No matter what the foundation is, the slab is not buried. The foundation for the house looks like a monolithic slab. Slab foundation - what is it
Fakhіvtsі divide it into non-neglected, frivolous, dull type. However, regardless of the type, this monolithic basis for the booths will always be subject to increased rigidity and weight.
Current types of monolithic foundation
As it was said above, after the step of sinking into the ground, the monolithic foundation comes in three types:
- non-negligence;
- debris;
- overshadowing.
The skin has its own characteristics and meanings depending on the type of sporud.
Particularly unsullied tiled foundations are those that are laid on the surface of the ground; there is no need to dig a pit underneath. The technology of its preparation is in no way different from other types, but here it is important to understand that an unburied foundation, regardless of its expansion above the ground, is still liable to be buried a few centimeters, then it will be buried not the pillow, but the structure itself, of course , will be on the surface of the ground.
A non-buried foundation is ideal for summer cottages and other spores that will grow on the soil, do not freeze deeply and are not heaving.
Dribnozagliblenie The foundation is a monolithic structure, dug into the ground to a small depth. Let's call it 10-15 centimeters. The main part rises above the ground. Drilled foundations are ideal for soils with minimal freezing, heaving soils, as well as for single-surface and double-surface booths.
Zagliblenie The monolithic foundation, due to its design, is completely unburdened and completely expands in the ground. There is a need to dig a pit. First of all, here are the recommendations for the snowy areas of our region, where the depth of freezing in the soil is great.
It is necessary to bury it in the ground to a depth of 1 meter to 25 centimeters, this indicator being dependent on the level of depth in the soil for the duration of the work. Booths on such a foundation can be placed on top of each other. The production technology is more labor intensive.
Having studied the types of slab foundations, you can move on to the features of this foundation. In front of us, the most important thing pillows. Try using a ball of compacted sand to fill 5-10 centimeters of crushed stone. The appearance of the pillow is obligatory. There will be an attack on the foundation of water and water.
For whom should I stagnate? waterproofing. The first ball of waterproofing will be placed directly on the crushed stone lining, and the other ball will be placed on top of the concrete formwork. So that the waterproofing lasts a long time, better than vicorized bituminous materials, for example, roofing felt.
The coming moment is insulation. Some experts recommend placing a ball of insulation directly on the foundation cushion, and another ball on the top of the base.
These rules can be followed, or not, except for insulation using additional heat-insulating materials - binding to a monolithic foundation.
Features of the design of a tile foundation
When erected, it is possible to use special concrete slabs, which are prepared in concrete structures factories. However, the technology of its installation will require lifting equipment. Under such a foundation, a foundation pit is carefully built, the bottom of which is perfectly level, so that the slabs do not warp.
The slabs between each other become covered with cement rubble. The plate can be ribbed or flat. The ribs and flat design do not compromise the rigidity and durability of the base. Booths that stand on such a foundation, with insufficiently advanced building technology, can soon become warped due to seasonal ground shaking.
The most important feature is the creation of a monolithic block base.
In this case, the structure is made from concrete blocks, which are also held together using cement-sand mixture.
These units will also follow the strict rules for monolithic units.
Stages of work on a slab foundation
Having understood what the foundation of a monolithic slab is, you can move on to the stages of its construction.
- Preparation of land plot Here we need to focus on two main points. The first step is to carry out the correct markings. In addition to the perimeter of the pit, it is necessary to add 2 meters to the new one, as required for the work. Step on - it is necessary to stand out from this depth. After everything is measured, the pit is dug, and its bottom is leveled. There are humps and ridges at the bottom.
- Pillow creation. As a result, the base of the slab foundation is created from a ball of sand and rubble. First, a 5-10-centimeter ball of sand is filled, which is poured with water and compacted. Water is needed to make the sand hotter and hotter. On top of this ball is poured a layer of 5 centimeters of crushed stone. It is also important to compact the crushed stone well. Once everything is ready, you can move on to the offensive stage.
- Overlay of waterproofing and insulation. With complete waterproofing, as it was said, it is better to use roofing material. Its leaves are overlapped on a crushed stone pillow. The place you have joined will need to be melted using a gas flame. After this, an insulation ball can be placed on top of the waterproofing. The first ball is ready for the foundation.
- Advancing robots are associated with buildings concrete screed. Vaughn may overestimate 5 centimeters. Prepare with the help of a cement-concrete mix. Waterproofing can be applied over the poured screed. An important point is that the roofing material, which will be used as waterproofing, must be larger than the perimeter of the foundation in order to cover the ribs. It is also necessary to have a sewerage and drainage system to remove waste and water from the ground.
- Offensive stage - opening formwork. The formwork is made from wooden planks that are stacked together. The formwork boards must be supported by wooden beams, with the help of which the slope is created, and also fixation is required until the pins are driven into the ground. Therefore, such a formwork design itself is rigid and does not fall apart when concrete is poured in.
- Once everything is ready, you need to start before construction of a reinforced frame and mesh. For which reinforcement is taken, behind it a frame and mesh are created that reinforces it. It is important to understand here that with such a structure it is better to make a foundation pit at home, tie the rods together, rather than weld them. Tied rods are more fragile and will not cause the slab to collapse due to deformation of the ground.
- Once everything is ready, you can start filled with concrete reinforcing mesh and frame. It is better to do it at a time, so that the concrete is homogeneous.
- Once the stove is ready, you can start re-insulation of the upper part of the base. For a better effect, the surface can be treated with bitumen mastic, and then the insulation ball can be laid. In the future, whose home will be warm and not burdened by the cold from the ground. Moreover, a floating ball of insulation will absorb heat into the cabin and prevent it from heating the ground.

A monolithic slab foundation is a miraculous basis for any structures or structures.
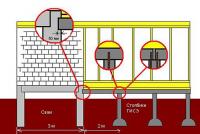
When building on heaving soils, a non-buried foundation is built mainly by erecting light frames, which allows for deformation of its frame in order to save operational components and the necessary appearance. When building on rocky and highly compacted soils, stone booths can be built on an unburdened foundation. A non-buried foundation is constructed in three options: as a unit, as a monolithic slab or as a slab (Fig. 46) .
Small 46. Types of unburied foundations: A – building parts; B – foundation slab; B - fundamental rocks
Stovpparts not buried foundation
Partially unburied foundations can be installed for small wooden and panel buildings, climbing frames, and outbuildings that are built on non-heaving or slightly heaving soils. When built on rocky or highly compacted soils, this type of foundation can be used as a foundation and is suitable for cutting from decks or timber frames.
Partial foundations on short supports (stiles), spread out with a cross-section of 1.5...2.5 m, are often used in individual situations. There are a lot of large companies that specialize in building wooden booths, without bothering themselves with foundation problems, laying foundation blocks on the ground, and on them - the booth itself (Fig. 47, a). This technique is particularly suitable when living on non-heaving and slightly heaving soils. If the soil is heaving, then downgrade You can pour heaving soil onto the booth by replacing the heaving soil under the support of a soft pillow (Fig. 47, b).
Ready-made wall or foundation blocks can be used as a material for supports. The supports can be made from solid masonry or made from concrete, rubble concrete or porous concrete. We deeply appreciate that the installation of a ceramic pot with low frost resistance and a silicate pot in the foundation is unacceptable.

Small 47. Unburied foundation steps: A – foundation blocks; B – support with a padded pillow; B - support on highly compacted soil; G – wooden support; D – waterproofing of the support; 1 – foundation block; 2 – padded pillow; 3 – concrete; 4 – rubble stone; 5 - deck; 6 – waterproofing; 7 - end
If the soil is rocky or coarse, then the supports can be installed on rigid, stable fragments of the soil, which have previously exposed the weaknesses and vitriols of the warehouse. The support can also be made from viscostans and sand cement, which will ensure the solidity of the base and the supports themselves (Fig. 47, c) .
If the supports are too weak, the trees may break. To do this, cut the butt part of a pine or oak log with a diameter of 20...30 cm. To increase the stability of the supports under them, dig a hole, fill it with a ball of concrete 10...15 cm deep and anchor the support itself at the concrete grooves. (Fig. 47, d). Lack of wooden supports - lack of availability - a little more than 8...15 rocks. To improve the service life of the wood, I char the wood on high heat and soak it in tar, treated oils, etc.
The creation of foundation supports is associated with the implementation of hydroisolating approaches, which are necessary to protect the structure of the booth from the formation of groundwater. Water easily rises behind the structure of concrete, catching wood through the capillary effect, creating mold, fungi and rot on its surface. A hydroisolating coating in the form of bituminous mastic, roofing felt, roofing felt, skloizol, etc., which is spread onto a stick with a foundation, binding for concrete (Fig. 47, d) .
Since expanded clay concrete blocks, which are weak in frost resistance, are used as supports, they are covered with bitumen mastic (on the side, hardened in the middle of the base). This allows the curing block to dry and helps dry it before the curing is ready.
As soon as the foundation supports are laid out, the screws on the supports are laid out. A large distance between them (more than 2.5 m) can cause stress on the skin support, which can cause changes in the structure of the tree. To change the changed wood, the edge of the supports should be changed, and the lower (frame) end of the frame should be made from timber or logs with a larger transverse cross-section and, if possible, from wood of larger species (oak, modrina).
When planning to build foundation supports, it is necessary to install the structure of the fence that is used to cover the underground space. Increased moisture in the lower part of the booth (dew, breezes from waste water, snow) requires collection from moisture-resistant materials. Ascement or metal corrugated sheets, cement-bonded particle board, frost-resistant plastic, façade decorative panels that are fixed directly to the wall or the top of the booth - a completely different solution.
Support height indicates the height of the roof of the house. If the legs are short, then the end and lower part of the walls of the wooden booth will begin to rot, rot, leading the booth to a state of disrepair.
The high height of the supports allows you to create comfortable washrooms for wooden structures, but other problems associated with heaving objects arise here. The heaving boxes move around the supports under the booth with large joints that span them. How does it work out?
If the soil is heaving, and the bottom of the booth is insulated, then in a slab of frozen soil, placed on top of the booth, an opening is made to the unfrozen soil (Fig. 48). During the freezing process, the heaving soil becomes increasingly exposed to all sides, including the opening of the frozen soil in the slab. On heaving soils, the horizontal displacement can reach 10...15 cm. Such heaving soil collapses can generally be thrown over high foundation steps. (Fig. 49), and narrow, weakly reinforced lines of unburied or slightly buried foundation.

Small 48. A slab of frozen soil with a “warm” base: 1 - foundation support; 2 – the slab was frozen; 3 - ground displacement vector

Small 49. Height of the foundation support with a “warm” subfloor: 1 - slab of frozen soil; 2 – frost boundary; 3 – foundation support; 4 - zvorotne zasipannya - insulation; 5 - snow cover
The reverse picture of distortions is due to the fact that a pound of snow is piled on top of the cabin, and a pound of snow under the cabin is cooled down to a temperature of excessive wind. In this case, the plate of the frozen pound is pressed against the side of the booth, where the pound freezes faster (Fig. 50). With such a frozen pound, the high support under the booth moves into another bin (Fig. 51).

Small 50. Slab of frozen soil with a “cold” base: 1 - foundation support; 2 – the slab was frozen; 3 - ground displacement vector

Small 51. Fixing the foundation support with a “cold” subfloor: 1 - slab of frozen ground; 2 – frost boundary; 3 – foundation support; 4 – perekrittya insulation; 5 - snow cover
In order to prevent the support pillars from transferring, they should be rolled onto a soft pillow (Fig. 47, b), Which neutralizes the heaving of the dented white of the supports. In addition, the supports themselves will be more stable: their height does not need to be greater, less than 1.5 times the width of the sole. Until further visits, all the smells are straightened out so that the cordon of frozen soil near the zone of spreading the supports does not sharply change its depth. For this purpose, in the basement part of the cabin, the booth should be closed for the winter, so that the underground space does not freeze too much. There is no need to take the snow from around the cabin all the way to the ground.
Forgetter, respect!
The winter cold may even singly span the high supports, as with an open underground the highly heaving soil freezes.
Parts of the process not only “unravel” the foundation supports, but also raise and lower them, unevenly, putting a lot of stress on the structure of the booth. If the booths stand on adjacent pillars-supports or on beams laid on heaving soil, with power supply, and under dry and warm conditions, then the supports under the outer walls will rise, and under visceral - to lose the place (Fig. 52). In a wooden booth this will lead to distortions in the door frames and window frames, damage to the frame and minor breathing problems; and in a stone hut - up to the cracks in the walls, as one can live in the hut for an hour at a time, without fear of cosmetic repairs.

Small 52. Deformations of a booth on heaving soil: 1 - booth; 2 - foundation; 3 - frozen boundary
What can you do to please yourself?
It is necessary to carefully insulate the substrate on top, then the soil under the booth will freeze the same way as around the booth; Otherwise, the manifestations will not appear so strongly. In addition, it is necessary to reduce the amount of soil around the booth to a minimum by organizing drainage and snow removal around the booth.
Monolithic plate
The monolithic unburied slab as the foundation is vikorized when standing on weak soils, when building. small be on highly heaving soils or in permafrost basins (Fig. 26). Such a foundation is particularly suitable for light buildings that do not require high stress from the slab itself, and for rigid stone structures whose walls will enhance the extreme rigidity of the slab.
The foundation, laid directly on heaving soil, sinks and rises when climate conditions change, and “floats” on the surface of the soil. It is clear that since the booth is installed on a slab, which has a layer of ground on top, the soil under it does not freeze, especially under the middle part of the booth. Due to the unevenness of freezing under the booth, a hole in the ground is created, which can reach 10...15 cm. The slab of such a foundation itself is too harsh for a long time and will take a long time with heavy reinforcements.
One of the widest options for an unburied foundation is one in which a ball of insulation is laid between the slab and the soil (hard expanded polystyrene of 10 - 15 cm). This solution allows not only to change the heat loss through the surface of the ground on top, but also to practically turn off the failure of the ground underneath it by adjusting the temperature field under the booth and white. The insulation unit itself is placed on a ball of coarse-grained sand of 30 - 40 cm. (Mal. 53) .

Small 53. Slab foundation on a padded cushion 1 – padded cushion; 2 – insulation; 3 – plate; 4 - frost limit
Such a foundation must be built entirely on soils with a consistently high level of groundwater, since drainage is important; as well as on weak, subsiding and highly compressive soils (water-saturated sandy or clay soils, peat, water-saturated muddy soils).
Another option to reduce the unevenness of freezing under a cabin with a slab foundation is to install insulation in the same soil near the cabin (Mal. 54) .

Small 54. Stove under light earthenware: 1 - slab; 2 – padded pillow; 3 – insulation; 4 - wall
The reason for the appearance of cracks in the monolithic stoves
The forgetter has arrived with a serious problem. Booth 8x10 m with two surfaces on heaving soil; the foundation is a reinforced concrete slab, built on a crushed stone slab with a thickness of 50 cm; walls made of foam blocks, reinforced with a seismic belt. There were no problems during the winter, but a crack appeared in the hinged axis of the inner wall, which extended to a width of 1 cm, and the pavement rose as it later turned to the exit position.
We started to figure out why. The winter of 2006 was particularly difficult for fate. The ground under the perimeter of the booth froze very hard. Having become increasingly social, he could not help himself to his important routine, causing him to become severely weakened. (Fig. 55, A). The pavement around the booth, tightly connected to the slab, did not create a great pressure on the ground with its force, so its outer edge would linger uphill. Spring has come. The soil has begun to thaw and change in temperature. There is a gap under the outer perimeter of the slab, which increases with the size of the ground. The moment had come when the slab began to collapse onto the ground without its central part. Without showing the vantage, the perimeter of the slab was sifted, and the inner wall of the booth was cracked. (Fig.55, B). The power turned to the exit position. All sorts of constructive ideas showed up here. The large dimensions of the booth increased the unevenness of freezing of the soil; The situation could have been compromised by insufficient reinforcement of the slab, which was taken care of at the first stage of demolition, with too much reinforcement in the lower part of the slab. It seems that the accessibility of the heaving soil has become a new peace, since the cold has already arrived.

Small 55. Heaving soil and booths on the slab - folding containers: A - cages for lifting; B – hanging booth; 1 - pavement; 2 – frost boundary; 3 - hardened soil; 4 – crushed stone; 5 – plate; 6 - crack near the wall
Gratchasty unburdened foundation
Gratch foundation (Fig. 46, c) Vikorist is used when working on weak subsidence and on highly heaving soils. A leveled foundation with a monolithic slab has such a foundation, while being highly rigid, which allows for a significant reduction in the loss of concrete and reinforcement. The traditional approach to laminating plank formwork for such a foundation structure is complex and expensive, which does not allow it to be widely used.

Small 56. Formwork for the foundation: 1 – padded cushion; 2 – waterproofing; 3 – formwork; 4 – slab insulation; 5 – concrete; 6 - fittings
Respect!
When planning a foundation near a monolithic slab or grate, first create a pit and install a utility line that runs under the booth (introducing the water supply and draining the sewerage system). Otherwise, after preparing the foundation slab, it will be much more difficult to carry out the work. The walls of the pit should be independent from the slab or the gratings to the foundation, so that their external vertical movements could not create structural stress in the slab structure.
To maintain a reliable foundation, different types of foundations will be set, which are divided into several types: strips, joints, slabs and joints with a grillage. The greatest expansion was achieved in the foundations of the strings, which were molded under the skin of the external and internal load-bearing walls, exactly repeating their contour. The walls of the string base are buried in the soil, whereby, when the basement is cleared, the stench immediately plays the role of a vegetable garden structure. Such foundations can be either monolithic or precast-monolithic, or with adjacent concrete or reinforced concrete elements. In some cases, there may be vicorized rubble, rubble concrete, and, at other times, concrete masonry, but today we’ll talk about the crushed slab foundation.
Stitch foundations are stagnant when different types of structures are built. For example, a strong stitch foundation is indispensable when working with a lot of important materials - concrete blocks, or other materials that need to be faced as a whole. At this depth, the laying of the foundation may exceed the depth of freezing of the soil by 0.2-0.3 m.
As a rule, strech foundations should be wetted only if there is no possibility of vicorization of the site - when living on a slope or on a relief terrain, where it is important to tamper with the most possible pressure of the soil. The addition of a stitch foundation is the most effective way to compensate for such uneven flow, since its elements are tightly and reliably connected to each other both transversely and laterally.
In addition, the construction of a strick foundation is indispensable for the construction of important solid or stone frames, as well as those made from monolithic reinforced concrete, laid out on weak soils. This type of foundation is ideal for lining the basement and basement areas. It’s good to stagnate and once again fix the foundation with shallow foundations.
In general, string foundations can be classified into two types:
- For other buried ones (they are called non-buried ones) - suitable for waking up three curls on more than two surfaces;
- Buried - a massive foundation made of concrete and buried up to 1.4-1.6 m) - suitable for large large structures.
As a rule, it is permissible to lay a slab foundation on soft, sandy or clayey soils, and it is permissible to install a crushed foundation on water-saturated soils, however, only in the case where light frame or timber frames are being built.
Since the booths will be on the ground, which is susceptible to seasonal deformations, then the non-burying of the string foundation is liable to form a structure that will independently redistribute the importance depending on the stage of deformation of the ground.
The strech foundation is made up of the following structural elements:
- Preparations and planning Maidanchik;
- Outer wall;
- Base;
- Vimoshchennya;
- waterproofing ball;
- It's pure fraud.
The technology for laying a strip foundation comes down to the implementation of a robotic complex - cutting a trench, leveling the bottom, pouring concrete, and reinforcing. The width and depth of the foundation are determined by the type of soil, the depth of freezing of the soil, and also the mass of the foundation.

Scheme of lashing of crushed mortared stitch foundation with pavement
Vidi
As a rule, a gravelly-stitched foundation is embedded in a frame or wooden building. Fakhіvtsі vykoristovat yogo for the creation of booths, which lie up to the II and III categories of performance in accordance with GOST 27751-88. The popularity of such foundations is determined not only by their high production value, but also by their pleasant performance. Below we will look at the different types of crushed strand foundations.
Monolithic grillage
The monolithic string grillage is laid directly on the ground, which prevents the influx of additional forces that occur during seasonal heaving of soils. The effect of vertically direct forces that cause seasonal heaving of soils is mitigated by a horizontally reinforced monolithic contour, which prevents the appearance of deformation.
Before laying such a foundation, prepare a base that is made up of several balls of hardened sand or other non-heavy soil that is not susceptible to deformation due to moisture and freezing. The use of sand of medium and high grain size for coating the base of the foundation is prescribed by GOST 8736-93. If there is an unburied foundation, the sand can be replaced with vicoristan gravel-packed or gravel-pebble sum, as well as blast furnace slag, the thickness of the cushion must be no less than 0.2 m.

A monolithic grillage is ideally suited for constructing small frames from wooden beams, including logs and frames built on the principle of frame-panel construction. A monolithic grillage can also be used in everyday use of summer kitchens, gazebos, terraces, summer garages, walkways, buttresses, state-owned units, capital canopies, etc. A monolithic grillage is an economical and practical option for fixing the foundation.
Depending on the type of building, the grillage can have the following dimensions:
- 200Х300 mm - fits for light frames;
- 300Х400 mm – suitable for light frames made of wooden materials, which do not exceed 200 mm;
- 400Х500 mm – suitable for lightweight wooden materials, which do not exceed 300 mm.
Prefabricated-monolithic stitch construction series 20
The treatment of any monolithic strip foundation made of reinforced concrete consists of several stages. The depth of laying the prefabricated-monolithic foundation should be approximately 0.4 m. So, as well as the monolithic grillage, it should be laid on a soft pad, the depth of which should be 0.2 m.
Pour a reinforced monolithic stitch onto the prepared base in such a way that its surface is on the same level as the surface of the ground. Such a device minimizes the influx of additional forces onto the structure that are generated through seasonal heaving of soils.
The base part of the foundation, raised above the ground, is to be molded from ready-made concrete blocks with a weight of about 30-40 kg and a size of 200x200x400 mm. This design is also advantageous because it makes it possible to divide the finishing of the foundation into two stages (monolithic and block parts), and therefore allows you to separate financial expenses over time.
The prefabricated monolithic stitch foundation of the 20 series is distinguished by its constructiveness and economy, as a rule, it is constructed in the following dimensions:
- 20X60 cm (with 20 cm rims and 40 cm bulges of the base) – suitable for light frame-panel type spores – toilets, lounges, summer kitchens, terraces, garages, greenhouses, etc. A foundation of this size is often stagnant as a base for supporting walls, fencing, zoning of the territory, and the installation of landscape design elements (kitchen beds, front gardens, flower beds, gazebos)
- 20X40 cm and 30X40 cm - suitable for light frame-panel booths, as well as booths made from timber and logs.
- 40x60 cm – suitable for living rooms with an attic and for cutting logs.
Monolithic base of stitch foundation series 20
The depth of laying such a foundation is within 0.4 m; it is laid on a similar, well-structured foundation. When it is wetted, the installation of a frame made of steel reinforcement is completed, after which a monolithic foundation line is laid at a 0.2 m depth to the ground. The result is a simple reinforced concrete structure with a thin and rigid horizontally oriented frame.
A non-buried foundation of this type will provide sufficient support for soil deformations, which means that in the cold season it is possible to smoothly transfer stress and damage. Such a foundation meets the greatest demands of private households with single-surface booths and booths with an attic with a series of wooden decks and beams. In this case, by widening the stitch itself, it is possible to have important booths equipped with pediments.
If you immediately increase the width of the stitch and the base, you can completely change the freezing of the soil in the basement. The monolithic stitch foundation of the 20 series is characterized by versatility and cost-effectiveness.
The most widely respected dimensions are:
- 20X50 cm – for light gospodar’s sporudas;
- 30x60 cm – for light budinki;
- 40X70 cm – for sporades with decks and beams with girders up to 300 mm;
- 50x70 cm – for frames with massive logs and beams.
Precast-monolithic stitch foundation series 60
A similar look to the prefabricated monolithic foundation is available in dimensions: 20x100 cm; 20X40 cm and 30X60 cm; 40x100 cm. The depth of the filling is increased - up to 0.8 m. In this case, the thickness of the cushion does not change - it becomes 0.2 m. Monolithic reinforced concrete line is poured into the trench from the bottom prepared base on a clay depth of approximately 0.6 m. The above-ground part of the basement, which is missing, is covered with ready-made concrete blocks measuring 20x20x40 cm.
The underground part of such a structure has greater rigidity, which is within the range of its massiveness. To better counteract the forces that arise during seasonal heaving, it is advisable to cover the walls of the trench with hydroisol. Similar design features to the foundation of the water supply system connected to the structure and the insulation of the foundation itself allow not only to reduce but also to completely eliminate the frozen ground under the base.
Prefabricated-monolithic cross-stitch foundations are built with single-surface frames, frames with an attic with decks or beams, frame-panel frames placed on plots with a slope of more than 5 degrees. The structure, similar to the foundation of the 20 series, provides advantages in terms of the division of financial investments into concrete and block parts.
Monolithic base series 60
This type of unburdened stitch foundation, as seen in the front section, is laid at a depth of not less than 0.8 m on a standard reinforced cushion of 0.2 m. A single monolithic reinforced stitch, the depth of which is varied become close to 0.6 m. Tsokolna Part of such a foundation should be about 0.5 m. For light standard ones, you can use a size of 20x60 cm.
Monolithic concrete stitching is characterized by reliability, durability and resistance to seasonal changes in soil. When controlling the water supply system and insulation of the soil and foundation, you can completely turn off the risk of soil freezing in the area of the foundation stitch.
A similar design is assembled when 1-2 surface booths are assembled from wooden beams and decks, including those with pediments. The possibility of keeping important double overhead booths can be reached through the extension frame. In this case, the level of freezing of the foundation base decreases due to the advances in the thickness of the base and the installation of insulation and water supply.
Monolithic settlements and non-buried foundation
This type of monolithic stitch foundation is characterized by a reinforced structure, which allows the flat support of the sole to be reached. Obviously, with the increased area, the building strength of the reinforced stitch foundation is moving faster. Installation work involves high labor and complexity, which leads to a high increase in price, leveled with the installation of a standard stitch-drilled foundation.
The dimensions of the reinforced monolithic base can be as follows:
- Base part 20x30 cm, bottom part 40x20 cm;
- Base part 40x30 cm, bottom part 60x20 cm;
- The base part is 40x50 cm, the bottom part is 80x20 cm.
The reinforcement of the reinforced monolithic stitch foundation is covered with 7-8 threads, which ensures sufficient rigidity of the structure. When the steel reinforcement frame is poured with concrete, the frame is converted into a concrete reinforced concrete frame, which is properly lowered and completely neutralizes the influx of additional forces directly onto the base of the foundation.
The operation of such a foundation can be matched to the characteristics of a floating slab, which will ensure a high level of resistance to the spores placed on it. In certain situations, it may be recommended to pour not just a reinforced monolithic foundation, but a whole slab.
Reinforcements of the type of unburied strech foundation are usually formed when the buildings are erected on important water-saturated soils in the form of clay and loam. With a reinforced monolithic string foundation, you can freeze it and create a hut on a slope at any time.
This design essentially reduces the pressure on the soil, changing the force that is created when the soil is heaved, not just on the base, but on the entire surface of the soil. On a reinforced monolithic foundation, it is possible to build massive single- and double-overhead buildings from logs and wooden beams of large cross-section, and with a significantly expanded line, you can build buildings from the target and blocks, leaving the building of the foundation significantly damaged moves on an increasingly flat base.
Hydration and shortcomings
Before we finally get involved in the installation of a crushed-edged stitch foundation and proceed to its construction, we must not be aware of the advantages and disadvantages of such a foundation. There are not a lot of shortcomings - there are only two, but they are even more significant.
First of all, unburied string foundations are effective when building booths on plots with soils that are slightly heaped, with a low level of groundwater. If you don’t lose your mind, you should give priority to the foundation of the finger type.
It is logical that such a structure, at the highest stage of reinforcement, cannot clearly withstand the ground, which rises unevenly, which, in error, will inevitably lead to deformation of the base and the structure itself.
Another shortcoming lies in the fact that such foundations can only be supported by lightweight structures, and the possibility of constructing solid and block buildings is achieved only by strengthening the foundation, and also by the absence of heaving soils .
Then the burden of crushing and embedding of the strech foundation is much greater:
- The financial economics of leveling with similar buried foundations, the value of which is twice as high, is significant;
- The technology of the construction is simple, durable and easy to use on any type of soil, including water-saturated, dry and heaving soils;
- To varnish a sanded-stitch foundation, no special equipment is required;
- Small little buildings house a great stock of non-existent items;
- The lowering of the front works, leveled with foundations of the buried type, which can be reached for the lowering of the earthen work and simple installation of formwork;
- The hour of washing of a sanded foundation is much lower than that of a buried one, which makes it possible to shorten the period of life.
It can be said that by treating the crushed slab foundation, it is possible to practically neutralize the negative effect of seasonally heaving soils, change the terms of the construction of the object, and reduce the financial costs of the project. with less labor and waste of materials.
The non-buried strech foundation is raised from the ground to the ground level so that its base is not buried near the zero mark. This technology for plating the foundation allows for a significant speed of operation and protects materials. The whole complex of robots can be removed from self-tightening.
Non-buried foundations (stitch, joint, slab) are suitable for building small foundations made of light materials - timber, foam concrete blocks, etc. Before us, the stench will be detected in everyday life of the ruler's apartments, garages, and country houses.
It is not recommended to place a cabin for permanent living on an unburdened base, since the foundation does not show any signs of damage, since the load bearing capacity of the ground is not high enough. The culprit is the rocky soils - the stench can permeate the entire huts on an unburied foundation.
Construction
A layer of unburied foundation can be poured so that the soil does not reach the floating or heaving surfaces. Under the reinforced concrete stitch, first cover the cushion - it should be 20-40 cm. The monolithic stitch must pass under all the walls (external and internal) and the frame of the supports , including a veranda, ganok, etc.
This type of foundation is allowed to rise, as long as the depth of the wall does not exceed 7 meters. The length of the stitch is thin until it collapses due to uneven shrinkage. This is due to the lack of mechanical value.

An unburied foundation is undermined by a fragmented foundation so that soil, which is susceptible to destruction, does not flow onto its walls. The forces of frost heaving only flow in a small amount onto the base of the specially coated cushion.
The structure of this foundation looks like this:
- Stitch made of reinforced concrete. Height – 20-50 cm, width – 30-50 cm.
- Pillow made of materials that are not too scratchy. Sand, gravel, crushed stone, and slag are allowed to settle. The best option is a mixture of sand (60%) and gravel (40%). Gravel can be replaced with slag or crushed stone.
The choice of the height of the pillow depends on the strength of the soil before swelling, on the depth of contamination of ground water, on the choice of materials from which the work will take place. The more strongly the soil bulges, the more important the structure is, the thicker and wider the cushion is. Its width may exceed the width of the foundation stitch by 1.5-2 times.
The power of the soil-gravel cushion to extinguish heaving on the base of the foundation is reduced when laid with subsequent freezing. To ensure that the moisture does not penetrate into the pillow from the outer side of the line, it is necessary to treat the pavement with a hydroisolated base and thermal insulation.

Preparation work before pouring the foundation
By creating an unburdened line foundation with your own hands, we first begin preparing the plot chosen for everyday life. It is necessary to remove the ball of rich soil and level the surface. Then the layout is completed with the project.
According to the plan, it is necessary to dig a trench, which must pass under the walls of the building. The width and depth of the trench must correspond to the design parameters of the foundation cushion. The soil and gravel mixture begins to dry up near the trench and is compacted firmly. If the pillow is compacted correctly, a person from the middle stage can walk along it without leaving any traces.
The offensive stage is the installation of formwork. You must mount everything completely, at the same height as the foundation, so that the string is monolithic. Cold seams sharply reduce the strength of the unsealed base, which is not necessary, but it is already small.
The walls of the formwork are tightly pressed together, otherwise, when poured, the structure is deformed. The trace of creaking is especially clear - they receive maximum attention. The gaps between the formwork boards must be properly caulked so that the cement “milk” does not leak out - this will reduce the value of concrete.

Armuvannya
To build a metal frame, it is recommended to use reinforcement bars with a diameter of 14 mm or larger. The distance from the reinforcement frame to the walls, the upper level of the formwork and to the floor cushion may become no less than 5-7 mm. A concrete ball of this type will protect the reinforcement from corrosion.
The length of fastening of the reinforcement frame to the supports is 70-80 cm. The sticks should be welded carefully, so that the fragments will change the value of the reinforcement strips. For fastening, it is recommended to use knitting threads or plastic clamps.
A correctly installed frame will have sagging horizontal elements, and the building itself will stand against the concrete without shifting or deforming.
Zalivannya
When laying out the foundation without filling it with your own hands, it is especially important to carefully add the fill. We first determine the height of the stitch. Since the height of the formwork is consistent with the design height of the foundation, additional entries are not required.

If the edges of the formwork are higher than the required level, carry out alignment and tighten the cords at the required height, first checking their horizontality and positioning them against the reinforcement frame. Fill the filling, focusing on these cords.
To fill, it is recommended to soak the mixer with concrete - this will allow you to fill the entire line without interruption. It is important to pour the fill in several places, and not from one place - this will save the mixture in the middle of the formwork.
Concrete is leveled along control cords or the upper section of the formwork, and then empty pieces are removed, for which a vibrator or reinforcing rod is used, which will pierce the material thoroughly throughout the entire volume of the formwork. The “tapping” method is also used - for which you hit the formwork panels with a hammer in many places, so that the vibration stirs up the winding bulbs to rise to the surface.
You can prepare a concrete mixer yourself, a concrete mixer with an electric drive, or a mobile concrete mixer with an electric drive. In this case, it is important to maintain the proportion of water, cement and filling when preparing the mixture and not to take long breaks when filling the lines in parts.

After drying, cover the concrete with melting material so that it does not waste moisture, which is required for the complete melting of the cement storage and collection of materials. On the sintered surface of the concrete strip, the traces are periodically sanded.
If the concrete gains strength, the formwork can be removed and construction can begin before the construction of the building, having first completed the waterproofing of the foundation.
Other types of unburied foundations
Prefabricated unburied foundation. The structure is assembled from foundation and building blocks. The pillow for stitching is prepared using standard technology after planning and laying out the plot.
The blocks are placed side by side one by one, aligned, and the horizontality of the stitch that came out is checked using a daily level. The blocks need to be tightly clamped together; cement cracking is likely to occur. When the blocks are assembled with metal embedded parts, welding is used for fastening.

Non-burdening of foundation parts. This basis is suitable for creating climbing frames, shield towers and garden towers on slightly heaving soils. The supports will be placed along the corners and under the edges of all possible door slots, as well as under all walls with a border of approximately 2 meters.
How short supports are discussed:
- foundation blocks;
- wall blocks;
- monolithic structures;
- structures, laying on wall structures (it is not possible to use silicate or ceramic materials with low frost resistance).
On the workpiece prepared before work, make a mark and dig holes under the skin support for sanding the gravel cushion. When installing the supports, it is important to stitch so that all elements of the foundation base are laid out strictly according to the markings, so that the horizontal surfaces form a single surface.
The monolithic, non-buried base is suitable for building light structures on highly heaving and low-subsidence soils. So that the monolithic slab does not “float” for changes in climate change minds, it is to blame for the mother’s high cruelty in the world. This is achieved by reinforced reinforcements and durable construction.

At the site, it is necessary to prepare a pit for the cushion from coarse sand with gravel or crushed stone. For this purpose, the soil is placed at the designed depth (not less than 30 cm), and the base is leveled. The sanded gravel needs to be compacted firmly. Next, the formwork is installed, the reinforcement cage is attached, and the concrete pot is poured.
Unburied foundations, first of all, are gaining popularity in individual everyday life due to the low complexity of the work and the quality of the materials.
The minimum budget of the building requires a non-burdening of the stitch foundation for trench, timber and frame structures. Vimogi SP 22.13330 for the foundations of sporuses and budivel allow any level of destruction for the mind to ensure neutralization of the forces of frost heaving.
Non-sinking stitch foundation (NSLF) comes in two types: monolithic belt and classic stitch. The width lies across the foundation - at the waist the width of the sole is greater than the height, at the waist it is smaller.
The assertion of the “fakhivts” of the budgetary companies that the unbroken lines of the NZLF stagnation is inclusive for the lungs of the industry, is not true. The standards TSN 50-303 (territorial), VSN 29-85 (domchi) specify the development technology and consistency of solid, gas-, foam-concrete boxes on heaving soils at NZLF. What can we say about sufficient reliability, but it is important to correctly design such a foundation. Without unraveling, the stitch on the surface of the plot can be done on high-grade or rocky soil.
Geology and development
Professional investigations are rarely completed by individual forgetters. For example, if you build frame booths at the NZLF with your own hands, the property of the geology of the plot (30 thousand rubles) will push the budget of the zero cycle twice.

Therefore, visual assessment of the soil storage is most often used. Statistics confirm that a linear meter of low-surface waste accumulates 15 – 20 tons (double-top cottages), 4 – 12 tons (single-surface, attic, sub-surface). Therefore, when swelling occurs and it is impossible to balance one another, deformations arise.
The growth of deformation due to heaving forces is observed inclusively in MZLF, NZLF. Uneven rise of the stitch is allowed, but it is due to less than the limit values that lie within the structure. Consider the rigidity of the walls and the foundation, which can be seen in the buildings as a single system. Regardless of the degree of destruction, for NZLF the standard defracture technology is used. For this you need to know the following data:
- rozrahunkovy support to the ground - take from the witness U.Z. Sazhin and SP 22.13330 for the results of visual self-tightening;
- collection of furniture – power structures, wind/snow protection, furniture, bags;
- rhubarb UGV – contributes to the water content of soils near the forgetting area;
- freezing icon – take the table for a specific region.
To store the soil, make sure to grab a cord or bags. Clay can be pumped to a minimum diameter, but it is even more difficult to produce in sandy loam. The loam periodically breaks down, becomes pulped, and cracks to the hands.
To calculate the width of the foundation, it is necessary to bring the units of all the characteristics to be calculated into a single form (kg, cm). Then divide the collection of vantage into a diversified support of the ground, the bottom of the perimeter of the NZLF.
- drainage of soils under the soil - the presence of water cannot be drained into clean clay;
- saving geothermal heat - the ground under the sole (behind the hanging grillage) is not frozen, if the pavement is insulated to a width of 60 cm, the cold cannot penetrate under the sides;
- replacement of soil - inert quarry materials do not wash the clay house, so when replacing the support ball (40 - 60 cm) with ASG, crushed stone, sand, the heaving is reduced.
Drainage for an unburied stitch foundation rarely stagnates (at a high groundwater level), and grout is poured into the perimeter of the pavement.
Layout and earthling robots
The established rules of practice SP 126.13330 (geodesy) indicate the value of losses (1 div) when real axes are inserted. At the marking stage, it is important to integrate the booth with the plot for maximum comfortable operation. For example, when parking the road parts, rely on the following engineering systems:
- wells for connection to centralized village communications;
- septic tanks of autonomous water supply systems that require periodic pumping;
- LEP stops for introducing electrics throughout the building.

The trenches run under all the walls, which must be carried, the depth is 40 cm or more, the soil ball is responsible for seeing damage everywhere.
These objects cannot be built closer than 3-4 m above the foundation. Along the cordons of plots, driveways, and roads, the line may be 3 to 5 m horizontally. The marking is carried out in stages:
- street wall - the front façade, parallel to the other part;
- The side walls are perpendicular to the anterior axis, they are formed using the straight-cut method with legs 4 m, 3 m, hypotenuse 5 m;
- Variation of diagonals - the cuts will be reduced to 1 cm.
The sides of the back wall come out automatically; for the skin side of the foundation, three strings/cords are stretched. All that is needed to control the geometry of the cottage, the beam cords allow you to install the formwork.
According to the design of the technology, the base of the bottom-on-top fireball is removed from the entire perimeter of the booth or only from the trenches. For example, to lay a foundation on the soil in the middle of the ridge foundation, it will be necessary to prepare a reinforcement with non-metallic material. Robiti tse on top of the orb, rich in organic matter, is categorically fenced off. After only 4 – 6 years, the organic matter rots, causing it to sag.
When choosing a slab slab or beam structure, replace the ball with inert material in the trenches under the base of the foundation.
Soft, gravel lining
Professional designers rely on inert materials as a foundation cushion. Among individual writers, the popular method is 20 cm sand + 20 cm crushed stone, although in the current literature the choice of non-metallic material is not standardized. Fahivtsi recommend that when preparing the ball, which is placed on it, you should wrap the factors with your own hands:
- When wet, sand becomes a shapeless mass and quickly loses its structure;
- crushed stone retains its shape, value when completely submerged in water, and has different powers;
- On the soft lining it is easy to attach a roll of waterproofing, the integrity of which is guaranteed to be preserved throughout the entire operational period;
- To ensure that the rolled waterproofing does not break the guest stones, you will have to pour 3 - 5 cm of concrete over the crushed stone;

A cushion is placed near the trench, with a ball-shaped vibration reinforcement. The trench will be filled to the brim. The pillow can be combined - 20 cm sand + 20 cm crushed stone.
The geotextile lining precedes the mixing of the inert material with the soil and the mulching with groundwater.
Formwork
For non-buried strip foundations, the formwork is very simple to prepare. Here is a list of popular options:
- polystyrene L-like modules – insulation of the side edges, similar to the angle grinder plate;
- board shape – for panels it is necessary to choose less than 3 cm lumber;
- plywood - 10 - 12 balls, then from it you can make a special lattice roof;
- oriented strand board - re-stuffed after removal of formwork in partitions and roofing.

The formwork is reinforced with bonded bevels, and after laying the reinforced frame, it is additionally secured on top with planks. You can further tighten the shields with a dart by drilling an opening in the shields and passing the dart through them.
There are no special considerations for stitching on heaving soils in the formwork. Fahivtsi do not recommend removing the opening from the NZLF lines to weaken the structure. However, when choosing a bottom subfloor on top of the joists, the slab in the lower part is deprived of a small subfloor. If you do not create ventilation in the new building, evaporation of water from the soil in three days will lead to unusability of the chipped wood. Therefore, there will be required openings, the area of which is 1/400 of the size of the surface of the base part.
Armuvannya and flooding
On non-buried line foundations, the same standards SP 63.13330 for concrete structures apply. Through small areas of the entrance to high-rise low-surface cottages, two reinforced belts with 8 - 14 mm of late shears are installed with periodic cutting.

Return respect to those who reinforce the cut.
To give them a spacious shape, clamps from round 6 - 8 mm rectangular fittings are assembled. The dry ball of the lower part is secured with concrete and polymer spacers, on which the first ball is placed. The main vimogs are:
- the presence of sticks in the joints and corners - the rods bend, go to the present side, stick on it;
- overlap of 40 diameters - with a spread in the rows of 60 diameters.

The reinforcements, just like they are, are reinforced not just like that, but with anchors.
For welded mesh, it is necessary to install support fittings with letter C in the marking (for example, A400C).

The reinforcement can be tied to the foundation, and then lowered into the formwork, which makes it easier for the robot.
Regardless of the small work involved, concrete pouring is guaranteed to be carried out in one step. The formwork will be completely filled, and will be laid in one straight line along the ring. After that, you need to tighten it with a clay vibrator for a few seconds. The strength of the brush is strengthened to ensure the smoothness of the mirror of the concrete when pressed with a tool, cement laitance and the presence of bulbs on the surface.

Before pouring, it is necessary to carry out strengthening with a vibrator or plastering. After pouring the concrete, it is necessary to water it with water several times as much as possible, covering it with spit, burlap or thyrso.
The non-buried foundation in most of the fallouts has a lattice structure with beam beams at intervals of 60 x 60 cm. This makes it easier to protect concrete structures that are in contact with the ground and water. Traditional technologies will be used:
- volumetric waterproofing – warehouses with water bodies that can be penetrated, to change the molecular structure of concrete (water spray water throughout the entire depth);
- adhesive waterproofing – rolled material (Bikrost, Technonikol) on a polymer or woven fabric base with a bitumen ball;
- Coating waterproofing – carried out with bituminous and epoxy mastics.

Waterproofing is applied in two or three balls (bitumen mastic), so don’t forget to lay horizontal waterproofing on top of the foundation, first you will begin to protect the walls.
When using Penetron, the waterproofing removes permanent waterproofing, the term of which is preserved until the concrete is completely damaged. Gluing is most effective after priming with primers and coating the surface of the stitch.
Particularities on heaving soils
The current living standards for low-surface soil VSN 29-85 provide recommendations for living on heaving soils. The main vimogs are:
- if the intensity of heaving is more than 0.05, one of the necessary monolithic foundations or a prefabricated stitch with tightly pressed beams in the middle of the structure
- In case of frames, the rigidity of the walls should be increased, which will reduce the deformation of the stitch
- the pillow is made from crushed stone, great sand or PGS from crushed stone instead of 60%
- when collecting stitches on medium heaving soils, the blocks are laid on 10 - 20 cm reinforced concrete, secured with a standard reinforced belt 20 - 40 cm in height
VSN 29-85 has indications for the design of non-buried foundations depending on the wall material and the technology of building the core box. For example, log, SIP panels, panel, half-timbered, frame booths can be supported on extremely heaving soils on:
- monolith;
- solid connection of reinforced blocks.
Since the soils are moderately heaving, it is allowed to lay blocks in rows in rows between 2 m beams 25 x 20 cm with reinforcement in the middle. For foam and aerated concrete blocks, solid masonry, you can best:
- highly heaving soil - armored belts on the level of the mauerlat, between the surface slabs, above the door and window openings + monolithic stitching;
- medium heaving soil - blocks are laid between an armored belt and a concrete base for rigid fixation.
The technology for keeping a straight line on heaving soils looks like this:
- trenches to a depth of 40 – 60 cm;
- ball filling of 20 cm with crushed stone, ASG, sand on geotextiles, laying on the bottom of the trench with the edges running on the walls, strengthened with a Maidan vibrator;
- installation of formwork; placement of the reinforcement frame;
- Concreting, pouring the material that gains value, in the first three days.
Removal of formwork for waterproofing is possible at 50% stitching rate, which in the end is equal to two levels. The maximum term for removing formwork is 27 degrees at a temperature of + 5 degrees.
In this way, a non-buried foundation is ideal for any kind of soil or wall materials. It allows you to reduce labor and costs by 40%, the budget for everyday life is reduced by 60% due to the sewn line. It is impossible to remove the underground memory book, but the one under the room can be present in the project for a low ground level.
Please! If you need contractors, there is a very handy service from their selection. Simply fill out the form below with a description of the work you need to sign up for and you will receive offers by mail with prices based on labor teams and companies. You can look at the videos about their skin and photos with butts. It's COST-FREE and doesn't bother you at all.