Spunlace material. Spunbond and spunlace. What is it? About the technology of production
Spunlace) - this is a modern non-woven material, the principle of which lies in the interweaving of fabric fibers with water jets in a high vice - the so-called hydrojet method of fastening fibers in the fabric. Nina has installed about 200 lines from the production of nonwoven materials using the hydrojet method. Various technologies and devices for spinning nonwoven materials in this way have been developed. One of the remaining innovations in this garment is the use of spun (unspun) bicomponent fiber of the “segmental” type, which is composed of 70% polyester and 30% polyamide. When the fibers are bonded together by jets of water, the polyester and polyamide storage areas of the skin fibers are divided, creating the microfibers. The surface of microfibers in such fabrics is 5-7 times larger than the surface of primary fibers, so these materials are absorbed approximately 1.5 times more, lower or viscose materials.
The superiority of non-woven materials spun using hydrojet technology can be achieved by good adsorption properties and high levels of tactile comfort for people, close to the effect of a natural additive. These displays are the most important for the white servetons, and therefore spunlace is actively on the market for the production of water-bearing servets airlaid materials.
The output material for the preparation of these materials is rayon, rayon, polyester or polypropylene fibers. It is important to combine different mixtures of fibers with the final product. For the production of fleece and other wiping materials, a mixture of viscose and polyester (polypropylene) fibers is used. To make cotton pads, either 100% cotton or a mixture of cotton and polyester fibers are used. For the production of disposable medical clothing, as well as for the purpose of monitoring the sick, a mixture of cellulose and polyester fibers is most often used.
The main problem in the development of the production of spunlace for hygienic purposes in Russia is the almost constant availability of the cheese-based protein. The cream of polyester and polypropylene fibers, and they remove more than 20% of all fibers that are needed for production, in the territory of the SND, other fibers are not generated. For those so necessary purposes, the production of viscose fiber in Russia died out, and the Bavovian fiber was still being recovered. I would like to hope that not everything has been spent yet, in the hour of negotiations with the head of the marketing department » a project made from the production of viscose fiber. Varto note that the production of viscose threads from the enterprise is already in existence. In the bag it is no longer necessary to add a line for stamping, and it is possible to remove the necessary for spunlace production.
And now a little about the projects.
In 2007, the Avangard company installed a production line for spunlace materials at its production site in Tosno (Leningrad region). Standing on the chest in 2008, this line was united in the Russian Federation, which allows release spunlace for the vibrancy of volatile servets. In early 2008, the Avangard company awarded a contract to the French company Rieter Perfojet for the delivery of another technological line from production spunlace various thickness materials with a maximum roll width of 2.4 m.
In 2007, the launch of Balenergomash LLC. (BAT “BEM”) signed a contract with the French company Rieter Perfojet for the acquisition of approximately 180 million rubles. Statements obsyag virobnitstva spunlace at the new enterprise there is a warehouse of 4000 tons per river, the maximum width of the rolling sheets is 2.4 meters. As of today, the installation work has been completed, and the trial run of the line is expected to begin in 2009.
In 2008, LLC "Paper Factory" began installation of the Fleissner manufacturing plant with the production of spunlace for the production of cotton cosmetic pads. Nakrikinzi fierce 2009 Rock -in -law meshir nam -patch Vedipu product to Kinzi Pershogny Pivrichi 2009 Rocki Odrimati Neckhodnu Yakist Matterial, and to Kinzi Roku, to see 100% of the plump -in -law. At the first stage, production is carried out based on the company's current needs, and the materials can then be found in commercial markets.
At the age of 2009RUE Svitlogirske VO "Khimvolokno" » began the installation of the equipment for the new line from the production of spun nonwoven hydraulic and thermally bonded materials. For this project, a daily line was purchased for the production of non-woven fabric by extrusion of continuous thin polypropylene threads with their subsequent hydro- or thermal bonding. The owner of the plant is Reifenhauser and Fleissner. The line tension becomes 5 thousand. tons per river At the moment, the first project in the SND territory is the production of non-woven materials using hydrojet technology from continuous threads.
Spunlace ( Spunlace) is a technology for spinning non-woven fabric, which involves mechanical bonding of fibers (threads) of the fabric into a fabric with the help of hydrospun. Vinykla technology began in the 60s of the last century, and was first officially introduced in 1973 by a new companyDupont (Sontara).Sontara is the result of activityDupontChicopee, none of the largest spunlace producers. Z 1990 rock. This technology has been refined and made available to other growers.
The hydrowoven technology is based on intertwining fibers of the material with high-speed water jets under a high vice. It is necessary to squeak hard on the perforated drum behind the help of jets of water, which are under the high pressure of the farsun beams. For the structure of these strings, the fibers of the fabric are connected to each other. As a result, the canvas cut in this way has specific properties, such as: softness and drape.
In fact, spunlace technology is just one of the methods for bonding fabric together. In your drawing, the canvas itself can be created in a variety of ways, including:
· Carding of staple fibers ( drylaid) . Let the fabric form until dry. In this type, the fabric is formed from staple fibers and cured as a result of carding the output fibers on carding machines. The fibers are combed by the working parts of a carding machine with a bare surface and placed in the canvas on the priming machine. Schematically the process of introducing baby 2.
· Aerodynamic method of fabric molding ( airlaid) ; This is the very dry method of finishing the canvas (dry -laid). However, with this method, the fabric is formed from very short staple fibers and is formed under the influence of a wind flow on the surface of a perforated drum or mesh conveyor. The previously fluffed and mixed fibers are sheared by a carding drum, which is then tightly wrapped (or on a sheet of drums), reinforced from the carding head with the help of a wind jet and transported.
· Hydraulic method of forming fabric ( wetlaid).
This method is also called papermaking (from the paper industry). The peculiarity of this method of canvas forming is that the production of non-woven fabrics is carried out by pouring an aqueous suspension onto the mesh part of the paper machine.
Malyunok 4.
· Spunlade - Spunbond ( spunlaid - spunbond) ; With this technology, the fabric is formed from continuous threads (filaments) separated from the melted polymer. The threads are molded from polymer using the spin-blow method and are laid into the fabric almost instantly.
Malyunok 5.
It needs to be said that initially all the spunlace fabrics were vibrated by the head rank for helpdry -laid (dry) method of preparing the canvas, tobto. before punching the fabric with water jets, after further cleaning the staple fibers. Soon the situation is changing. Obligations for the production of paintings from wikisairlaidwet -laid technologies will increase. In addition, wired light transmittersspunlace ownership (RieterFlessner) were recently able to demonstrate to their neighbors a technology that combines two technologies -spunlaid (as a method of creating fabric based on uninterrupted threads with melting polymer) andspunlacing (as a method of bonding fabric). The technology is givenspunbond-spunlace is expected to be even more popular in the future, as a result of the success of this method of production, the product combines the power of both technologies.
Thus, the typical spunlace spinning process consists of several stages, similar to most technologies for spinning nonwoven fabrics:
· Fiber stack;
· Molding of the canvas;
· Punching the canvas with jets of water;
· Cloth drying;
When passing through a water circulation system, the formed fabric (whether from the methods described above) is compressed in order to remove all possible damaged bulbs, and then creased. The pressure of the water increases from the first to the last injector. Approximate indications for the process of hydrospinning can be the following:
· pressure on level 2200psi (pounds per square inch);
· 10 rows of injectors;
· The diameter of the opening in the injectors is 100-120 micrometers;
· Stand between the openings - 3-5 mm;
· Number of openings in one row (25 mm) – 30-80;
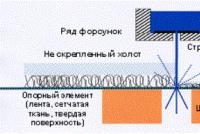
It is strongly squeaked by water jets on a perforated drum. The vacuum at the drum removes water from the canvas, in order, first of all, to prevent the product from being re-converted, and otherwise, not to reduce the force of penetration by the jet.
The perforated drum plates (conveyor plates) play an important role in the process of processing the finished product. In front of the little grater, lay the little ends of the fabric. The special design of the burrs allows you to remove the different structure of the surface of the canvas (corrugation, terry, “cut”, etc.)
Small picture 6 shows modifications of conveyor grids and the surface of the finished fabric lying underneath them:
Malyunok 6. See the gratings and the finished canvas
Ensure that the canvas is punched through on both sides. The canvas can pass through jets of water many times (depending on the need for the canvas). Place the bonded fabric on a drying device to dry it thoroughly.
For a standard process (6 rows (spreaders) of strings, pressure 1500psi, thickness 68 gsm) requires 800 lbs of water per 1 lb of product. It is therefore important to develop a good filtration system to efficiently supply clean water, otherwise the injector openings may become clogged.
The advantages of this technology lie ahead:
- The number of fiber trimmings (mechanical on the internal structure of the fiber);
- The technology allows different types of fibers to be processed in the same way.
- The elasticity of the molded fabric is great – 300-600 m/h;
- The production process is environmentally friendly
- Behind its principle is sterile technology;
Sirovina for virobnitstva spunlace
The output materials for the production of fabrics using the spunlace method are most often staple fibers containing viscosity, polyester, polypropylene, cellulose, and raw materials.
Viscose
Synthetic fiber made from pure cellulose.
The advantages of viscose materials are the same as those of natural fibers:
- reception on the dotik;
- do not evoke physiological reactions;
- looming high in the graveyard;
- easy to sample.
Cellulose
Pulp fiber - this fiber, which is prepared from wood, is supplied in the form of rolls or stands.
Authority:
· Hydrophilicity;
· Shvidka has lost the water of other lands;
· Endowed resource;
· Possibility of laying out biological path;
· very reasonable price on par with other natural and synthetic ones
fibers.
Polyefir (polyester, PEF, PET, PET, polyethylene terephthalate)
It is prepared by melt molding. Today, PET fibers form the largest group of synthetic fibers.
Powerful
· Thickness 1.38;
· Especially mitsny;
· Elastic;
· Resistant to erasure;
· Light-resistant;
· Does not lend itself to the infusion of organic and mineral acids;
· Water-filling is only 0.2 - 0.5%;
· The value in a wet state is as high as in a dry one.
Polypropylene (PP)
A synthetic fiber that is spun by melt spinning from isotactic polypropylene.
Authority:
· Lower thickness 0.91;
· Melting area 165-175 ° C;
· Softening area 150-155 ° C;
· fiber is resistant to aggressive chemicals;
· practical day-to-day vologgopolyannaya;
· reliable resistance to washing;
· sensitive to ultraviolet radiation;
Bavovna
Bavovna is a fibrous material that is widely recognized among consumers for the structure of their natural style.
Positive power of the bavovni:
- absorption;
- laid out in a biological way;
- gas permeability;
- ease of sterilization;
- heat resistance;
- high value in the rural area;
- excellent insulation characteristics;
- the presence of allergic authorities;
- regeneration potential;
- softness.
Due to the high absorption capacity, good tissue-like structure with low fluffiness and high value of the hair, it is also the finest material for medicine, technology, cosmetics, special survival of vulgar bacteriums. Bavovna, which follows the spunlace method, in addition to the medical industry, can be successfully used for the production of dishcloths, serverets and tablecloths, which can last 6 - 10 washing processes. Products prepared using this method look like flax and can be subjected to preparation and stuffing to remove the desired appearance.
As a rule, over-reinforced fibers are recovered in bags. Synthetic fibers (polyester and polypropylene) are mixed with viscose and natural fibers (bavon, cellulose). Also, based on the descriptions of the fibers, you can use them independently without houses.
Consistent with world practice, the following spunlace warehouses have emerged in the market:
· Viscose / polyester;
· Viscose / polypropylene;
· viscose;
· Polyefir;
· Bavovna;
· polypropylene;
· bavovna/polypropylene;
· bavovna/polyefir;
· Bavovna / viscose;
· Cellulose/polyester;
The spunlace warehouse means the final sphere of vicorized material. For the most popular viruses from spunlace
Dry/hairy cleaning materials : polypropylene/polyester + viscose;
Vologi servetki : polypropylene/polyester + viscose; polypropylene/polyester + viscose + wax;
Clothes and whiteness for operating rooms : polyester/polypropylene + viscose, cellulose + polyester; polypropylene/polyester + viscose + wax;
Vlastivosti spunlace
Once bonded by water jets, the non-woven material “spunlace” reveals the unique powers of non-woven materials, among which we can immediately see:
· High degree of claying (high hygroscopicity);
· High permeability to moisture (best among bulky non-woven materials);
· Softness and tactile garnish are similar to natural fabrics.
In addition, the outstanding advantages and advantages of this non-woven material are:
· Understanding of values and subtleties;
· Resistance to tearing;
· Lint-free structure;
· Non-toxic;
· Antistatic;
· Good drape;
· Dialergenicity;
· Subject to peeling;
Vibration technologySpunlace ( Spunlace) is a technology for spinning non-woven fabric, which involves mechanical bonding of fibers (threads) of the fabric into a fabric with the help of hydrospun. Vinykla technology began in the 60s of the last century, and was first officially introduced in 1973 by a new companyDupont (Sontara).Sontara is the result of activityDupontChicopee, none of the largest spunlace producers. Z 1990 rock. This technology has been refined and made available to other growers.
The hydrowoven technology is based on intertwining fibers of the material with high-speed water jets under a high vice. It is necessary to squeak hard on the perforated drum behind the help of jets of water, which are under the high pressure of the farsun beams. For the structure of these strings, the fibers of the fabric are connected to each other. As a result, the canvas cut in this way has specific properties, such as: softness and drape.

In fact, spunlace technology is just one of the methods for bonding fabric together. In your drawing, the canvas itself can be created in a variety of ways, including:
· Carding of staple fibers ( drylaid) . Let the fabric form until dry. In this type, the fabric is formed from staple fibers and cured as a result of carding the output fibers on carding machines. The fibers are combed by the working parts of a carding machine with a bare surface and placed in the canvas on the priming machine. Schematically the process of introducing baby 2.

· Aerodynamic method of fabric molding ( airlaid) ; This is the very dry method of finishing the canvas (dry -laid). However, with this method, the fabric is formed from very short staple fibers and is formed under the influence of a wind flow on the surface of a perforated drum or mesh conveyor. The previously fluffed and mixed fibers are sheared by a carding drum, which is then tightly wrapped (or on a sheet of drums), reinforced from the carding head with the help of a wind jet and transported.

· Hydraulic method of forming fabric ( wetlaid).
This method is also called papermaking (from the paper industry). The peculiarity of this method of canvas forming is that the production of non-woven fabrics is carried out by pouring an aqueous suspension onto the mesh part of the paper machine.

Malyunok 4.
· Spunlade - Spunbond ( spunlaid - spunbond) ; With this technology, the fabric is formed from continuous threads (filaments) separated from the melted polymer. The threads are molded from polymer using the spin-blow method and are laid into the fabric almost instantly.

Malyunok 5.
It needs to be said that initially all the spunlace fabrics were vibrated by the head rank for helpdry -laid (dry) method of preparing the canvas, tobto. before punching the fabric with water jets, after further cleaning the staple fibers. Soon the situation is changing. Obligations for the production of paintings from wikisairlaidwet -laid technologies will increase. In addition, wired light transmittersspunlace ownership (RieterFlessner) were recently able to demonstrate to their neighbors a technology that combines two technologies -spunlaid (as a method of creating fabric based on uninterrupted threads with melting polymer) andspunlacing (as a method of bonding fabric). The technology is givenspunbond-spunlace is expected to be even more popular in the future, as a result of the success of this method of production, the product combines the power of both technologies.
Thus, the typical spunlace spinning process consists of several stages, similar to most technologies for spinning nonwoven fabrics:
· Fiber stack;
· Molding of the canvas;
· Punching the canvas with jets of water;
· Cloth drying;
When passing through a water circulation system, the formed fabric (whether from the methods described above) is compressed in order to remove all possible damaged bulbs, and then creased. The pressure of the water increases from the first to the last injector. Approximate indications for the process of hydrospinning can be the following:
· pressure on level 2200psi (pounds per square inch);
· 10 rows of injectors;
· The diameter of the opening in the injectors is 100-120 micrometers;
· Stand between the openings - 3-5 mm;
· Number of openings in one row (25 mm) – 30-80;
It is strongly squeaked by water jets on a perforated drum. The vacuum at the drum removes water from the canvas, in order, first of all, to prevent the product from being re-converted, and otherwise, not to reduce the force of penetration by the jet.
The perforated drum plates (conveyor plates) play an important role in the process of processing the finished product. In front of the little grater, lay the little ends of the fabric. The special design of the burrs allows you to remove the different structure of the surface of the canvas (corrugation, terry, “cut”, etc.)
Small picture 6 shows modifications of conveyor grids and the surface of the finished fabric lying underneath them:

Malyunok 6. See the gratings and the finished canvas
Ensure that the canvas is punched through on both sides. The canvas can pass through jets of water many times (depending on the need for the canvas). Place the bonded fabric on a drying device to dry it thoroughly.
For a standard process (6 rows (spreaders) of strings, pressure 1500psi, thickness 68 gsm) requires 800 lbs of water per 1 lb of product. It is therefore important to develop a good filtration system to efficiently supply clean water, otherwise the injector openings may become clogged.
The advantages of this technology lie ahead:
- The number of fiber trimmings (mechanical on the internal structure of the fiber);
- The technology allows different types of fibers to be processed in the same way.
- The elasticity of the molded fabric is great – 300-600 m/h;
- The production process is environmentally friendly
- Behind its principle is sterile technology;
Sirovina for virobnitstva spunlace
The output materials for the production of fabrics using the spunlace method are most often staple fibers containing viscosity, polyester, polypropylene, cellulose, and raw materials.
Viscose
Synthetic fiber made from pure cellulose.
The advantages of viscose materials are the same as those of natural fibers:
- reception on the dotik;
- do not evoke physiological reactions;
- looming high in the graveyard;
- easy to sample.
Cellulose
Pulp fiber - this fiber, which is prepared from wood, is supplied in the form of rolls or stands.
Authority:
· Hydrophilicity;
· Shvidka has lost the water of other lands;
· Endowed resource;
· Possibility of laying out biological path;
· very reasonable price on par with other natural and synthetic ones
fibers.
Polyefir (polyester, PEF, PET, PET, polyethylene terephthalate)
It is prepared by melt molding. Today, PET fibers form the largest group of synthetic fibers.
Powerful
· Thickness 1.38;
· Especially mitsny;
· Elastic;
· Resistant to erasure;
· Light-resistant;
· Does not lend itself to the infusion of organic and mineral acids;
· Water-filling is only 0.2 - 0.5%;
· The value in a wet state is as high as in a dry one.
Polypropylene (PP)
A synthetic fiber that is spun by melt spinning from isotactic polypropylene.
Authority:
· Lower thickness 0.91;
· Melting area 165-175 ° C;
· Softening area 150-155 ° C;
· fiber is resistant to aggressive chemicals;
· practical day-to-day vologgopolyannaya;
· reliable resistance to washing;
· sensitive to ultraviolet radiation;
Bavovna
Bavovna is a fibrous material that is widely recognized among consumers for the structure of their natural style.
Positive power of the bavovni:
- absorption;
- laid out in a biological way;
- gas permeability;
- ease of sterilization;
- heat resistance;
- high value in the rural area;
- excellent insulation characteristics;
- the presence of allergic authorities;
- regeneration potential;
- softness.
Due to the high absorption capacity, good tissue-like structure with low fluffiness and high value of the hair, it is also the finest material for medicine, technology, cosmetics, special survival of vulgar bacteriums. Bavovna, which follows the spunlace method, in addition to the medical industry, can be successfully used for the production of dishcloths, serverets and tablecloths, which can last 6 - 10 washing processes. Products prepared using this method look like flax and can be subjected to preparation and stuffing to remove the desired appearance.
As a rule, over-reinforced fibers are recovered in bags. Synthetic fibers (polyester and polypropylene) are mixed with viscose and natural fibers (bavon, cellulose). Also, based on the descriptions of the fibers, you can use them independently without houses.
Consistent with world practice, the following spunlace warehouses have emerged in the market:
· Viscose / polyester;
· Viscose / polypropylene;
· viscose;
· Polyefir;
· Bavovna;
· polypropylene;
· bavovna/polypropylene;
· bavovna/polyefir;
· Bavovna / viscose;
· Cellulose/polyester;
The spunlace warehouse means the final sphere of vicorized material. For the most popular viruses from spunlace
Dry/hairy cleaning materials : polypropylene/polyester + viscose;
Vologi servetki : polypropylene/polyester + viscose; polypropylene/polyester + viscose + wax;
Clothes and whiteness for operating rooms : polyester/polypropylene + viscose, cellulose + polyester; polypropylene/polyester + viscose + wax;
Vlastivosti spunlace
Once bonded by water jets, the non-woven material “spunlace” reveals the unique powers of non-woven materials, among which we can immediately see:
· High degree of claying (high hygroscopicity);
· High permeability to moisture (best among bulky non-woven materials);
· Softness and tactile garnish are similar to natural fabrics.
In addition, the outstanding advantages and advantages of this non-woven material are:
· Understanding of values and subtleties;
· Resistance to tearing;
· Lint-free structure;
· Non-toxic;
· Antistatic;
· Good drape;
· Dialergenicity;
· Subject to peeling;
Avangard Company - leader in the production of biological servet insects in Russia. We were the first to discover the power of spunlace non-woven material in our country and for over 15 years now we have been producing products both under our own brands and under the brands of our company, steadily developing, promoting high an obvious product for co-workers and the brightest minds for partners.
Find out more about us
The Avangard company announced itself for the first time in 2001 by starting to produce products under the famous Diva trademark. Having taken off rich evidence The grower, having created a distribution network for the sale of their products, gradually expanded their activities and in 2002 they established the first plant for the production of white servets near the town of Tosno (Leningrad region).
This is why, with the method of reducing logistics costs and further development, the first in Russia began to grow non-woven material in-house. Currently, there are four non-woven fabric spinning lines in operation on two spinning areas that allow the fabric to be produced. different structure and thickness. The spun non-woven material is used for the production of wet and contract fibers of biological servets, as well as ready-made products for our clients in the cosmetic, medical and industrial sectors.
The company has 2 factories: near the town of Tosno (Leningrad region) and near the town of Shakhti (Rostov region).
At the moment the company "Avangard" - leader on the Russian market vologih servetok. Our products can be found in all the great trading areas of the country. More 300 companies They trust us to release products under their own brand, and millions of people today are profiting from the vulgar servers of our production.
Zgornuti
Virobnitstvo
Our factories are equipped with high-quality European equipment, modern production control technologies and a well-established acidity control system. We're releasing it right away 36 thousand tons spunlace material of different structure and thickness and 260 million packages of fiber servers. 







Find out more about our production
Virology follows the international standard ISO 9001-2011.
Virobystvo vologo servetok
The virobic plants, which are used for the release of biological servets, are designed accordingly to “clean zone” principles.
When designing and everyday life, solutions were stagnated that would be used in pharmaceuticals and microelectronics. And the “shop-by-shop” technology, due to which the wind preparation system, which creates an excessive pressure of cleaned air in the middle of the work area, avoids any incoming microorganisms and mechanical parts. The internal workshops are hermetically sealed, they are controlled by special washrooms behind the warehouse, the temperature and humidity of the environment. These minds will be protected by a special ventilation and air filtration system, as well as phlegm cleaners.
Access for security workers to the workshop is achieved through a system of vestibules, which is based on the principle of operation of the gateway. In the first vestibule, the workers take off their outer everyday clothes and put them up; in the other, they change into white robes, put on special caps and masks, and spray their hands with antiseptic. Permission to work is granted after a visual inspection and control by the change operator.
Virobnitstvo in Bladnane high-acid European transmission lines, how to ensure:
- automatic preparation of ingredients that will leak, in exact accordance with the recipe.
- ultraviolet treatment of nonwoven material
- automatic dispensing
- Milk-free packaging of viruses
- 100% guarantee of hermetically sealed seams on the packaging of serverets
- water that is vicorized during the process of vibrating goes through three stages of purification
Adjustments and verification of the accuracy of the robot lines are carried out regularly. The technological process is broken down into a number of simple operations that are easy to follow visual and technical control. Control procedures are clearly regulated and form a Just for You management system.
Constantly adapting to market needs, development of new products and technologies, a liquidity control system, a mechanism for prompt response to changes in customer service, as well as professional training for personnel of all levels - from a simple worker to a director from sale - to become "Just for You" production control system. This system will ensure the maximum satisfaction of the partners of the Avangard company, and ultimately guarantees prompt and clear products that meet the most demanding needs.
Virobnitstvo spunlace
Non-woven material of the spunlace type is fabric, which is made up of natural and piece fibers, with advanced characteristics of softness, clayiness, hygiene and handiness in vykoristan.
The peculiarity of this material lies in its preparedness - high acidity hydrojet method fiber bonding. By infusing jets of water, the remaining parts of fibers that are not suitable for vykoristan are washed out from the preparation fabric; Then the canvas goes through a stage of thermal processing and drying in a special chamber at high temperatures, which ensures additional hygiene and cleanliness of the material. This technological method of removing non-woven material allows its use in medicine, pharmaceuticals, cosmetology and general human hygiene.
The variety of products that are produced through spunlace is large: these include sanitary pads, diapers, medical dressing materials, surgical gowns, disposable bedding, etc. Medicines, products for salon and medical activities are being used in hospital. However, the greatest contribution to this material comes from the production of basal servetons.
High-yield spunlace nonwoven material is produced in Europe using the latest technologies. We vibrate spunlace whatever the format in the range from 0.06 to 3.4 m, thickness from 29 to 80 g/sq.m, practical with any winding option and a choice of nine types of structures. Several production lines produce up to 2.5 thousand tons of material per month.
The presence of the ham plant in non-woven material makes it possible to develop and expand the scope of its production in medicine and cosmetology by ham companies, based on the Russian cheese, with regulation Russian market needs.
Products in disposable packaging
Since 2015, we have been producing products in disposable packaging.
The won is presented in three types:
· Cosmetic hair servers
· Alcohol-based servings
Zgornuti

Our brandies
We produce food servers under brands Diva, Salfeti, Pamperino, Top Gear, House Lux, OptiClean, Mon Rulon, Teddy Pets, Fresh Royal, as well as dry products made from non-woven material for the cosmetic and medical industries under the brand White Whale.

Reach
The Avangard company has repeatedly won prestigious Russian and international cities. Customers appreciate the strength of our products, as well as our efficiency and flexibility in cooperation with partners.
Look around the city










Non-woven spunlace material is very popular, and its main advantage is high hygroscopicity. Popular spunlace in rolls, for which a wide range of products are prepared. The beginning of the era of spunlace production lasted until the 30s of the last century. Non-woven textile material spunlace is widely used for government and hygienic needs, as well as for the production of medical uniforms and technical wear. The main producer of spunlace in Central Europe is Mogilevkhimfiber, a product bearing the trade name Sontara and composed of 50% cellulose and 50% polyester. The basis of spunlace lamination is that when it is prepared, a thin ball of polyethylene is applied to one side of the fabric, which significantly expands the scope of its lamination. For light-woven spunlace nonwoven material, the warehouse can be different: viscose and polyester, viscose and polypropylene, bulk and propylene, cellulose and polyester, etc.
Spunlace is a technology for spinning non-woven fabric, which involves mechanically bonding fibers (threads) of the fabric into a fabric using additional hydroweaving.
Vibration technology
Spunlace technology was introduced in the 60s of the last century, and was first officially introduced in 1973 by the DuPont company (Sontara). Sontara is the result of the activities of DuPont and Chicopee, one of the largest spunlace manufacturers. Z 1990 rock. This technology has been refined and made available to other growers.
The hydrowoven technology is based on intertwining fibers of the material with high-speed water jets under a high vice. It is necessary to squeak hard on the perforated drum behind the help of jets of water, which are under the high pressure of the farsun beams. For the structure of these strings, the fibers of the fabric are connected to each other. As a result, the canvas cut in this way has specific properties, such as: softness and drape.
In fact, spunlace technology is just one of the methods for bonding fabric together. In your drawing, the canvas itself can be created in a variety of ways, including:
. Carding of staple fibers (drylaid). Let the fabric form until dry. In this type, the fabric is formed from staple fibers and cured as a result of carding the output fibers on carding machines. The fibers are combed by the working parts of a carding machine with a bare surface and placed in the canvas on the priming machine.
. Aerodynamic method of fabric molding (airlaid); This is the very dry method of finishing the canvas (dry-laid). However, with this method, the fabric is formed from very short staple fibers and is formed under the influence of a wind flow on the surface of a perforated drum or mesh conveyor. The previously fluffed and mixed fibers are sheared by a carding drum, which is then tightly wrapped (or on a sheet of drums), reinforced from the carding head with the help of a wind jet and transported.
. Hydraulic method of forming fabric (Wetlaid). This method is also called papermaking (from the paper industry). The peculiarity of this method of canvas forming is that the production of non-woven fabrics is carried out by pouring an aqueous suspension onto the mesh part of the paper machine.
. Spunlaid – spunbond; With this technology, the fabric is formed from continuous threads (filaments) separated from the melted polymer. The threads are molded from polymer using the spin-blow method and are laid into the fabric almost instantly.
It should be noted that initially all the spunlace fabrics were pressed using the dry-laid method of creating the fabric. before punching the fabric with water jets, after further cleaning the staple fibers. Soon the situation is changing. The production of fabrics using airlaid and wet-laid technologies is increasing. In addition, wired light spunlace fabricators (Rieter and Flessner) have recently been able to introduce to their peers a machine that combines two technologies - spunlaid (a method of creating fabric based on of the first threads from melting the polymer) and spunlacing (as a method of bonding the fabric). This “spunbond-spunlace” technology has proven to be even more popular in recent years, and as a result of the demand for this method of production, the product is influenced by the power of both technologies.
Thus, the typical spunlace spinning process consists of several stages, similar to most technologies for spinning nonwoven fabrics:
. Fiber stack;
. Fabric molding;
. Punching the canvas with jets of water;
. Linen drying;
When passing through a water circulation system, the formed fabric (whether from the methods described above) is compressed in order to remove all possible damaged bulbs, and then creased. The pressure of the water increases from the first to the last injector. Approximate indications for the process of hydrospinning can be the following:
. pressure at 2200 psi (pounds per square inch);
. 10 rows of injectors;
. injector opening diameter – 100-120 micrometers;
. stand between the openings – 3-5 mm;
. number of openings in one row (25 mm) – 30-80;
It is strongly squeaked by water jets on a perforated drum. The vacuum at the drum removes water from the canvas, in order, first of all, to prevent the product from being re-converted, and otherwise, not to reduce the force of penetration by the jet.
The perforated drum plates (conveyor plates) play an important role in the process of processing the finished product. In front of the little grater, lay the little ends of the fabric. The special design of the burrs allows you to remove the different structure of the surface of the canvas (corrugation, terry, “cut”, etc.).
Ensure that the canvas is punched through on both sides. The canvas can pass through jets of water many times (depending on the need for the canvas). Place the bonded fabric on a drying device to dry it thoroughly.
For a standard process (6 rows of strings, pressure 1500 psi, thickness 68 g/sq.m.) requires 800 pounds of water per 1 pound of product. It is therefore important to develop a good filtration system to efficiently supply clean water, otherwise the injector openings may become clogged.
The advantages of this technology lie ahead:
. The number of fiber trimmings (mechanical on the internal structure of the fiber);
. The technology allows different types of fibers to be processed in the same way.
. The elasticity of the molded fabric is great – 300-600 m/h;
. The production process is environmentally friendly
. Behind its principle is sterile technology;
Sirovina for virobnitstva spunlace
The output materials for the production of fabrics using the spunlace method are most often staple fibers containing viscosity, polyester, polypropylene, cellulose, and raw materials.
Viscose
A synthetic fiber that is removed from pure cellulose.
The advantages of viscose materials are the same as those of natural fibers:
. reception on the dotik;
. do not evoke physiological reactions;
. looming high in the graveyard;
. easy to sample.
Cellulose
Pulp fiber - this fiber, which is prepared from wood, is supplied in the form of rolls or stands.
Authority:
. hydrophilicity;
. The Swedish waters are washed out and washed out from other rivers;
. new resource;
. the possibility of laying out a biological path;
. very reasonable price on par with other natural and synthetic ones
fibers.
Polyefir (polyester, PEF, PET, PET, polyethylene terephthalate)
It is prepared by melt molding. Today, PET fibers form the largest group of synthetic fibers.
Powerful
. thickness 1.38;
. especially Mitsny;
. elastic;
. resistant to erasure;
. light-resistant;
. does not lend itself to the infusion of organic and mineral acids;
. water absorption is less than 0.2 - 0.5%;
. The value of a hairy plant is as high as a dry one.
Polypropylene (PP)
A synthetic fiber that is spun by melt spinning from isotactic polypropylene.
Authority:
. lower thickness 0.91;
. melting area 165-175 ° C;
. softening area 150-155 ° C;
. fiber is resistant to aggressive chemicals;
. practically every day of vologgopolyannaya;
. reliable resistance to washing;
. sensitive to ultraviolet radiation;
Bavovna
Bavovna is a fibrous material that is widely recognized among consumers for the structure of their natural style.
Positive power of the bavovni:
. absorption;
. laid out in a biological way;
. gas permeability;
. ease of sterilization;
. heat resistance;
. high value in the rural area;
. excellent insulation characteristics;
. the presence of allergic authorities;
. regeneration potential;
. softness.
Of high absorption capacity, rich tissue-like structure with low fluffiness and high value in the cellular tissue, in addition to the finest material for medicine, technology, cosmetics, special about the growth of voluminous tertiary virobes. Bavovna, which follows the spunlace method, in addition to the medical industry, can be successfully used for the production of dishcloths, serverets and tablecloths, which can last 6 - 10 washing processes. Products prepared using this method look like flax and can be subjected to preparation and stuffing to remove the desired appearance.
As a rule, over-reinforced fibers are recovered in bags. Synthetic fibers (polyester and polypropylene) are mixed with viscose and natural fibers (bavon, cellulose). Also, based on the descriptions of the fibers, you can use them independently without houses.
Consistent with world practice, the following spunlace warehouses have emerged in the market:
. viscose/polyester;
. viscose/polypropylene;
. viscose;
. polyefir;
. bavovna;
. polypropylene;
. bavovna/polypropylene;
. bavovna/polyefir;
. bavovna/viscose;
. cellulose/polyester;
The spunlace warehouse means the final sphere of vicorized material. For the most popular viruses from spunlace
Dry/hairy cleaning materials: polypropylene/polyester + viscose;
Wool fabrics: polypropylene/polyester + viscose; polypropylene/polyester + viscose + wax;
Clothing for operating rooms: polyester/polypropylene + viscose, cellulose + polyester; polypropylene/polyester + viscose + wax;
Vlastivosti spunlace
Once bonded by water jets, the non-woven material “spunlace” reveals the unique powers of non-woven materials, among which we can immediately see:
. High level of clay (high hygroscopicity);
. High permeability to moisture (best among bulky non-woven materials);
. The softness and tactile garnish are similar to natural fabrics.
In addition, the outstanding advantages and advantages of this non-woven material are:
. Understanding the values and subtleties;
. Resistance to tearing;
. Lint-free structure;
. Non-toxic;
. Antistatic;
. Good drape;
. Dialergenicity;
. Subject to peeling.
You can marvel at the confusion about the purchase and sales of ownership
You can discuss the advantages of polymer brands and their power at
Register your company with the catalog of enterprises