Early harvest cucumbers. What is the time when greenhouse cucumbers ripen? Chinese cucumber varieties
 Crop varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses are bred by the breeders all the time. Now on the market and in stores there is a large selection of cucumber seeds from domestic and foreign producers, which will satisfy even the most demanding customers. The right choice will be your good help of a large and tasty crop of cucumbers.
Crop varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses are bred by the breeders all the time. Now on the market and in stores there is a large selection of cucumber seeds from domestic and foreign producers, which will satisfy even the most demanding customers. The right choice will be your good help of a large and tasty crop of cucumbers.
Only after many years of sustainable agricultural practices can we hope to see a decrease in the cost of nitrates. “Agrobiodiversity” Scientists have so far identified about 1.4 million animal and plant species on Earth, and almost every day a new species is added to this list. This diversity is vital to people. We depend on him for food, for healing, water, energy, and more.
Wild species are at risk of extinction if the habitats in which they live are contaminated by pollution, urbanization, and deforestation. This destructive process can be accelerated by poor management of agriculture, forests and fish resources.
Greenhouse cucumber varieties - what do we know about them
Choosing a variety of cucumbers for the greenhouse, first of all, determine your preferences. A clear understanding of what you want to get, will become your guide when choosing seeds: collect a large amount of cucumbers, get early vegetables, grow late cucumbers or for harvesting.

The biodiversity of agriculture is represented by countless plants that serve to feed and treat people. It is found in crop varieties with special nutritional characteristics, in livestock breeds that are adapted to hostile environments, insects pollinating the fields, and microorganisms that regenerate agricultural soil. But even in agriculture, biodiversity is in danger. In fact, people who consume food depend on fewer agricultural products, and this reduces the likelihood that some of the cultivated plants and raised animals can adapt to abrupt changes in the environment.
variety "Courage"
Different varieties are the same in appearance, and taste criteria, the pulp and thickness of the skin can vary significantly. For salads and winter blanks, these signs are decisive. Some pickled cucumber varieties turn out crispy and tasty, while others simply fall apart.
There are universal cucumber varieties for greenhouses, which are good both in blanks and in natural form, have excellent taste. Such cucumbers, as a rule, have a low yield.
About 10,000 years ago, people, starting with the biological diversity that existed in nature, began to collect seeds and wild plants and grow them, choosing the most productive or most resistant varieties adverse weather conditions. More or less at the same time, they began to tame animals, using their strength, eating meat and drinking milk.
Farmers and agronomists must adapt plants to changing living conditions or expand their production to new areas that have not previously been grown. Plant genetic diversity is critical to increasing yields and the availability of crops that produce more food and have higher nutritional value. Today, four species — wheat, corn, rice, and potatoes — provide more than half of the vegetable calories of the human diet alone, while about a dozen animal species provide 90% of the world's consumption of animal protein.
Tip! In order not to rot the roots of cucumbers in the greenhouses, it is necessary to spray it with an iodine solution of 5 ml per 5 liters of water every 10 days. Bottom neck from the soil and 10 cm up the stalk to process a solution of iodine 1 part iodine 2 parts water. Sprinkle the ground with a solution of 40 ml of syrup per 10 liters of water every 10 days after planting cucumbers.
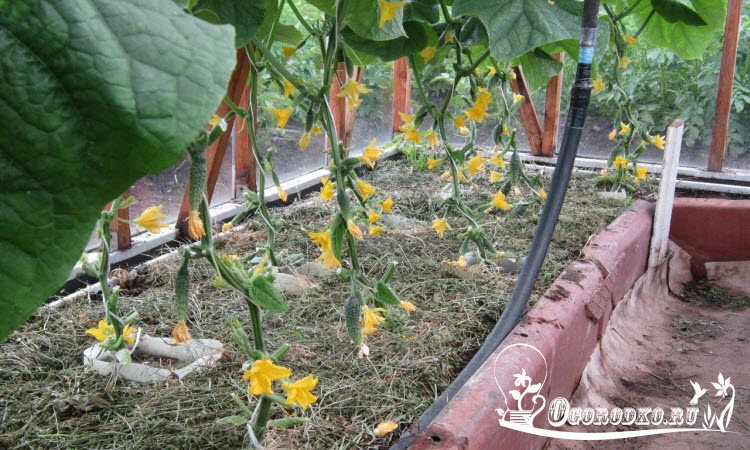
Hybrid greenhouse cucumbers have excellent resistance to disease and withstand temperature fluctuations, and it is this moment that is very important for many vegetable growers. As a rule, they are self-pollinating, crops sprout well, fruits ripen quickly, and yields are very high.
The best and early varieties of cucumbers for closed ground: photos and specifications
In addition to the diversity of species used for food purposes, it is essential that genetic diversity is maintained in different species: many farmers accept the uniform qualities of high-yielding plants and animals, but when avoiding diversity, species and race can be quenched, as well as their specific features.
The desire to increase agricultural production and profits actually sent a choice to a limited number of plant varieties and high-yielding breeds of animals. This is another legacy of the “green revolution”: instead of growing the most different plants, as in the past, focused on a single crop of crops, called monoculture, which significantly reduced the biodiversity of agriculture in the world. Monoculture plants are often hybrid varieties of traditional species.
Great value when choosing greenhouse varieties Cucumber has a type of pollination. Bee pollinated varieties in the greenhouse will pollinate poorly because of the enclosed space. So many bees like open garden, does not seem possible. And in winter, bee pollinated varieties will produce only barren flowers. The problem is solved by manual pollination, but this method is suitable only for small greenhouses.
The best variety produces more, so the farmer does not want to plant the oldest variety, which is slowly disappearing. In traditional farming, peasants tended to grow a wide variety of plants and often raised livestock. With the advent of monoculture, traditional farming practices were largely abandoned. A large number of species of plants and animal breeds quietly disappeared. This extinction is known as “extinction” and is irreversible. Therefore, agriculture loses its ability to adapt to environmental changes, such as global warming or new insects and diseases.
Breeders have developed and presented a huge number of parthenocarpic hybrids of cucumbers that do not need pollination and are intended for growing specifically in the greenhouse.

grade "Herman"
Experienced agronomists advise planting several varieties and hybrids of cucumbers at once in order to obtain high yields of cucumbers with excellent taste.
If the current availability of food does not adapt to changes in the environment, we could find it with great difficulty. It is imperative to protect these resources and ensure their sustainable use. Farmers, as biodiversity keepers on the planet, have the opportunity to grow and maintain native trees and plants and reproduce native animals, thus ensuring their survival. But the loss of biodiversity is not only associated with agriculture. Forests are perhaps the most important deposit of biological diversity, but every year we lose thousands of hectares of forest cover.
The best cucumbers for greenhouses of domestic and foreign producers
Cucumbers for greenhouses, both domestic and foreign breeding are in good demand among summer residents and gardeners. When growing cucumbers in the greenhouse, it is better to dwell on self-pollinated varieties.
The most the best cucumbers for greenhouse are considered:
- - self-pollinating, very productive hybrid of early maturing. No bitterness, great taste, good for conservation. With proper care, the stems grow very powerful, the fruits have the same dark green color and large tubercles;
- Emelya - refers to the pickling varieties. Indeterminate bushes, bundle ovaries, yield 12-16 kg per square meter of plants. The hybrid does not need pollination. It is well resistant to olive spot and cucumber mosaic;

Oceans, lakes and rivers are a marshy planet of life, but overexploitation and fishing methods that damage the environment threaten aquatic biodiversity. Experts are seriously concerned about this rapid decline in genetic stocks. With a wide range of unique features, you can choose plants and animals that can react to changes in state. It also gives scientists the raw materials they need to develop crop varieties and more productive and sustainable breeds.
For a poor peasant, biodiversity can really be the best defense against hunger: in fact, in regions of the world where underutilization is highest, farmers need crops that grow well in difficult adverse weather conditions, and not varieties with good yield in favorable conditions or less. but more disease resistant. Consumers, both developed and developing countries, benefit from a wide variety of plants and animals, as this makes a decisive contribution to a nutritious diet: rural communities often have limited access to markets and the availability of the widest range of local food products become indispensable.
variety "Zozulya"
- Zozulya is a well-known early hybrid, fruits are harvested as early as 45-50 days after germination. Cucumbers of deep green color with faded white stripes, taste without distinctive features, suitable for pickling. Differs in its resistance to root rot, therefore valued by gardeners;
- Courage - very high-yielding, from one plant it is possible to collect up to 20-25 kilograms of cucumbers. Treats hybrids of early maturing, the first vegetables can be picked already in 38-39 days. Cucumbers green, bumpy, excellent in taste. Resistant to. Appreciated for good keeping quality;
- Masha is the only one early hybrid from cucumber gherkins. The plant grows powerful, with a high predominance of female flowers. Fruits form a lot, at each node from five to seven cucumbers;
Hothouse cucumber varieties such as Annuta, Crystal, Sunny, Connie, Berendey, Marfinsky, Zarya, Manul are not inferior in their qualities to their fellows.
The preservation of plants, animals and their environment means, ultimately, the protection of a number of important functions that nature provides. The international commitment to keeping plants and animals in gene banks and in botanical and zoological gardens is vital. To protect this precious heritage, the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture was adopted, which entered into force on 29 June. The soil due to the silent and continuous work of insects, bacteria, fungi, worms becomes fertile and farmers can grow food.
If you want to grow unusual cucumbers, among exotic species, you can note the Chinese. Chinese white, Chinese snakes, Chinese miracle - all these varieties can be grown in a greenhouse. Unusually tasty, and at the same time easy to clean, fruitful, rarely affected by diseases.
Having come to us only in the 15th century, this vegetable rapidly gained popularity among all segments of the population, and it was so strong that foreigners who had heard about pickles and pickle considered their native Russian dishes with a thousand-year history. And indeed, a rare home farm does without beds with crispy cucumbers hiding among the rough leaves.
Cattle, fungi and microorganisms disintegrate organic material by transferring nutrients to the soil. Ants and other insects control parasites. Bees, butterflies, birds and bats pollinate fruit trees. Bogs and ponds pollute pollutants. Forests prevent flooding and limit erosion.
In the Italian agro-industrial system, greenhouses are of great economic importance both for their expansion, more than 40 thousand hectares, and for the production of fresh fruits and vegetables and flower products. In recent years, a growing plant, growing greenhouses has been the subject of a complex evolutionary process through technological upgrading of the food production phase. Greenhouse cultivation, although it finds the most favorable climatic conditions in the Mediterranean areas, it has to solve technical, environmental and energy problems, since, by definition, they should ignore the natural environmental factors such as temperature, water and food, typical of the climate.
Bouquet grade Sort Atlet F1
And if so, then the question is: what kind of cucumber is the most fruitful, is on the agenda of almost every vegetable grower.
And before choosing specific varieties for private households, it is necessary to analyze all their wishes for culture, as well as the possibilities of cultivation and processing.
The “defenses” used to create the greenhouse go from a simple plastic tunnel located on the same crop row, windshield barriers, plastic tunnels, to iron or aluminum greenhouses with glass or plastic covers, the last material that led to the growing development of greenhouses in recent decades. Protected crops mainly affect horticultural crops, as well as vegetables, such as tomatoes and peppers, such as zucchini, watermelon, cantaloupe, cucumber, eggplant, in addition to flower varieties and, to a lesser extent, fruit crops.

July is the most cucumber season
Classification by physiological features
This approach takes into account the mechanism of formation of cucumber fruit. The ovary of the female flower, located under the bright yellow perianth, already looks like a tiny cucumber. In order for it to grow and become a full-fledged green leaf, the cells of the ovary need some hormonal signal, the occurrence of which is associated with fertilization of the eggs contained in the pistil. Fertilization follows pollination, and according to the method of pollination, varieties of this crop are divided into:
A greenhouse is a very complex agricultural system in which the use of various innovative technologies eliminates the existing contrast between the need to grow crops, on the one hand, and the need to limit energy impacts, environmental and economic, on the other. Among the most important functions of environmental control are soil heating, air heating or cooling, aeration, shading with shading, lighting and, of course, irrigation with the addition of fertilizers. Greenhouse growing potentials are remarkable: on average, a greenhouse crop increases production costs many times per surface during a year.
- bee-pollinated;
- parthenocarpic;
- self pollinated
The first ones tie fruit only after pollination, therefore they need enough insects in the vicinity, mainly bees. In the absence of pollinators, female flowers wither and fall off, since it is the ensuing seeds that produce plant hormones that cause the fruit to form.
However, the problem of greenhouses is energetic: in fact, it is a voice that has a great influence on the cost of production of greenhouse crops, and also has a serious impact on the environment. In Italy, "conditioning", that is, the regulation of environmental factors, covers about 30% of greenhouses and considers the main factors for controlling temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide in the air, soil temperature, intensity and duration of light.
This is accompanied by indirect energy consumption associated with the structure of the glass and covering materials and, above all, plastic: for cultivated crops, in Italy about 80,000 tons of plastic are consumed each year, with significant problems associated with waste management. Although the greenhouse appears to be a territory-free system, external factors, such as local climate, exposure, slope, altitude and windiness, significantly affect the energy balance of the greenhouse. It is for this reason that the focus of the study should be directed to a new type of greenhouse "greenhouse" or "spontaneous climate", called "bioclimatic" greenhouse, or industrial solutions that optimize the indoor climate using automated systems is very effective.
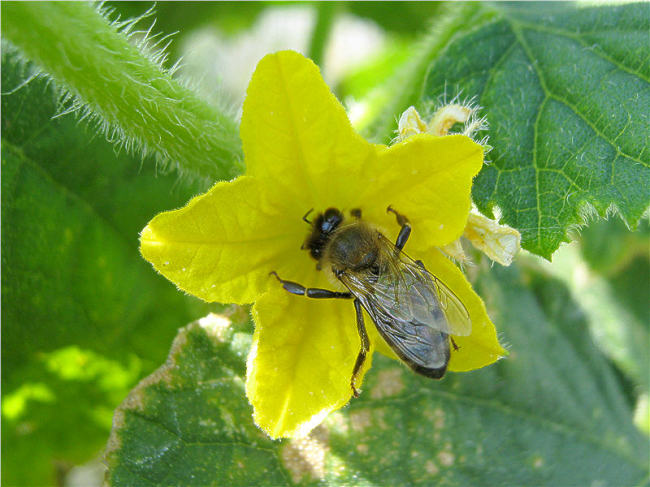

For the ovary of the cross-pollinated variety to start growing, the flower must be visited by a bee.
The second group of varieties is capable of producing seedless fruits. This phenomenon in the plant world is not widespread, however, it occurs, for example, in grapes (raisins), bananas. Partenocarpic cucumber varieties are convenient in greenhouses, because they do not need to deliver hives.
In the flowers of the third group, a curious morphological detail is noted: their flowers are oboepoly, which is considered to be a rather ancient, almost lost feature for cucumbers. Self-pollinated mainly include hybrids. They also do not need bees, so they can be considered when choosing a variety for greenhouses, although in open ground they give decent yields.
Agrotechnical division
Often the main factor in the selection of varieties is the cultivation area (Moscow region, Leningrad region, Krasnodar region), the size of the greenhouse, the condition of the soil, the possibility of systematic care. For example, in the northern regions, the growing season comes to the fore, and in very modest areas the size of the plant. Based on this, varieties are divided by:
- early maturity (early, middle, late ripening);
- the length of the shoot and its tendency to branching (bush, short, medium and long-varietal);
- the ability to withstand low temperatures (zoned for the northern regions and all others).

Beauty-whip already started flowering
Probably, only one sign is not taken for classification - attitude to water. In this regard, all greenhouse varieties of cucumbers are almost the same.
It is enough to allow a substantial drying of the soil once to ruin the entire crop of any variety. The scourge will turn yellow, and the fruits will begin to produce a "stressful bitterness" - cucurbitacin.
Consumer Quality Classification
Already choosing a bag with the seeds of the most fruitful varieties, it is important to understand exactly how the crop will be consumed. There are varieties of three directions:
- salad dressing;
- pickling;
- gherkin (canning).
Salad varieties are eaten immediately after removal from the lash or stored for some time due to its more dense skin. In salting they are not suitable, because they crawl away, they become soft, like boiled. Their external distinguishing feature is the white spikeiness of the fruit surface.
Salt varieties, as the name implies, behave perfectly in brine, while maintaining their elasticity and crispness. Outwardly, they are distinguished by a thin peel with large tubercles and black spines.
Gherkin cucumbers in salting get worse, their purpose - conservation. Marinated with various satellites: garlic, mustard seeds, spices, roots - they are an indispensable winter snack on weekdays and holidays.
A few words about hybrids
Often there is a temptation to find high productive variety cucumbers, do not buy seed, and bring the vegetables to full maturity and extract the seeds from them. In the case of the usual well-established variety (Nezhinsky, Murom) this is quite acceptable. However, there are varieties in the marking of which there are the Latin letter F and the one near it, for example, “Masha F1”, “Prestige F1”. Seeds of such varieties to harvest in their own beds is meaningless.
The letter F (from the Latin “familia”) in this case means that before you is a hybrid, that is, the product of the crossing of plants belonging to two different varieties.
Perennial selection experiments make it possible to find such combinations of parental forms, the descendants of which inherit the best complexes of characters, but such complexes appear exclusively in the first generation and only with such parents.
For example, “F1 Courage” grows well in a greenhouse. Who pollinates him? Another copy of the same hybrid? Growing through the passage "F1 Relay"? In any case, the “parents” will be different, therefore, the complex of signs in the descendant will also be. Varietal qualities disappear.
Varieties for closed ground - what to look for
When choosing the most productive varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses, you can safely dwell on hybrids, since they are produced precisely for the sake of a significant number of fruits. The second reason why serious funds are spent annually on the selection of certain parent pairs is the properties found in hybrids to resist certain diseases, for example, powdery mildew. To be sure of the quality of the seeds, they cannot be acquired from the hands, only at seed-growing stations or in specialized stores.

Seeds are best purchased from reputable manufacturers.
In order to “populate” greenhouse cucumber seedlings as early as possible, especially in the absence of heating, other than solar, it is necessary to give preference to varieties that are regionalized for the Moscow region, the Urals or Siberia, which are a little easier to relate to Russian cold weather. As for precocity, this is a matter of taste, but in the most northern areas an attempt to grow late-ripened cucumbers even in protected ground may be unsuccessful.
When thinking about precocity, it is necessary to remember about the upcoming battle with the harvest. If all vegetables ripen at the same time, there may not be enough resources to process them. Therefore, it seems reasonable to divide the area of the greenhouse between the varieties of different ripening terms. This is especially true for salad varieties, the fruits of which are convenient to find on the whips all summer, but little by little.
It is necessary to immediately abandon the bee-pollinated forms in favor of parthenocarpic, especially if, due to weather conditions or the design features of the greenhouse, it is not planned to be planted frequently.
Isolated insects are unable to visit all the flowers. Alternatively, you can place a hive in the structure, but the greenhouse must be of considerable size to provide food for thousands of bees.

In large greenhouses they put such bumble-bee hives
How to choose the best hybrids for closed ground
Any freshly cultivated variety or hybrid passes the varietal tests, during which its important qualities are established:
- yield;
- cold resistance;
- the ability to bear fruit in certain light zones.
If the tests are successfully passed, the variety is zoned - it is recommended for cultivation in certain regions and is entered into the State Register of the Russian Federation. The best varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses near Moscow and all of Russia need to look here.
First of all, these are early ripe parthenocarpic hybrids, which tolerate small temperature differences and light shading. The following is a partial list of the most deserving varieties.
"Advance F1" - an early harvest
Early ripe (fruits about the 40th day from shoots) Parthenocarpik female type of flowering. Rapid growth is accompanied by limited branching, which allows the fruit to comfortably form, not being constrained by abundant leaf mass. Zelentsy of medium size, up to 130 g, dark, white-tipped, with well-marked tuberculosis. Up to 10-12 kg of beautiful fruits can be removed from a square meter.
The hybrid is considered universal, however it is unsuitable for salting. It can be cultivated in greenhouses of any type, as well as under the film. Its resistance to perinospora and powdery mildew is very attractive for vegetable growers.
"Break F1" - crispy cucumber
One of top grades cucumbers for polycarbonate greenhouses. Early, powerful, well leafy partenocarpik kornishonnogo and salad type. Flowering so-called Bouquet type. This means that in the bosom of one leaf it can lay up to 8 ovaries. On the other hand, abundant fruiting requires regular complex fertilizing, and if they are not carried out, the unique properties of the hybrid may disappear.

"Break" is recognized by the bright spot on the top
Cabbage leaves are small, short, up to 90 g in weight, tuberculate, with a light greenish spot at the apex and abundant white pubescence. Tasty, sweet, crunchy. With proper care, give more than 15 kg per square meter. The variety is in unison in the phase of fruiting, so it makes sense to plant uneven-aged seedlings if this variety is the only one on the farm.
"Voyage F1" - the perfect choice for the suburbs
Indeterminant, in other words, requiring the pinching and formation of a sprouting system, a hybrid of parthenocarpic type. Fruiting on the 48-64 day from germination, friendly, abundant. Zelentsy small, up to 110 g, moderately striped, white-pubescent, fragrant, consumed fresh and well preserved.

"Voyage" - a great option for the Moscow region
“Voyage F1” is one of the best greenhouse cucumber varieties, zoned according to the III light zone, i.e. it requires a sum of LIGHTS (photosynthetically active radiation) of at least 600-900 cal / sq. The third light zone includes Smolensk, Lipetsk, Moscow Region, Krasnoyarsk Territory, Tatarstan, Yakutia, Khakassia and other regions.
"Courage F1" - the favorite of summer residents
One of the most popular hybrids grown on an industrial scale. In terms of biological and agrotechnical features, it is similar to the hybrid “Voyage F1”, but sets fruit first, 40-43 days after germination. Its greenhouses have pronounced ribbing and tuberosity, crispy flesh of delicate flavor and white pubescence. Excellent salad and gherkin hybrid for any greenhouses and film shelters.

Favorite public "Courage"
Productivity "Courage" reaches 18 kg per square meter. m, which indicates the necessity of a careful approach to systematic feeding of culture. Doses of once applied fertilizers should be calculated taking into account the actual state of the soil. An excess of nitrogen nutrition adversely affects product quality: fruits can become soft or tarnish.
"Typhoon F1" - a productive large-fruited variety
Medium early hybrid, zoned to I-III light zones. This means that it needs 100-200 cal / sq. For aging. see PAR - a kind of record, given the Indian origin of culture. Typhoon F1 can be cultivated in greenhouses of the Leningrad, Arkhangelsk, Magadan regions, in the republics of Komi and Karelia.
Indeterminate partenocarpic salad type, from those that are popularly called "long cucumbers."
The fruit is smooth, evenly colored, with a glossy shine and a pleasant taste, its mass reaches 260 g. With such large fruits, the yield is impressive - up to 37 kg per square meter. m. Greenhouse owners value it for its resistance to the gall nematode.
Other high-yielding varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses
Actually, the majority of hybrids for cultivation in greenhouses and under film have similar properties: early ripening, decent yields, impeccable taste, no need for insects. However, several other varieties of hybrids should be mentioned, whose characteristics may be useful in specific conditions:
- "New Nezhinsky F1" - the leading pickling hybrid;
- "Masha F1" - the earliest of the existing today;
- "Hedgehog F1" - small (9-10 cm) gherkin, not afraid of temperature changes;
- “Obskaya F1” is a medium late black-fruited crop variety, zoned across Siberia and which behaves well when salting.

Compact cold-resistant "Hedgehog"
Traditional varieties are grown in greenhouses, whose seeds can, without fear of splitting, be extracted from mature Zelentsy and used for breeding. These are, for example, “Zozulya”, “Robinson”, “Spring” - early, tasty, fragrant varieties, however, most of them require pollinating.
It turns out that the answer to the question, what kind of cucumber is the most fruitful, does not have the only correct answer. The geographical breadth of the area, the material from which the greenhouse is built, the wind rose, even the quality of the water - all affect this capricious tropical newcomer, his majesty the cucumber. Personal experience, advice from experienced gardeners, recommendations of an agronomist from the nearest vegetable farm will help to choose a truly fruitful variety for a particular greenhouse.