Registration of overtime hours for the Russian Federation. We make overtime
What you read in this article
- How to fix overtime in the contract
- How to calculate overtime pay
Overtime work governed by the provisions Labor CodeIn particular, the definition of overtime work is established by article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: overtime work is work performed by an employee at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours for the employee: daily work (shift), and for summed up working time for the accounting period.
In accordance with the provisions of Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, overtime work requires increased pay or the provision of additional rest time at the request of the employee, who must be at least as long as the overtime hours worked. At the same time, your employees should know that recycling on their own initiative cannot be considered overtime, so you are not required to pay for it. Also overtime can not be considered work outside the working day, which is performed by employees with irregular working hours.
In addition, it should be borne in mind that engaging in overtime work should not be systematic. However, it is possible to periodically engage in overtime work and in certain cases. At the same time, the total duration of overtime work per employee should not exceed 4 hours for two consecutive days and 120 hours during the year.
How to legally attract an employee to work overtime
An employer may recruit an employee to work overtime with his written consent in certain situations.
- When it is required to perform (complete) the started work, which due to unforeseen delay on technical standards could not be completed for the prescribed duration of the working day - if non-performance of this work can lead to the destruction or damage of the employer's property (including property of third parties with the employer), municipal or state property, or lead to a threat to human health and life.
- During the period of temporary work for the restoration and repair of structures and mechanisms, when due to their malfunction it is possible to stop the work of a large number of employees.
- If it is necessary to continue the work, when the changer did not appear, and the work does not allow for a break.
The employee has the right to refuse to work overtime, he must notify you in writing. But in some cases, this rule does not apply:
- When performing work to prevent a catastrophe, an industrial accident, or to eliminate the consequences of an industrial accident, a catastrophe, or a natural disaster.
- To perform publicly necessary workaimed at eliminating unforeseen circumstances leading to disruption of the normal operation of heating, gas supply, lighting, water supply, transport, sewage and communication systems.
- Work that is caused by the introduction of martial law or emergency, also urgent work in emergency situations - in case of disaster or threat of disaster, also in other situations that lead to a threat to life or the normal living conditions of people.
Is it possible to attract employees for overtime work in case of staff reductions?
Anna Vasenina, Publisher and editor-in-chief of the magazine “Personnel Business” and Reference Books of the Personal Consultant Series (Aktion-Media Publishing House), Moscow
First of all, let's answer the question, for what reasons in the organization most often there is a reduction of employees. As a rule, this is a decrease in production volumes and rendered services. And, as a result, lack of work for some employees. Therefore, to talk about overtime work and unregulated working day in this case is not quite logical. However, many employers today resort to staff reductions in order to save on the wage fund, although the amount of work in the organization has not decreased. Here, apparently, the question arises about overtime work and irregular working days. Let's see if the employer wins.
If we act according to the letter of the law, in addition to no small payments to redundant workers (Art. 127, 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), it is necessary to compensate for overtime work (Art. 152 of the Labor Code) and irregular working hours (Art. 116, 119 of the Labor Code). In most cases, it is necessary to obtain written consent of employees to work in non-standard mode. Now let's take a closer look at the conditions under which overtime and part-time work are possible.
Overtime work. On the initiative of the administration, without the consent of employees, overtime work can be attracted only in cases of emergency, for example, to eliminate an industrial accident (article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Such work is paid in the following way: for the first two hours - not less than one-and-a-half amount, for each subsequent hour - not less than twice the amount. Instead of increased pay, an employee may take time off (for example, an hour of rest for each hour of overtime; additional time rest can not be less than the time worked beyond the limit). Overtime work should not involve pregnant women, minors, employees during the term of the student contract, employees who are prohibited from working beyond their normal length in accordance with a medical certificate. Therefore, before making a decision on staff reduction, it is necessary to analyze whether the organization will actually reduce the amount of work and whether you will not have to look for working hands later. After all, if you reduce some of the staff, then you will force workers to work completely selflessly “for yourself and for that guy”, and you are unlikely to succeed without conflicts with subordinates and problems with the law.
Irregular working hours. One of the important points that leaders often forget about: working under irregular working hours means that an employee is invited by the administration to perform his work tasks beyond the usual working hours sporadically. In other words, work in an unregulated regime should not be permanent (art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The list of employees who can work in this mode should be fixed in the local regulatory act of the organization (for example, in the internal labor regulations). Each case of attracting an employee to unregulated work should be made out by the appropriate order. The exception is the Director General, since he himself plans his work and is delayed on his own initiative, and is not involved in work after the end of the working day (but nevertheless, the condition on an unregulated working day must be included in employment contract, and the position of director - in the above list). As compensation for an irregular working day, employees are granted annual additional paid leave of any length (set by the administration), but not less than three days a year. And if in the organization and so fewer employees work than the workflow requires, then it will be necessary to replace these absent employees additionally.
Summarizing what was said, I once again advise you to think through all the options for the development of events before making a decision to reduce the number or staff in order to reduce the wage bill.
Who should not be involved in overtime work
Labor legislation introduced restrictions on the involvement of certain groups of employees in overtime work:
- pregnant women;
- employees under 18 years old. In addition to underage athletes, creative employees of cinema organizations, the media, video and television crews, concert and theater organizations, theaters, circuses, and other individuals who are involved in the creation and / or performance of works. The list of these positions and professions is regulated by the norms of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 28, 2007 No. 252.
- disabled people;
- women with children under 3 years;
- mothers and fathers who bring up a child under the age of 5 years without a spouse;
- workers with disabled children in the family;
- staff caring for sick family members.
How to get overtime
For an employer, it is very important to arrange overtime work. The provisions of the Labor Code require the written consent of an employee to involve him in overtime work, and an order must also be issued. No written consent of the employee is required only when performing work caused by extraordinary circumstances.
It is necessary to indicate in the order the reason for overtime work, the dates of commencement, completion, duration, list of employees involved, the procedure for granting additional work rest time or pay hours.
If a changer did not show up for work when the break is unacceptable, the manager simply does not have time to issue an order. You can choose another option. First, a fact is recorded that will represent the basis for an employee's overtime work. Then, non-appearance (or other grounds for overtime) should be reported to the head of the organization or another person authorized to involve employees in overtime work. In this case, the head of the department should make an office note describing the incidents and the rationale for involving a specialist in overtime work.
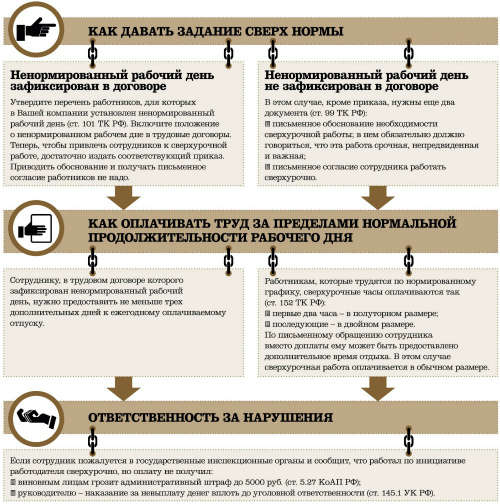
How much to pay for overtime
Payment of overtime work, in accordance with Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, must be made at an increased rate during the first 2 hours - at least one and a half salary; during the following hours - minimum double salary.
Labor legislation establishes a minimum wage. However, the employer has the right to pay more remuneration. For this, it is necessary to regulate the amount of payment for overtime work by the provisions of the local regulatory act of the company.
Compensation for overtime work can be not only increased pay, but also the provision of additional time for rest — no less than the time spent on overtime. Allowed to replace only on the basis of a written statement of the employee.
Says CEO
Maria Lavitskaya, Director of Premium Business School, Krasnoyarsk
Example 1. In our region, the company operates in the field of supply and installation of climatic equipment. In order to gain reputation as a reliable partner, it tends to stay ahead of the deadlines for performing work. For this purpose, it is planned to enter the facility and on weekends. The head of the company personally explains to each employee the need for overtime work, explaining the importance for the company of operational project implementation. Assistance that is truly important to employees becomes an incentive. In particular, after the birth of the child, one employee was given a loan to purchase all the necessary things - an interest-free loan. A team for the execution of works faster than the deadline were given an additional weekend.
Example 2. A pharmacy chain operates in the city. The manager regularly adds new functions that are distributed among employees without staff expansion. There is a gradual increase in responsibilities. Because of this, after some time, the employee is forced to work after hours. The head regularly communicates with each employee, but does not try to build relationships like the first case, but draws attention to the quality of work. Tactics involve distraction. Demonstrates to the employee that he does not have time to complete the work in time. At the same time expresses concern and offers assistance in planning work time. Attention and help from the head compensate for the negative from the increase in work tasks.
How to overtime reflected in tax accounting
The amounts accrued for employees during overtime work, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 255 of the Tax Code, should be included in the cost of payment of ore. However, it is possible to exercise this right only if these charges are consistent with the law. Accordingly, it is necessary to follow all the conditions for the registration of overtime work indicated above.
It is known that often in practice the maximum allowed overtime is violated. At the same time, this issue is not clarified by the relevant departments, their explanations only contradict each other, not allowing to make a single conclusion.
A violation of the maximum permissible number of hours constitutes a violation. However, this should not affect the employee’s right to pay for overtime work. Consequently, when working overtime for more than 120 hours per year, the costs may fall into the category of labor costs, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 255 of the Tax Code.
The tax legislation of the country does not impose restrictions on taking into account the rate of payment for overtime work. At the same time, violation of labor standards does not cause tax violations. Therefore, even with overtime work over 120 hours, the company has the right to recognize this supplement in tax accounting in full.
If we talk about personal income tax, the position is unambiguous. Charges for overtime work is not compensation, but part of the salary. Consequently, the provisions of paragraph 3 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on exemption from personal income tax do not apply to them. In respect of them, there are also insurance premiums to the Federal Fund for Mandatory Medical Foundation, the Pension Fund, the Social Insurance Fund, and insurance contributions for injuries.
You also need to pay attention to the need to register overtime, including documented.
The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation does not establish any violations that employers allow for overtime work, and there is also no responsibility for them. Art. 5.27 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation only establishes responsibility for the fact of any violation of labor legislation and labor protection in the form of:
- For organization, a fine of 30-50 thousand rubles, or administrative suspension of work up to 90 days.
- Officials - a fine of 1-5 thousand rubles. If you repeat a similar violation during the year - disqualification for 1-3 years (Part 3 of Art. 4.5 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation).
There are similar measures in case of violation of overtime.
Says CEOArtem Milakov, General Director of Pro-Line Event, Yaroslavl
I formed a number of rules that help to work effectively in an unpredictable schedule.
Pick the right staff for your business. After all, not everyone can be involved in work for 16 hours. Try to surround yourself with easy-going staff.
Give employees the opportunity to implement the ideas themselves. This approach becomes a powerful motivation - in the form of a specific blank check and financial support.
When overtime is necessary, I work with employees. I do this not so much from a production need, as for the motivation of my employees.
8 rules of additional motivation of employees
- Act any motivation will be no more than 3 months. Then the effect starts to decrease. Therefore, you need to work on different levers of influence.
- If employees work at computers, they should be able to rest for 10 minutes every hour.
- To reach the peak of working activity, a person needs 30 minutes. continuous work. Any third-party distractions nullify the results, you have to start again. Try to protect your team from excessive noise.
- Do not demand maximum productivity from employees all the time. Try to find out the biorhythms of your employees, passing them important tasks during the activity.
- It is not always possible to encourage overtime financially. Some may be interested in communicating with different people or travel.
- Give thanks and acknowledge the family of the employee for his work. For example, an open letter.
- One must always remember that one who rests well works effectively. Therefore, after difficult overtime work or heavy projects, the employee should have the opportunity to rest. In particular, extra rest within a few days or unscheduled vacation.
- During overtime, the risk of errors due to fatigue increases. This must be treated with understanding.
How to convey to employees what to spend working time
Sergey Kolesnikov,Director of Organizational Development of the Holding "LBR-group", Smolensk
During the period of rapid growth, we did not notice how from a small agile company turned into a large trading holding with all its inherent shortcomings: the market scent worsened, the staff swelled to indecent sizes, the cost increase became uncontrollable, the expediency of many projects and tasks was in doubt.
The sharp drop in demand during the 2008 crisis made us think about costs. For several months, each meeting of the board of directors began with reports of functional managers on how much they managed to save, which they were able to refuse. However, we soon realized that it was impossible to reduce costs to infinity. In addition, the main cost items relate to staff.
Then the idea to do to increase the efficiency of labor. As a result, a project called “Useful Work” was prepared and is being successfully implemented.
On the development of the new payment system, we gave six months. Promoting the idea of useful work included two important areas: working with opinion leaders and mass informing employees about what kind of work was really useful. This important task fell on the shoulders of middle managers.
Work with opinion leaders. We searched in the team for those who share the principles of the “Useful Work” project and will be able to act as a volunteer. Those who believed that the project will not give anything, we did not try to persuade. Looking ahead, I will say that there were also four middle managers setting up subordinates against the project, they had to part with them. There were explanatory conversations with the others. This is how the process was organized.
To begin with, they made a list of potential supporters of the changes, which included most of the top managers and some of the middle managers - only 18 people. The principle of choice is simple - on the project should work people who have eyes and no doubt about its success. A good leader always knows which employee can count on. Candidates were sent a letter with a detailed description of the situation in the company and a list of proposed measures to improve it. Everyone agreed to participate in the project.
Then, in the corporate media, the launch of the “Useful Work” project was officially announced and an important event was announced - a round table, which was to work together to define the specific goals of the project and develop steps for their implementation. So that the participants did not feel the pressure of the leadership, we invited an external coach as a leading round table.
In addition to managers, four ordinary employees who were respected by the performers took part in the round table. Initially there were doubts whether it was worth including them in the same working group with top managers, but the result was positive - four more people appeared in the ranks of the project supporters. Moreover, later we regretted that we did not invite representatives of the branches - it would be easier to bring the ideas of the project to remote offices.
Drawing up a publication plan on the corporate portal. The first on the list of events developed at the roundtable was to inform staff about future changes. The main media platform has become a corporate portal.
Now, an initiative group meets monthly, which includes heads and ordinary employees of various departments, representatives of HR and PR departments. They approve the media plan for the month: news topics, which projects they are attached to, who is responsible. The note on the project should carry the following meaning: for a company to survive in difficult market conditions, so that each employee can save well-paid workplace, everyone should reconsider their attitude to work, every hour of time that a company buys from an employee should be filled with meaning and business benefits. The staff of the HR department has a separate employee whose task is to pre-read materials, administer a media plan and count the results. For the density of news and their compliance with the interests of the company is personally responsible for the personnel director.
On the day, one or three news items are published, which top managers wrote first, and then ordinary employees joined. They talk about real examples of improvements in different divisions. For example, an assessment of the load of economists revealed several duplicate functions. The employees themselves dealt with the problem, prepared TK for programmers and, after the implementation of the changes, released about 60 hours per month. Every month, all notes are evaluated according to several criteria and the number of views. Best authors get tickets to the cinema or theater.
Reorganization of employment managers subordinates.The middle managers were to distribute all the tasks of their subordinates into three groups related to useful work. Tasks that did not fall into any of the groups, but were important, had to be entered into the accounting form as a separate item at the time of closing the working day.
So, changes in the work of sales managers have touched on two areas: work with documents and interaction with brand managers.
Work with documents. According to statistics, 29% of work time was spent on this job. During the reorganization, such changes occurred.
- Some of the functions for the preparation of documents shifted to the accountant. Its functionality, in turn, was also simplified thanks to another project - the optimization of the accounting system.
- They made a more convenient interface of the automated program and conducted training, since it turned out that some managers do not know how to use the existing capabilities of the system.
- Reduced to the minimum the number of trips associated with the documents. Previously, instead of going straight to the meeting prepared, managers made out a repeat trip to “sign the documents”. Electronic accounting of working time opened the eyes of managers on such facts of inefficient use of resources.
Interaction with brand managers. Previously, sellers spent 21% of their time on this, asking many recurring questions about products. Now we have automated requests and forbidden to call with the same problems several times. Based on the questions and answers, we have formed a knowledge base. For example, if a brand manager answered once to the seller the question “how does this product fit in with the client’s equipment?”, Then this answer is recorded in the database, and any manager can use it.
reference
Pro-Line Event LLC
Area of Operations: organization and provision of events
Number of staff: 15
Number of completed projects per year: more than 100.
Premium Business School
Area of Operations: business training, consulting
Number of staff: 3. Net profit: 1.1 million rubles.
Oksana Sherstneva, Legal Adviser on civil matters, Moscow. Practicing lawyer, experience more than 5 years, including in the field of registration of property rights to real estate.
Sergey Kolesnikovhe graduated from the Faculty of Radiophysics of the Belarusian State University. He has been working as a top manager in large Belarusian and Russian holdings since 2000; in HR-sphere - since 1997. Founder of one of the first Belarusian recruitment agencies, Kvadrat. Business consultant, author and presenter of trainings in the field of organizational management and in the field of personnel management. Author of over 200 publications in Belarusian, Russian and Polish business media. In the holding "LBR-group" has worked as a director of organizational development since 2005.
LLC LBR-group
Field of activity: sale of agricultural equipment
Territory: head office - in Smolensk, branches - in 26 Russian cities
Number of staff: 700
Revenue: 3.6 billion rubles.
Aktion Media
Field of activity: b2b periodicals publishing.
Form of organization: CJSC (publishing holding).
Territory: head office - in Moscow, branches - in St. Petersburg, Vladimir, Voronezh, Nizhny Novgorod, Novosibirsk, Ufa, Khabarovsk and other cities.
Number of staff: 950.
Monthly total circulation of publications: more than 1 million copies.
The article was prepared with the participation of N.Z. Kovyazina, Deputy Director of the Department salary, labor protection and social partnership of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia
In what cases is work allowed outside the normal working hours? What are the guarantees and compensations for employees? How to apply for overtime work? Answers to these questions can be found in the article. And in the next issue we’ll talk about overtime pay.
According to article 97 of the Labor Code, an employer has the right to engage an employee to work beyond the limits of his working time for overtime work.
What work can be recognized as overtime
Overtime is recognized as work performed on the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee. At the same time, the content of overtime work may not correspond to the labor function of the employee, established by the employment contract.
For workers with reduced working hours, work outside of this area is also recognized as overtime.
If an employee is delayed on his own initiative, such work is not considered overtime (letter from the Labor Ministry of 18.03.2008 N 658-6-0).
Non-normalized working day does not equal overtime
Non-normalized working day is a special mode of operation, which gives the employer the right to occasionally involve an employee in the performance of labor functions outside the established working time (Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Rostrud referred to this legal provision in a letter dated 07.06.2008 N 1316-6-1. The condition on the regime of an unregulated working day should be necessarily specified in the employment contract (part 2 of article 57 of the Labor Code of the RF). By signing the contract, the employee agrees to work in this mode. Note that the agreement to work overtime can not be fixed in the employment contract.
Work done in unregulated working hours is not subject to additional payment. However, employees with irregular working hours are provided with annual additional paid leave of three calendar days (part 1 of article 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Employee Guarantees
Labor legislation establishes:
- a closed list of grounds for engaging in overtime work without the consent of the employee;
- circle of persons who cannot be involved in overtime work;
- limiting the duration of overtime work for one employee;
- the procedure for attracting overtime work;
- increased salary for overtime work.
Next, we will talk about the mechanism for exercising the rights of workers involved in overtime work, and the obligations of the employer.
Reasons for engaging in overtime work
International norms and Russian legislation proceed from the fact that the circumstances in which an employee can be involved in overtime work are exceptional * (1). Overtime work cannot be included in the production schedule in advance (letter from Rostrud of 07.06.2008 N 1316-6-1).
Overtime without employee consent
Under special circumstances, the employer has the right to involve the employee in overtime work without his consent.
According to part 3 of article 99 of the Labor Code, the exceptional circumstances include the need for work:
- to prevent a disaster, industrial accident or eliminate the consequences of such phenomena;
- to eliminate unforeseen circumstances that disrupt the normal functioning of water supply systems, gas supply, heating, lighting, sewage, transport, communications;
- caused by the introduction of a state of emergency or martial law, in the event of a disaster or its threat (fires, floods, epidemics) and in other cases endangering the life or normal living conditions of the population.
When an employee’s consent is required
In addition to extraordinary exceptional circumstances, the need for overtime work may arise (Part 2 of Art. 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- if necessary, perform (finish) the work begun, which could not be completed during the main working time, if its non-fulfillment may result in damage or loss of the employer's property or create a threat to the life and health of people;
- the performance of temporary work on the repair and restoration of mechanisms or structures in cases where their malfunction may be the reason for the termination of work for a significant number of workers;
- non-appearance of a replacement worker if the work does not allow for a break.
In these cases, the employer has the right to involve the employee in overtime work with his written consent, and the employee has the right to refuse to perform overtime work. Employee refusal can not be equated with violation of labor discipline. According to article 379 of the Labor Code, an employee in order to protect his labor rights may refuse to perform work not covered by the employment contract. He must inform the employer of this in writing. This rule does not apply in situations listed in paragraph 3 of Article 99 of the Labor Code, when an employee’s consent for overtime work is not required.
Employee consent and consideration of the views of the trade union organization
In all other cases of attraction to overtime work, written consent of the employee and consideration of the opinion of an elected body of the primary trade union organization is required (part 5 of article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Taking into account that these cases are not defined by labor legislation, it is permissible to include their open list in the text of a collective (labor) contract.
Limitations of engaging in overtime
Labor legislation establishes restrictions for engaging in overtime work for certain categories of workers, as well as its duration.
The employer is obliged to observe the restrictions in attracting certain categories of workers to overtime work. The degree of restriction is established by labor law.
Categorically it is impossible to involve in overtime work:
- pregnant women (part 5 of article 99 and part 1 of article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- workers under the age of 18 years (part 5 of article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The exceptions are minor athletes (part 3 of article 348.8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), as well as creative media workers, film organizations, television and video crews, theaters, theater and concert organizations, circuses and other people involved in the creation and (or ) execution (exposure) of works (Art. 268 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The list of jobs, professions, positions of these workers was approved by the RF Government Resolution No. 252 of April 28, 2007.
With written consent and in the absence of a prohibition to work overtime for health reasons, in accordance with a medical report, it is allowed to engage in overtime work:
- disabled people (part 5 of article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- women with children under the age of three years (part 5 of article 99 and part 2 of article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- mothers and fathers who bring up children under the age of five without a spouse (part 2 and 3 of article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- workers with children with disabilities (Part 2 and 3 of Art. 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- workers caring for sick family members (Part 2 and 3 of Art. 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, it is necessary to familiarize the employee with the painting with his right to refuse overtime work.
Some additional guarantees for employees are provided for by industry agreements (regulations).
Duration of overtime
The duration of overtime work must not exceed four hours for each employee for two days in a row and 120 hours per year. For drivers of vehicles with summed-up work hours, overtime during the working day (shift) along with work on a schedule should not exceed 12 hours. The exceptions are cases when it is necessary to finish the flight or the shift attendant did not appear (clause 23 of the Regulation on Peculiarities of the Mode of Working Time and Rest Time of Drivers of Automobiles, approved by order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia of August 20, 2004 No. 15).
Overtime Documentation
Each case of attraction to overtime work must be issued separately. It is not allowed to include in a collective (labor) contract, a local regulatory act of provisions containing the employee’s consent to perform overtime in the future, for example: “By the employer's order, the employee (s) agree (dream) to work overtime.”
The step-by-step procedure for documenting overtime will be considered by example.
Step 1. Fixing the fact
At the first stage, the fact that is the basis for engaging in overtime work should be recorded. The most common case of a no-change maker to work, not allowing a break. A non-appearance (or other reason for engaging in overtime work) should be notified to the head of the company. For this, the head of the department writes a service note. It describes the incident and justifies the need to involve workers in overtime work.
See the sample memo below.
Sample Service Note
Get the employee’s consent to the CEO
prepare a draft order of Avral LLC to Myagkov M.T.
on bringing to overtime from the head of service
incident recording work
Zabodaeva GD
Myagkov M.T. Myagkov
Memos
In connection with the non-appearance of dispatcher L.K. Suddenly, which can not leave a sick six-year-old child, which she reported by phone 10 minutes before the shift, I ask on November 16, 2009, from 8.00 to 12.00, to attract overtime work of another employee who has the appropriate qualifications and skills.
On the basis of the memorandum, the head of the enterprise makes the appropriate orders: if necessary, notify the employee involved in overtime work about his right to refuse it, get his consent, prepare a draft order on engaging overtime work.
Step 2. Does the employee agree
In almost all cases, with the exception of those listed in paragraph 3 of Article 99 of the Labor Code, it is necessary to obtain the consent of the employee for his involvement in overtime work. At the same time, employees of privileged categories should be notified in writing of their right to refuse to perform overtime work. Notification can be included in the text of the appeal to the employee with a request to work overtime. A sample recourse to an employee is given below.
Sample treatment
Registration Dispatcher
accidents LLC Avral
Blagova Yu.E.
Dear Yunna Epifanovna!
In connection with the non-appearance of dispatcher L.K. Suddenly, I ask you to remain after work on November 16, 2009 and continue to perform the duties of a dispatcher instead of a non-present resident in the period from 8.00 to 12.00.
As the mother of a disabled child, you have the right to refuse to work overtime in accordance with parts 2 and 3 of Article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
I refuse to perform overtime work on November 16, 2009 from 8.00 to 12.00.
————
I agree/
I refuse
Step 3. If the employee refused
In the event of the refusal of one employee to perform overtime work, the employer has the right to make this proposal to another employee who is able to fulfill it. See below for a sample re-request to another employee.
Reuse sample
Senior Service Manager
incident registration
Avral LLC Goridze N.G.
Dear Nina Georgievna!
In connection with the non-appearance of dispatcher L.K. The sudden and refusal of her shiftmaster, Yu.E. Blagova, I would like you to perform overtime work on November 16, 2009, to remain after work and to perform the duties of a dispatcher from 8.00 to 12.00. As an invalid, you have the right to refuse to work overtime in accordance with part 5 of article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Overtime work on November 16, 2009 from 8.00 to 12.00 I agree.
———-
I agree/
I refuse
Step 4. Overtime Order
If the employee agrees, an order is drawn up to involve him in overtime work, indicating the time of its beginning and end. For a sample order, see p. 90.
Sample order
Limited Liability Company "Avral"
Order N 164
In connection with the non-appearance of the dispatcher LK Sudden and inability to interrupt work in accordance with Part 4 of Article 99 of the Labor Code
I order:
1. Senior dispatcher N.G. Goridze, personnel number 3244, with her consent, should be involved in overtime work as a dispatcher on November 16, 2009, from 8.00 to 12.00.
2. The head of the incident registration service, GD Zabodaev to provide accounting for overtime work.
3. Chief Accountant OA Help pay for overtime work at a higher rate in accordance with article 152 of the Labor Code and clause 7.4 of the Labor Remuneration Regulation.
Reasons: office paper GD Zabodaev from 11/16/2009, notice N.G. Goridze, written consent N.G. Goridze.
General Director Myagkov TM Myagkov
Read the order:
Goridze N.G. Goridze
November 16, 2009
Zabodaev GD Zabodaev
November 16, 2009
Helpova O.A. Helpova
November 16, 2009
Continued in the next issue.
A.A. Mikhin,
lawyer
O.S. Ovchinnikova,
Deputy Editor-in-Chief of the Salary Magazine
————————————————————————-
* (1) The Charter of Social Rights and Guarantees of Citizens of Independent States (approved in St. Petersburg on October 29, 1994 by the Resolution of the CIS Interparliamentary Assembly), ILO Convention No. 1, ILO Recommendation No. 116.
As of: Dec 10, 2010
Magazine: Everything for the personnel officer
Year: 2011
Author: Batura Anna Vladimirovna
Subject: Records of personnel service, non-standard working day
Rubric: Is there a problem? Here is the solution
- Document Templates
- Time Sheet Log
Regulations
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation (extract)
- All employment records burned out. What to do?! Providing leave strictly on schedule Employer branding - new fashion or the future of HR?
Last month our chief accountant changed. And everything would be fine - it establishes contact with the personnel department, arranges the work. But on some issues we can not come to a common opinion. For example, such a problem. Our company has employees who work in the irregular working hours. For this, as expected, we give them additional leave. In the sheet of the accounting of working hours such workers were always put "eight". And the new chief accountant claims that those days when they are recycled must be recorded in the report card, because we are obliged to keep accurate records of the time worked by each employee. Have we been doing it wrong all the time?
A non-standard working day is a special mode of operation in which employees, by order of the employer, are occasionally involved in work outside normal working hours.
Compensation for this mode of operation is not increased Payment labor, and the annual additional paid leave of a certain length, but not less than three calendar days.
The question of how to fix the work in irregular working hours, in practice raises many problems. On the one hand, the employer is really obliged to keep accurate records of the time actually worked by each employee. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation directly speaks about this (part 4 of article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this, your chief accountant is absolutely right.
On the other hand, such processing, in contrast, for example, to overtime work is not paid to employees. In this regard, the question arises: how to simultaneously fulfill their obligations to record time worked and not get lost in payment? Let's get a look.
So, for those who work in the unregulated working day mode, the number and duration of processing over the established working time does not affect the amount of wages and the duration of their additional leave.
Accounting for working time allows you to control labor discipline, monitor the presence of workers at workplaces, and, if necessary, decide on the place and time of any incidents, such as accidents at work, etc. Also, accurate recording of working time will allow the employer to prevent violations of labor laws in the form of systematic involvement of an employee in the performance of labor functions outside the established working hours for them. As we have already noted, irregular working hours are sporadic work and should not be transformed into a rework system.
By general rule To record the working time worked by each employee, the timesheet is used. It has the unified form No. T-12 or No. T-13, approved. Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1 “On Approval of Unified Forms of Primary Accounting Records for Labor Accounting and Payment” (hereinafter referred to as Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 05, 2004 No. 1).
The purpose of this document is defined in the Guidelines for the application and filling out forms of primary records, approved. Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1.
The time sheets are compiled in one copy by an authorized person, signed by the head of the structural unit, an employee of the personnel service, and then transferred to the accounting department for the calculation of wages. Thus, the amount of the employee’s wages will depend on the length of working time recorded in this document. And we have already found out that work in the mode of irregular working hours does not affect wages.
Our reference
If the unregulated working day is set for the employee, it is necessary to keep track of the time that he actually worked outside the working hours established for him, not to “justify” the provision of additional paid leave to the employee. Unfortunately, such an opinion is sometimes found even among the inspectors from HIT, but it is erroneous.
Additional paid leave is granted to employees for whom an irregular working day is established, for the very possibility of their occasional involvement in work beyond the established working hours for them. The right of an employee to such leave does not depend at all on how many times and for how long they stayed after work during the year for which the leave is granted. Such paid vacation days should be provided to employees whose positions are included in the list of employees with irregular working hours, even if during the year they have never fulfilled the instructions of the management outside the normal duration of their working day.
The availability and duration of processing do not affect the duration of the additional paid leave provided. The number of his calendar days is fixed in the local regulations of the employer or in the collective agreement, and must also be indicated in the employment contracts of employees.
YOU MUST KNOW IT
The time sheet is a document of the basis for charging the employee a salary.
The time sheet reflects the time of work in conditions deviating from normal when it is associated with additional payment. Thus, the time sheet, overnight work, weekend work and non-working hours are taken into account in the report card. holidays.
But to fulfill the duty, under Part 3 of Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is possible not only with the help of a time sheet. When an employee works in an unregulated working day, occasional processing should be taken into account in any other way that the employer chooses. For such accounting, you can keep, for example, a logbook of working hours worked by employees in the mode of non-normalized working day. Let's look at an example.
EXAMPLE 
For the personnel inspector Gavrilova A.P., the regime of irregular working hours is established, which is compensated by four calendar days of annual additional paid leave.
By order of the head of the organization, the personnel inspector carried out an urgent assignment outside of her working day on January 17, 2011. To prepare for the audit, she was engaged with overtime work on January 28, 2011.
In the time sheet, the upper line is used to mark the notation (codes) of working time costs, and the lower line is used to record the duration of hours worked (in hours, minutes) by the corresponding working time cost codes for each date.
On January 28, overtime work was recorded in the time sheet (the working time on that day was 10 hours), while processing in irregular working hours 1 January 7, 201 1 was not marked in the time sheet example 1). Moreover, the duration of work on the instructions of the head on the specified day is recorded in a special journal ( example 2).
The Labor Code imposes an obligation on employers to maintain a time sheet. In principle, it would have been possible to do without this document if the employees worked according to a strictly defined schedule, were not ill, did not process, did not go on business trips, did not go on maternity leave, etc., etc. In practice, the ideal situation is almost unreal. Moreover, there is another reason why a formal approach to the compilation of a time sheet is not welcome.
The duty of the employer to keep records of the time worked by employees is established by article 91 of the Labor Code. In this case, use one of the two unified forms, approved by the State Statistics Committee of January 5, 2004 № 1:
- № Т-12 “Time Sheet of Accounting and Calculation of Remuneration”;
- № T-13 “Time Sheet”.
In the same resolution of the State Statistics Committee you can find instructions for filling them (hereinafter - Instructions). So, first of all, we note that the form number T-13 is used when an organization has an automatic system for controlling the presence of workers.
As can be seen from the name of the form number T-12, it can be used not only to account for the working time of employees, but also to reflect the calculations with employees on wages by type of charges. However, if the company maintains a temporary record and payroll accounts separately, then it is only acceptable to fill in section 1 of the timesheet. In the end, it was to summarize information about the use of working time by employees, that is, about the hours and days actually worked and not worked for various reasons, the timesheet is intended. Due to this, it is a primary document confirming such a fact of economic activity as the fulfillment of employee obligations under an employment contract, and serves as the primary document for payroll. In turn, this means that both the tax authorities and the inspectors of extra-budgetary funds, especially the Social Insurance Fund, will pay attention to it when conducting audits. And of course, the data sheet will be interesting to the representatives of the labor inspectorate. The fact is that according to Article 91 of the Labor Code, the normal duration of working time cannot exceed 40 hours per week. Nevertheless, hours worked beyond this are overtime and payable at an increased rate (art. 152 TC).
The order of the timesheet
According to the Guidelines, an authorized person shall maintain a report card. At the same time, there are no restrictions regarding who can act as such. Consequently, this mission can be entrusted to any employee, securing it in a labor contract with him or by issuing an order to assign him the relevant functions. Only to find the "elected" will have in each unit, since the report card is compiled for each of those in one copy, signed by the person leading the report card, as well as the head of the structural division (employee of the personnel department).
Information on the employee’s performance of duties under the main employment contract according to the principle “one position - one position” is entered in the time sheet. The fulfillment of duties in another position during the main working time by way of combining occupations or replacing a temporarily absent employee is not reflected in the report card. Also, performers working on the basis of civil law contracts are not included in the document. But if the employee is an internal part-time worker, then in the report card information on it must be reflected twice.
The basis for the appearance of a new position in the card, or, conversely, the exclusion of the old one, are personnel documents, namely, orders for employment and dismissal, an employment contract, etc. (paragraph 19 of the Basic Provisions on Accounting for Labor and Wages in industry and construction, approved by the letter of the State Labor Committee of the USSR, the Ministry of Finance of the USSR, the Central Statistical Bureau of the USSR dated April 27, 1973 No. 75-AB / 89 / 10-80).
Each employee is assigned a personnel number, which is affixed in all documents on the accounting of labor and wages and is retained by the employee under any circumstances. Moreover, as a rule, the personnel number of the dismissed employee is not assigned to any other employee for at least several years.
The completed report sheet shall be submitted to the accounting department at the end of the calendar month or at least once every fortnight if the advance on wages in the organization is charged for the actual hours worked.
The procedure for filling the sheet
So, the time sheet is necessary to reflect the time actually worked by the employee. At the same time, the normal working time is 40 hours per week or for the reference period, but in reality, deviations from this figure are possible as a result of the employee’s illness, absenteeism or just being late (or, conversely, when working in overtime). Accordingly, all such events should be reflected in the report card. So, one of the methods of accounting for working time in the report card is the registration of only these deviations. However, it is more suitable for situations where wages do not depend on the amount of time worked, for example, if an employee is given irregular working hours. Otherwise, the method of continuous registration of appearances or non-attendance at work is applied.
The order of filling the sheet is based on the system codes. So, each document position contains two lines. The top one is intended to reflect the conditional code of working time, the bottom one - for the amount of time worked. Alphabetic and numerical codes of attendance and non-attendance are given on the title page of form No. T-12. They also apply when filling out the form number T-13. So, if we are talking about normal working hours, then the code “I” or “01” is affixed in the upper lines, and in the lower lines - the duration of work in hours, minutes.
Time sheet
Overtime work. Overtime is recognized as work performed by an employee at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours (shifts) established for him, and in case of summed-up accounting of working time - over the normal number of working hours during the reference period (Part 1 of Art. 99 TC).
To account for the hours of "processing" per employee in the report card, two positions must be redeployed: one for the time worked within the normal range, the second for overtime. The first is filled in the general order. In the top line of the second position the code “C” or “04” is put down, and in the bottom line - the duration of the working time is indicated. On the basis of these data hours are paid "processing".
Work on holidays and weekends. In addition to overtime at an increased rate, work is also paid on a holiday or a day off. In the timesheet, such is indicated by the code “PB” or “03” in the upper line, and an indication of the actual hours worked in the lower one.
Day off The day when the employee took the day off is indicated in the report card with the code "НВ" or "28". In this case, the line on the hours worked is left blank.
Shift work, including night shifts. According to Article 103 of the Labor Code, in cases where the duration of the production process exceeds the permissible duration of daily work, as well as in order to use equipment more efficiently, increase the volume of output or services rendered, shift work - in de, three or four shifts. In this case, employees go to work in accordance with the shift schedule. Moreover, if the work shift is fully accounted for during the daytime, then the report card is filled in the general order. Work at night (from 22:00 to 6:00) is marked with the code "H" ("02"). If the change falls on the line of day and night time, it is advisable for an employee working in such a shift, simply to take two positions in the card.
Irregular working hours. For some employees, the employer has the right to establish irregular working hours - work hours, occasionally the employer has the right to involve the employee in the performance of labor functions outside the working hours established for him without additional payment (Art. 101 TC). In other words, overtime is not meant. "Processing" is compensated in this case by another means in the form of additional paid leave. Its duration is determined by collective agreement or internal labor regulations, but may not be less than three calendar days (Art. 119 TC).
Unfortunately, the Instructions do not contain explanations on how to keep track of working time with irregular schedules. However, it is advisable to reflect all the actual time worked, putting the code “I” or “01” on the top line, and actually hours worked on the bottom line. The main thing in order to prevent mistakes in payroll, to note that the employee is set irregular working hours. When providing an employee with an unregulated working day additional leave in the report card indicates the code "OD" or "10".
Part-time job. An employee can perform extra work both at the place of main work (internal part-time worker) and at other employers (external part-time worker). In the first case, as already mentioned, the information in the employee card is reflected twice: under one personnel number, but with different posts. At the same time, both the main work and the part-time work are indicated by the code “I” or “01”.
Note! According to Article 284 of the Labor Code, a part-time worker can work no more than four hours during a day, except for situations when he is free from work duties at the main place of work. However, in any case, within one month, the working time of the part-time worker cannot exceed half the monthly standard of working time established for the relevant category of workers.
Part-time work. Under it refers to part-time employment of an employee during the working day or week. For example, an employee may work six hours a day instead of the prescribed eight, or work three days a week instead of five days.
The initiative for part-time work can come from both the employee and the company. This means that during the working day or week the employee is only partially employed. For example, his working day is only 5 hours or work week takes only three days. If a similar schedule was initiated by an employee, then in the timesheet the code “I” or “01” is indicated in the cells of the top row, and the time worked (in hours and minutes) in the cells of the bottom row. If part-time work is entered by the employer, the code “НС” or “25” is put on the top line, and the time worked on the bottom line.
Business trip When an employee is sent on a business trip, the days that fall on her time are indicated in the report card with the letter code “K” or the numerical indicator “06”. At the same time, the number of hours worked is not reflected.
It should be noted that a business trip may well capture weekends and holidays. In general, they are also marked with the code "K". However, if the employee, while on a business trip, was working on a weekend or holiday, by order of the company, then it is necessary to put down the code "PB" or "03". As follows from clause 5 of the Provision on the specifics of sending workers on business trips, which was approved by Government Decree No. 749 of October 13, 2008, these days must be paid to the employee in an increased amount in accordance with article 153 of the Labor Code. Similarly, the “K” code must be abandoned if an employee is sick on a business trip and has a sick-list. During the days of illness, the employee is paid a temporary disability allowance and should be marked with the code “B” or “19”.
Temporary disability. As already mentioned, the days of illness in the report card are marked with the code "B" or "19". Moreover, it is necessary to affix it, including in respect of weekends, falling at the time of illness. This conclusion follows from the fact that temporary disability allowance is paid for calendar days of illness (clause 8 of article 6 of the Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-ФЗ).
Vacation Both working days off and holidays in the report card must be marked with the code “OT” or “09”, since the rest is granted to employees in calendar days. However, holidays that fall during the holidays are marked with the code “B” or “26”, since they are not included in the calendar days of vacation (part 1 of article 120 of the Labor Code).
Absence for unexplained reasons. Not always the reason for the absence of an employee in the workplace is clear immediately. Accordingly, it is impossible to put down any code in the report card. If we are talking about the beginning of the month, then the cell can be left empty, until the situation is clarified. If the reason is not identified at the time of submission of the timesheet to the accounting department, then the timesheet is submitted with a no-show mark for unexplained reasons, that is, with the code “NN” or “30”. At the same time, after the employee submits vouchers, he will have to be replaced. The necessary code in this case is indicated in an additional sheet, which is attached to the main report card.
Alevtina Kryukova, Expert, Center of Economic Information LLC