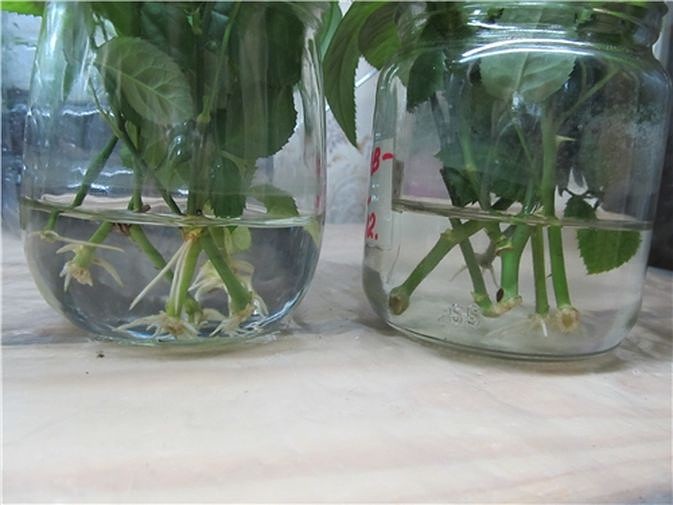

The roots of this method will appear in a month, then you can transplant the cutting in.
If you plant a stalk in the ground, then the problems are much less. Just make a hole in twice as many roots and stick them to the ground.
Stick a stalk and cover with a can. If you decide to leave the pot on the window, cover it with a cloth to create darkness.

Reproduction climbing roses layering
Choose escape in the spring and dig it into the groove up to 15 cm. The depth of the hole should not be more than the shovel bayonet.
Put on the bottom of the humus, lightly pour the earth.

Take the shoot and cut the bark under the kidneys, put in the ground and prikopite.
Pin the shoots to the ground and leave the end vertical.
Reproduction by budding climbing roses

Not all roses apply this method, only some varieties.
Additive should be in August. Should:
- take a sleeping peephole;
- cut the bark in the root of the rose hips;
- insert a sleeping eye into it;
- wrap a place around the budding tape very tightly.
The landing is carried out in the pits at a distance of 12-15 centimeters, leaving the bottom leaf of the cutting on the ground.
Winter wearable climbing roses
Care must be taken not to damage them. There are 2 options:
- remove from the structure;
- cover on the design.
How to insulate climbing roses by removing from the design
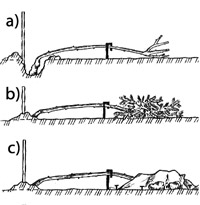
Remove them from the supports by removing all the leaves. If necessary, trim (if you have more than 12 lashes), removing weak shoots.
Tie a whip and fold to the ground, lock at an angle and cover with spruce branches.
Spud the rosary and sprinkle with peat, not revealing the root system.
You can priporoshit bushes with dry foliage or sawdust and wrap agrofiber.
How to insulate climbing roses on designs
![]()
This training is suitable for warm regions.
Secure the spruce branches with a twine and wrap insulation over the top.
Remember, the better you hide a bush from frosts, the better it will be and please you.
Such beauty will be pleasant to see anyone passing by. And you will be deservedly proud of yours. Let this pleasure troublesome, but worth it!
Climbing roses are mostly grown in southern areas, as they like heat. But selection does not stand still, and many varieties have been developed, which it has become possible to grow in more northern regions. What types, you ask, are popular for garden decoration?
At this time, there are many species and varieties, but the most common.
Pierre de Ronsard
Remontny grade. Spread bush up to 2 m in diameter and 3 m tall. Scourge is quite tough, so in some cases it can be grown in standard form.

Pierre de Ronsard
They have small buds that are richly covered with shrub, from cream to pale pink shades, sometimes with internal color saturation.
Flowers densely up to 14 cm in circumference. In the conditions of the central part of Russia, the buds do not have time to fully open their buds, but this makes it even more attractive.
Since Pierre has a faint fragrance, it is planted mostly near the jasmine bushes. It turns out a magnificent floral ensemble, giving in combination, an amazing smell.
What else is so attractive for gardeners Pierre de Ronsard?
- frost resistant, withstands up to -25 ° C;
- increased immunity to powdery mildew;
- long and abundant flowering;
- minimal care is required.
Handel

Remontny grade. It is used for decoration of arbors, arches, fences. High decorative. Bush height from 1.5 m to 3.5 m.
After pruning, it becomes lush and scatters its lashes up to 2 m in volume. Frost resistant Disease prone.
Long flowering. Buds, goblet-shaped form in diameter up to 8-10 cm, collected on a long peduncle of 1-2.
Two-colored, original color that attracts attention. In the middle part, it is painted in a creamy shade, turning to the edge in a bright crimson.
Flamingants

Flamingants
Great variety of domestic breeding. Cultivation is possible in the northern regions, as it has high frost resistance.
Not damaged by diseases and pests.
Requires minimal maintenance.
Large up to 12 cm in circumference, bright red flower buds, look amazing on the dark green foliage of the bush. It blooms in early summer. It has a bright, floral scent.
With good care, whips grow to 5 m.
Polka
Even a beginner can cope with growing this type. Unpretentious care. Frost resistant. Not prone to disease. Decorative, which allows its use in landscaping landscaping.
The bush 1.5-2 m high is covered with flowers of delicate peach color. Abundant, long flowering allows you to admire until the autumn. Many roses like her light, delicate scent.

Planting and care
Climbing roses have long been chosen by designers for vertical gardening. After all, it is convenient for decoration of arbors, arches, verandahs and various fences. Therefore, before planting it, consider the design of your garden.
Tips when and where to plant:
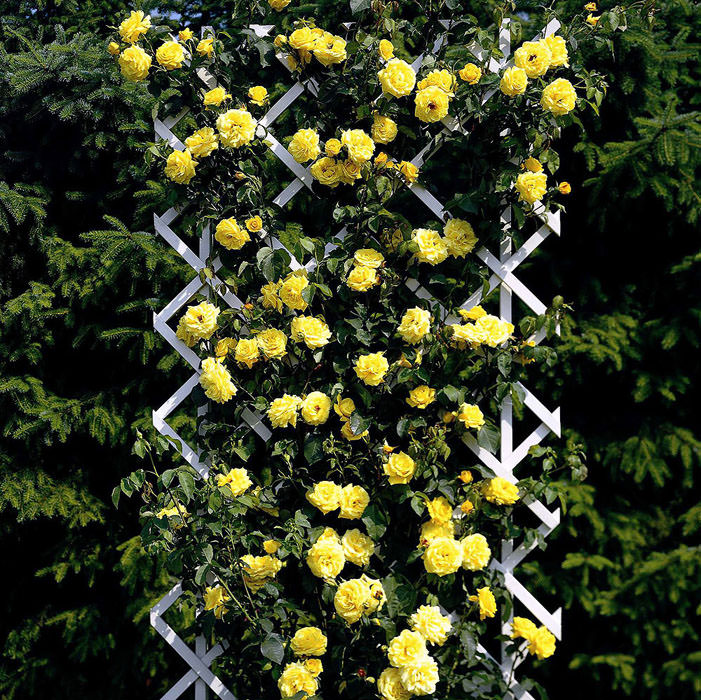
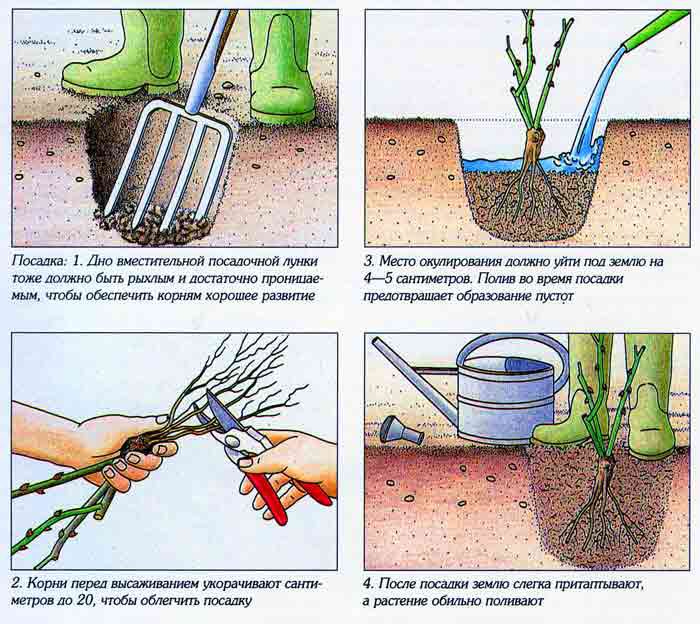
Landing
- For planting seedlings need preparation. To do this, inspect the root system. Remove all damaged, dried and broken roots. Dip 20 minutes into a weak manganese solution for disinfection. Including required to shorten the aboveground part. Cut the shoots in the third part of the sharp sector. Make a clay mash, add to it 1 tablet of heteroauxin per 10 l. Drop the roots in it.
- We plant it in the ground. Dig a hole. She must be bigger sizethan the sapling root system. Put a mound in the hole and put a bush on it. Spread the roots around the mound and cover it with soil prepared beforehand. Garden soil thoroughly mixed with humus and sand.
The root collar should be deepened by not less than 10 cm. This will protect against freezing and will contribute to the formation of additional roots.
- Press and pour the soil around the stem. After a few days, when the ground has settled, it needs to be filled.
The distance between plants for free growth is at least 1 m and 1-2 m between rows. To decorate the garden with a screen, landing is done in a staggered manner with a distance of 0.5-1 m.
- When planting bushes in the spring, cover them with a film. The film will create a greenhouse effect and they will take root better. Do not forget to open it for airing. First, once a day for 15 minutes. In the following days, open for a longer time, thereby preparing the plants for outdoor conditions.
- In the first year, roses do not need fertilizer.. They have enough nutrients from the soil.
Climbing Roses Care
Curly bushes in most cases undemanding to care.
 What you need to do to the plants were healthy and well-groomed?
What you need to do to the plants were healthy and well-groomed?
- In the spring to prune, remove and burn plant residues;
- carefully dig the ground around the plants, grind with peat or humus;
- do not allow the soil to dry out;
- fertilization;
- spray 3% solution for protection against diseases;
- carry out treatment with pests;
- pruning the branches that have faded;
- at the end of September, pile up the plants, remove the supports, and carefully lay the branches on the ground;
- shorten all shoots by 30 cm;
- with the onset of temperature at -5 ° C remove all leaves, damaged branches and fasten with twine;
- cover for the winter with any material;
- pruning should be done in autumn and spring.
Pruning
After flowering
What is it for:
- develop and grow better;
- more young shoots appear on the branches;
- a powerful root system is being formed;
- nutrients are equally distributed throughout the plant;
- for the prevention of disease;
- for greater access of light and air.
To trim branches correctly and without consequences, you need a tool:
- sharp knife or pruner;
- different sizes of loppers;
- gloves for work.
All tools should be kept clean and dry. After any work, they should be washed and disinfected in a solution of manganese, hydrogen peroxide. After that dry.
Autumn
Autumn haircut takes place from October to November. Removed most of the shoots:
- removal of old shoots;
- broken;
- shortening shoots in the winter by 1/3;
Bushes easier to endure the cold winter without the extra mass of branches.
Spring
Spring should be cut:
- broken branches;
- dry branches;
- stuck in frost.
Cold protection
Despite the fact that they write about the frost resistance of a variety, roses should be covered for the winter. If there is little snow in winter, they can freeze.
How to cover:

If climbing rose wraps around the arch, then we shelter it on it. For this:
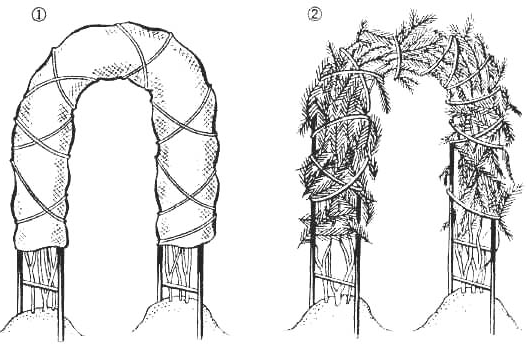
In the spring when the onset of heat shelter should be removed gradually, layer by layer. This is done in order to accustom the plant to the light. Avoid sunburn on the plant.
Breeding
Seeds
For seed breeding material is better to buy in the garden store.
Collected seeds from your bushes do not have varietal characteristics. But this way you can withdraw new variety. Experiment yourself in fun.

Under all conditions, the first buds you will have in 2 months after planting. They need to be removed to allow young plants to gain strength before subsequent transplantation into the ground.
With the onset of heat seedlings to plant in the beds under the film.
Cuttings
The most popular way of breeding roses -. In mid-summer, cut shoots from the bushes. Segments should have more than 2 internodes.

How to cut the cuttings?
- Secateurs or a sharp knife make cuts so that the bottom falls under the kidney at an angle of 45 °, and the top - straight and above the kidney.
- Remove from the bottom row of leaves. Upper shorten.
- Fill the pots with primer (a mixture of earth and sand) and stick cuttings into them. Cover with a transparent cup and place in a bright place.
- When the first leaves appear, take off the glasses. In the future, care before planting in open ground is watering and making complex fertilizer.
Layering

Inoculation
Not the most popular and laborious method of reproduction is grafting on a stock or, in a different way, budding:

Tip! Before vaccination dogrose should be abundantly watered. Sector cut off the aerial part, while leaving 10-15 cm.
Looking at the splendor of climbing roses, it is impossible to refrain from planting it in your garden. Moreover, the selection offers us a variety of species and varieties, nowadays grown in any region of Russia.
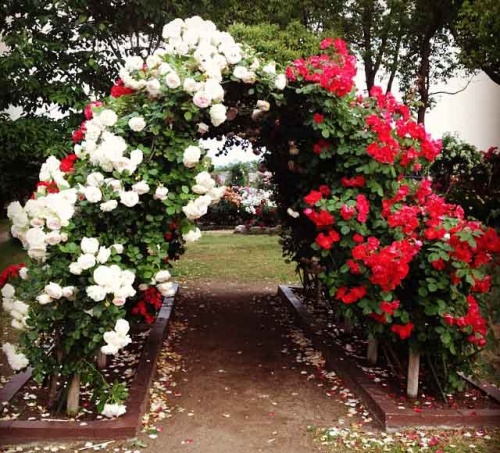
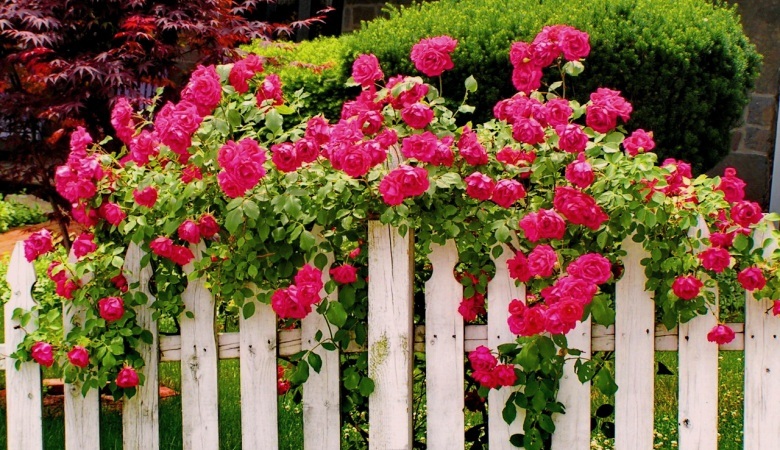
It is impossible to walk past a fence that is wound around a climbing rose, and it’s impossible not to admire the flowering splendor and the riot of colors. Climbing roses are often planted to decorate arbors, as a chic vine with large buds around a flower bed. Landscape designers have long used luxurious flowers for arranging garden arches and monolithic columns.
Being curly green space, climbing rose shoots up to 5-6 m long. Beginners in floriculture mistakenly believe that planting climbing roses and care activities are similar to other varieties of roses. However, long shoots require the owner of the estate to carefully care for this flower.
How to determine the landing time
The rose is the flower of an exceptional constitution, so the “beauty queen” often behaves capriciously, planting requires planning the process to the smallest detail.
Ideally, it is better if the landing will be in May days and warm weather. Planted in the spring bushes will be able to get stronger before the onset of winter cold. If dormant buds are seen on the stems, start planting in the dacha at the moment when the trees are just starting to bloom and the ground warms to 10-22 degrees Celsius.
If the sapling is bought in a nursery and has already been grown in a greenhouse before, the planting is postponed to a later period - you have to wait for the buds to bloom on the trees.
Some gardeners take great risks, starting to plant a climbing rose in the fall - without a special shelter that will support the greenhouse conditions of the plant, the flower most likely will not survive.
Choosing a place to land
 Focus on a well-lit area of land, it is better if the sun warms up the culture from morning till noon. The sun's rays perfectly drain the morning dew on the leaves, which means that a climbing rose is not afraid of fungal diseases.
Focus on a well-lit area of land, it is better if the sun warms up the culture from morning till noon. The sun's rays perfectly drain the morning dew on the leaves, which means that a climbing rose is not afraid of fungal diseases.
Completely open area will not work - it is possible to get plant burns, after which individual shoots may dry out completely. Not welcome planting climbing roses in a place not protected from drafts, for example, at the corner of the building.
Pay attention to the composition of the soil. Collect rainwater in a barrel and pour the soil in the spring. If the fluid easily penetrates deep into, then the earth is in proper condition for planting crops. If the water is delayed, most likely, there is a waterlogging here, which the climbing rose does not tolerate. Planting on such a ground is prohibited, the roots of the bushes will rot, which means that food will not flow to the vines, which naturally causes the death of the plant.
How can I fix this situation? Choose the most exalted site on your estate. If the garden is a plain type, you can do the following:
- Using a shovel, dig a hole, the depth of which allows you to bypass the groundwater.
- Process the bottom of the concrete solution.
- After drying, lay a large flat stone. This measure will protect the rhizome from groundwater, in addition, the branching of the roots will be fixed in a horizontal, not vertical direction.
- Pour fertile soil over the stone, then plant a rose.
To make the spring planting successful, it is advisable to additionally fertilize the site with nutrients. For this it is enough to add humus or humus. You can experiment with complex compounds containing phosphorus. Experts advise the use of “Baikal EM – 1”, the beneficial bacteria of which recycle harmful elements for planting.
Preparation of climbing roses
Planting bushes, retreat between them in the furrow from 0.5 to 1 m, between rows you need to lay at least 1 m. If you plan to decorate a gazebo or fence with a climbing rose, measure 0.35-0.5 m from the blind area.
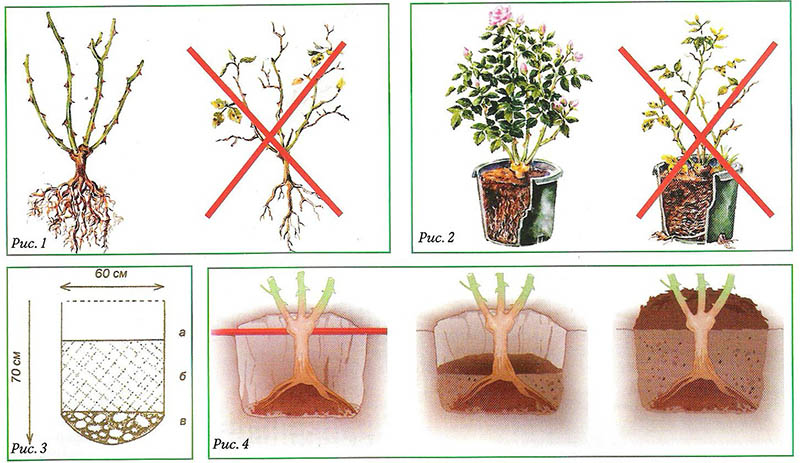
Preparing the seedling before planting in the spring consists in a thorough examination of the root system - you need to get rid of the broken and rotten roots, and then carry out a series of manipulations:
- cuts of separate parts of the rhizome process with crushed charcoal, which will protect the planting from rotting of the formed wounds;
- do the so-called talker with your own hands: mix the clay, fresh manure (one tenth of the whole composition) with 3 tablets of phosphorus bacteria, pour 0.5 l of water and measure 9.5 l of the resulting talker;
- in the absence of cow dung, add 1 tablet of heteroauxin with the calculation of sufficiency per 10 l of solution.
Planting seedlings in the spring involves pruning of the buds, 2 formed buds are left on strong stems, and weak ones - one presence is enough.
Features planting young plants
 Step by step follow the steps for planting a climbing rose in the ground in spring:
Step by step follow the steps for planting a climbing rose in the ground in spring:
- Using the spatula, make a hole, the size of which will allow you to freely lay the roots of the bush. Determine the root collar 10 cm deep.
- Over time, the rhizome planted in this way will grow, and the temperature of the earth at a specified depth, even in extreme cold, will not fall below -2 degrees.
- Place the shrub in the groove, flatten the roots and well sprinkle with soil.
- Carefully tamp your feet.
- In order for the plant to stick successfully, it is preferable to treat it with a solution of phosphobacterin and heteroauxin.
- Cover the beds with thick plastic - you get a homemade greenhouse. It is important to provide daily ventilation of the greenhouse, temporarily uncover part of the film, thereby providing free access to fresh air.
- Gradually increase the time of "hardening."
- The film is completely removed after 14 days.
If the integrity of the rhizome is damaged, fill it with Korneyn or Zircon. If there is a sprayer, process the sapling Epin.
Climbing roses include species of wild rose, as well as several varieties garden rosesbranching rather long stems. They are directly related to the genus dogrose. And these plants are very popular in vertical gardening as various structures, buildings and walls, and gazebos. These flowers are able to decorate as a large structure, and very small. These plants are widely used to create various designs in the garden, namely, columns, arbors, pyramids, garlands, as well as arches. And they are wonderful combined with other plants, in this regard, their popularity is no less than that of a room or spray rose.
There is no general description for this type of plant, because they have many different forms and varieties. However, there is a classification of climbing roses, which was adopted in the international floriculture practice.
First group
Such plants are called climbing roses or ramblers (Rambler) roses. These flowers have long flexible shoots that are arched or creeping. They are painted in a rich green color, and spikes are located on their surface. In length, they can reach more than 500 centimeters. Glossy leathery leaves are small. Flowers can be double, semi-double and simple, their diameter, as a rule, does not exceed 25 millimeters. They have a rather weak aroma. The flowers are part of the inflorescences, which are placed along the entire length of the stems. The flowering of these plants is quite abundant, and it lasts a little longer than 4 weeks. Observed flowering in the first half of the summer period. A very large number of varieties have frost resistance, and such plants are able to winter well even under relatively light shelter. This plant was born thanks to such species as: multi-flowered rose (multiflora) and Vihura rose.
Second group

Climber or large-flowered climbing roses (climber) were bred by breeders when they cross groups of ramblers with tea-hybrid, tea, reparative roses, and floribunda roses. The length of the stems of such climbing roses can reach 400 cm. The flowers are rather large (diameter is more than 4 centimeters), and they are part of small loose inflorescences. Abundant flowering. A large number of varieties of flowering is observed 2 times during the season. Flowers have a shape similar to hybrid tea roses. These flowers are relatively frost-resistant and resistant to powdery mildew.
Third group

Climbing were formed by large-flowered mutating shrub roses, namely grandiflora, hybrid tea, and floribunda. The difference of such plants from the producing species is that they have even more powerful growth and very large flowers (diameter from 4 to 11 centimeters), while they can be both single and part of not very large inflorescences. They also differ in fruiting, which occurs at a later time. Most varieties are characterized by repeated flowering. These plants are cultivated only in the southern regions of the temperate zone, where the winter period is relatively warm and mild.
Planting climbing roses in open ground

Absolutely all types of such plants have a very capricious nature. The same applies to climbing roses. To plant and care for such a plant, you need to adhere to certain rules. And you should also consider the advice of experienced flower growers on the cultivation of climbing roses. It is necessary to approach the choice of a site for landing with all responsibility. Such plants simply need a plot that will be lit from morning to afternoon by the sun. In this case, the dew that is on the plant will be able to dry, which will help avoid the appearance of fungal diseases. At lunchtime, when the sun's rays are the most scorching, this area should be shaded, otherwise burns may occur on the surface of the foliage and petals. Also, a suitable site should have protection from northeast and north wind because it is rather cold. It is not recommended to decorate the corner of buildings with climbing roses. The fact is that the draft present there can destroy a delicate plant. For planting such flowers, experts advise choosing a site on the south side of the building. In order to plant climbing roses, you need a strip of soil the width of half a meter, but it should be noted that any building, building or plant should be located at a distance of about 50-100 centimeters from such a flower.
Suitable soil must be able to pass water well. If, on the site chosen for planting, groundwater is located very close to the surface, these plants are planted on a special pre-prepared elevation. The roots of this type of roses in some cases can be buried in the ground up to 200 centimeters. In order to prevent stagnation of fluid in the root system, the selected area should be located at least under a not very large slope. Loam is considered ideal for planting climbing roses. If the soil is sandy then it needs to be repaired before planting, adding clay during digging, and sand should be added to the clay soil. Such plants need a land rich in nutrients, so the introduction of humus or humus is mandatory. You should also add bone meal to the soil, which is considered an excellent source of phosphorus. Soil preparation should be carried out in advance. Ideally, this should be done 6 months before planting, but preparation can also be carried out 4 weeks before planting a rose.

If you are going to plant a climbing rose, you must first learn how to choose the best quality. planting material. Nowadays, you can buy seedlings of roses, which are own-rooted, as well as those that are grafted on the wild rose. But how do they differ? Grafted saplings have one important difference from their own. The fact is that the root system of such a seedling belongs to the dog rose, and on it is a graft relating to a varietal climbing rose. In this regard, planting and caring for your own-rooted rose should be somewhat different than for the grafted one. So, for example, the grafted seedling needs to be buried in the soil during planting so that the place where the graft is located is underground at a depth of 10 centimeters. With this method of planting that part of the plant that was grafted, begins to form its own root system, with the hips of the hips eventually becoming unnecessary and die. In the case when the planting of the graft was not buried in the ground, and remained above its surface, can lead to the death of the plant. The fact is that wild rose is a deciduous plant, and the grafted rose belongs to the evergreen. If the planting was made in violation of the rules, then this mismatch of rootstock and scion can lead to the death of the cultivated part of the plant.
Saplings with an open root system should be immersed in a container with water for 1 day, and this should be done immediately before planting in open ground. After that, it is necessary to tear off all the leaflets and cut them off using a pruner, those stems that are unripe or damaged. You should also undercut the root system and the aerial parts, leaving 30 centimeters. Slices should be treated with crushed charcoal. If you use grafted seedlings for planting, then they need to carefully remove all the buds that are located below the scion. The fact is that one of them will begin to grow wild rose. Next, planting material should be disinfected. To do this, it must be dipped in a solution of copper sulfate (3%).
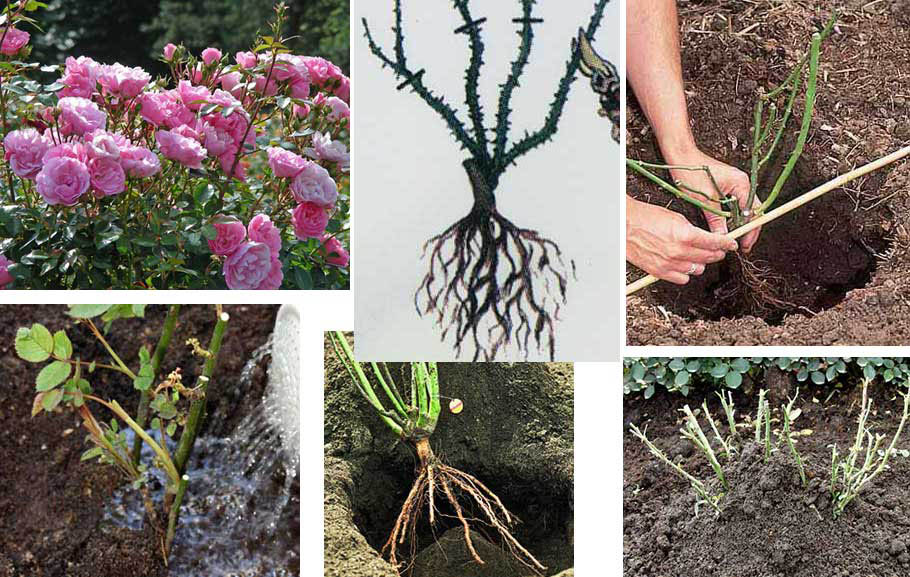

The hole for planting roses should measure 50x50. In this case, a distance of at least 100 centimeters must be maintained between the landing pits. The top layer of the soil most nutrient-rich needs to be removed from the excavated pit and connected with ½ part of the manure bucket. Part of the resulting earth mixture should be poured into the hole, and then a relatively large amount of water should be poured into it. This procedure should be carried out for a day or two before the intended planting of the plant. On the day when you plan to plant a seedling, you need to prepare a special solution in order to process the root system before planting. To prepare the solution, it is necessary to dissolve 1 tablet of heteroauxin, 3 tablets of phosphorobacterin in 500 ml of water. Then pour this liquid in 9.5 l of clay mash. Before the seedling is lowered into the hole, its roots should be dipped in the prepared mixture. In a hole should be poured a mixture of soil soil with manure. Then in the hole you need to put a sapling, while gently straightening its roots. Fill the hole with the same mixture of soil with manure and firmly seal the surface of the soil. Do not forget that the place where the vaccination is located must be buried 10 centimeters into the ground. At the same time, at the root-bearing seedling you need to bury the root neck by 5 or more centimeters in the ground. Planted plants need to be watered well. After the liquid is absorbed into the soil, it will be necessary to add a mixture of soil and manure to the well. Then the plant spud to a height of 20 centimeters or more.
Planted in the autumn, roses overtake the development of those that were planted in open ground in the spring. In this case, the latter need special increased attention to themselves. Before planting seedlings, they should cut the root system to 30 centimeters, and the stems must be shortened to 15-20 centimeters. When the plant is planted, you need to water it well and spud it highly. Then it should be covered on top with a transparent film, creating at the same time something similar to a mini-greenhouse. In these greenhouse conditions, the rose will take root relatively quickly. Do not forget to air the sapling every day, for this you need to raise shelter for a few minutes. Experts advise airing every time to spend longer and longer, so the rose will also be hardened. After the threat of night frosts is left behind, it will be possible to remove the shelter altogether, and put a layer of mulch on the surface of the soil in the hole. If the seedling was planted at the time when the weather was warm and dry, then the surface of the wells should be covered with a layer of mulch (peat or other).
Care for climbing roses in open ground

In order for a climbing rose to grow and develop normally, it is necessary to learn how to water, feed, cut the plant. You also need to monitor the health of roses and time to destroy pests. It is very important to learn how to properly prepare bushes for wintering. This type of roses needs reliable support. These plants can easily tolerate drought and therefore should not be watered abundantly. As a rule, they are watered 1 time in 7 days or in a decade, 10-20 liters of water should be poured into 1 bush. Remember that it is better to water more often, but less. To hold water in the hole around it, it is recommended to build a not very low shaft from the ground. When it takes 2–3 days from the moment of irrigation, it will be necessary to loosen the surface of the soil of the near-bar circle to a depth of 5 to 6 centimeters. This will help retain moisture in the soil, as well as improve air access to the root system. In order to reduce the number of irrigations and virtually eliminate the loosening of the soil, it is necessary to cover its surface with a layer of mulch.
Young plants do not need to fertilize the soil before the end of the summer period, as there is a large amount of nutrients in the ground since planting. At the end of the summer, the plant should be fed with a solution of potash fertilizers, this will help the rose to prepare for the winter period. It is recommended as a top dressing in this case to use an infusion prepared on wood ash. In the second year of life, such plants need to be applied in the soil and mineral and organic fertilizers should be alternated. And the roses of the third and subsequent years of life should be fed only with organic fertilizers. So, for this perfect solution consisting of 10 liters of water, 1 liter of manure and 1 tbsp. wood ash. If desired, instead of manure, you can take another organic fertilizer. During the period of intensive growth, climbing roses must be fed 5 times, while it must be borne in mind that during the flowering period fertilizer cannot be applied to the soil.
Support for climbing roses
For this type of roses there is a huge variety of supports. So, as a support, you can use the old dried wood, wood, metal or polymer arch or grating, as well as arc rods made of metal. But the most best support for such a plant is a building or any structure, but we must remember that plants should be planted no less than 50 centimeters, retreating from the wall. On the surface of the wall it is necessary to fix the guides, for which the shoots of plants or the grid will cling. But it should not be forgotten that if the stems are arranged horizontally, the flowers will grow along their entire length. If they grow vertically, in this case, the flowers bloom only at the tops of the stems.
In order to fix the stems on the support, it is necessary to use plastic twine. It is forbidden to use a wire for these purposes, even wrapped with a cloth or a sheet of paper. The escape must be fixed on the support securely, but so that the fastening material does not damage it. It is necessary to conduct a systematic examination of the plants for the integrity of the mounting materials. The fact is that under the weight of the plant itself or from wind gusts the twine can break, and in this case there is a risk of significant damage to the rose. Depart from 30 to 50 centimeters from the bush and then dig support in the ground.
Transplanting climbing roses
An adult rose may need a transplant only if it becomes clear that the place where it grows does not suit her at all. Transplantation is carried out in the autumn in September or early November, you should not do this later, because the bush will not have time to settle down before the beginning of the winter period. In some cases, the plant is transplanted in the springtime, but this must be done before the awakening of the kidneys occurs. Plants need to be removed from the support structure. At ramblers, young shoots are not removed, but they nip their tops in the last days of August, which will help them to woody as soon as possible. Stems older than 2 years pruned. All long stems need to be shortened by ½ part for climing and climber. After that, the bushes should be carefully dug around in a circle, while at the same time it is necessary to retreat from its center to a distance that equals 2 bayonet shovels. It must be remembered that the roots go deep into the soil, and they must be tried to dig completely, while causing them as little damage as possible. From the roots should shake off the soil, and after that it is necessary to conduct their inspection. With the help of a pruner, shaggy, as well as damaged root tips should be cut. Dip the plant in the prepared hole and be sure to straighten the roots. Then fill the hole with soil and thoroughly seal its surface. Water the plant well. A few days after transplantation, you need to pour the required amount of soil in order to level the surface of the trunk circle. At the same time it is necessary to hold an earthing up of a rose.

Aphids and spider mites can live on a climbing rose. In the case when aphids on a plant are not very much recommended, try to get rid of it using folk remedies. So, you can make the removal of insects from the plant manually. To do this, you need to pinch the part of the plant on which the aphid is located with your fingers and remove it. Do not forget to wear gloves. But this method can be used only at the very beginning of the infection. If there are a lot of insects, then manually removing them will be ineffective. In this case, it is recommended to make a soap solution. Soap should be crushed with a grater, pour into a container, where you need to pour in water. Allow the solution to stand, as the soap needs time to dissolve. Strain it and treat the plant with a sprayer. If, after processing, the insects still remain, then you need to buy an insecticidal agent in the special store, which should be marked "for grapes and roses." For processing in this case it is necessary to choose a windless sunny day. Spider mites can live on a rose only during the arid hot period, and only when the plant is watered very rarely. Such insects live on the seamy side of the leaves. They feed on vegetable juice and entangle the leaves with a thin cobweb. In infected roses, leaves become green-silver. Very often, for the destruction of such mites, they use an infusion prepared in wormwood, tobacco, yarrow or tobacco. After 3 days after treatment, this infusion should kill 80 to 100 percent of the pests. To make an infusion of wormwood, you need to pour 500 g of freshly picked wormwood into a container made of wood. There also need to pour a bucket of cold water. When the mixture is infused for half a month, it is filtered and diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. It is necessary to process both the plant itself and the ground surface around it. If you want to get rid of insects in the near future, then you will need to get Fitoverm. You can re-process a couple of weeks after the first. Before proceeding with the treatment of this tool, it is necessary to examine the instructions attached to it, where the features are indicated, as well as the required dosage.
Also climbing roses can harm: cicadas, thrips, rosan sawflies, moths. However, if you take care of the flower, observing all the rules, they will not settle on it. As a preventive, land marigolds in close proximity to roses; they will be able to protect this plant from most pests. Also in the fall and spring, preventive measures should be taken. To do this, the bushes need to be treated with a Bordeaux liquid sprayer.
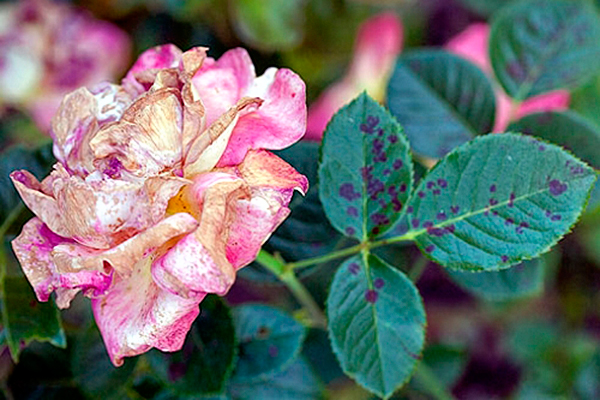
For roses, diseases such as bacterial canker, gray rot, coniotrium, powdery mildew, and black spot are most dangerous.

Growths of various sizes appear on the surface of the plant; they are very soft and lumpy. After some time they become harder and darker. This leads to drying and death of the plant. Cure such a disease is impossible. During the purchase of seedlings, they must be carefully inspected, and before they are planted, the root system must be disinfected, plunging it for 2–3 minutes. in a solution of copper sulphate (3%). If there are signs of disease on an adult plant, the affected parts should be immediately cut off, and the sections should be treated with the same 3% solution.

This disease is fungal, which is considered a burn of the cortex or cancer. You can see that the plant is sick, in springtime, after the shelter has been removed. On the surface of the bark can be seen specks of brownish-red color, which eventually turn black and turn into rings around the stem. These stems should be immediately cut, at the same time capturing part of the unaffected tissue, and destroyed to prevent the spread of the disease. As a preventive measure, in the fall, the nitrogen fertilizer should be changed to potash fertilizer, which will make the rose tissue stronger. And with thaws, it is necessary to ventilate the plants, raising the shelter.
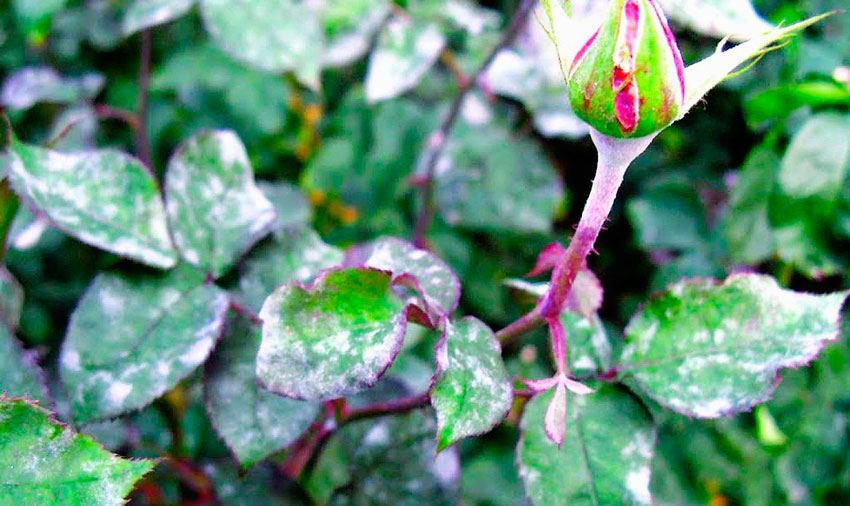

On parts of roses, a whitish bloom appears, which gradually becomes brown. The occurrence of such a disease can be provoked by high humidity, a sudden change in temperature, an excessive amount of nitrogen in the soil and violation of irrigation rules. Parts of the rose that are affected by the disease must be cut and destroyed. Next, you should carry out the processing plants using a solution of copper sulfate (2%) or ferrous sulfate (3%).
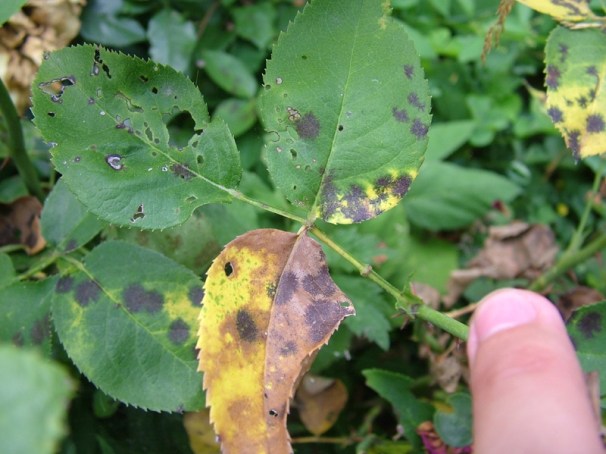

On the surface of the leaves appear dark brownish-red specks, which are bordered by a yellow rim. Over time, they merge with each other and cause the leaf plate to die. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to add phosphate-potassium fertilizer to the root in the fall. And still need a three-step treatment of the plant itself and the soil next to it with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (3%) or iron sulphate (3%). The intervals between treatments are 7 days.

Able to destroy almost all parts of the plant (buds, leaves, shoots). Such a rose loses its beauty, and also its flowering becomes relatively scarce. In the case of a highly frisky disease, the rose should be dug out and burned. If the disease has just appeared, it is recommended to treat the bush with a solution prepared from 5 liters of water and 50 g of Bordeaux mixture. In order to cure the plant completely, as a rule, it may take 4 treatments, the interval between which should be 7 days.
It happens that seemingly healthy and well-developed climbing rose does not bloom. The point here may not be in a disease at all, but in the fact that a sapling of poor quality (poorly flowering) was purchased, and besides, the wrong place was chosen for it, and the soil is also most likely not suitable for this plant. And sometimes it happens that last year's stems are damaged during the winter.

When to trim climbing roses
These plants need pruning, as it allows to form a beautiful crown, make flowering more abundant, and to improve its decorative qualities along the entire height of the bush. If you cut the plant correctly, it will delight its flowering during the entire period of intensive growth. Vegetative stems deserve special attention, since the main part of the flowers is formed on last year's stems. Cut the rose should be in spring or autumn. At the very beginning of the period of intensive growth absolutely all climbing roses must remove dead stems, as well as areas that have been frostbitten. Also, the tips of the stems should be cut to the strongest external bud. The following pruning procedures will be directly related to how many times a particular rose blooms, one or more.

For those plants whose flowering is observed 1 time per season, flowers grow on last year's stems. Basal (faded) stems replace the shoots of recovery, which can grow up to 10 pieces. Flowers will grow on them only on next year. In this regard, the withered shoots will need to be removed, cutting them out at the root, and this procedure is recommended to be carried out in the autumn time during preparation for wintering. Those climbing roses that bloom several times a season, flowering branches of different orders grow on the main stems for 3 years - from 2 to 5. In the fifth year of the life of these stems, their flowering becomes more scarce. In this regard, at the beginning of the spring period, the main shoots must be removed, cut to the ground, and this should be done in the fourth year of their life. On the re-flowering bushes there should be 3 annual stalks of restoration and 3–7 flowering stalks, which are the main ones. But it must be remembered that the majority of these roses form flowers on overwintered stems, so in springtime only the upper part with buds, which are underdeveloped, should be cut off.
Young roses that were grafted and were planted in the past or this year, need special attention. Until the rose has its own root system, you will have to systematically remove the wild rose. After 1–2 years (after the dying of the root of the wild rose, the growth of the rose will begin to appear.
Climbing Climbing Roses
It can be propagated by seed, cutting, layering, as well as grafting. Easier to do this layering and cuttings. Seeds need to be purchased at a specialty store. If you want to sow those seeds that were collected from roses by you, then you need to understand that such plants do not retain the varietal characteristics of the mother plant, and therefore you can grow anything.

Seeds need to be folded in a sieve and immersed for 30 minutes in a container filled with hydrogen peroxide. Thus, disinfection of seed material is carried out, as well as prevention of the formation of mold with further stratification. Moisten cotton wool disks with hydrogen peroxide and place seeds on them. Place the same wet cotton pads on top of them. Each resulting “sandwich” should be placed in a separate bag of polyethylene. Sign the date and name of the variety, and then place the seeds in the container of the refrigerator for storing vegetables. Need to arrange a systematic check. At the same time, if mold is detected, the seeds should be washed and again kept in hydrogen peroxide. The fleeces are replaced with fresh ones, and the seeds are again placed in the refrigerator. After 6–8 weeks, the seeds, which should appear sprout, should be planted in peat tablets or separate small pots, while on top of them should be sprinkled with a layer of mulch, which you need to take perlite, which will help to avoid black leg disease. Provide the plant daylight at least 10 hours and timely watering as the substrate dries. If the plant develops normally, then after 8 weeks after planting, they will have buds, and after another 4-6 weeks the plant will bloom. You can produce a weak fertilizer solution of complex fertilizer. In the springtime, they are planted in open soil, and then they are looked after, just like adult roses.
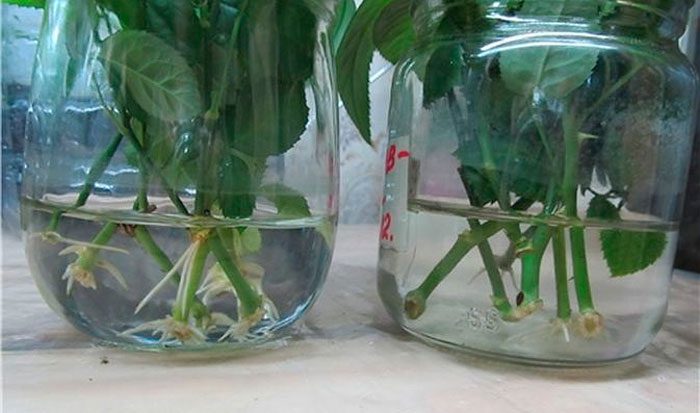

Eavesdropping is the easiest breeding method, which gives a good result. For cuttings can be used as flowering stems, and flowering. They should be cut from the second half of June to the first days of August. The lower oblique cut must be done directly under the kidney, while the angle of inclination of the cut is 45 degrees. The upper cut must be straight and as far as possible above the kidney. On the handle should be at least 2 internodes. Lower leaflets should be cut off, and those on top shortened by ½ part. Planted it at a depth of centimeter in the mix consisting of sand with the ground, or in the sand. Cover it from the top with a glass jar or a cut bottle of plastic. Clean in a well-lit place, protected from direct sunlight. Watering is done without removing the shelter. Processing means accelerating the growth of cutting roots cuttings can be useful only when the variety has a long rooting.

In the springtime, make an incision escape over the kidney. Then you need to put it in the prepared groove, the depth and width of which should be from 10 to 15 centimeters. At the bottom of the groove, you must first pour a layer of humus and cover it from above with soil. Fixation of the shoot produced in several places. Then it is covered with soil so that the upper part rises above the surface of the soil. Layers need systematic watering. After the onset of the next spring period, cuttings should be cut off from the parent plant and planted in a new place.
Grafting of climbing roses
Budding - inoculation of the eye of a cultured rose on the rhizome of wild rose. This should be done from the last days of July to the last days of August. Before making the vaccination, rosehip must be watered properly, then on the root neck of the stock you need to make an incision in the shape of the letter T. The bark should be hooked and slightly torn off from the wood. From the cutting of a rose, it is necessary to cut out the peephole together with part of the bark and wood. It is then placed tightly into the prepared incision and is very tightly rewound. this place okulirovnoy film. Then it is necessary to produce hilling rosehip, so that the soil rises above the site of inoculation for not less than 5 centimeters. After half a month, the bandage is slightly weakened, and next spring it is removed altogether.
Features care after flowering
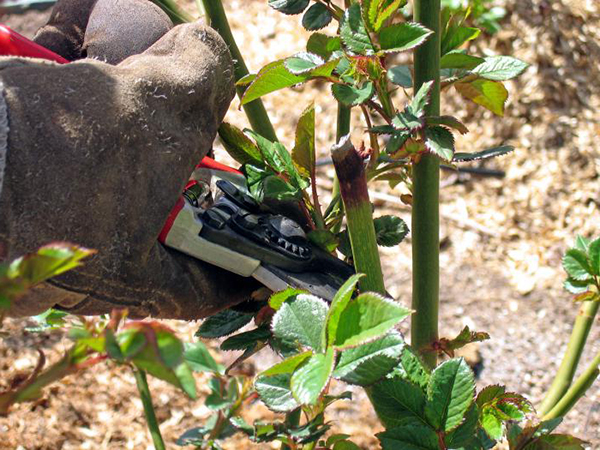

What to do when roses bloom
With the beginning of the autumn period, you should start preparing roses for the winter period. From the last days of August you need to completely stop watering and loosening the land and start feeding with potassium instead of nitrogen. The upper part of the undemanding stems must be removed. Such roses must be covered for the winter, but first they are removed from the supporting structure and laid on the soil surface. A young plant laying on the ground is very simple. An adult copy is not easy to lay on the ground, and it can take up to 7 days. It should be remembered that at low temperatures the shoots become fragile and can break.

Cover the plant is necessary when the air temperature falls below minus 5 degrees. This should not be done before, because the flowers should be hardened, and they can also begin to stretch or grow (which is associated with a long stay under the shelter without air). Shelter should be made in not rainy windless weather. With the shoots taken off, remove the leaves, cut off the damaged stems, tie the rods using a rope, and then carefully lay them on the litter. To create it, you can use dry leaves or lapnik. Do not lay the plant on bare soil. Squeeze or fix the plant on the surface of the soil, and top it up with dry leaves or grass, and you can also use spruce branches. The base of the bush should be sprinkled with soil or sand, and then cover the plant with lutrasil, a film of polyethylene, roofing material or other material that can not get wet. Between the plant and the shelter should remain a layer of air.
Winter care
In the event of a thaw in the winter, you need to raise the shelter for a while. Plants use fresh air in winter. But to remove the leaves or lapnik should not. When the real spring begins to come, the shelter must be removed, otherwise the plants may begin to ache. Lapnik at the same time save roses from freezing.
Varieties of climbing roses with photo and names
The most popular varieties are described below.
Ramblers (small-flowered climbing roses)

Such a vigorous variety can reach a height of 800 cm in height, while the crown is up to 300 cm wide. Saturated green leaves are almost invisible due to the many creamy white flowers, which are 4–5 centimeters in diameter. They smell like musk. It needs a lot of space and reliable support. Not afraid of frost.
Ramblin rector

Five-meter whips are decorated with light green leafy plates. Semi-double cream flowers are quite small. They are 40 pieces in the composition of large inflorescences in the form of a brush. When exposed to the sun fade to white color. This plant is also cultivated as a bush.

Bushes two meters in height and width are decorated with terry flowers, painted in a rich crimson color, which are collected in racemes. It blooms until the end of the summer period, but the bright color burns out in the sun. It is frost-resistant and is not subject to infection by mealy dew.
Climming and Climber (large-flowered varieties)

The height of a tall, tall-growing bush reaches 250 cm, and its width is 150 cm. The diameter of the densely-flowered flowers is 14 centimeters. They are painted white with a greenish tinge and smell of fruit. Flowering until the end of summer. It has resistance to diseases.
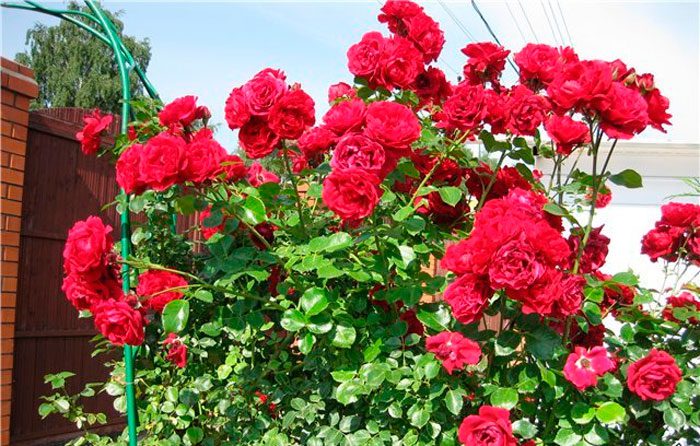

The four-meter bush is decorated with dark green carved leaves and semi-double velvety large ones (diameter of 8–10 centimeters). Have a rich red color. Not afraid of frost, resistant to disease. Blossoms several times per season.
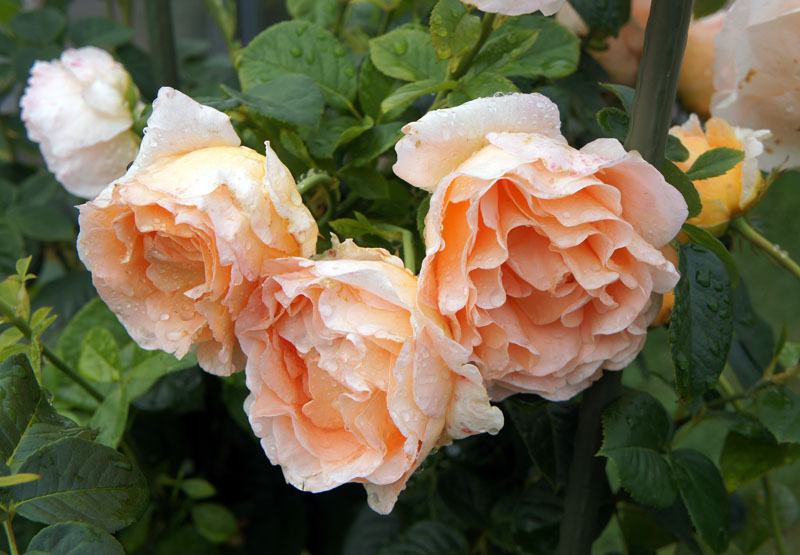

The height of the bush can exceed 200 centimeters. Glossy leaves have a dark green color, and double large (diameter 12 centimeters) flowers - apricot. During the season flowering is observed 2 or 3 times. Powdery mildew resistant. For the winter you need a good shelter.

The vigorous three-meter bush has a one and a half meter diameter. Leaflets dense dark green. Terry lilac large (diameter up to 10 centimeters) and fragrant flowers are part of the inflorescences. It grows quickly and blooms several times per season. Resistant to diseases.
Cordes hybrids (they are not separated into a separate group, but referred to Rambler)

The fragrant tall plant has a diameter of 100 cm, and a height of 300 cm. The racemes of the racemes consist of large terry (up to 10 centimeters in diameter) flowers of a dark pink color. Flowering is observed 2 times per season. It has resistance to powdery mildew and black leg.

Bush has many shoots, and its height is 350 centimeters. Crusiform inflorescences consist of semi-double large (diameter up to 10 centimeters) flowers, painted in a yellowish-golden color. They smell like fruit. Flowering is observed twice per season.

The height of a branchy, strong-growing bush is up to 300 cm, and the width is up to 200 cm. Small inflorescences consist of rich red flowers. Flowering per season is observed several times, but the first is the most abundant. He is not afraid of frost, bad weather and disease. Fast growing