Preparation for planting and transplanting trees - features of the technology of work. Is it necessary to whiten a newly planted sapling for the winter? Care for young plantings
Autumn is the right time to plant new trees in the garden. We talked with the candidate of biological sciences Raisa Matveeva and asked her questions that often arise from amateur gardeners.
We hope that after reading this material you will not doubt your strength and without any problems “settle” new tenants in the garden.
1. What should be the roots of a sapling? What to look for when buying?
The further fate of the plant depends on how well developed and viable the roots are. The length of the skeletal roots of seedlings of seed and stone fruit cultures must be at least 25-30 cm. Plants with very short roots either do not take root at all, or take root very poorly and lag behind in growth. Short roots after planting do not go deep, but spread in the upper soil layer, which is characterized by unstable water regime. Also, they are formed less growth points.
In addition to the length, the quality of the root system is indicated by its structure - seedlings with a taproot root system and poorly developed lateral roots take root poorly. Plants that, in addition to large roots, have many thin, overgrown (fibrous) roots, are much better and quicker.
The roots of high-quality seedlings should be healthy, without signs of freezing and drying.
Remember! It is better to buy a seedling with an insufficiently developed crown, but with good roots, than with a strong above-ground part and a well-formed crown, but with shortly cut roots.
2. Sometimes seedlings are sold with apples hanging on branches. This is normal?
With the leaves and especially with the fruit seedlings can not buy!
3. How to save a sapling after purchase?
It is not enough to choose a good varietal seedling, it must also be carefully delivered to the garden. Any young plant, be it an apple tree, pear, cherry, sweet cherry, currant bush or gooseberry is a living organism. When such a seedling is dug out of the soil, the roots no longer supply it with water, and the leaves continue to evaporate it.
It is often necessary to witness how the purchased seedlings are delivered to the landing site: at best, the roots are wrapped in newsprint, or simply bare, the branches are not connected.
What should I do? First of all, take care of the roots: overlap them with moistened sacking, a rag, grass (and not only outside, but also inside the bundle), and then pack into any material.
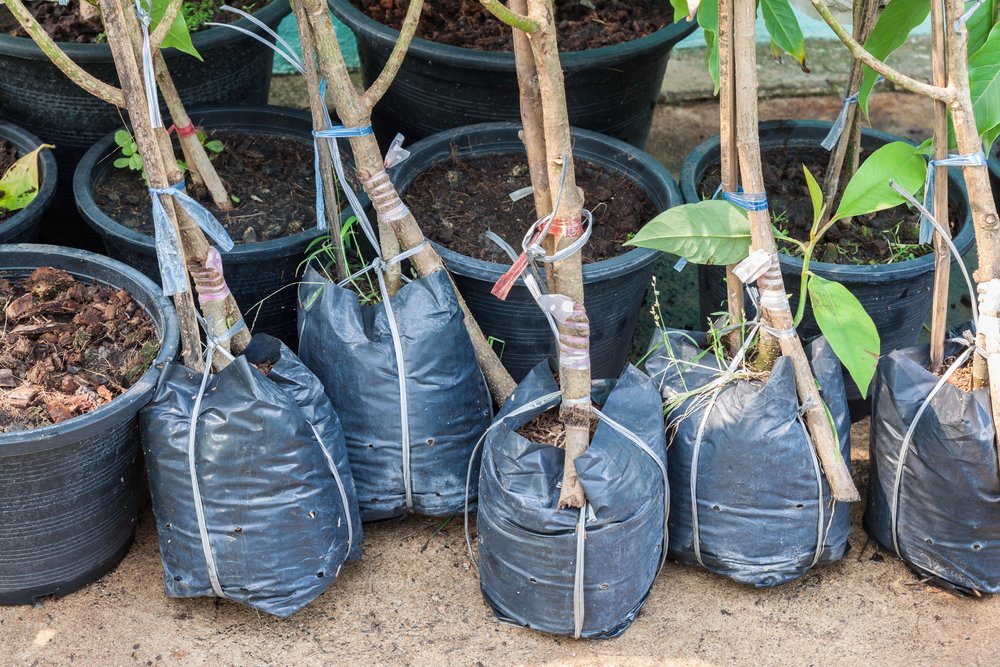

If there are leaves on the seedlings, immediately cut them off carefully, without damaging the buds, and tightly tie the branches in the bundle of seedlings with soft twine. It is desirable to wrap the whole bunch of saplings (trunks, branches) at least with paper. When the seedlings are in the path for a long time, be sure to water their roots and branches with water to prevent drying.
4. What should I do if the plant is dry during delivery?
In this case, the seedling must be dipped in water for a day.
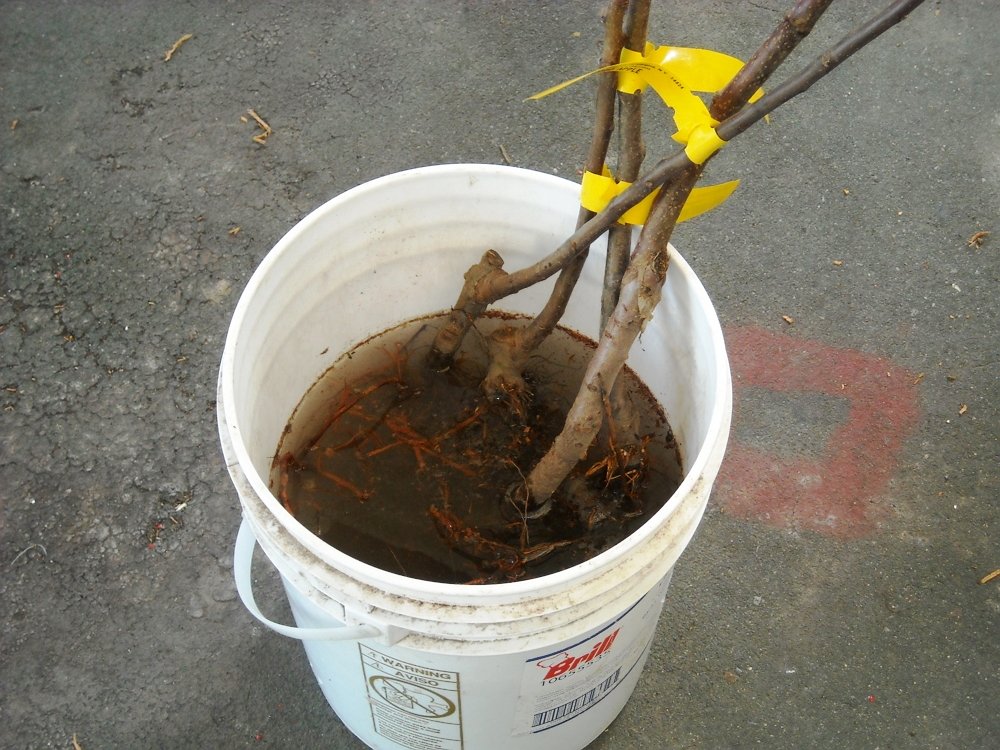

5. Do I need to prune the roots when planting?
In all cases, when digging up seedlings in the nursery, the roots are damaged, their ends are kneaded and shredded. Therefore, before planting, young plants and, above all, the roots must be carefully examined: they must be fresh. Dry, frozen, rotted, moldy roots should be cut, broken down - shortened to healthy parts. The healthy root in the cross section is white, and the frozen and withered root is brown.
Cut the roots with a sharp knife. Secateurs do not give a smooth cut, knead the root.
After preparation, the roots should be dipped in a clay mash and temporarily prikopat seedling in wet ground before planting.
6. At what depth should be planted fruit and berry crops?
At first, it is very important to provide the young plant with the roots that are very short when digging out from the nursery, the best conditions for survival and growth of new roots.
Planting pits for proper and uniform development of the roots is better to do round with steep walls. Pits narrowed to the bottom - not the best option: in them the roots will curl and grow in the middle of the pit.
7. How often should the newly planted seedling be watered?
After planting, as soon as the roots are covered with a layer of soil 10-15 cm thick, landing pit pour out 2-3 buckets of water. Water-diluted soil fills the resulting voids around the roots, which take root better under these conditions.
When moisture is absorbed, the pit is filled up to the top and the plant is no longer watered. The upper soil layer remains loose and breathable. In the future, the need for irrigation depends on the weather and the degree of drying of the soil. Garden crops need not frequent watering, but moisturizing the soil to the depth of the root system.

8. Is it necessary to drive a stake into the landing pit?
Planting stake - support for the young seedlings. It protects it from the wind and does not allow it to sway and bend. In the early years, such a prop also serves as the basis for winter hare strap or frost action.
If you plant a standard seedling without twisting the stem in a windless corner of the site and are confident that the hares will not pick it, then the installation of planting stake is optional.
9. Is it necessary to mulch the planting site?
Mulching delays the evaporation of moisture from the soil, improves the temperature and soil structure, protects the ground from weathering, and suppresses the development of weeds. A layer of organic matter on the surface of the soil is not recommended to touch the whole season. Plants whose tree trunk has been mulched are almost twice as fast and develop better, especially in dry years (as compared to the naked).
10. How to grind a garden?
Pristvolnye circles of fruit and berry trees You can mulch with cardboard, compost, raw dung, fallen leaves, pine needles, sawdust, humus, freshly cut grass.

Fresh sawdust, shavings can be applied as a mulching material under raspberries and other berries without adding nitrogen fertilizers.
Strawberries for the winter period can be covered with pine needles, and in the summer period it can be used as mulch. Needles - an excellent mulch material. And for strawberries it is also protection from slugs and snails.
11. Is it possible to plant fruit seedlings at the place where there were garden beds?
Can. The main thing is that the groundwater at the site for planting fruit crops should not be too close to the soil surface. The minimum allowable depth is 1.5 m.
12. In the summer, a hurricane broke an apple tree. Is it possible to plant a new plant in its place this fall?
If a old apple tree uprooted, planting a new seedling on this place is not recommended. No other place? Then, before planting, it is desirable to completely replace the soil in terms of the volume of the landing pit (at least 1 × 1 m).
13. How to correct a shallow or deep tree planting?
Fruit trees, especially apple and pear, react sensitively to planting depth. Shallow planting, when the root neck is located slightly above the soil surface, they suffer painfully, but it is easily fixable and does not cause much harm. In this case, the roots of the newly planted tree can be sprinkled with soil from the aisle. In addition, after planting manure, humus, and tree trunks are mulched in a tree trunk. And during the autumn digging, the soil shifts somewhat toward the root collar.
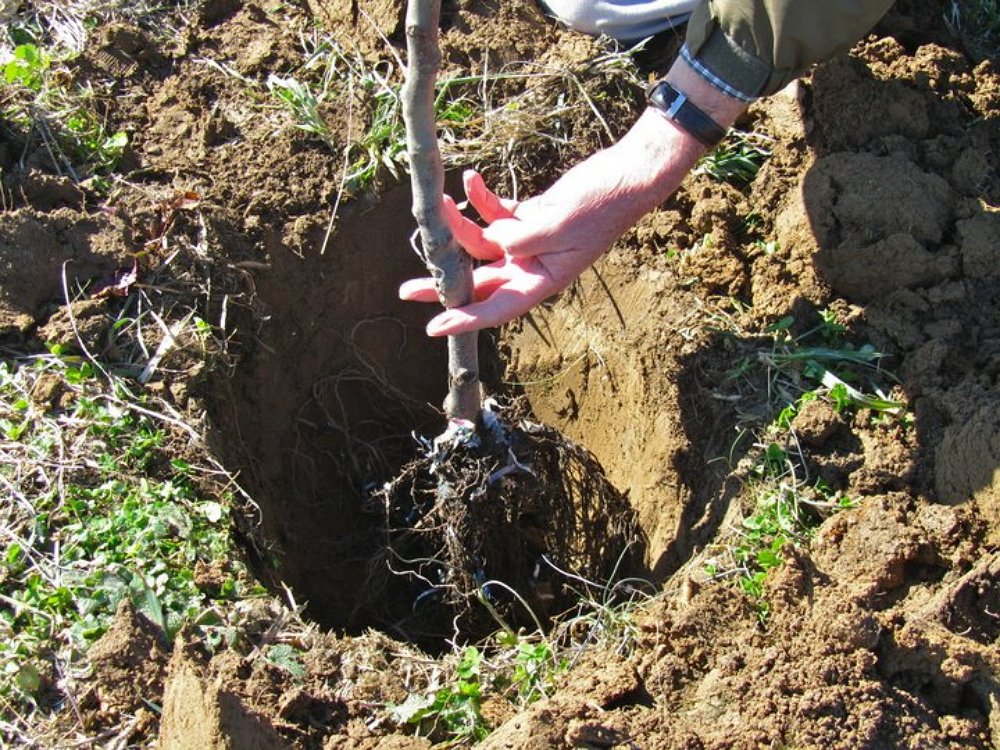

It is more difficult to correct excessive root penetration. This happens when during planting does not take into account the subsequent sedimentation of the soil in the planting pit. As a result, the root neck is significantly below the soil surface, which violates the relationship between the aerial part of the plant and the root system. The tree seeks to compensate for this violation by excessive vegetative growth and much later enters fruiting.
Thus, it is better to correct the error in the year of landing. To do this, cutting the tree, tighten the tree to the desired height so that the root collar is slightly above the soil surface, and nutritious soil is pushed under the bottom of the coma. At the end of the work the tree is well watered.
14. Is it necessary to whiten a newly planted seedling for the winter?
Young trees with smooth bark to whiten is not only not useful, but even to some extent even harmful. Whitewashed trees grow worse, they have slowly thickened limbs, clogged pores in the bark, gas exchange slows down. Especially harmful to whitewash lime solutions with the addition of sticky (hard-to-wash) substances. In this case, the plants can even occur serious burns and bark death.
On the other hand, the trunks and bases of the skeletal branches of fruit-bearing trees must be whitened, using a solution of freshly topped lime. The folds, cracks and roughness of the hardened bark of adult trees serve as a winter haven for garden pests. Autumn (in October) whitewashing boles helps to destroy them and, moreover, is a disinfectant that destroys mosses and lichens settling on the bark.
Recipes of a solution of freshly sour lime: 2 kg of lime, 0.5 kg of copper sulfate and 2 tbsp. Milk diluted in 10 liters of water or 3 kg of lime and 1.5 kg of clay diluted in the same amount of water.
And this treatment also protects the bark from sunburn and temperature extremes (whitewashing is a kind of thermal insulating "fur coat", thanks to which the tree trunk does not overheat on a winter day and does not freeze at night).
Sergey Shkarinov, Candidate of Agricultural Sciences

The sludge of trees and shrubs is one of the most important operations in their cultivation. In many respects it depends on it, whether the seedlings will turn into beautiful plants or get a miserable look, or even die. We will understand the reasons that determine the success of planting and transplantation.
Of primary importance are: selection of planting sites and healthy seedlings adapted for this climate zone; proper planting in optimal timing; proper aftercare.
Time to land
Spring should hurry: when the leaves begin to unfold on the seedlings, their survival rate decreases sharply. Therefore, the spring planting boom is swift and fleeting. More sizeable and thorough autumn landing period. It is not profitable for kennels to leave seedlings in the fields, so in the fall the assortment of planting material is the richest and there is an opportunity to choose the best.
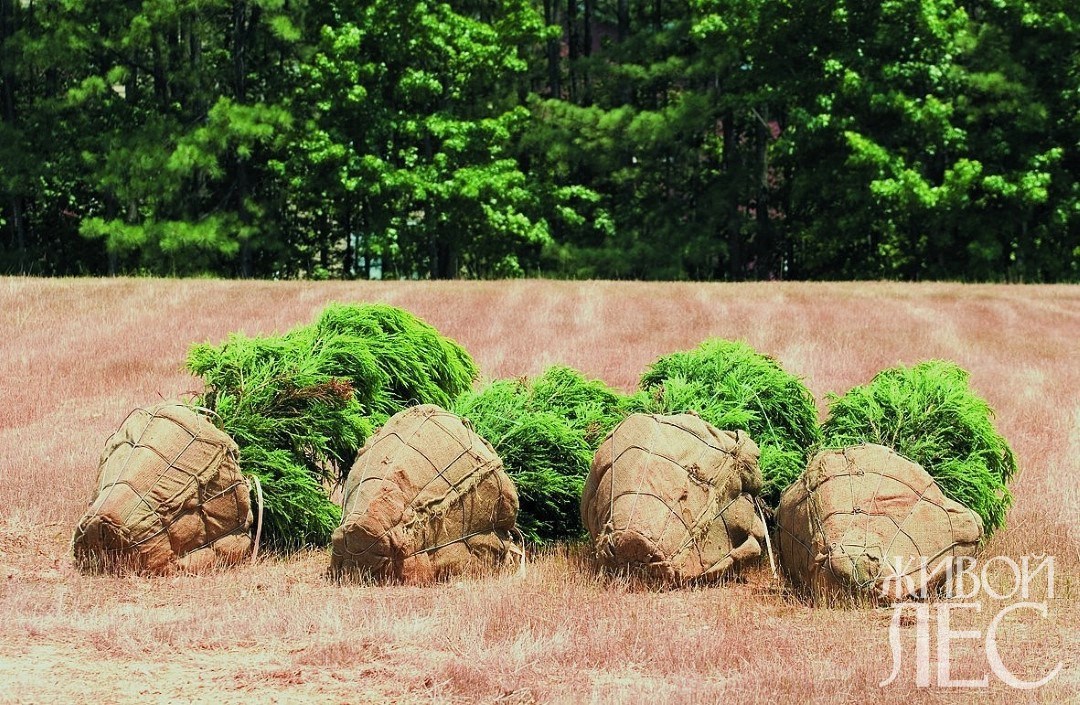

We are talking about seedlings with an open, root system released from the ground. In such a state, in dry weather, they can be in the open air for no more than 15 minutes, after which the most tender root ends (the basis of the root system), which suck in water, begin to dry out and die. Therefore, acquiring planting material with an open root system, you need to take care of its protection against draining and stock up with a suitable container.
Helpful adviceFor small plants, you can use boxes (preferably plastic with small ventilation holes), for medium-sized plants, garbage bags ranging in size from 20 to 40 liters are good, for large seedlings, you should buy double plastic wrap up to 1.5 m wide.
Upon arrival at the site of planting, seedlings should be prikopat as quickly as possible.
- To do this, you need to prepare a ditch with one vertical, and another with an inclined wall (at an angle of 30 °), where the seedlings are placed, and their roots are sprinkled with earth.
- When digging, the seedlings remain until planting; after their extraction, the roots cannot be left open for more than 15 minutes.
- Dug-out seedlings can be stored for a long time, without losing their viability.
Shrubs better planted in the fall, and trees - in the spring.The rule is based on the fact that shrubs planted in early autumn (during September) have time to take root in the new place, and the trees do not have time and are damaged by frost in winter. Therefore, tree saplings are best left in the prikop until spring.
RecommendationIt is best to purchase and transport seedlings with an open root system in cool overcast and even rainy weather.
Selection of seats
To begin with, it is necessary to assess the conditions in which the planted plants will develop:
- sunny or shaded;
- too wet or dry;
- with rich clay or poor sandy soils.
This will determine the range of trees and shrubs, and by setting the size of these areas, make the calculation of the desired amount of planting material.
The most common mistake is too tight landing.The reason for this is the lack of knowledge of how large a plant reaches in adulthood. An authoritative specialist in Europe, Dr. DG Hessayon recommends that when designing footprints, the following calculations be made:
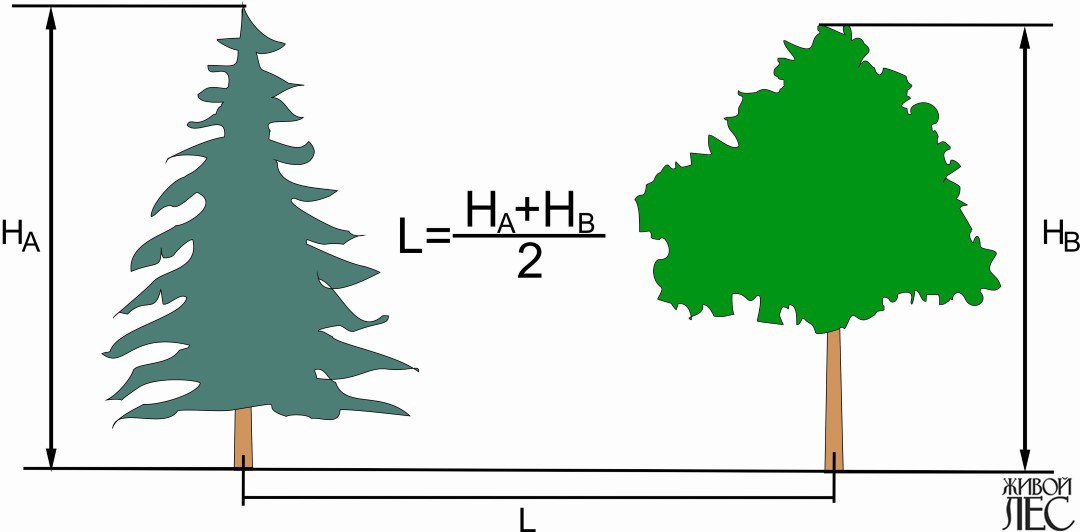
Fig. 1. The calculation of the distance between the places of planting trees
For most trees (except for columnar) you need to add down the height of mature trees A and B and divide the resulting amount into two - this will be the optimal distance between the centers of the planting pits (Fig. 1).
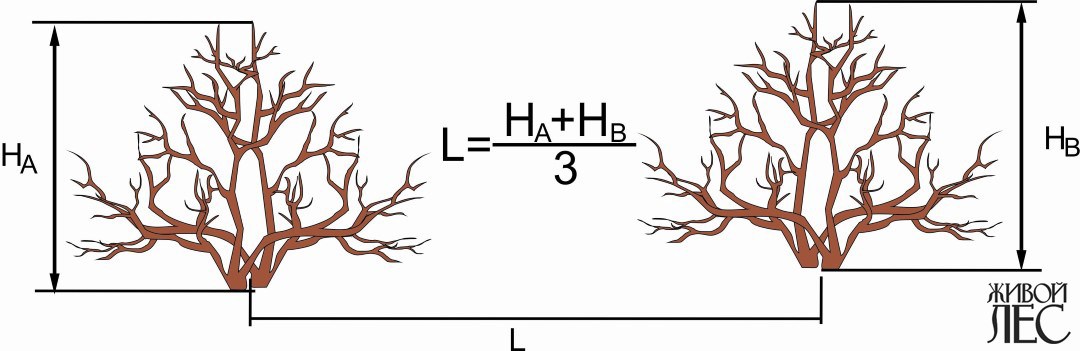
Fig. 2. The calculation of the distance between the places of planting shrubs
For most shrubs the height of the adult bush A and the adult bush B should be added and the sum obtained should be divided into three (Fig. 2).
Trees:
- spruce spruce (typical form) - up to 25 m (80 years);
- english oak - up to 25 m (100 years);
- platanovid maple (gold-leaved) - up to 20 m (60 years);
- tatar maple - up to 9 m (20 years);
- river maple (Ginnala) - up to 6 m (15 years);
- large-leaved linden - up to 25 m (80 years);
- siberian larch - up to 25 m (80 years);
- white willow (silver) weeping form - up to 20 m (80 years);
- norway willow - up to 8 m (20 years);
- five-willow willow - up to 12 m (30 years);
- willow fragile spherical shape - up to 10 m (30 years).
Shrubs:
- common hazel - up to 3 m (10 years);
- european euonymus - up to 2.5 m (10 years);
- sea buckthorn - up to 5 m (10 years);
- privet - up to 3 m (8 years);
- chubushnik - up to 3 m (10 years).
- lapchatka (Kuril tea) - 0.4–0.9 m (5 years);
- rhododendron - 2 m (5 years);
- japanese spirea - 0.6 m (5 years);
- spirey Bumolda - 0.15–1.5 m (5 years).
A large range of heights in small shrubs is associated with the presence of a large number of decorative forms and specially bred varieties in each species).
You can set the height of trees at any age you are interested in, for example, 10, 20 or 40 years, using the regional growth tables used in forest management.
Preparation of landing holes
The dimensions of the planting pits should correspond to the peculiarities of the root systems of plants. Nevertheless, even in such trees as pedunculate oak and pine, whose skeletal roots go down to the soil to a depth of 5–6 m, the main mass (up to 90%) of the small suction roots is located in the upper 40-cm layer. Therefore, even when planting large-sized trees with a lump, the depth of the landing pit rarely reaches 1 m, and most often it is 60–80 cm.
It is much more important for plants to have an opportunity for the development of lateral roots, which, constantly branching, develop upper, rich in food and well-aerated layers of the soil horizon. In these layers, a huge amount of soil bacteria (up to 5 million in 1 cm3) and fungi lives, without the vital activity of which the plant roots cannot exist. Therefore, the width of the landing pit should be done as much as possible, within reasonable limits.
For detached trees and bushes and during group planting, individual pits are dug for each plant, and trenches are prepared to create hedges and borders.Digging:
1. With a bayonet spade a slit is cut through - the top layer of soil along the perimeter of the future pit, which should be at least 1 m for trees, and 60 cm for large bushes.
2. The top fertile soil layer is removed along with the sod and is folded on one side of the pit.
3. The underlying soil horizon lying beneath the fertile layer is dug out, which differs from the upper humus content (color) and mechanical composition. In some cases it is lighter (sandy), and most often heavy - loamy. There will be much more soil from the underlying horizon, and it will be piled on the other side of the pit.
4. The walls of the pit are made steep, the bottom is loosened to a depth of 15–20 cm.
5. On soils underlain by heavy loams, it is imperative to install drainage systems that drain water accumulating from the bottom of the pits from precipitation and spring melting of snow.

Fig.3 Pit digging
- Trench They are dug out in compliance with the same rules, only the drainage of water into the general drainage system should be done in the lowest place along its length, and in cases where there is no natural slope, it should be created with a small increase in the depth of excavation of the soil.
- For planting a hedge even from the largest shrubs or small conifers (for example, western thuja) or deciduous (for example, Ussuri pears) it is quite enough to dig a trench 60 cm deep.
- For medium sized shrubs (cotoneaster brilliant, privet, rose wrinkled) the depth of the trench should be 40-50 cm.
- To create borders of small bushes (Spireas of the Japanese, p. birch-leaved, undersized forms of the village Bumolda, Potentilla bush and many others) it is enough to dig a trench 30–35 cm deep.
The trench width depends on the size of the planted plants and the planting pattern:
- For single-row planting of trees, it should reach 40–50 cm.
- For plants of medium size - from 30 to 40 cm.
- For small bushes - from 20 to 30 cm (i.e., the width of the shovel).
- When laying two-row hedges trench width is doubled.
____________________________________________________________________
There are several ways of planting trees and shrubs, of which we consider the two most different in their technology. This is a planting with bare and closed root system.
Open root planting
Pre-prepared pits should immediately fill up one third of the land mixture after digging. The fertile layer of soil with turf folded on one side of the pit should be lightly crushed with a shovel and laid on the bottom.
On the other side of the pit, we have left less fertile soil from deeper soil horizons that needs to be refined. If this soil is heavy loamy, then it is necessary to add the same amount of sand in terms of volume, if it is sandy - the same amount of loam (as loam it is best to use soddy earth, or bottom mud of lake sediments, or any soil of heavy mechanical composition).
Then add 2-3 parts of organic humus (peat, sheet, grass, compost or lowland peat). High-quality humus has a dark brown, almost black color. All these components must be thoroughly mixed with the addition of dolomite flour or hydrated lime and full mineral fertilizer.
Earth mixture: 3 parts of organic humus, 1 part of loam, 1 part of sand, 0.5 part of dolomite flour (or 0.2 part of hydrated lime) with full mineral fertilizer added to it, preferably complex (“Kemira” or “Akvarin”) ). We fill the landing hole approximately 1/3 of its depth. The rest of the land mixture is left on the surface before planting.Before planting you need to prepare enough water.
The seedlings extracted from the digging are placed in the center of the pit so that their roots, without bending and not resting against the walls of the pit, evenly spread in different directions. If the roots are too long, they are pruned with shears or hemmed with an ax on a wooden block.
It is necessary to ensure that the root neck of the plants is located above the soil surface, for which the required amount of the land mixture is selected from the buried 1/3 pit. For the purpose of the most uniform arrangement of the roots at the right level in the pit, a hillock is arranged, on which the roots are laid out (Fig. 4).
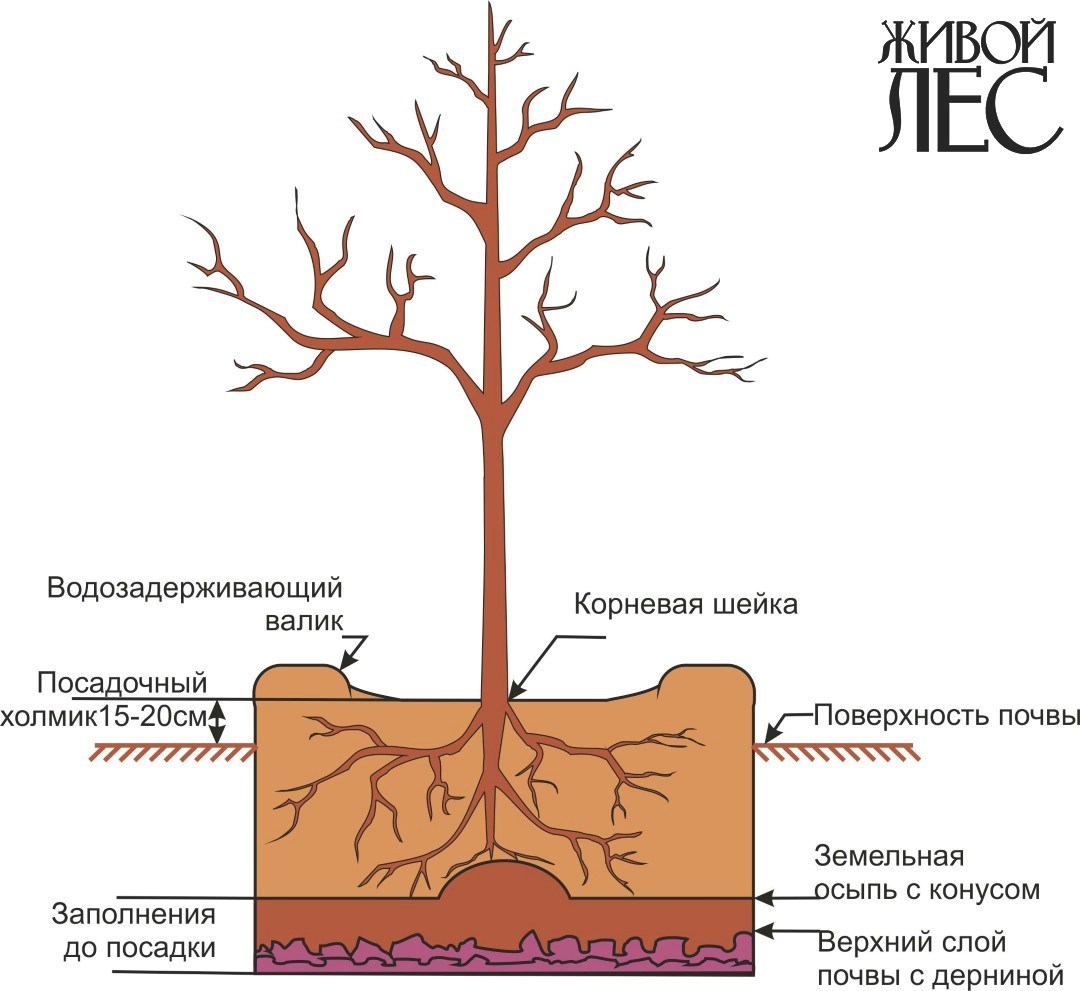
Fig. 4. Properly planted seedling
After installing the seedling in a hole, approximately 2/3 of its total depth is filled with a ground mixture covering most of the plant's root system. Then a large amount of water is poured. Filling should be continued until the water level is set at 2/3 of the depth of the landing pit, after which the pit is finally filled with dry land mixture.
All this time, the seedling must be maintained in an upright position, slightly supporting and pulling it up. So that during shrinkage the root neck of the seedling is not below the level of the soil surface, the pit is filled up 15–20 cm above this level.
The planting method described above practically guarantees the survival of plants, since the slurry formed in the root zone envelops their lobes, ensuring the contact of the suction root hairs with the soil aggregates.
With all other methods of planting, including the most common dry planting followed by abundant watering, the effectiveness of planting is much lower due to the weaker contact of root ends with the soil and the formation of air sacs in the zone of location of the roots.
In addition, when water is poured directly into the pits, the formation of dirt around the landing site is prevented, which cannot be avoided by watering from above.
In conclusion, a landing mound is formed around the ring roller, which will retain water in the root zone during irrigation.
It is also useful to mulch the surface of the mound with peat compost or other material in order to prevent the formation of a crust on the soil surface, causing a violation of its aeration, as well as slowing down the evaporation of moisture.
Landing with closed root system
Saplings with a closed root system can be planted almost throughout the year. Of course, nobody will plant small and medium plants in the snowy winter, but for large trees the winter planting with a frozen lump remained for a long time the only method widely used in Russian practice.
The technology of planting container saplings is quite simple and essentially differs little from the planting of seedlings with an open root system described in detail above. Therefore, taking it as a basis, we consider the specific features of planting container plants.

First of all, You should be aware that the soil (land mix) is included in the list of quarantine materials prohibited from being transported across state borders, and therefore for official delivery of seedlings from abroad they are placed in containers with peat or other material allowed for transportation, completely unsuitable for further growth of these plants. These seedlings need to be removed from the containers as soon as possible and planted on permanent place at open ground or containers with a normal land mixture.
In recent years, organizations engaged in the supply of seedlings from abroad, have established a process of peering of planting material at their bases, and plants with a good land mix in containers, as a rule, go on sale.
However, there are cases of direct deliveries.
RecommendationTherefore, before purchasing a plant in a container, you should make sure that the mixture is of good quality in case you have to keep it in it for 2-3 weeks before planting in a permanent place.
Immediately before planting, the seedling must be carefully removed from the container. If the roots came out of the coma and spun along the walls of the container, they should be cut with multiple vertical movements of the sharply sharp knife around the entire circumference of the coma or cut into a coma several shallow triangular-shaped slots along its side surface.
Further operations are not much different from planting seedlings with an open root system:
- first, the ground mixture is poured into the landing pit so that the surface of the coma placed on it protrudes 5–10 cm above the soil level;
- then water is poured into the pit and backfilling with a ramming of the dry earth mixture is made into the gap between the clod and the edge of the planting pit along its entire perimeter.
In conclusion, we can recommend for the best engraftment of seedlings planted by the two methods described above. use root formation stimulants, the most famous of which is “Kornevin”. Working solutions are prepared at the rate of 0.0001% concentration. Solutions of higher concentration can lead to burns of root tissues and their death.
Fastening
In places of natural growth, trees are held at the expense of roots, tightly covering a large amount of soil space. Seedlings are deprived of such support, so after planting they need to be fixed.
Planted shrubs are usually fairly well kept in the soil, as their escape system has a low center of gravity. The center of gravity of the trees is much higher, so after planting, young trees need to be fixed.
Strengthening landings made with the help of supports:
- for seedlings with an open root system, one support is enough, which is driven in before planting in the bottom of the pit 10–15 cm from its center.
- seedlings planted with a lump, it is best to strengthen with the help of a pyramid of three pillars.
- for large seedlings, the only fastening system that does not interfere with the proper development of the tree is safety cobra system (Cobra®) for seedlings.
Planting large trees
Immediately you need to make a reservation that planting and transplanting large adult trees is a laborious process. It requires high material costs. However, it is very popular because of the rapid achievement of the decorative effect of green areas.
- Large-sized trees with a height of 2.5 to 4.5 m can be planted or transplanted on their own using small-scale mechanization.
- Planting trees above 4.5 m requires special equipment and equipment, so it is best to contact companies that specialize in this type of activity.
As mentioned above, winter transplanting large trees with a frozen lump gives in most cases positive results. However, it should be carried out at steady frosts not lower than 10–15 ° C.

Landing large size
Spring transfer (before leafing)most favorable for large trees, but its duration is very short. Frozen soil in winter makes it difficult to dig up the plants to be transplanted. When it is thawed, it becomes necessary to pack a lump in a special container to give it strength.
Period autumn transplant Lasts a long time, since the fall of the foliage to the establishment of low temperatures. This allows you to work in large quantities. In case of steady moderate frosts in autumn, it is possible to transplant trees with freezing of coma. In this case, there is no need to pack a lump in a special container, which significantly reduces the cost of the work. In the fall, it is necessary to take into account that the trees that are planted need root-weatherization for winter.
It is important to knowAll species shedding foliage in late autumn (poplar pyramidal, acacia is white, black alder, winter forms of oak) do not survive the autumn transplant, and it is better to plant them in spring.
Summer transfer trees in leafy condition is the most risky. It requires the protection of trees from high temperatures and direct sunlight.
The following tree species satisfactorily tolerate transplantation in adulthood:
- deciduous: linden, poplar, maple, horse chestnut, ash, oak (preferably red), apple, pear, plum, mountain ash, and in the south - mulberry;
- conifers: spruce (preferably prickly), fir, thuja, juniper.
Poor tolerate transplant in adult condition birch, pine and elm.
Care for transplanted large trees should be particularly careful and continue for two to three years after planting.
Selection of planting material
In the nursery of Western and Central Europe, well-established cultivation of seedlings, the root systems of which are enclosed in containers. The technological process, starting with grafting or sowing seeds and ending with the production of finished products that meet the standards, has been thoroughly worked out and perfected.
Our nurseries, located in a colder climate zone, could not compete with them due to the huge costs of sheltering container plants in winter. In this regard, Russian manufacturers were forced to switch to the purchase of cheaper products abroad in order to sell them or grow them. They invest the profits from this in suitable for our climatic conditions growing plants in open ground.
Attached images:

As a rule, planting raises many questions. How to plant? When is it better to plant? What to do with the packaging of the root system during planting? Is it easier to plant container plants?
The rules for handling plants and planting technology are quite simple, their strict observance, along with high-quality planting materials and attentive care of plants, guarantees you excellent results: high survival rate, healthy and ornamental plants for many years.
Basic rules for handling plants during unloading and planting
First of all, in order to avoid scrapping of branches and other damages, during the loading and transportation of plants, they are necessarily connected. It should be very careful to treat fragile and brittle plants, such as winged euonymus, hydrangeas, heathers, junipers, as well as dwarf coniferous and standard forms.
If the weather is hot, do not transport seedlings in a sealed body if it is not an insulated container. High temperatures can damage leaf and sprout tissue. Best for plants within the region are suitable cars with an awning or open (side). Isothermal containers are better for long-haul transport.
Plants at the site can be unloaded manually or by mechanical means: an auto-loader, a crane-manipulator.
Heavy trees require special handling. Plants with a lump can only rise behind a lump, and you should definitely support a tree trunk or crown, if it is a bush form. Rough handling of the trunk can cause serious mechanical damage to the bark and wood, as well as damage to the coma and roots, if you raise the tree for the trunk.
Coma of large trees and shrubs are usually packed in a metal sheath (grid). This greatly facilitates their unloading and movement - for lifting plants use special hooks that cling to the grid. However, if a lump is packed only in burlap, the use of hooks is unacceptable - this leads to severe damage to the burlap and the integrity of the coma, and, consequently, the root system of the plant.
When unloading large-sized plants with a large lump using a crane, 3 rods are used: 2 of them hold the main weight of the coma, and the third supports the tree trunk in a horizontal position or slightly higher (see figure). It is very important to protect the trunk in the place of attachment of the chalka from damage and burrs of the bark, for example, by wrapping it with a thick layer of burlap.
Unloading container plants is much easier. Plastic containers and soft bag-containers (Easy Lift), as a rule, are equipped with 2-4 comfortable handles.
After delivery of seedlings to the site, it is desirable to immediately begin their planting. The shorter the shelf life of plants and the faster the planting, the greater the survival rate. This rule is especially important during spring planting, when the air temperature rises every day, the plants enter the growth phase and require more and more careful care.
If, however, planting fails immediately, it is best to leave them in the shade for a while. Tall trees have great windage and can fall. Therefore, they need to tie up to any support, while protecting the trunk from damage by burlap. If this is not possible, it is permissible to carefully lay the trees on the ground.
Coma and plant containers need to be watered and, for storage, to cover from overheating and drying with burlap, or to mulch with a thick layer of sawdust, humus. Watering plants is done daily, and if necessary, 2 times a day.
If you purchased plants with an open root system and can plant them only after a few days, try to place them in cooler conditions: a basement, a cold garage or the north side of the house, where there is no direct sun. Roots need to be covered with a damp cloth, and best of all prikopat. You can not keep the root system of seedlings constantly immersed in water - the roots can not breathe.
Choosing a landing site
Ideally, plants should be planted according to the assortment list for the places marked in advance (project, planting drawing and dendroplan). This will allow you to avoid many mistakes in the selection of the range and placement of plants on the site.
If you do not have a planting project, be sure to consider not only the decorative qualities of one or another species, the size of adult plants, but also the requirements for growing conditions, but rather entrust the selection and placement of plants in the garden to a professional landscape designer.
A planted plant will grow successfully only under optimal conditions for soil, air, light, heat and moisture. If at least one of the conditions does not meet the requirements of the plant, then it will determine the result.
Usually, if during planting the requirements for growing conditions are not taken into account (for example, a light-shrub shrub is planted in the shade), this will not lead to the immediate death of the plant, but its development will be slowed down (the shoots will stretch, the crown will not be thick), decorative qualities will deteriorate (no bloom), frost resistance and disease resistance will decrease.
As a rule, most plants develop well if they are provided with the following conditions:
Illumination: optimal sun or partial shade; if the direct sun in the area is less than half the daylight hours, you should choose plants that tolerate partial shade and shade;
Soil moisture: optimal is average, that is, neither coma drying nor stagnation of water is allowed. For excessively dry soils, if it is impossible to ensure regular watering, choose drought-resistant species. With a high position of groundwater and stagnant waterlogging - respectively, plants resistant to flooding.
The soil: loamy or sandy, light, rich in organic and mineral substances. pH close to neutral (6-7). If the soil on your site is heavy or very acidic, be sure to take this into account when selecting the range, planting moisture-loving plants (or preferring the acidic substrate) and give preference to low-demand species and varieties.
Wind: Many heat-loving and capricious breeds winter well only on condition of landing in the place protected from wind where in winter more snow accumulates.
To choose plant species and varieties to the growing conditions, as well as to find a place in the garden for the specimen you like, you will be helped by the section “Planting Material” on our website with a detailed description of species, varieties of ornamental plants and a convenient search.
Planting plants with a lump
1. Terms of landing
Usually, planting is carried out in two terms: in spring and autumn.
During spring planting, the main danger is the drying of the root system. Therefore, during transportation and storage of plants, care must be taken to ensure that the roots (lump of the earth) are always wet, and the branches (especially those with full-blown leaves) are protected from the scorching sun and wind.
The terms of spring planting - immediately after thawing of the soil and before the start of active growth of shoots (in middle lane usually from early April to the first week of May).
But, despite the fact that the period between the maturation of the soil and the beginning of growth for plants is only two or three weeks, in which it is necessary to keep within, the spring planting has many advantages.
First, plants planted in spring during summer and autumn will be able to root well in a new place and adapt to our climate. Timely spring planting with the observance of all the rules of agricultural technology gives the highest survival rate.
Secondly, from a practical point of view, it is preferable to plant in the spring, since the choice of planting material is the widest in April-May: the peak of deliveries falls just in the spring. You can not only place an order for plants of the desired type, variety, size and quantity, but also choose the items you like on the site.
When choosing a planting date, some biological features species. Thus, the autumn transplant is poorly tolerated by such species as oak and birch. These breeds are traditionally planted in the spring (for container plants this is not relevant). Heat-loving capricious plants (for example, rhododendrons, azaleas, privet), also in our climate, preferably planted in the spring - this will allow them to better take root and prepare for winter.
In addition, during the spring planting, you can already enjoy new plants in your garden this year.
A very typical mistake during the spring plantings: "We need to wait until the earth warms up." In fact, plant better earlier, as soon as you can dig a planting hole.
Season autumn plantings begins with the beginning of leaf fall. Compared with the short spring period, the search and planting of the necessary species or plant varieties can continue until the first frost, but the peak of the autumn season is September-mid-October.
Do not over-delay the landing: in late autumn, the choice of planting material in nurseries and garden centers is not so rich.
In this case, it is much more convenient to place an order for plants and get high-quality planting material by a certain period in the right range and quantity.
2. Seat preparation
Planting starts after the completion of construction and part of the landscape works on the site. The area for planting should be leveled (if necessary, a vertical layout is performed), cleared of debris, and necessary measures are taken to improve the soil. This will protect your new plants from unintentional damage to the bark during work, soil compaction in the root zone, filling of excess soil covering the root collar, etc. and will avoid many problems in the future.
Planting pits and trenches are dug in accordance with the project after performing the centering works (project removal in nature). For early spring planting, the pit can be dug in the fall, insulating them for the winter with foliage, moss, sawdust, straw.
When digging holes, the upper fertile layer of earth is folded separately from the lower, less fertile. When filling pits, first use fertile soil. In case of unsuitability of the excavated soil, it is partially or completely replaced with the brought fertile soil.
Optimally, if the properties of the soil, its mechanical composition at the site and within the planting pit will be close. Significantly change the composition of the soil only within the planting pit should not be.
For some plants (rhododendrons, heathers, roses) a special soil substrate is required, which has a certain structure, composition or pH, which is prepared in advance, in accordance with the requirements of the plants or bought ready-made.
If the soil at the site is broken, the soil contains a large amount of debris and clay (removed from the basement) and there is no possibility to take measures to improve it, planting is carried out in holes filled with imported soil.
The shape of the pit do round with steep walls. Since after planting the roots of the plant mostly grow to the sides, a large depth of the planting pit is not needed. It is better if it is a little more than the height of the coma of the plant - this will subsequently reduce the subsidence of the soil.
The diameter of the planting pits depends on the size and age of the plant, and, most importantly, on the size of the root system. On average, the diameter of the pit should be 1.5 times the diameter of the coma.
For dense group planting of shrubs, common pits are dug in the shape of the landed group, for hedges - trenches.
Separately, it is necessary to consider the issue of planting on heavy, clay soils. As a rule, improvement (replacement) of the soil within the planting pit (especially for large trees) is ineffective, since a large difference in the mechanical composition of the soil between heavy clay and light planting soil will retain the “container” effect: the plant roots will most likely not leave the planting limits. pits. In this case, you need to improve the soil throughout the site. The situation is similar with excessively light, sandy soils.
3. Planting technology
After preparing the seat proceed directly to the landing.
When installing a plant in a hole, it is very important to track the position of the root collar (thickening of the base of the trunk, where it passes into the roots).
Have woody plants root root penetration, especially on heavy clay soils, leads to the formation of rot. The fact is that with prolonged stagnation of water, which often happens in the spring near the trunks during snowmelt or in rainy weather, oxygen-free conditions are created, the bark on the trunk cannot breathe normally and can be damaged in the lower part by rot.
This process is slow, so these plants can first grow and develop normally, but gradually become depressed and die.
To properly install the plant, first examine the root system and the base of the trunk: whether the root neck is visible. If it is buried, it is necessary to release it, removing part of the soil from the surface of the coma (or container).
The position of the root collar during the installation of the plant can be checked with a flat bar on the edges of the planting pit. Ideally, the root collar should be at the level of the soil (permissible, slightly higher), but should never be buried. Therefore, taking into account the subsidence of the soil, the plants are planted at 5 - 20 cm above the desired level. In order not to take out a large tree several times and not to pour in the ground, it is advisable to compare in advance the depth of the planting pit and the height of the plant coma.
After installing the tree in the pit at the right level, it must be aligned so that the trunk is vertical and the plant is oriented in the direction you need.
If necessary, you need to take care of the garter of planted plants. In order to secure the tree in a vertical position, use two durable pegs, which are driven into the bottom of the landing pit, and elastic twine. Such support is needed in the first 1-2 years after planting, until the tree consolidates in a new place in a natural way.
Very often, our customers ask whether it is necessary to remove burlap and wire braid (mesh) from a coma before boarding.
Metal braid and burlap serve to preserve the integrity of the coma during transportation and planting, and prevent damage to the roots. In the ground (after planting) the mesh decomposes in 1.5-2 years, sacking - even faster. Therefore, it is not necessary to completely remove the packaging from the coma.
However, the net tightens the plant comfortably tight enough, and in the first year after planting it does not impede the growth and respiration of the roots, we recommend that after installing the plant in the prepared planting hole, use the wire cutters to carefully cut off the upper third of the wire braid and release the root neck and top of coma from burlap. At the same time it is very important that everyone remains whole.
After installing the tree, you need to properly shed a room so that it is completely soaked with water. This should be done carefully, without eroding the soil. Often the water is not poured on whom the plant, and fill the very pit.
After that, you can begin to fill the pit with earth. First, the lump is poured on 1/3 of the height, the soil is thoroughly compacted and shed with water. Then the remaining part of the pit is filled in layers, ensuring that there are no voids left. Empty cavities near the plant lump left by inaccurate planting cause the roots to dry out and can cause a depressed state of the plant, shrinking of part of the branches and even death.
An earthen roller with a height of 10–20 cm is formed around each perimeter of the planting pit. It serves to hold water during irrigation: so that it does not spread, but penetrates to the roots of the plant.
After planting, the plants are thoroughly watered and the soil is loosened in order to preserve moisture. Pristvolny circle of plants is recommended to mulch. Mulch protects the root system from overheating, retains moisture in the soil, limits the growth of weeds. Chips, shredded pine bark, humus and other organic materials can be used as mulch.
4. Post-treatment care
At first, after planting, a very careful care is taken after the plant: watering, straightening bent plants, checking the garters of trees to the stakes, pouring the ground into the settled landing pits.
Regular watering in the first year after planting provides a high survival rate. Watering is carried out depending on the weather, on average - at least 1 time per week. In the heat watered more often. In rainy weather, if the plant gets enough moisture, limit watering. Abundant watering of trees and large shrubs (75-100 liters of water per 1 sq. M.) Is carried out with a hose. Watering with sprinklers is often ineffective, as it provides moisture only the top layer of soil and is applicable for lawns, flower beds, small shrubs, and the roots of large trees to a depth of 50-60 cm and more water does not reach.
In the first year after planting, while the plant survives and adapts, the likelihood of developing diseases increases. Only high-quality, healthy planting material, the choice of the optimal place, the right timing, planting technology and competent post-planting care are a guarantee that your plants will have sufficient immunity against diseases and pests.
If you suspect that the plant is affected by pests or diseases, it is important to accurately determine the pathogen and take action. For this you need to have a sufficiently broad knowledge in the field of entomology, phytopathology and plant protection. Today, there are many drugs on sale, most of which are highly specialized and may be ineffective if the diagnosis is erroneous. You can use special literature, reference guides and advice from garden forums, but it is best to contact phytopathology specialists who can give a professional opinion and recommend remedies.
Features planting container plants
Saplings grown in containers can be planted from spring to autumn, including in the summer. However, plants grown in a container have their own characteristics: they are grown in a light container substrate, with regular dressings, have a very compact and dense root system. In order for such a plant to adapt to the new conditions of your site, more careful and regular care will be needed, especially if you plant in the phase of active shoot growth (end of May - July).
Before planting the container plant must be well shed. This will save small roots from drying out and make it easier to release the plant from the container.
If, after removing the container, it turns out that the roots of the plant are strongly elongated and twisted, they should be trimmed before planting, and straightened in the planting pit. If the roots are excessively entangled and intertwined, then you can use a knife or a sharp shovel and make shallow notches from two opposite sides of the root coma, removing long roots. Planting a plant with twisted roots leads to the formation of an irregular root system, the plant takes root worse and needs support longer.
In the first season after planting, watering is especially important for container plants. The root system of a plant grown in a light container substrate is very thick and dense, concentrated in a relatively small volume and has a large water-absorbing capacity. Therefore, immediately after planting, until the roots germinate into the surrounding soil, regular timely watering is very important for such a plant, and it must never dry out.
Features planting plants with an open root system
Most often, this method produces small 2-3 year old fruit trees: apples, pears, plums, cherries, and unpretentious shrubs in groups and hedges (cotoneaster, deren, etc.).
Terms of planting plants with an open root system are more concise than those of plants with a lump - in spring, planting should be completed before budding (for Moscow and Moscow region - until the end of April), and in the fall from the beginning of the mass leaf fall to the end of October. To reduce the risk of drying out of the roots, it is advisable to plant the plants in cloudy weather.
Preparation of the seat does not have any special features: single pits are dug in accordance with the size of the root system of the plant. If dense groups are planted, it is advisable to prepare common pits according to the shape of the group. When digging a trench under hedge based on the following dimensions: for a single-row hedge (W x D) 0.5 x 0.5 m, for a two-row hedge - 0.7 x 0.5 m.
In seedlings, they carefully examine the root system and prune all damaged and too long roots.
Before planting, a mound of earth is poured at the bottom of the pit, the plant is set up, gently straightening the roots. When the plant goes to sleep, the plant is slightly shaken so that the earth evenly fills the voids between the roots. Poured soil compacted from the edges of the pit to the center.
The root neck of the planted plant should be 5–10 cm higher than the soil level, since the ground with which the pit has been buried will subsequently settle.
Around the planted plant around the perimeter of the planting pit (trench) form an earthen roller, 10-20 cm in height. It will not allow water to flow when watered. After planting the plants watered abundantly. The irrigation rate is at least 25 liters. for standard wood and 12 l for shrubs.
The plant nursery and garden center Paer + has been operating since 1998. During this time we have gained vast experience and knowledge in planting, caring for ornamental plants, conifers and fruit trees and shrubs. Here you can purchase plants to create a hedge, fruit trees and shrubs for your garden, as well as order work on landscape design and design, landscaping and landscaping. Trees and shrubs come from the oldest nurseries in Germany and Poland, as well as from our Voronezh nursery planting material. Plant nursery and garden center Paer + is conveniently located and located on the territory of the Main Botanical Garden in Moscow. The range of plants includes krupnomer, coniferous plants, leafy plants, perennials, roses and rhododendrons, bonsai, molded plants, as well as any ornamental trees and shrubs to order. All information (articles, photos, etc.) posted on this site is the property of LLC “PAER +” and is protected by the Copyright Law.
Gardening in Russia was considered to be not only useful, but also noble. We do not get tired to be surprised and rejoice at the creations of landscape art created by the hands of old masters. Traction to the ground irresistible makes you create your garden. And even if it is very small, it will delight you, your children and grandchildren - this is already wonderful.
Spring began, and with it the search for seedlings for the garden. There are endless questions: what is better, when and how to plant. So…
When
Trees and shrubs are planted in a dormant period - in the spring before bud break and in autumn when growth ends. In the conditions of the Central regions of Russia, early spring planting is preferable. It provides the best survival rate of plants. In the spring, there is a significant supply of moisture in the soil, which helps plants to settle in a new place. Before the onset of hot days, the sapling will have time to get stronger and harden. Planting can begin as soon as the soil thaws.
There is a third landing time - winter. Yes, do not be surprised, winter landing gives very high results due to the least injury to the root system. Large trees are generally planted only in winter. But such a landing requires strict implementation of a certain technology, and only a specialist can perform it competently.
Which seedling to choose
Before you go to buy seedlings, you need to calculate the amount of planting material you need. It should be borne in mind that the garden grows in one place for many years and the trees should not overshadow each other. For landing fruit trees the following areas are allotted: under apple trees, 3/4 m, pears, 3/3 m, plums, 2/3 m, cherries, 2? 2 m. Planting with "stock" is the traditional mistake of an amateur gardener. Yes, the seedlings are small, but it will take several years, and the grown trees will begin to interfere with each other. No pruning will help, and attempts to uproot extra trees will damage the overgrown roots of other trees. When landing berry bushes located at a distance of 1.5 m from each other in single row arrangement. If you are laying a whole plantation under the gooseberry or currant, the distance between the rows should be 3 m.
So you decide what you need. Buy seedlings only in specialized nurseries. Having bought a sapling from a dubious seller, located on the side of a highway, you may sincerely be surprised to find out after a while that the elite apple variety you have purchased will turn out to be ordinary rowan or something else. When purchasing planting material, it is necessary to carefully monitor the quality of seedlings, excluding plants with mechanical damage to the roots, stem, crown, poorly developed, with a strong curvature of the stem, with poorly combined graft and rootstock, influx of root cancer on the root neck or main roots. The root system of the seedlings put up for sale should be in the ground or at least covered with a wet sacking. Be sure to consider whether the roots have dried up. If they look dry, bend badly, discard this plant. This is very important, since the active, suction roots are located at the ends of the main conductive roots, they are very thin, they dry quickly. Such a tree will not be able to absorb water. If you choose a seedling in a container, pay attention to the size of the container and the plant in it. Unscrupulous nurseries can offer you a two-meter sapling in a 30 cm deep container. This applies primarily to seedlings of those tree species that have a strong taproot. Most likely, in this case, the main root, when planted in a container, was cut off and the plant would not survive for long.
Healthy biennial saplings of fruit trees must meet the following requirements: have intact roots (at least 3 branches of 30 cm or more in length), a well-developed bud, a trunk at least 2 cm thick, well overgrown inoculation site, 3 correctly arranged branches 40-60 cm long .
Immediately after purchase, wrap the roots of the seedling with a cloth; do not transport the purchased plant with an open root system on the trunk of the car. Headwinds will not only break off thin roots and twigs, but also dry them. If you don’t immediately go to the plot, but you will over-keep the seedlings in a city apartment, find a cool place and wrap the roots with a damp cloth, otherwise the buds may begin to open. Do not let the fabric dry. Keep the roots of a seedling in a container of water should not be, as they may suffocate or begin to rot.
How to prepare landing pits
Landing pits are prepared in advance. Ideally, for spring planting, the pits should be dug in the autumn, and for the autumn - 2-3 weeks before planting. The optimal size of the pits for trees is 1 m in diameter, the depth is up to 0.8 m. For shrubs, a pit of 0.6–0.8 m in diameter and 0.5 m in depth is sufficient. Such a large volume is necessary so that the young and still weak roots of the seedling, developing, at least for the first year or two, do not spend power on breaking through dense layers of untouched soil.
When digging the pit, first remove the upper, fertile soil layer to the depth of the spade bayonet and fold it to the edge of the pit. The lower, barren layer is taken out and folded separately. Fertilizers are laid in the pit: 1-1.5 kg of double superphosphate, 50-100 g of potassium sulfate, the same amount of potassium chloride, up to 1 kg of wood ash, up to 1.5 kg of fluff lime, 1-2 compost buckets or well-rotten manure . All fertilizers are thoroughly mixed with half of the soil taken out of the top of the pit.
A third of the mixture mixed with fertilizers is again removed from the pit and then used when planting the seedling together with the remaining soil. If the soil is on your garden plot heavy enough, add a couple of buckets of sand to the ground extracted from the pit. When light, sandy soil in the lower part of the pit, fill with clay or loamy soil.
Seedling preparation for planting
Before planting trees, cut off the damaged ends of the roots to healthy tissue. The remaining roots are preserved, since the larger the seedling of the roots and the longer and branching they are, the better and faster it will take root and grow. A couple of hours before planting, soak the seedling root system in water. This will help the thin roots deal and get water. Thus prepared seedlings after planting easier to absorb moisture in the soil. If the seedling is poorly developed root system or the volume of the crown significantly exceeds the volume of the root system; pruning of the seedlings is carried out. This must be done because a small amount of roots will not be able to deliver to the leaves and branches the necessary amount of water and mineral substances dissolved in it. It is better if the root system is not overloaded during the sapling adaptation period. Allowed to trim the main stem and side branches for 1/3 of the length.
Landing
From the land that has already been buried in the landing pit, make a mound. Place the seedling on this mound so that the root neck of the plant (the transition point of the trunk to the root) is 3-5 cm above the level of the edge of the pit. This is one of the most important conditions for planting, especially in fruit trees. From the correct location of the root collar in the soil will depend on all further growth of your tree. With recessed landing fruit trees stop growing, crown is poorly formed, plants suffer from various diseases. In the future, these trees bloom badly and bear fruit. With high planting, when the root collar is well above ground level, wild growth may occur below the grafting level. Such trees do not tolerate winter.
Make sure the roots are evenly distributed across the planting pit. Then pour the sapling into the prepared soil. It is more convenient to plant together: one supports the sapling, and the other pours the earth in such a way as to leave as few voids as possible. As the pit is filled up, shake the seedling from time to time for a more even distribution of the earth around the roots. After backfilling, compact the soil around the seedling with your foot. Do this carefully so as not to tear the roots. About the seedling driven stake, which is attached to the seedling. When the pit is filled, the roots are reliably covered with soil, around the tree they make a hole along the contour of the pit and pour it with at least one or two buckets of water. The main purpose of irrigation is to ensure good soil contact with the roots. When water is absorbed, the earth around the seedling is sprinkled with a mixture of earth with humus or peat. This will reduce the evaporation of water from the pit and prevent surface drying and cracking of the soil.
With a high location of the groundwater level - above 1-1.5 m from the soil surface - it is recommended to plant fruit trees on knolls or earthen ramparts 30-50 cm high and up to 1 m wide. The pit is dug smaller, the soil is prepared in the same way as for normal landing. Then the pit is filled up with the prepared soil mixture, leveled, a stake is driven into the center. The seedling should be tied to a cola so that the roots are located above the soil, and the root collar is 5-7 cm above the level of the future hillock or shaft. Pour the roots in such a way that they are evenly distributed over the prepared embankment and covered with soil. Around the tree planted on an elevation it is necessary to make an annular hole, piled around the seedling slightly to tamper the ground, carefully pour.
Care for young plantings
The first few weeks should ensure that the trees are in the same position as when planting. Uneven subsidence of land can cause unwanted tilting of seedlings and exposure of the roots. If this happens, water the seedling very abundantly so that it can be returned to its upright position without harm to the roots. After that, secure the tree with an additional inclined peg. Sprinkle the ground with a strong subsidence or exposure of the roots, do not fill the root neck.
Young trees have thin and thin-skinned bark. To protect seedlings from sunburn, mechanical damage and pests, treat the trunks with copper sulfate solution and whiten garden whitewash. Use for this pure lime is not recommended.
The roots of young trees are located close to the surface of the earth. They cannot get water from the depths. On hot summer days, try not to allow the wheel circle to dry. Do not be too lazy to water the trees abundantly, and after watering, if possible, grind the soil with peat, sawdust, finely chopped bark or other loose material.
In the reference literature, you can find other ways and methods of planting and caring for young seedlings. Do not be surprised that they differ, because the art of gardening for hundreds of years and a variety of techniques perfected for different areas, soil types, slope plots and other features of land allocated for the garden. Evaluate and implement the landing method, which is more suitable for your site, and you will get a high result. Never rely on chance. Here is what P. N. Steinberg wrote in the book “Gardener's Ordinary Recipe” in 1911: “Honor a fruit tree, like any domestic animal that is created for the benefit of man. Feed it. Drink it. Fruit tree, like any living the creature has many diseases and enemies: cure its diseases and drive out the enemies, the tree will reward you for this tenths. "
Galina Korovina
Provided by ID Business World
The result of planting trees and shrubs - their survival rate, depends on many factors:
- plant selection;
- preparation for landing;
- proper landing;
- care.
In this article we will consider the technological features of the preparation for planting various trees and shrubs. If you have not yet decided on the choice of plantations for your landscape, then a specialist dendrologist of the company LandGrand will help you.
He will answer all your questions and tell the main tree planting rules. For your site will be developed dendroplan. You can order the turnkey service of any plantings all year round or simply buy planting material in our nursery.
Preparation of krupnomer
Large trees are planted only with a lump of earth, which should be ten times larger than the base of its trunk. Best of all this process takes place in the winter.
During this period, the trees rest, and the earth firmly rests on the roots. It is always possible to properly form a strong lump, which increases the survival rate of plantations.
Preparing for planting trees, depending on the location of the site, can be carried out using special equipment or manually. The latter method contributes to better survival, but more laborious.
When in a warmer period, it is necessary to ensure reliable protection of coma from destruction. To do this, use the normal burlap or special containers.

Fruit trees
Fruit trees are planted with or without a lump. Tree planting time - the main factor on which the choice of technology works.
Landing with a lump can be carried out almost the entire season - from spring to autumn. Fruit trees with an open root system are planted only in spring or autumn.
Autumn transplants of fruit trees should end a month before the onset of frost. Trees spud a layer of soil with a height of 20-30 cm. This operation will protect their roots from freezing.
Tree planting is individual, but it is best to carry out work at a time when the plants are at rest:
- in early spring;
- late autumn;
- in the winter.
Spring activities require early work, as soon as the soil dries up a little. All soil preparation operations should be carried out in the fall.
The shape and size of the pit should correspond to a particular seedling. The pit must be filled with soil mixture, which is prepared from black soil, sand, peat, humus and other fertilizers.
The recipe for the "right" mix is best ordered from experts. Further, there is nothing difficult in its preparation. Using a shovel, all components are mixed in the pit.

Shrubs planting
Full landscape design is impossible without the use of a variety of shrubs. Even ornamental trees are used less frequently.
It requires proper preparation, and the process itself can be implemented using two technologies:
1) the use of earthy coma or plastic packaging - is used year-round;
2) planting with open roots - is carried out in early spring or late autumn. It is important for the plant to “rest” during this period.
Training deciduous shrubs necessarily provides an assessment of the state of the root system. Successful development of a plant depends on its condition. So that the root processes do not dry out, the seedling should be placed in water for a day.
Planting deciduous trees
Such plants can be planted year-round. Main conditions:
1) landing occurs with a closed root system;
2) after planting, regular and proper care is provided.
Saplings with a bare root are planted in early spring or late autumn. Under such conditions, the chances of plants taking root in a new place are quite high.
There are situations where you may not have time to finish all the work before the onset of cold weather. In this case, you need prikopat seedlings at an angle of 40-50 degrees, leaving to wait for the spring planting.
Preparation of container seedlings consists in the fact that several hours before planting they are immersed in a container with water. For tar large volumes use abundant watering of plants.
The development of the root system occurs much more actively in breadth of the planting pit than inland. This should be considered when preparing for planting. In this case, the best conditions will be in trees that are planted in wider pits.
It is extremely important, when digging a hole, to do a seemingly uncomplicated work in the correct technological sequence:
1) mark the perimeter of the pit;
2) remove the top layer of turf and pile it up;
3) dig up a fertile layer of soil and put also separately;
4) loosen the bottom of the pit and place the removed upper layer of turf downward on it;
5) prepare a special mixture for filling the pit, mixing fertile soil with humus and mineral fertilizers.
Each tree species has its own planting technology. But there are general, simple rules for preparing for transplantation, which will help increase plant survival.
Entrust the tree inspection to a dendrologist.
This service must be ordered necessarily. It will not be superfluous to be personally present during the inspection operations.
When ordering trees from foreign nurseries, as a rule, you have no such opportunity. And only at the time of delivery is possible deviations or defects in the development of the tree visible.
In any case, various certificates must be supplied with the products. Trust only reputable kennels.

Prepare the landing hole in advance
To do this correctly, determine where the root of the neck is located. This will allow you to know the depth of the pit, which is necessary for planting this plant.
The root neck is in the place of a thickening of the trunk with the first lateral roots. It may be necessary to remove the soil layer from the surface of the coma to determine it.
Dig a wide planting hole, the diameter of which is at least three times the diameter of the roots of the seedling (earth coma). Loosen its bottom and walls, prepare the fertilized soil mixture.
Tree planting rates Provide the following: the height of the pit should be less than the height of the earth coma by the amount of shrinkage of the tree, which is on average about 5-10 cm. Such preparatory work is preferably carried out 7-14 days before planting.
Study well the landing site. Especially pay attention to the location of various communications on the site.
Provide maximum protection for planting material.
For such purposes, use the packaging earthy coma burlap or its placement in special containers. During lifting and transport work, it is important not to damage the trunk of plants. Raise plants can only be for whom.
Manual technology of planting trees and shrubs is more gentle in this regard. During the work with krupnomer, taking into account their weight, it is necessary to apply special equipment. Especially if the layout of the site allows travel to the landing site.
The specialists of LandGrand, depending on each specific situation, apply the most rational solution. We guarantee safety and a high percentage of plant survival. This is achieved through proper preparation for planting.