When to put manure. Humus: characteristics, selection and preparation, application in the garden
How to improve the composition of the soil? When is it best to fertilize? How to apply fertilizer?
Fertilization and soil improvement measures
Poor humus is available to improve by regular organic fertilizer application. The mechanical composition of the light sandy soil can be improved by adding crushed clay.
Heavy loamy, clayey and uncultivated soils are easy to improve by applying organic fertilizers, loosening materials, and liming.
Autumn soil digging - This is the right time to add the bulk of organic, phosphate and potash fertilizers, lime materials and mineral additives in the form of sand or clay.
Autumn is good time for land phosphate fertilizers. In order for them to reach the roots of plants, we need a long period of time. These fertilizers are not washed out of the soil for quite a long time; if they are brought in the fall, the earth will become saturated with them all winter. At the same time, potash fertilizers containing chlorine are added to them. Until spring, the movement of soil water will transfer chlorine to deeper soil horizons.
The formation of a fertile soil layer is favored by digging the entire free surface of the site to which such natural fertilizer as wood ash has been previously applied.
If you intend to grow on the site If garden crops such as zucchini, cabbage, cucumbers, lettuce, celery, then during the autumn digging it is necessary to bring manure, humus or compost into the soil. If on the site where it is supposed to grow carrots, beets, scorzonera, radish, organic fertilizers were patched up in the previous season, then it is enough to add mineral fertilizers. You can limit a small amount of humus or compost. Organic fertilizers include manure, bird droppings, slurry, humus, peat and composts.
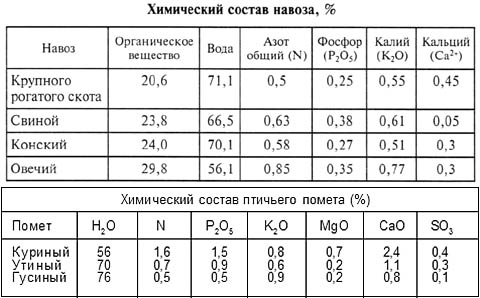
Manure,enriching the soil with microorganisms, simultaneously improves its structure, increases looseness, reduces acidity and makes the soil "warm". Cow dung is the most familiar to use. It contains almost all of the nutrients needed by plants: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and trace elements. However, even more nutrients, in particular nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, are contained in horse manure. Horse manure is regarded as an optimal organic fertilizer that improves the soil that needs to be applied to the soil in the fall. When using fresh horse manure it should not be embedded very deeply. When injected into deep layers of heavy soil, it practically does not decompose. Horse manure deposited in the upper soil layers during the winter, before spring processing, will already decompose somewhat and serve as food for soil microorganisms. It is better to use half-rotted manure for autumn processing, then it will almost mature over the winter. The rate of its decomposition depends on the presence of moisture in the soil, on its temperature and the degree of aeration. On 1 m 2 of soil it is recommended to bring 3 - 4 kg of horse or 5-8 kg of cow manure.
It is not recommended to put fresh bird droppings, rabbit, sheep and goat manure into the soil during digging. It must first be compiled. Many vegetable growers generally prefer to apply only rotted manure to the soil. From autumn, they put fresh manure in layers in a compacted pile on a dry, well-compacted site, which is covered with a thick layer of clay so that the manure does not touch the ground. Layers are shifted by turf or peat, covering the top with the same turf, sawdust, straw or peat. In order that moisture from an atmospheric precipitation did not get inside a stack, it is covered with a film. Manure that has lain in the winter cold is used in early plantings. vegetable crops. After applying rotted manure to the soil, it is possible to grow greens, onions, carrots, cucumbers and pumpkins on it. If on the site as manure was used in sufficient quantities, then other organic fertilizers can no longer be used.
Particularly bountiful harvest give vegetables for the 2nd year after the introduction of manure. Good bow grows after incorporation into the soil of horse manure, and beets and parsley - after sheep manure. Radishes get more in those areas that have been fed cow dung.
Bird droppingsit is considered a strong and fast-acting fertilizer. It contains a large number of batteries, decomposes soon. Usually bird droppings are stored with peat, combining them in equal parts. The greatest effectiveness of litter brings in the composition of the liquid fertilizer with a solution of mullein.
Chicken droppingsit is advisable to collect and store in the same way as ordinary manure, warming the pile with peat chips, sawdust or foliage. If heaps of droppings are frozen, the droppings will stop decomposing, and many plant nutrients will be lost.
➣ All residues of damaged plants and vegetables, infected tops of tops should be carefully collected, dried and burned in dry weather. The resulting ash can be used as a fertilizer when digging.
Significantly increases the content of humus in the soil making a large amount of manure compost. In addition, such an event inhibits the activity of pathogenic fungi and bacteria. The manure compost contains antibiotics, they are isolated by separate soil microorganisms that suppress the causative agents of diseases.
Readiness of the compost pledged in the previous year should be checked on the eve of winter, in November. It is required to shovel, and then insulate. Compost heaps before frosts should be covered with branches and ground with a layer of up to 50 cm, which will protect them from freezing.
Peat as a fertilizer used in manure-peat mixtures. Peat alone is used to improve soil structure as a loosening material.
Some gardeners fertilize the soil with leafy soil, considering it a relatively good fertilizer. The foliage in the fall is collected in a heap, covered, so that the wind does not spread it across the site, and leave for the winter. In the spring, if the leaves are decomposed, mix them with the soil. If they have not decomposed by spring, they are dug up and left until autumn.
Often, gardeners rake the bulk of the vegetable garbage, garden leaves, tops and lay in the compost pile, considering it as an ideal material for humus. Plant residues and garbage from spring greenhouses and greenhouses are also placed there. However, such a fertilizer increases the likelihood of soil contamination by one or another fungal disease. If there is the slightest suspicion that weeds, grass, vegetable shoots are infected with pathogens or eggs of various harmful insects, then they cannot be used as future fertilizer. The causative agents of plant diseases and harmful insects usually settle in the pre-winter period specifically among plant debris, dry tops, on dry branches and trunks of old trees. Nevertheless, it is better to burn the leaves and other plant residues and feed the land with the resulting ash.
During autumn digging, many gardeners on manure bring manure mixed with sawdust, which was used as bedding for cattle. Sometimes pure sawdust is also used, pre-scalded with boiling water. Sawdust on heavy soils is useful as a loosening material. But wood decomposes very slowly in the soil, consuming too much nitrogen, which is highly undesirable. This process should be warned by moistening sawdust with a solution of urea (urea) or a solution of mullein (3 l of mullein per 10 l of water). For 3 buckets of sawdust will need 10 liters of solution with mullein. For pretreatment of sawdust, it is permissible to use a special solution: dissolve 150 g of superphosphate, 100 g of ammonium nitrate and 50 g of potassium chloride in 10 liters of water. When digging in the autumn, it is enough to add half a bucket of sawdust “and every 1 m 2.
During the digging of the soil under the garden in the newly developed areas of the non-chernozem strip, where it is necessary to create a humus layer, about half a bucket of organic fertilizers should be applied per 1 m 2 of the treated area. On uncultivated, previously untreated plots, it is necessary to remove the roots of old plants from the soil, remove stumps and snags, select stones. When grounding with a shovel or plow, such a soil should be cut into thin layers and additionally, 3-4 cm of podzolized earth or subsoil ore clay should be added in addition. During the autumn digging in heavy clay soil should be loosened materials and organic fertilizer in larger volumes than in the cultivation of cultivated land. Peat, manure, at least half a bucket for each 1 m 2 should be added, supplementing them with wood ash.
With autumn processing virgin clay soil to organic fertilizers you want to add respectively 1 or 2 liter cans large river sand and hydrated lime.
Humus or humus - the most effective complete organic fertilizer with long-term trace elements. Simply put, if you rent a plot for a period of up to 5 years and the prospect of a lease renewal is not clear, then it is advisable to apply fast high-level fertilizers, incl. compost and rotted manure. If you have your own farm, which you intend to pass by inheritance, then regular fertilization with humus will preserve and improve soil fertility for many years. Although quick, from spring to autumn, the effect of the use of humus for fertilizer is quite noticeable. In the case when the plot is small and does not allow to organize the correct crop rotation, it is difficult to do without humus - regular additional feeding is necessary during the season, but without thorough knowledge of agrochemistry, local conditions and soil properties it is easy to deplete it within 3-5 years, and reclamation is difficult and road. Humus will serve as a tonic for the earth and will create a stable soil-friendly environment for plants. Artificially prepared humus is a friable, earthy mass of various shades of brown, see fig .:

The humus is formed from the manure of herbivores and plant debris with the proper alternation of their aerobic and anaerobic decay. Unlike compost in a pit, for the formation of humus, aerobes must completely complete their work and smoothly pass the baton to anaerobes that do not form volatile nitrogen and sulfur compounds. This requires a small access of air to the zone of formation of humus, which does not allow the most aggressive anaerobes to "roam".
Humus and fertilizing
Even the richest in humus soil, for example. steppe, in agriculture needs replenishment of humus. Under natural conditions, its natural influx is provided by winter-spring rotting of dead vegetation residues and waste of wild animals. In the cultivated area there is no such thing, and the humus horizon is continuously thinned by commercial crops during the growing season, leaching under the influence of precipitation and just irrigation water. Operational fertilizing with mineral fertilizers makes it possible to harvest good yields on lean land, but replenishing the natural loss of humus will significantly reduce their costs, as well as eliminate the risk of over-feeding of plants or a sharp drop in yields in bad years.
What is humus
The composition of the humus on nutrients for plants remains generally the same as that of the feedstock, see fig. since the maturing mass is not subjected to leaching during preparation, see below. But with organic matter in the process of ripening humus fundamental changes occur. Aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, replacing each other, transfer the organic components of manure and plant residues, first to active organic acids and then to humic ones.
Agrotechnical properties of humus are largely due to the presence of humic compounds. Thanks to them, the microstructure of the humus - elastic slightly sticky lumps with gaps between them. The mechanical properties of humus microgranules are preserved in a wide range of humidity, temperature and pH of soil moisture. As a result, humus:
- It absorbs a lot of moisture, holds it well and gradually gives off, i.e. possesses high exchange moisture capacity.
- Structures the soil - its dust particles stick around the humate granules without creating a continuous slightly permeable mass. On a soil that is regularly fertilized with humus, a capillary crust that drains the earth does not form during the normal season, and can be removed in a very hot summer by loosening a week.
- When feeding with mineral fertilizers regulates their transport to the plants for the above reasons. It is difficult to overfeed the plants on moderately humus-filled soil, and the loss of active substances for leaching and weathering is minimal.
- Also, the need for operational seasonal supplements is reduced, right up to the uselessness, since humus itself is a complete fertilizer. Practically, at the cottage with the land, filled with humus by mineral fertilizers, only emergency top-dressings are carried out in case of signs of starvation on any element.
- Does not interfere with the maintenance of intensive trade with regular feedings due to the ability to regulate the transport of nutrients. On the contrary, the use of humus in an intensive crop makes it possible to carry out soil recultivation less often and at lower cost.
- Contains carbon dioxide in a bound form more than other organic fertilizers, which improves gas nutrition of plants.
- In contrast to mineral fertilizers it attracts very useful earthworms to the site, at the same time scaring away moles.
- Allows in some cases to do without plant or mineral mulch. Mulching with humus during the season (see below) does not create breeding grounds for slugs, harmful insects, like plant mulch, and does not disturb the metabolism in the soil, like mineral.
In general, humus as a fertilizer by activity, i.e. the availability of plant nutrients in it is inferior to fresh manure, slurry and rotted manure. Therefore, it is much less likely to burn the roots of plants with humus than with fresh or freshly rotted organic matter. Nevertheless, it is necessary to introduce humus into the soil in a certain way, see below. At the same time, the regulatory properties of humus will ensure its long-term effect. If you need to get a quick effect from humus (during the harvest season, but not immediately for 2-7 days), it should be used where the migration routes of food to the plants are minimal, also see below.
Note: the use of humus for fertilizer on normal and alkaline soils does not require their obligatory liming periodically, since in the process of maturation of humus, the pH value of the maturing mass falls from 7.8–8.1, as in fresh manure, to 7.2–7.5, i.e. to neutral value.
Buy or do?
Offers on the sale of humus is quite enough, but the introduction of purchased humus in open ground will cost much more expensive than “doping” from mineral dressings to depleted soil or foliar. It is advisable to buy humus for a pot or greenhouse greenhouse culture: it spends faster in them, and in the winter it may simply not be mature. In this case, when you purchase you need to check the quality of humus. It is easy to do this by taking a handful of heaps and not fully clenched in a fist. The sample of humus should be compressed as a non-excessively moist loam, see fig. on right:

- Humus should be various shades of brown down to almost gray (see fig. At the beginning), but not black;
- Weight - 5-8 kg per bucket. Light, possibly overdried and not matured, and heavy from overwetting may turn out to be suffocated;
- Moisture from the sample should not be squeezed out;
- The sample should not stick to the fingers and palms;
- Compressed areas should be sealed in a viscous crust with at least papillary pattern of the hand visible at least in places;
- The areas not subjected to direct pressure should retain a finely lumpy structure, without crumbling and squeezing between the fingers with tongues.
Garden or garden?
It is best to use humus in a private farm for own consumption or commodity for a vegetable garden and, from spring, for berries. In the garden, the food from the humus just does not have time for the season to get to the small suction roots of trees. Fruit trees it is necessary to provide humus in a natural way (see also below), introducing manure from the fall into a trench along the contour of the tree trunk. However, manure is another topic.
How to make humus?
So, for giving and a garden site a humus cheaper, although more troublesome, will cook yourself. Formation of humus instead of compost (see also at the end) requires compliance with certain conditions:
- Source animal component - herbivores. Best rabbit droppings; then - sheep. The use of pig and goat manure for the manufacture of humus in an artisanal way should be avoided.
- The plant component is dry biomass of cereals and legumes (hay, straw). Plant weeds and garden crops are suitable for compost, but not for humus.
- Time of aging of ripening mass: 4-5 years in a collar, 3 years in a box.
- Shelters of ripening mass from precipitation to avoid leaching of intermediate products of the process. Without this, compost will also be released instead of humus.
In general, you can make humus yourself in a collar or in a box. Compost will be produced in the pit, but not humus. Burtovy method is suitable with a lack of initial components on not completely depleted soils that require refueling with humus once every 4-5 years. A typical example is ordinary garden soil in a country house or household plot for own consumption and partially, in the presence of surplus products, for sale. For predominantly merchandising with annual soil filling with humus, as well as in cool and rainy summer edges, it should be prepared in a box.
Note: Burtovy humus can be obtained ready and more often if you lay several heaps in a year or two, because take it from an immature heap is impossible. Dimensions of collar in terms of approx. 1.5 x 1.5 m, so that the owner will decide how much more sense there will be from this land area.
In fairly humid places with warm winters and unstable snow cover it is possible to prepare humus in a natural way directly on the site; then any special technique of its introduction is not required. Within the Russian Federation, it is possible to cook humus naturally in the regions from Voronezh to the Caucasus, except for the arid strip in the east (south of the Volgograd region, Astrakhan, Dagestan).
In collar
To cook humus in a collar, so called. in the French way, a plot of dense barren land is needed: it does not sink under the heap and does not suck the moisture out of it. Place under the collar in sizes from 1.2x1.2 to 2x2 m encircled with boards and fall asleep in the resulting tray drainage of rubble or gravel. Without fencing, the drainage during the aging of the mass will spread under the pile and it will sit on the ground. This is fraught with capillary leaching of the mass and its infection with weeds and pests.
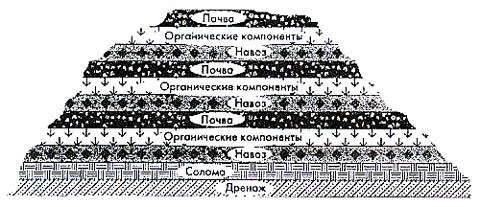
On the drainage stack litter of straw, reed or reed. Material filling is done as for a compost heap (see fig.), In layers of 10–15 cm, but organic components are needed only from those indicated above. The soil for seed bacteria - garden soil from the site. Heap height - approx. 3/4 of her side; 0.9-1.5 m for the above dimensions. Each layer on the application is sprayed with moderate moisture.
Note: if the organic matter in the pile is hay from the floodplain meadow (plow), every soil layer, except the top one, will be useful to powder with crushed eggshell approx. polustakana per square. m. This will prevent the lack of calcium in the humus.
Over the collar arrange a canopy of any opaque waterproof material; ventilation gap between the canopy and the top of the heap approx. 0.5 m. After the spring thunderstorms until the beginning of autumn, the canopy is rearranged obliquely to the south side so that the shoulder is wetted by rain. Drying the heap under direct sunlight is unacceptable, it will immediately spoil the entire batch!
Humus is considered ripe when heap sedimentation stops. Usually this happens at 4-5 year, when the apparent volume of the heap will be reduced by three to four times. Mature humus should quite smell like damp earth, so called. spring odor and tested for suitability as above. Ammonia, sulfurous, chlorine and other extraneous odors - an accurate sign that this party failed.
In the box
For annual use, especially in adverse climatic conditions, it is necessary to prepare humus with your own hands in the American way in a 3-compartment box, its device is shown in Figure; the outer skin of the first section is conventionally not shown. In contrast to the compost box, in the humus it is better to make not sliding up the door for the extraction of the finished compost from under the bottom, but folding of the boards. As the heap subsides, the upper boards are removed to release the gases, otherwise the heap may suffocate.

Note: since the humus box must act for many years, the material for it must be taken sufficiently high quality. The best option for a combination of price and durability - boards from building pallets. How to make a compost box from pallets, see the video below.
Video: compost pallet box
As in nature
The natural way of enriching the soil with humus is very simple: scorched, dry, crushed manure is scattered over the ground before winter. Too much throwing is not necessary, soil bacteria can not cope with excess. It is necessary to throw so that the earth everywhere looked through under manure. Usually buckets are enough for 2-4 square meters. m and more. It is also useful to pre-scribble a straw chop and plow or perekopat site. It is necessary to scatter manure on damp earth so that it will immediately stick and not be blown away by the winds.
Using
The use of humus for fertilizer is also possible in several ways, depending on the cultivated culture and the desired time of effect:

- When planting for seedlings - the effect is long lasting, for 3-4 years;
- For seedlings - provides an increase in yield with operational supplements during the season, reducing the risk of over-feeding of plants;
- From the autumn after the harvest - for any crops, the effect is as in claim 2 for the whole trail. season;
- In the spring - the same as under item 3 for garden crops with not extensive root system;
- Promptly during the season - allows you to fully realize the potential crop growth in favorable years.
Humus for planting is mixed with vegetable land 1: 2 by volume. In the pits for seedlings pour out half a bucket bucket (bush / tree), sprinkle 10-15 cm of land and plant. Planted plant is abundantly watered. For seedlings, peat pots or a box are filled with a mixture of 1 / 3-1 / 2, covered to the top with earth and seeds are sown. Then they also prepare furrows or holes for planting seedlings in the ground, but the mixture is made from humus and earth 1: 4.
In the fall and in the spring, immediately after the snow melted, humus is scattered around the site at the rate of a bucket of 2-3 square meters. The treated area is harrowed, cultivated or raked. Autumn-spring application of humus should be carried out on moderately moist soil.
Operational feeding of garden crops with humus during the season is done by mixing it with the ground 1: 4 - 1: 5. A mixture of mulch plants under the roots, departing from the root of the neck by 2-3 cm, or, with a tight fit, in the aisle. Seasonal dressing with humus should be carried out, observing general rules dressings: after watering in the evening or in cloudy weather.
Why humus is not compost
The proportions and nutrient content in the compost can be the same as in the humus, especially since both vary within fairly wide limits. However, the main difference from humus is that the former does not structure the soil and does not have a long positive effect on its fertility. Compost also has a much weaker regulatory effect on the transport of nutrients from the soil to plants. Quite it is also important that the risk of infestation of plants with fertilizer with humus is almost zero: in the anaerobic environment created in the ripening mass of humus, germs of weeds and pests do not survive.
From organic fertilizers I want to highlight manure, the decomposition of which produces minerals that affect the increase in humus in the soil. Due to the properties of manure, sandy and sandy soil becomes more viscous, and clay, on the contrary, friable. Manure in the soil contribute every year, it is not a one-time feeding. On clay soils is active for 6-7 years due to slow decomposition, and on sandy loam - up to 4 years. There are different types of manure: cow, horse, goat, sheep, pork, bird droppings.
The most frequently used manure is cow, but the best is horse. Cow manure is dense in structure, a long period is required for decomposition. Horse manure - loose, contains more of all nutrients. Goat and sheep - very dry, sheep on the speed of decomposition equals to horse, and swine - too wet, which is used more on sandy and sandy soils, it must be composted for at least 1 year. contains a lot of nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus. All types of manure are not recommended to be used fresh, as plants often get burned, and nitrogen and phosphorus are drawn from the soil.
Manure quality
The quality of manure will directly depend on the conditions of storage and harvesting. If the manure is laid in layers, trampling down each layer, then filled with straw or peat, and covered with a film on top, the decomposition will take place slowly but surely. After 4-5 months of storage, it will take only a semi-overheated form with a high content of ammonia nitrogen, and after 1 year it will be a great humus.
If manure is not trampled when laid down, but simply put in bags, then its quality will be low, a lot of nitrogen will be lost. To reduce the percentage of loss and increase the rate of decomposition, you need to add phosphate flour (3% of the amount of manure).
The more manure decomposes, the more nutrients are released.
Just scatter manure on the garden, taken only from under the livestock can not. Manure is divided into groups:
- fresh;
- slightly decomposed, when the storage time was short, and the straw almost did not change color and strength;
- half-broken, when the straw is of dark color and easily disassembled into pieces;
- rotted, when the mass is black, and the consistency of smearing jam;
- humus, the last stage of decomposition of manure, when the mass is friable and earthy.
Cow dung can be mixed with water and thus obtained mullein infusion. To do this, mix 1 part of manure and 10 parts of water, insist week. By its composition, the amount of nitrogen exceeds in pig manure, which can cause burns of the roots of plants, as well as in the pig and cow reaction, the pH is in acidic terms, whereas in horse horse it fluctuates in neutral. This is important.
How to use manure
In the fall, when digging up the soil, it is usual to bring manure of a semi-extinct form so that it reaches the desired condition until spring. It is impossible to simply spread manure over the surface of the soil, thus reducing its effectiveness. On light soils, it is buried to a depth of 20-22 cm, and on heavy soils - 12-15 cm. It is better not to distribute a small amount of manure, but to add it directly to the wells or trenches.
The chaotic use of manure can lead to the accumulation of nitrates in the soil, so be sure to follow the rules. Horse and cow dung make under the flower and garden crops at the rate of 3.5-8 kg per square. m, depending on the level of soil fertility and its structure. Dry bird droppings - 50 g per 1 sq.m. A solution of bird droppings is obtained by mixing with water (1:20). In a garden under a tree over the age of 7 years old, 70 kg of manure are introduced, from 5 years old - 40 kg, for a young one - up to 20 kg.
Any organic fertilizer needs to be combined with mineral fertilizers, since organic fertilizer starts to act not so quickly, but for a long time, and mineral fertilizer - quickly, but for a short period. Therefore, combined fertilizing plants have a better effect.
What crops, after what period can be planted after making fresh manure
So, if you have fertilized the soil with fresh manure, then you can plant crops in this area:
- for 3 years eggplants, parsnips, celery, root parsley, beans, garlic;
- for 2 years - cabbage, onion, carrot, radish, beet, turnip, radish, tomato, spinach, dill;
- for 1-2 year beans and peas;
- In the spring, after the autumn application of manure, you can plant cauliflower.
Work with organic is better in the most favorable days by (last lunar quarter). Try to avoid fertilizing with organic fertilizer on a full moon or new moon.
Measures to promote good harvest
Plants enriching and improving the soil, the use of sideratov
The problem of the frequency of fruiting
The effect of thinning on the keeping quality, leaves and shoot growth