Currant disease. Diseases currant photo
Among the common shrubs in the gardens you can find different types of currants. Distinguish: black, red and white variety of berries, as well as golden currants, species that got its name from the color of flowers.
These berry bushes attract gardeners with a beautiful appearance, and most importantly the usefulness of the fruits of which you can cook delicious jam, fruit compote, jelly.
Leaves, especially black currants have a pleasant fragrant smell. These shrubs tolerate various weather conditions well, but at the same time are prone to many diseases, which need to be able to distinguish and take action in a timely manner, otherwise you can lose the harvest.
Currant diseases can spread to all species, but there are also those that are inherent in any particular type. Therefore, already with the onset of spring, it is necessary to inspect the plants in order not to miss the changes taking place.
Currant diseases and their treatment, photo
Very often, the cause of all diseases of currants becomes a fungus. It is not easy to get rid of him. Basically, it begins to spread under favorable conditions for it - high humidity.
Common diseases of currant are: anthracnose, Terry, rust and others.
Currant anthracnose, treatment
This disease is caused by a fungus. It appears in the summer, it can be recognized by the red spots on the leaves, sometimes brown, in the center of which there are dark hillocks. Over time, the spots cover the area of the whole leaf, they dry and fall.

All kinds of currants can become infected with this disease, but red is more susceptible. Especially the disease is actively spreading when the weather is wet and rainy. Spores of the fungus are so adapted to different conditions that they tolerate winter frosts well.
When a disease is detected, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment. For this recommended Bordeaux mixture. It is mixed with water by adding 100 grams of the drug to a bucket of water. Spray currants immediately after the detection of the disease and the second time in the fall, after the harvest of berries.
It is necessary to observe preventive measures, they include:
- the collection of fallen leaves and its burning;
- do not plant new plants in the places where the bushes of diseased currants used to grow, without having previously treated the soil.
Currant Rust Control Measures
A common disease of currant is rust. It occurs in two species, at any time of the season.
One of them is the glass rust. It can be recognized by the convex tubercles of orange color, in the form of warts.

Glass rust on currants, control measures
The sedge and conifers, which can grow nearby, are considered the carriers of this disease.
Treatment should be carried out Bordeaux mixture, taken 1 tsp. 8 liter bucket. Handle up to 4 times every 10 days.
Pillar rust on currants, control measures
Another type is columnar rust, it is formed in the form of an orange deposit on the inside of the sheet.

Vector columnar rust often become coniferous trees. Fitosporin is used for treatment, it is necessary to follow exactly according to the instructions.
Mealy dew on currants
One of the rare diseases of currants is powdery mildew. The causative agent of the disease is considered a variety of marsupial fungus.
It can be easily recognized by white bloom, which initially covers the young leaves, but gradually it extends to the berries.

This disease is well treatable. Currant bushes can be processed, following the instructions, Fitosporin, Baktofit.
Effective in the fight against marsupial fungus - iodine. A bottle of iodine is taken and added to 10 liters of water. Then spray about 3-4 times twice a week. If the result is not noticeable, it is recommended to apply copper sulfate. For this, take 1 tsp. powder and added to 8 l. bucket with water.
For the prevention of the disease, it is necessary to take care of the bushes - cut off old branches, remove fallen leaves, make timely feeding.
Striped mosaic, photo
When the appearance of yellowness on the leaves among the summer, which mainly pass along their veins, is detected, it means that currant bushes were infected with a striped mosaic virus.

Unfortunately, these bushes will have to be completely removed and burned, it is impossible to cure currants. It is not recommended even to cut off or shake off infected bushes, because during subsequent work there is a chance to infect other plants on the site due to the sap remaining on the blade and hands.
After it is desirable to cultivate the land with 1% solution of potassium permanganate, watering the area with a watering can.
Diseases of black currant and their treatment, photo
Along with common diseases, there are still those that infect only black currants, and other species in very rare cases.
Currant Curling and Fighting
One of the common diseases of black currant, is considered - terry. The causative agent of the disease is a kidney tick.
With the spread of the disease, the fruiting of the currant is largely reduced and its gradual degeneration is observed. Terryness is distinguished by appearing signs:
- reduced number of veins on the leaves;
- altered, blue-violet color of inflorescences;
- elongated buds, with short petals on peduncles;
- lack of specific flavor of currants.

This disease is most noticeably manifested in the spring, when the currant begins to bloom, the flowers of the diseased plant immediately catch the eye.
A feature of the treatment of the disease is that it is useless to treat diseased currant bushes with special preparations, since the causative agent of the disease is contained in the sap of the plant. Therefore, currants will have to be eliminated to prevent infection of healthy plants. Even if the disease is visible only on a few shoots, it is necessary to uproot the entire shrub and burn it entirely.
Planting new seedlings, you must comply with preventive measures. These include:
- planting only healthy plants;
- regular fertilizing of complex fertilizers;
- no abuse of nitrogen fertilizers;
- treatment with karbofos, strictly following the instructions.
Red currant disease and their treatment photo
A distinctive disease of red currant is the non-stray drying of young parts of the stem. The causative agent is considered - marsupial fungus.
This disease is diagnosed by orange circles on the stem, they gradually grow and resemble a voluminous appearance, when the spores mature, they turn black. Young shoots gradually dry and die. It is very important to notice the disease in time.

The measure of the struggle is pruning the affected branches and their subsequent burning. Places pruning need to be sanitized Bordeaux mixture, and then garden pitch.
When carrying out preventive measures, this disease can be avoided. These include:
- fertilization, in the form of fertilizers;
- weed removal;
- burning autumn leaves fallen.
When conducting the proper farming practices, the disease will not occur.
Diseases of white currant and fight with them photo
Very often, diseases of red white currant are the same; septoriosis belongs to such a disease.
This disease mainly occurs when adverse growth conditions occur, and they include:
- high humidity;
- growing in the shade;
- density of planting bushes.
The causative agent is considered a fungus of the genus Septoria. The disease is diagnosed by the brownish spots that appeared at the beginning, which after some time become white with brown edges.

The treatment is the treatment of bushes Bordeaux mixture, all diseased leaves are recommended to remove and burn. Preventive measures of the disease is considered - this is the burning of fallen leaves, thinning plants, digging the soil around the bushes. It is advisable to plant young plants in a well-lit area.
About less known, but no less remarkable form - golden currant and diseases to which it is subject can be read in the article:.
Unfortunately, currants are prone to disease and treatment in some cases is impossible, the photo will help to recognize the signs of the disease. But to avoid trouble, and not to destroy individual bushes, it is necessary to observe preventive measures.
Given that photos of various diseases of currants are available in any literature describing the intricacies of growing this crop, many avid gardeners can identify an existing disease, even by minor symptoms. The following diseases of red currant are the most common:
- powdery mildew;
- anthracnose;
- rusty septoria;
- white septoria;
- marhovost;
- sphere library
American powdery mildew is an extremely common fungal disease capable of infecting shoots, leaves, and even currant fruits, forming a spider or mealy plaque on them. Leaves and shoots damaged by this fungal disease stop growing and die.
Another common disease of red currant is anthracnosewhich develops at high humidity and affects mainly the leaves, forming on them characteristic brown spots. Later on, black spots and lacquered bumps appear on these spots, which contain spores of the fungus. If your red currant has similar symptoms, diseases of fungal etiology should be treated with special chemicals.
Septoria is a fungal disease that occurs almost everywhere where they grow red currants in large volumes. With rusty septoria, the appearance of characteristic bright orange cones on currant leaves are observed, but with a strong infection, such tumors can appear on shoots and berries. In white septoria, the appearance of grayish cones bordered by a brown border occurs. Further on such cones, black specks of spores are formed, and the pathogenic fungus begins to multiply. In any photo, similar pathological changes of the leaves against the background of their fungal infection are very noticeable.
Features of growing red currant (video)
Signs of defeat currant fungal diseases may be noticeable in early spring. Even before blooming buds, it is necessary to carefully harvest all the fallen leaves under the currant, which were not harvested in advance in the autumn, and also treat the plant shoots with Nitrafen solution at the rate of 30 g per 10 l of water. The soil around the plant can be treated with the same solution. If the signs of fungal lesions were detected after the beginning of flowering, then you should wait for its completion and process the leaves and stems of plants with 1% boric acid.
In addition, soda ash, ammonium nitrate and mullein infusion are excellent means for powdery mildew, but red currants can be treated with such agents only after it has faded. Processing should be carried out every 10 days, so that fungal diseases of currants do not return.
The most dangerous viral diseases that can affect red currants terry. This disease can affect absolutely all parts of plants. In the bush, affected by terry, there is the appearance of three-lobed leaves instead of five-lobed ones, and the cloves at the edges of the leaves become smaller. In addition, there are genetic abnormalities in the formation of flowers, sepals and stamens, so the crop, as a rule, is not observed on plants strongly affected by this virus.
Given the viral nature of this disease of currant, there are no good chemical agents that can completely eliminate terry, so the treatment of this disease is very difficult. In autumn it is recommended to prune the bushes and remove all the leaves that have fallen from the affected plants in order to prevent the spread of the disease.
How to remove red currant pests from the garden plot
Currant diseases are often tolerated by pests that can cause considerable damage to plants. The most common currant pests include:
- black currant;
- glass bowl;
- leaf louse;
- currant mole renal;
- gooseberry ovnevka;
- aphid shoot;
- spider mite;
- pale-footed sawfly;
- gooseberry moth.
In order to eliminate the currant goldfish in the fall, all shoots are cut and burned, since it is on them that the harmful larvae overwinter. The treatment of plants against common spider mites is carried out by treating currant bushes directly after flowering with a preparation such as a phyto farm, and after picking berries as a preventive measure, also with Malophos.
To eliminate the tick, plants can be sprayed with infusion of wormwood or tobacco throughout the season.
Red currant: protection from pests (video)
To prevent the plants from damaging the plants with currant moth bud, early spring treatment of swollen buds by Carbofos is carried out. If, however, traces of the gooseberry moth are found at the site, then Karbofos treatment is carried out after the flowering of the plants. Karbofos is actively used to remove various types of aphids from the currant bushes, but it is very important to spray not during the formation of flowers and berries.
In order not to lose the material, be sure to save it to yourself in the social network Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki, Facebook, simply by clicking on the button below:
Attention, only TODAY!
Red and black currants are on any garden plot. Unfortunately, these plants are often affected by various diseases. And today we consider the main diseases of currants, as well as methods of treatment of affected plants.
White leaf spot (septoria)
Symptoms: Fine brown spots are formed on the surface of the leaves, which then turn white. But the brown border remains. Such specks can cover and berries. With a strong defeat, the bushes start dropping foliage.
Treatment: Both the bush itself and the soil around it must be treated with nitrophene or copper sulfate solution. The treatment is carried out before the buds bloom, i.e. in early spring. You can also use the drug "Home" (40 grams per 10 liters).
During the summer period, treatment with 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid is allowed. The first time - before flowering, the second - after its completion, the third - 15 days after the second, the fourth - after harvesting the berries. Bordeaux liquid can be replaced with copper oxychloride solution.
American powdery mildew (sphere library)
Symptoms: All parts of the bush are affected. Manifestation of the disease in the beginning or in the middle of summer in the form of an easily removed white bloom. Gradually, it becomes more dense and visually begins to resemble brown felt. The affected shoots are bent, the leaves twist on them. The berries are not poured and fall.
Treatment: Removal of diseased branches. It is also necessary to treat the bush and the soil around it with a solution of ferrous sulfate (300 grams of the drug per 10 liters of water).
It is also effective to treat the plant with a fresh solution of bleach (2 spoons per 10 liters of water).
The next method is spraying a solution of soda ash (5 grams of soda and 50 grams of soap chips are added to 10 liters of water). The treatment is carried out with an interval of 10 days 3 times.
Treatment with any solution can be carried out from the moment it appears. white bloom with an interval of 10 days. Last spraying - two weeks before harvest.
Before flowering and after picking berries, currants can also be treated with sulfur, foundation, or Topaz.
Glass rust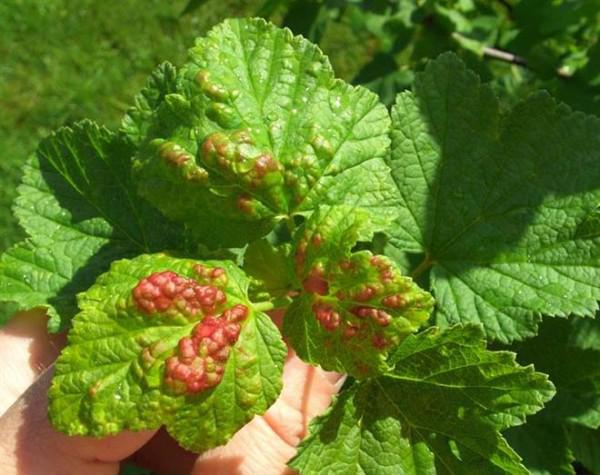
Symptoms: The leaves, flowers and ovaries are covered with rather large bumps of yellow color. It is in them that the fungus spores mature.
Treatment: It is recommended to treat 1% Bordeaux liquid. The first - when the leaves bloom, the second - when the buds appear, the third - immediately after the end of flowering. If the bush is struck too much, then carry out the fourth treatment (10 days after the last spraying). Currants can also be treated with phytosporin.
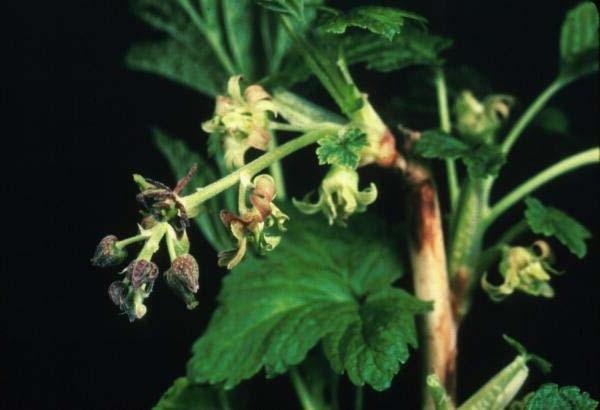

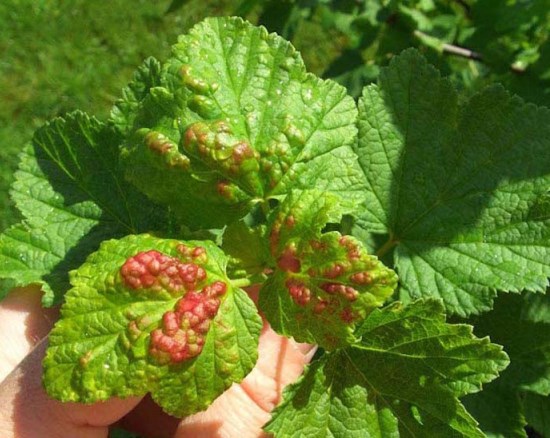
Symptoms: For diseased plants characterized by the appearance of barren flowers ugly form. Petals take an elongated shape and turn purple. With a strong defeat flower brush resembles a sprig with numerous scales. The foliage on new shoots also changes. The classical five-blade form is replaced by a three-blade, and the leaf streaks become very coarse. The leaves take on a dark green color and lose their characteristic currant odor.
Treatment: Terry is a viral disease, and therefore the plant is subject to destruction.

Symptoms: The affected plants begin to dry out and die off the branches. If you look at the affected escape, then on the lower part you can see the numerous tubercles of red-brown color. Then they turn black.
Treatment: Affected branches must be cut and burned.
Striped (streaky) mosaic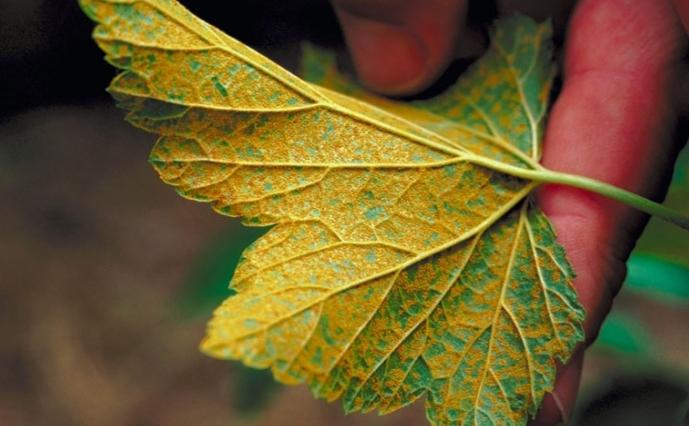
Symptoms: After blooming, a bright yellow pattern appears on the foliage, located around the main veins.
Treatment: Missing. Infected shrub to be destroyed.
Columnar rust
Symptoms: Both the upper and lower surface of the sheet are affected. Small yellow spots form from above, and characteristic growths resembling yellow hairs are formed on the lower part.
Treatment: It is necessary to carry out treatment with any fungicide. Not bad proved spraying 1% Bordeaux liquid. It is carried out three times: during the blooming of leaves, during budding, after the completion of flowering.
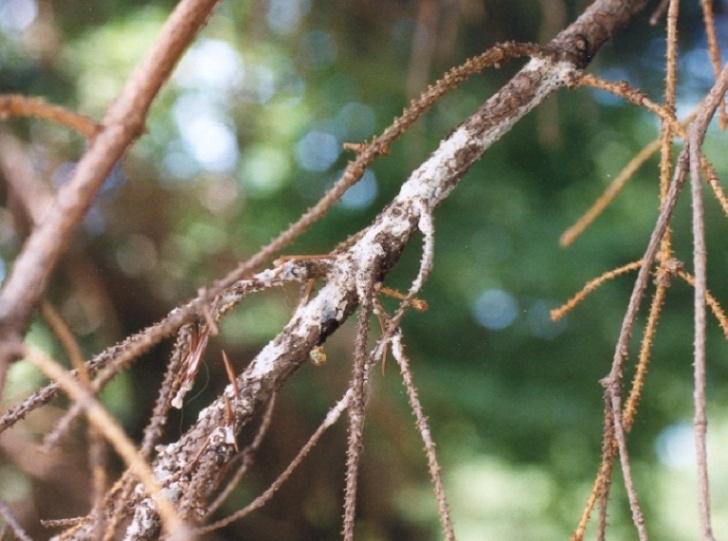

Symptoms: The bark on the branches loses its elasticity and begins to dry. Most often affected weakened bushes.
Treatment: Compliance with the rules of agricultural engineering. After the prophylactic pruning of the cut, it is necessary to gloss over the shear.
Anthracnose (fly sniper)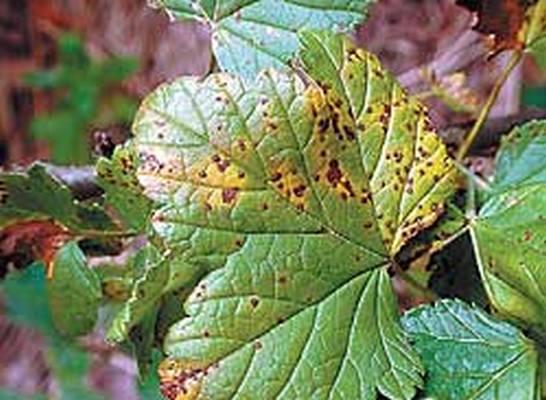
Symptoms: Small brown spots appear on the surface of the leaves. Then they begin to merge into a single spot, which causes the sheet to dry. Anthracnose also affects young shoots, stems and cuttings.
Treatment: Spraying with nitrofen should be carried out either before blooming or after the leaves fall. In the summer, you can use kuprozan or 1% colloidal sulfur. Spraying in this case is carried out before flowering, then upon completion. The third treatment is carried out 10 days after the second. And the last, fourth treatment, should be carried out after harvest. You can also use 1% Bordeaux liquid.
Prevention of currant diseases
The following agrotechnical measures can be attributed to preventive measures:
- Autumn digging the soil around the bush;
- destruction of fallen leaves or its incorporation into the soil;
- timely.
Disease prevention is also the acquisition of healthy planting material. It is best to buy seedlings in specialized stores.
Despite the fact that the taste of black and red currants is quite different, they belong to the same species and genus, and have similar diseases, and methods of dealing with them do not differ. Red currant pests are almost the same as black ones.
Diseases and control of red currant
Photo: Manifestation of fungal diseases of red currants on leaves.
The cause of diseases of the bushes of red currant, as well as black can become fungi. This plant suffers greatly from the disease of anthracnose and, to a much lesser extent, from powdery mildew. Only some varieties of red currant are exposed to this disease of red currant, for example, Varshevich, and even then it is subject to frequent rains. But septoria disease, a white spot caused by a fungus, often suffers from red currant bushes. The onset of red currant disease most often occurs in May. At the same time on the foliage of the plant appear spots of arbitrary configuration, bordered by a strip of drilling color. Over time, they turn white. In their middle you can see black dots - spores of the fungus. If during the time not to take appropriate measures to combat currant disease, then gradually the spots spread to the entire surface of the sheet, and it falls. The disease Septoria affects the berries of currants, which at the beginning of the disease are covered with small brown spots, as well as shoots. They are exposed to the fungus in the places of attachment to them of leaf stalks.
Diseases of the fungus are not terrible winter cold, it is easily tolerated, remaining in the fallen leaves and affected parts of the plant. White spot most often occurs with inadequate care of plantings and during prolonged rains. In addition to fungi, red currant diseases can be caused by various pests on red currants.
Red Currant's Disease - Terry

Photo: Disease manifestation of red currant leaf on the leaves
The pest is a kidney tick, which is a carrier of a pathogen that causes a red currant disease such as Terry. It manifests itself in the presence of a large number of shoots with leaves that differ in shape from the traditional ones. And instead of simple inflorescences of red currant, this disease contributes to the appearance of purple terry flowers.
In order to avoid the occurrence of the disease of red currant terry disease, it is necessary to purchase seedlings of this plant only from well-known producers, and preference should be given to varieties that are weakly affected by this ailment. Regular inspection of the red currant plantations will allow you to quickly identify a diseased bush, and stop the further spread of the disease.
Red currant disease - bacteriosis

Photo: Bacteriosis disease on red currant leaves
This disease of currant, which affects the seedlings of fruits and plants. When a disease occurs, the leaves of red currant are covered with bright brown spots. In order to avoid the appearance of this defect, it is necessary to get rid of diseased fruits and process the plants with 0.25% ziebom. Bordeaux liquid It is also perfect for processing with such a disease of red currant bushes.
Red currant pests and control
Red currant pest - spider mite
If the plant is damaged by a pest spider mite, then there is a decrease in winter hardiness and yield. This pest lives in winter mainly under the leaves that have fallen or in the upper soil layer. At the moment when the bud breaks, the mite climbs onto the plant and gradually spoils the leaves. He lays his eggs at the bottom of the sheet. Ovipositions and greenish larvae that appear are clearly visible in a magnifying glass.
Often the reproduction of the pest mite in the first generation occurs on the weeds. After some time, he begins to move to garden plants. In order for the spider mite to multiply well, hot and dry weather is necessary. Mass pest development is often scheduled for August and July. Already closer to the autumn, the females begin to leave for the winter.

Photo: Spider mite on red currants
Ways to treat pest spider mites on red currants
In the spring, when the buds start to bloom until the female has laid the eggs, the plant should be sprayed from acaricides: acartan, anti, zolone, karbofos, metaphos, vatatox, colloidal sulfur, tedion, phosphamide, cydial, etc. Do not forget that the improper use of the drug causes burns of the plant red currant. And if you use them for treating currants, it will be much more effective than, for example, on a gooseberry. When processing it is recommended to alternate drugs periodically. If you use the same, then there is the emergence of immunity in the pest mite.
When the red currant plant is already very badly damaged by the pest it is recommended to spray again. For example, this can be done before the currant blooms. Also, additional spraying should be done with yellowing and twisting of the leaves.
In order for efficiency to increase slightly, you should add acaricides and stir them in chlorophos. This is very helpful in controlling pests that gnaw sheets. This mixture perfectly kills them after the plant has bloomed.
Red currant pest - leaf gall aphid

Photo: Aphid leaf on red currants
Sheet gall aphid damages leaves of red currant in such a way that red swelling appears on its outer surface. If you do not intervene in the course of currant disease, the currant foliage dries and begins to fall off before the deadline. Exposure to aphid pest leads to a decrease in the yield of berries.
Red Currant Pest - Yellow Sawfly

Photo: Yellow sawfly on red currants
The pest yellow gooseberry sawfly also causes damage to the planting of red currants, because it eats the leaves of this shrub.
Red Currant Pest - Glass

Photo: Glass cup on red currants
The currant glass bowl lays its eggs in the cracks of the currant bark. The caterpillars that hatch from them penetrate inside the shoot and eat away the middle.
Red Currant Pest - Blackberry Mite

Photo: Blackberry mite on red currants
A pest is an insect that has two pairs of legs. And it spreads with the help of wind streams, as well as with some insects or initially infected material for planting. When this pest of currant grows up, it goes into the lower side of the leaves and begins to suck juice from it. In this process, they release enzymes. Due to this, galls are formed on the leaves (small protuberances that have a yellow or reddish color). And for the season, this pest can form several generations. He tolerates winter very well, settling under the bark or at the base of the buds. In order to get rid of the pest mite, it is necessary to carry out several treatments. To begin with, the first spraying is done, and the second after harvesting.
Red Currant Pests - Zlatka

Photo: Red Currant Pest - Zlatka
This is an insect that has a flat body shape. It often just lays eggs on the bark and shoots. When the larvae appear from them, the spoilage of the shoots occurs. This is due to the fact that the larva begins to gnaw them, and the passages are clogged with brownish flour. After some time, they go deep into the wood. In the event of damage by a pest of shoots, they wither and dry. This whole process takes place in early spring. Larvae hatching begins around the beginning of May and lasts about three months. When zlatka grows up, it begins to eat leaves. If you want to get rid of it, then the most effective method of struggle will be only shaking. This must be done in the morning, while the beetles are not flying yet.
Fight against diseases and pests of red currant: Video
Diseases and pests of red currants can destroy your crop, if you miss their appearance and do not carry out treatment.
The queen of berries, red currant, with proper maintenance turns into a real garden decoration.
Unfortunately, even the most careful care does not guarantee the complete absence of fungal and viral diseases, to which the plant is predisposed. However, the fight against red currant diseases cannot be ignored.
What diseases threaten red currants?
Like other species, red currants are susceptible to fungal and viral diseases. The most dangerous among them is the terry. This is a very insidious virus, as it develops, changes the appearance of the bush and leads to currant infertility. Most often it affects the black currant, but since the carrier is a kidney tick, settling on a red one, the bushes with scarlet berries are also not insured from it. If no signs of a kidney tick were found on the currant, the virus was transferred from planting material or through contaminated garden tools. Reversal - Terry is a popular name - it does not develop in one year, and the longer the infected shrub stays in place, the higher the risk of disease of other plants.
Determine the presence of the virus during flowering:
The currant lacks flavor;
Flowers ugly, greenish or dirty pink shade (up to purple), with pointed elongated petals;
The leaves are darker than usual, more dense and wide, with three corners instead of five.
Because of the terry, the inflorescences do not develop: not having had time to give the ovary of the berries, they fall down on the ground. The virus is not cured: the infected bush will lie down for removal. For several years, currants in this place can not be planted.
Another common virus is striped mosaic. On the leaves of an infected plant, along the vein, a bright pattern appears, gradually filling the entire surface of the leaf. This leads to a decrease and a complete lack of harvest, and the death of the plant. Just as with terry, a bush with a virus is uprooted and burned.
Red currant: disease and treatment. How to beat anthracnose?
In common people it is called a flyworm. For red currants, it is even more pernicious than for black or white. Infection can be identified by spots: first, small brown dots on the leaves gradually increase in size, and, merging, form tubercles that deform and disfigure the leaves.

This leads to their fall: in the red currant even a few spots can cause premature leaf dumping and a sharp decrease in yield.
It is good that anthracnose is treatable:
Spraying the bush and the ground around it with a solution of copper sulfate or “Nitrafen”: this must be done before bud break;
Three times spraying with 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture after flowering with a frequency of two weeks;
Prevention of the disease gives a very good result, not allowing the fungus disputes to spread through the garden:
In autumn and spring, they dig up the soil around the bush;
Fallen leaves, in which the fungus winters, are collected and burned;
Do not allow thickening of the bush and carry out timely pruning;
Before use, scalded gardening equipment is boiled with boiling water so as not to transfer spores to healthy plants.
Since anthracnose leaves leaves and shoots other than leaves, treatment must be quick and complex.
Glass rust
One of the most unpleasant diseases. The lower surface of the leaf is covered with small orange spots, which, if you do not take measures, grow into “glasses”: it is in them that the fungus spores ripen, which at the end of summer are transferred by wind to neighboring bushes and ... sedge. If there are thickets within a half kilometer radius of the site, it is from there that rust has flown over to your site. It is necessary to get rid of the sedge: in the spring the rust spores are carried by the wind onto the currants.

In addition to standard processing bordeaux mixture and fungicides, there is a proven popular recipe:
Make two infusions: for the first, take 1 cup of garlic cloves and 2 liters of water, for the second 200 g of tobacco and 3 liters of water. Both infusions to keep in a dark place for 2-3 days, drain, and then drain into a 10-liter bucket;
Add to the bucket 1 tsp. ground pepper, 1 tbsp. l any liquid soap, insist 3 hours, drain.
The composition is prepared in advance: to spray the plants to combat the diseases of red currant need to bloom before. The residue of garlic, tobacco and pepper can be used as mulch. After a couple of weeks, the bush is sprayed with an infusion of onion peel.
And if there is no confidence in folk remedies, you can purchase special preparations: Agrolekar, PropiPlus, Prognoz and Chistoplor.
Septorioz on red currants
It should be noted that red currants are not as often affected by white spot as other species. However, sometimes this happens - it means you need to be treated.
The disease begins with the appearance of brown spots. As they grow, the center of the spot turns pale, and as a result a large gray-white spot with a brown border remains on the leaf plate.
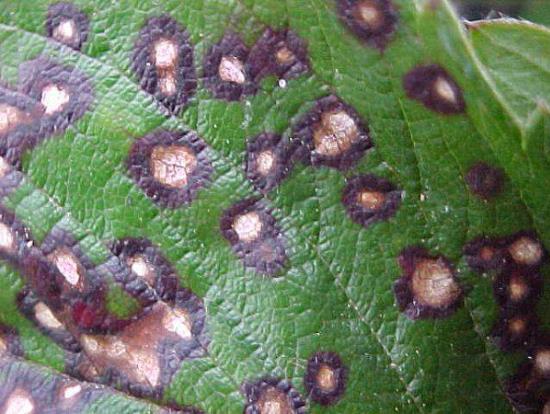

Septoriosis is treated by practically the same methods as anthracnose, its pathogen also tolerates winter in fallen leaves. In addition, you can use the fungicides: "Cichome", "Fitosporin-M", "Chistophlor" and "Prognoz". For the prevention of the appearance of the disease, the currant bush is sprayed with Bordeaux mixture, copper sulphate or Nitrafen before flowering. Be sure to thinning the bush and removing shoots with signs of septoria.
Sphereotek red currant: what is this disease? Powdery mildew treatment
The name "powdery mildew" is more familiar to the gardener. This disease delivers a lot of trouble with its frequent relapses, but it is already well known and studied, so there is a chance to win. Signs of defeat currant powdery mildew:
The appearance on the leaves and fruits of light gray bloom, which gradually acquires a brown color;
Leaf deformation: twisting, shedding;
Cessation of growth;
Fall of immature berries.

The danger of the sphere library is that, due to the disturbed growth, the plant becomes less winter-hardy, and if it survives the winter, the powdery mildew will overcome the bush completely next year and move on to the next plant.
The measures of struggle include:
Full sprinkling of currant fungicides;
Folk remedy: solution of soda ash (50 g per 10 l of water);
Prepare a solution of mullein and water in the ratio of 1: 3, insist 3 days, once again bred in the same proportion and weekly spray the infected shrub.
Among the fungicides, “Alirin-B”, “Baktofit”, “Tiovit Jet”, “Fitosporin-M”, “Topaz” can be used.
There are preventive measures to combat powdery mildew. This is a mandatory pruning of damaged shoots, cleaning and burning of fallen leaves. You can not treat this with disdain, because if you do not destroy the infected parts of the plant, then the spores of the fungus-pathogen will sooner or later be on other plants, and the whole course of treatment will have to start all over again.
In general, methods of combating diseases of red currant do not differ from the treatment of bushes with black or white berries. It is just that some diseases are subject to more or less: this must be taken into account before starting treatment in order to have time to save the plant.