What are the varieties of remontant raspberries most fruitful. What is a repair raspberry and how to distinguish it from the usual
Practically every summer resident attentively follows the berry crop on his own plot, but this crop happens only once a year and, for example, if you have tasted strawberries, currants or raspberries in early summer, then in the fall you will not have to try fresh and fragrant berries. We propose the use of remontant varieties that bear fruit twice a year and we want to consider this method of growing raspberries.
Features of raspberry varieties: how to distinguish
Repair raspberry - berry bush, which is practically no different from ordinary crimson, it can give, as one, and two crops in the summer, it all depends on the breeding variety that you plant in the summer cottage. Right combining varieties and following all the rules of agricultural technology, you can provide yourself with a good harvest for the whole warm season. If the remontant raspberry is grown in conditions when care for it is weak, then this is reflected in the second crop - all the strength and sap of the berry bushes go to the formation of the berries of the first crop that ripens in late June. The second harvest turns out to be worse quality - small, dry berries, reducing their number. In order for the first and second crops to be of excellent quality, it will be necessary to work well and ensure that the plant has the right care - timely pruning, watering and feeding. Many summer residents, due to lack of time, choose to use remontant varieties for only one crop. Today I would like to consider ways of caring for a remonty raspberry, crossing them with caring for raspberry ordinary. We will do this in order to understand how to properly optimize the production of a crop, form it and determine it for the period necessary for us.
What does "repair raspberry" mean? (video)
Planting raspberry repair
Planting occurs seedlings, than does not differ from landing of a raspberry ordinary. Seedlings are planted in the soil in spring or autumn. If the process occurs in the fall, then it must be carried out in a warm period so that the raspberry can take root. The bushes are planted in the planting holes 30x30 cm. The depth is also about 30 cm. If you decide to plant the raspberries in rows, then keep at least one meter between them. This will enable good ventilation and disease prevention.
When planting, each hole is filled with organic fertilizers - rotted manure, peat or humus. The roots of each seedling straighten and fall asleep soil, well compacting. Then pour one bucket of water under each bush. The soil is mulched, and the top layer is constantly loosened.
When planting, the repair raspberry changes only a few moments, it is necessary to root it at a greater depth, up to 50 cm. Saplings should be laid horizontally in the holes and after cutting it with the ground, cut off the entire above-ground part.
Pruning after fruiting
Pruning raspberry pruning is done every year, it contributes to obtaining a quality crop. It should be removed shoots that otplodonosili. In the case of summer varieties, all shoots are subject to removal, they are cut in July, to ground level. You can leave the strongest shoots of this year to enhance future yields. Raspberries are also pruned at the end of the period of autumnal fruiting, in November-December, and all shoots are cut, leaving even young one-year-olds. This enhances the future summer-autumn harvest.
Spring sanitary pruning
If you have not done autumn pruning or simply decided to form annual shoots in the spring, then this should be done very carefully. Since the raspberry begins to bear fruit from the top, then cutting the stems from the top and forming their growth, you, thereby, delay the start of fruiting, and possibly reduce the yield.
If you want to ensure a high yield and quality of berries, then you should spend only spring sanitary pruning. Those branches and stems that have not survived the wintering are removed, or they are cut to the first healthy bud. Pruning should occur in April, when the kidneys swell and determine healthy simply.
Now, knowing how to prune a raspberry bush, you will be able to regulate the time of ripening. In addition, you can adjust the quality of the crop, which is a considerable advantage.
Raspberry remontant and ordinary: how to distinguish (video)
What is good pinching shrub
Circumcision of the upper parts of the stems is necessary in order to delay the fruiting period slightly. If necessary, pruning is carried out in May, the upper part of the stem is cut, 20-25 cm.
If we are talking about early and middle-late varieties, then pinching will be relevant only for the latter. Here, a small amount of berries is maximally compensated by the later periods of ripening of the crop. As a result of the correct pinching, in June it will be possible to try early raspberries, in July - to try middle-late, and in August-September to enjoy the taste of the remontant one.
Density adjustment
Proper care of the remontant raspberry and ordinary regulates the quality of the crop, the opponent of which is the thickening of the raspberry. Thickening leads to inhibition of berry bushes and often provokes fungal diseases., which negatively affect not only the quality of the fruit, but also on the life of the plant itself.
It is advisable to cultivate a crop in strips, the distance between which should be about one meter. If a trellis is used, the strip remains 20–35 cm wide, with free growth - 50 cm.
On each meter of the formed strip, 15–20 shoots are left, half of which should be two-year-old fruitful, and the second half should be annual, replacement shoots.
Fertilization
Top dressing should be applied to the soil in March. For balanced soil apply complex fertilizers (nitrogen-potassium-phosphorus). If the soil needs nitrogen, the leaves of the raspberry turn yellow, and then additional addition of 15-20 g of ammonium nitrate, diluted in a bucket of water, is required per 1 square meter.
Second feeding produced before flowering and fruit ovary - 3 tbsp. l double superphosphate diluted in 10 liters of water, add 2 tbsp. l potassium sulfate and give a little brew. This amount of top dressing is calculated on 1 m2.
Next feed produced in the fall, after cutting the shoots. It passes in the same way as the previous one, only the amount of fertilizer decreases - 1 tbsp. l potassium sulfate and 2 tbsp. l superphosphate on a bucket of water.
In addition, remontant raspberry and ordinary, like other fruit-bearing shrubs on the territory of your site, need organic fertilizers. Make them necessary, at least 1 time in 3 years. Use cow, horse, sheep, pork or goat manure, 5 kg per square meter of planting.
Repair raspberry variety Heracles (video)
Plant protection
All sorts of diseases and pests that often attack the dacha plants do not bypass the raspberry. Therefore it is worth thinking about its protection. Use chemistry for this process is recommended only before flowering. From fungal diseases - in March-April. Or after the harvest. Use copper-containing drugs and Bordeaux liquid.
From harmful living creatures that attack raspberries, use special biopreparations. Some of them are effective for only 7-10 days, so be careful when you check the plants for pests at the end of this period. You can handle raspberry and manual way, but only if the plant is not completely affected by the beetle or larvae. In this case, they can be collected by hand, and the stems can be saved; in a different situation, the stems and leaves are subject to cutting and burning, preferably outside the suburban area.
Shrub protection from frost
Planting and caring for the repair raspberry is a laborious task, but it can be in danger if one more rule is not observed - protection during the winter period.
Preparing for winter is better to start early, in September. After you have collected the last harvests and cut off the extra stalks, the remaining annuals, tilt to the ground and press to the first snow, which will soon soon, covered them in the first place. This also applies to winter-hardy varieties, since the plant dries out very hard in severe frosts. It is also required to ensure that the snow cover covers all the stems at least 50 cm thick. If the winter is with little snow or snowless at all, then the stems should be pressed down to the ground with plywood or board. You can fall asleep dry leaves. It is possible to lift bushes in the spring only when all frosts disappear, even at night.
Popular and high-quality varieties
In each individual country, a multitude of craftsmen work on selection projects who, over the years of their activity, produce varieties capable of growing and bearing fruit in each specific region. At the moment, a huge amount of ordinary and remontant raspberries, which is intended for planting in our country, have been bred. We can refer to them the following, the best varieties of remontant and ordinary raspberries:

Knowing how to care for a repair raspberry, you can grow a good harvest.. It remains only to find out how it is more appropriate to use it. Of course, with a berry, you can cook pies and pies, cook compotes and jelly, but do not forget to make raspberry jam, which in addition to the huge amount of useful properties carries with it excellent anti-cough indices.
Rating 2.67 (3 votes)Attention, only TODAY!
The repair raspberry is often called continuously fruitful, or autumn-bearing fruit.
"Indian Summer" - the firstborn of the national selection of raspberry remantle. Although suitable for cultivation in the south of the country, it marked the beginning of the development of new varieties by means of interspecific hybridization. Thanks to the invaluable contribution of Professor IV Kazakov, modern domestic remontant raspberry varieties are distinguished by early ripening and high yields. "Indian Summer" 1 and 2, "Diamond", "Golden Domes", "Augustine", "Elegant", "Hercules", "Apricot" - varieties made to the State Register of the Russian Federation.
Harvest in the first year
Initially, during the season, the repair raspberry produced two crops. The first was formed on two-year-old shoots that threw out new fruit branches in the spring. This significantly weakened the plant, reducing the ability to re-fruiting. Over time, the breeders focused on getting a "second" crop, hence, in fact, remontrance.
At the end of fruiting, full root cutting of the bushes is made. This not only increases the future harvest, but also protects it from pests, which are mainly focused on the periods of fruiting of ordinary raspberries. Stems it protects against freezing winter. The new shoots, grown in spring, grow ripe and give a generous harvest, without requiring tying to the trellis.
The disadvantages of repair raspberries
Against the background of indisputable advantages, the lack of remontant varieties is the scarce formation of root branches, and, consequently, replacement shoots, which, however, facilitates care.
There are several ways to fill the shortage of planting material and increase the multiplication factor. The first is the harvesting of green stalks. It is produced during the period of awakening and the formation of root buds (May-June). To do this, choose three-centimeter above-ground shoots with mandatory bleached (underground) area.
The second - stimulating the development of root branches - cutting out the central part of the root (with a diameter of not more than 1-1.2 dm) on a 2-3 year old raspberry bush, with the subsequent development of up to 20 new future seedlings. The third is sowing of seeds, with more than half of the seedlings retaining their repair properties.
Planted seedlings in the lighted areas in loose, light soil, with a density of 1.5 m by 0.7 m, with a depth of 30 cm. Even with minimal care - regular watering, mulching 10 cm with a layer of overheated organic matter, applying nitrogen fertilizers (at the beginning and in late spring) - the yield of the bush reaches 3 kg.
Doctor of Agricultural Sciences I. KAZAKOV, Candidate of Agricultural Sciences S. EVDOKIMENKO, Kokinsky stronghold of the All-Russian Breeding-Technological Institute of Horticulture and Nursery (Bryansk region). Photo I. Kazakov.
It is impossible to name the completely new berry culture remontant raspberry, because its first varieties were obtained almost a hundred years ago. Naturally, the selection all these years did not stand still, and modern remontant varieties created by Russian scientists are unlike their ancestors. As a result of various combinations of crosses, domestic breeders created raspberry varieties of repair type that have no analogues in the world. The fruits of these varieties begin to ripen in early August, the height of their fruiting falls at the end of August - early September.
Indian summer! Wondrous rubies
caressed quiet dawn.
Generously remontant raspberry
Falls in the basket of September.
I. Kazakov
The raspberry owes its popularity to the great taste and unique aroma of berries with a high content of vitamins and other biologically active substances with unique healing properties. Unfortunately, it is not long to feast on fresh berries: with a wide choice of varieties (from early to late) - a little more than one month, from the end of June to the beginning of August. In addition, adverse environmental conditions, pests and diseases, weather anomalies significantly reduce the yield of berries. Extend the season of consumption of fresh raspberries to 3-3.5 months - from August to autumn frosts - and you can significantly increase the harvest using remontant varieties.
Remontrance, as the ability for continuous (throughout the vegetative season) fruiting, is a well-known phenomenon. For example, many gardeners grow remontant varieties of garden strawberries, the first crop of which ripens simultaneously with ordinary varieties. But unlike ordinary remontant varieties, after the first harvest, the inflorescences are thrown away, they bloom and bear fruit again. Thus, the fruiting is almost continuous. Repair raspberry varieties have another property: they are able to bear fruit on both biennial and annual shoots. In principle, such varieties can give two harvests: the first - as in ordinary varieties and the second - on annual shoots. However, obtaining two harvests in one season is impractical, since the first harvest on biennial stems weakens the plants and delays the start of ripening of the second, usually more valuable crop. Therefore, it is much more profitable to grow remontant raspberries as an annual crop and get only a late summer - early autumn harvest. With this technology in the first half of the summer annual shoots grow intensively in remontant varieties. Toward the middle of summer, fruit sprigs appear, then the raspberry blooms, and at the end of summer the crop ripens.
The popularity of remontant raspberries is due to the fact that, thanks to its biology and special cultivation technology, it is devoid of many of the drawbacks that ordinary raspberries possess. First, the problem of the shocks' winter-hardiness disappears, because the above-ground part of the raspberry is cut to the ground level in the fall, and there is nothing to freeze. Secondly, the maintenance of planting is simplified, since there is no need for cutting the otblodonosivshih stems, bending the shoots to the ground and shelter for the winter. Low bushes (up to 1.5 m) do not need repairing raspberries, and the installation of a trellis and the garter to it shoots. Thirdly, removing the otter-bearing stems from the garden in the fall, removes a significant part of the infection and wintering pests. The reparative raspberry and such dangerous pests as the raspberry beetle and the raspberry-strawberry weevil do not cause damage, since the phenophases of their development and plants do not coincide. All this allows you to grow remontant raspberries without the use or with limited use of chemical agents and thereby obtain an environmentally friendly berry.
Despite these advantages, the repair raspberry for a long time did not "inhabit" the gardens of the Russians. The reason - the lack of reliable varieties that can ripen before the onset of autumn frosts. Until the beginning of the 70s of the last century, domestic breeders did not work on the creation of remontant-type varieties, although in some cases the forms giving berries on the tops of annual shoots were distinguished. The raspberry varieties of foreign breeding with autumn type of fruiting were of little use for the central part of the country: by the beginning of the frost, their crops had time to ripen only by 15-30%.
Bryansk DYVO
Purposeful selection of repair raspberries in our country has been carried out for a little more than three decades. The leading institution implementing this program in Russia is the Kokinsky stronghold (Bryansk region) of the All-Russian Breeding and Technological Institute of Horticulture and Nursery, where a model of the “ideal” remontant raspberry variety for this region, including more than 30 traits, was developed, donors and genetic sources of these signs. Over the past period, more than 300 interspecific remontant forms of raspberry have been economically and selectively selected, and more than 250 thousand seedlings isolated from controlled crosses, free pollination and inbreeding (forced pollination) have been obtained and analyzed on their genetic basis.
The main objectives of breeding - the creation of high-yielding varieties adapted to adverse environmental factors, having high taste, commodity and technological qualities of berries, suitable for mechanized harvesting.
A reliable level of adaptation of remontant raspberry varieties in central Russia means the ability of plants to fully complete their fruiting before the onset of autumn frosts with a sum of active temperatures (t\u003e 10 ° C) of 1800-2000 ° C and a frost-free period of at least 130 days. They must be resistant to the main pathogens and pests, tolerate soil and air drought without a noticeable decrease in yield, accumulate a minimum amount of ecotoxicants (heavy metals, radionuclides, herbicides) in the berries.
The most important indicator of the competitiveness of a variety, especially in a market economy, is the quality of the fruit. In practical breeding, work is carried out in three directions: 1) the external attractiveness and marketability of the berries; 2) high taste; 3) high content of biologically active substances.
One of the main objectives of the selection of remontant raspberries - increasing the yield of its varieties. In modern breeding programs, the yield from a raspberry bush is not less than 2 kg of berries or 15 tons per hectare with a mass of fruits of 6-8 g.
By creating remontant raspberry varieties suitable for machine harvesting, the task of obtaining genotypes with straight bush habit, high density of berries, good separation from fruit trees and harmonious ripening is solved.
As a result, more than 20 first domestic varieties of raspberry remontant type were created, of which eight (Abrikosovaya, Avgustina, Indian summer, Indian summer-2, Diamond, Heracles, Golden domes, Elegant) are included in the State Register of selection achievements of the Russian Federation approved for use. The rest pass state and production testing.
Repair raspberry varieties give from 1.7 to 3.7 kg of berries from a bush. Under favorable soil and weather conditions, special yields — more than 20 tons per hectare — are characterized by the Atlas, Bryansk Miracle, Ruby Necklace, and Elegant varieties. In the interspecific offspring of raspberries, it was possible to isolate remontant hybrids, the harvest of which fully ripens in late August - first half of September. Of particular interest are the Indian Summer-2, Bryansk Jubilee, Reliable, Eurasia and Penguin varieties, combining the early ripening of berries with a vast area of autumnal fruiting and other valuable traits.
Modern inter-species varieties of remontant raspberries are large-sized, according to this indicator they can easily compete with the summer assortment of raspberries. Among the varieties with an average weight of berries 3.1-4.5 g - Augustine, Indian Summer, Indian Summer-2, Bryansk Jubilee, Golden Domes, Firebird, Mulatto, Nadezhda, Elegant, Amber. Golden autumn, Hercules, Ruby necklace, Merchant, Atlanta, Orange miracle, Bryansk miracle are the most large-fruited, the weight of their berries reaches 7-11.5 g, which is two to three times the size of the most common varieties raspberries. These genotypes are valuable complex donors for further work on improving remontant forms of raspberries. They are of great interest for growing in conditions of central Russia.
An important indicator is the one-dimensionality of the berries. By this indicator stand out: Augustine, Diamond, Firebird, Penguin, Elegant. It has been established that the one-dimensionality of berries, to a greater degree than large-fruited, depends on agricultural technology. Adequate nutrition and watering provide a manifestation of the hereditary size of the fruit.
In the conditions of market relations, aesthetic components are of particular relevance. The most popular with gardeners are varieties with large, leveled in size, brightly colored fruits - red, raspberry, yellow, apricot, black.
The most attractive bright berries are distinguished: Indian Summer-2, Ruby Necklace, Bryansk Jubilee, Firebird, Snegirek, etc. Intensively colored fruits with strong shine form the varieties of Augustine, Diamond, Mulatto, Kupchikha and elite forms 1-125-1, 26 -139-1, 18-183-1, etc. The berries of the varieties Apricot and Golden domes have an unusual golden-apricot color. Large “lanterns” of berries of amber-yellow color of the variety Golden Autumn look spectacular on the branches. Very beautiful fruit from the variety Orange miracle.
The “turned”, elongated-conical shape, large fruits are distinguished by the genotypes of Golden Autumn, Heracles, Merchant, Atlas, Orange Miracle, Bryansk Miracle. The original elongated-cylindrical shape of the berries - "ladies' finger" - is of the Ruby Necklace variety.
One of the main quality indicators of berries is their taste, which is largely determined by the ratio of sugars, organic acids and other biologically active substances. It is known that the specific and varietal composition of raspberries varies considerably in this indicator. Unfortunately, the fruits of the raspberry of most hybrids of the first generation, the origin of which, in addition to the red raspberry, was attended by black raspberry, hawthorn, fragrant and wonderful, are somewhat inferior in taste to the berries of the best varieties of the usual type. Four to five generations of these parental forms with raspberry red turned out to be insufficient to create genotypes with a dessert taste of fruits. However, interspecific remontant varieties created in further generations have good taste qualities of berries (4.0–4.1 points). Among them: Indian summer, Apricot, Augustine, Indian summer-2, Reliable, Diamond. The result of the last years of many years of focused work was the creation of high-yielding remontant forms with the dessert taste of berries and a subtle “raspberry” aroma (varieties Orange Miracle and Firebird).
The density of the berries is considered the decisive factor determining the preservation of the berries during harvesting and transportation - this is a necessary requirement for machine harvesting. Raspberry varieties differ significantly in this indicator, which often determines their suitability for one or another type of processing.
The density of berries depends significantly on weather conditions. A significant decrease in density (up to 50%) is observed in all varieties during rainy as well as during extremely hot seasons. The formation of a thicker skin of the stones leads to dry and warm weather, as well as a contrast change in day and night temperatures (the amplitude of oscillations is up to 15–18 ° C). For this reason, the berries of the autumn harvest of remontrant raspberries, as compared with the summer harvest, are usually denser and more suitable for machine harvesting.
Unique genotypes with high berry density (Penguin, Eurasia, Ruby Necklace, Bryansk Miracle, Heracles, Atlas, elite forms 15-146-2, 23-70-2, 3-62-1) were created by stepwise hybridization of interspecific forms among themselves. Some of them (Penguin, Eurasia, Atlanta), along with increased density of berries, are distinguished by good separability from the fruit bearing, upright bush habit, as well as early and friendly ripening. According to basic characteristics, these varieties meet the requirements of machine harvesting.
AUTUMN BERRIES IN YOUR GARDEN
For the successful cultivation of remontant raspberries, you need to know some secrets of agricultural technology. So, it should be planted in the most lighted areas of the garden. Even a slight shading, which is permissible for common raspberry, significantly delays the onset of ripening berries in varieties with autumnal fruiting and leads to a decrease in yield.
In central Russia, it is better to place the plants on the south side of the house and fences, in areas protected from cold northern winds by fruit trees or berry bushes. A microclimate is formed in such corners: the snow melts faster and the soil warms up in the summer, due to the accumulation of solar heat by the wall or fence in the summer is much warmer, and in the fall light frosts "come" a little later. It has been noticed that the earlier the snow leaves the landings of raspberries and the growth of shoots begins, the earlier the first berries ripen and the higher the yield.
When digging for light and medium loams, differing in average fertility, it is advisable to add to one square meter two or three buckets of well-decomposed humus, compost or high (red) peat and a glass of complex mineral fertilizers enriched with microelements (Kemira wagon, Stimulus, Growth, nitroammofosk ). Complex fertilizers can be replaced with one cup of superphosphate and a glass of potassium sulfate. Fertilizers are applied to the planting pit: one or two buckets of well-decomposed organic fertilizer and four to five tablespoons of complex mineral. Instead of minerals, organic fertilizers can be applied during soil preparation, increasing their dose 1.5 to 2 times, and the lack of potassium and trace elements in the soil can be compensated by adding wood ash to a half-liter jar per 1 m 2. Lime or dolomite flour is used on acidic soils.
A year before planting, on the site where they plan to grow raspberries, they feed the siderats, in the fall they are crushed and buried in the soil. You can not plant the plants in places where the previous year grew solanaceous crops (potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants) that have common pests and diseases with raspberries.
In the conditions of central Russia, the optimal time for autumn planting of remontant seedlings is the period from the beginning of October to the steady autumn frosts. During early autumn plantings (until the second half of September), the plants do not take root well and overwinter unsatisfactory, because the biorhythm of development of the repair raspberry differs significantly from the biorhythms of other berry bushes, including ordinary raspberries. In remontant varieties, the outflow of plastic substances into the roots, the growth of the root system and the accumulation of nutrients in it occur somewhat later.
Plants are planted in pits with a diameter of at least 30-35 cm and a depth of 25-30 cm. When planting, both the penetration and the protrusion of the root neck of the seedling are unacceptable. For properly planted plants, the root collar should be at the level of the soil surface, and only on light soils its depth by 3-5 cm is permissible. With a deeper planting, the seedlings develop slowly, their seedlings appear out of time, and the plants often die. If the root collar is too high, drying of the roots in the spring-summer period and their freezing in winter are possible.
For most varieties with an average soil fertility, the distance between the rows is 1.5-2.0 m (sometimes up to 2.5 m), between plants in the row - 0.7-0.9 m. Shrubs with this arrangement are much better illuminated.
You can plant such a raspberry in the garden and in the form of small, well-lit groups (one or three plants), reducing the distance between them to 50-70 cm. Raspberry varieties that form only one or two shoots of replacement in the bush, it is advisable to put two seedlings in the hole . It is desirable to mulch the soil around the seedlings.
Often, after planting, the seedlings are completely cut off from the seedlings. This is done in order to prevent the spread of dangerous diseases, the pathogens of which overwinter on the stems of plants. However, the removal of the above-ground part of the seedling has negative consequences. In the part to be removed, nutrients important for a young plant are concentrated, which are necessary for bud break in spring and intensive growth of roots and annual shoots. It is thanks to the leaves on the left part of the seedling for the first few weeks that the whole plant is nourished, the roots are stimulated. Therefore, seedlings with uncircumcised aerial parts take root better.
Caring for remontant raspberries is reduced to regular loosening of the soil, fertilizing, weed control and, if necessary, watering. Simultaneously with the loosening and mulching of the soil from the second or third year after planting, fertilizers are introduced. In the first half of summer, during the intensive growth of raspberry shoots, preference is given to nitrogen fertilizers, in the second half - complex, containing nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and a set of trace elements. Doses of fertilizer are selected, guided by the instructions on the packaging, as well as the level of fertility and the quality of preplant soil preparation. Particularly effective feeding with liquid organic fertilizers: fermented (one to two weeks) infusions of bird droppings (the ratio of fertilizer and water 1:20) or mullein (1:10 ratio).
In the fall, with the onset of stable frosts (in central Russia - at the end of October or in the first half of November, in the southern regions - until the end of November) all annual shoots are cut off from the repair raspberry. (This can be done in early spring, before the beginning of the growing season). The remaining garbage and fallen leaves are composted and burned. The soil is loosened shallowly; if the weather is dry, water and mulch. Hurry with trimming should not be. It can be done even when the top layer of soil already freezes through or even the first snow falls. Before the soil freezes from the leaves and shoots, nutrients will be supplied to the roots, which will allow the plants to develop more intensively next year. In this way, a one-year crop formation cycle is maintained annually.
The high annual yield of new varieties and the environmentally safe technology of their cultivation create real prerequisites for the successful cultivation of remontant raspberries in both industrial and amateur gardens.
Sadovod - note
MALINA - ELIXIR OF HEALTH AND LONGEVITY
Raspberry berries are rich in fiber (4.8-5.1%), which stimulates the bowels and promotes the removal of harmful substances from the body. A beneficial effect on the digestion and pectin contained in the berries. A valuable component of the fruit is biologically active substances: ascorbic acid (up to 50 mg), catechins (up to 80 mg), anthocyanins (100-250 mg), vitamins B 9, B 12, E, etc. Of the mineral compounds in raspberries there are quite a few iron (1200 mg), zinc (200 mg), copper (170 mg) and manganese (210 mg per 100 g of the crude product).
A special substance has been found in the raspberry fruit - beta-sitosterol, which prevents the deposition of cholesterol in the walls of blood vessels and, consequently, the occurrence of sclerosis. According to the content of beta-sitosterol, this berry is second only to sea buckthorn. The high hematopoietic effect of its fruits has been proven, the use of which helps to prevent leukemia.
Not only raspberry berries, but also leaves, inflorescences, stems, and roots have healing properties. In raspberry leaves, for example, vitamin C content is 8-10 times higher than in berries.
In October, collect the remaining buds on the branches, flowers, leaves, green berries. Rinse freshly harvested leaves with cold water, dry them, put them in a bowl, close the lid and leave until they are tucked in. Then roll your palms into tight rollers, cut the rollers into small pieces and wrap in a towel, slightly moistened with water. In this form, soak for 2-3 days without access of light, then immediately dry in the oven or dryer at a temperature of 50-60 o C.
Delicious, aromatic tea is obtained from the flowers of raspberry. Brew it as usual tea: 1 tablespoon per cup of boiling water. Well add a slice of lemon and a teaspoon of honey.
In order to have a raspberry harvest in the first year after planting, gardeners grow remontant varieties on their plots. They are cultivated both in the middle belt of the country and in the south of Siberia. Most varieties have time to completely otplodonosit before the onset of frosts, the harvest from one bush reaches 6 kg, and the mass of one berry - 15 g. These varieties can withstand short-term frosts to -5 degrees and continue fruiting. Pests and diseases are the same as those of common raspberry, but the overall susceptibility to diseases is less.
What is repair raspberry?
Remontrance, the ability of plants to bear fruit several times during the growing season, with respect to raspberries has a different meaning. Ordinary varieties give fruit twigs in the second year after planting. Raspberry remontant forms flower buds and berries on annual shoots. The rate of fruit ripening does not depend on the light of the day, as for the remontant strawberries, but on the period of appearance of the fruit branches. Therefore, these varieties are precocious. Traditionally, the name “remontant” has taken root.
In amateur gardening, berries are harvested twice a year - at the beginning of summer from one-year stems, and in early autumn from two-year-olds. But such a cultivation scheme weakens the plants and reduces the quality of the second, more abundant crop. Therefore, it is necessary to annually support the annual cycle of plant development.
Advantages of remontant varieties:
- high yield (2-3 times more than conventional varieties);
- fresh berries ripen until frost and the first snow;
- good winter hardiness due to the absence of the ground part after pruning in the autumn;
- berries can persist for a long time without spoiling, so they can be harvested once a week;
- agrotechnical features create unfavorable conditions for reproduction;
- requires the introduction of fewer chemicals to control pests, the harvest of berries is environmentally friendly;
- autumn mowing (trimming) of the branches eliminates the need for their shelter for the winter and garters for trellis in the spring;
- precociousness of varieties determines a high level of their profitability for farmers' garden farms;
- the ripening of berries at the end of summer allows for a higher yield, since during this period there is an intensive wetting of the earth by rains. This is especially noticeable in the southern regions of Russia, where the beginning of summer is accompanied by dry and hot weather.
Among the disadvantages are the increased need for fertilizers and the relative difficulty of reproduction of seedlings.

Varieties of raspberry raspberry
One of the first varieties of remontant raspberries in domestic horticulture was the Indian Summer variety, obtained by crossing the American variety Sentyabrskaya with the Russian hybrid. As of 2017, 19 varieties of repair raspberries in Russia have been registered in the State Register of Breeding Achievements. There are other species that are grown in farms and breeders.

Monomakh's hat
Recommended for southern areas, as the ripening of berries occurs late - in late August. When conducting special agrotechnical measures that increase the growing season, can be cultivated in a short summer.

Dense berries of bright red color have an elongated conical shape, their weight is on average 6-7 g, and under good growing conditions it can reach 14 g. It is one of the most large-fruited varieties. The yield of berries from the bush - up to 5 kg. Berries are easily separated from the stem. The shoots are powerful, with a small number of thorns.
Hercules
Straight-growing shloboraskidisty bush. Annual shoots purple. Stems have a strong spike. It gives a lot of offspring, so it breeds easily. The berries are dark red, conical in shape, dense, the average weight is 7 g; ripening occurs in early August. Productivity - from 3 kg from a bush.

Good resistance to pests and diseases. It is best cultivated in the central part of Russia (Bryansk, Moscow, Vladimir, Ivanovo, Kaluga, Ryazan, Smolensk, Tula regions).
Diamond
A feature of the variety of berries is a pronounced brilliance. The color of the berries is ruby, the annual stems are purple, biennial are light brown. Thorns on stems only at the base, few leaves. The mass of conical berries at the first harvest reaches 12 g. Harvest from one bush below - up to 3 kg. The flesh is tender, without aroma.
![]()
Stems under the weight of the crop lean to the ground and require a garter on the trellis. The number of shoots that form is average, 5-6 shoots per season. It is characterized by high heat tolerance. Recommended for central areas.
Orange Miracle
The berries have an unusual bright orange color and a high content of vitamin C in the pulp. The average mass of berries - 5 g, maximum - 10 g. The shape of the fruit is elongated-conical. The bush is powerful and tall, it can have more than a hundred berries.
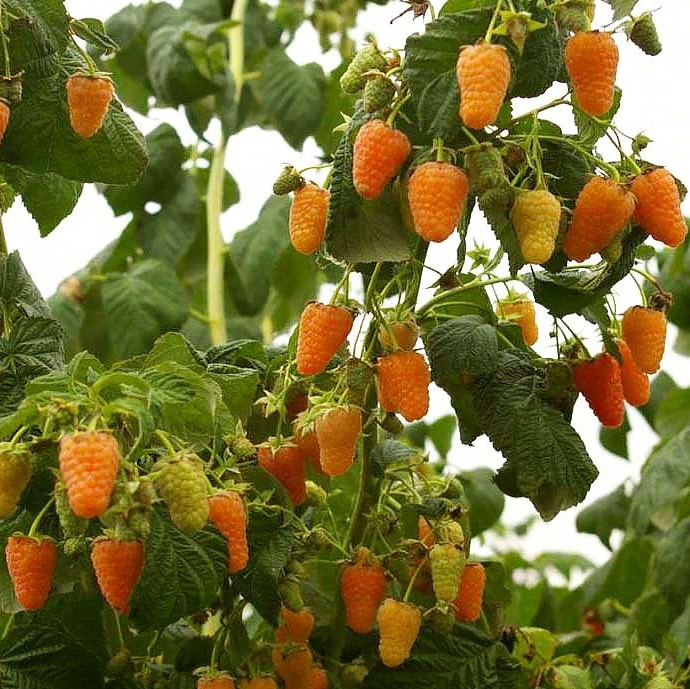

Forms a large number of shoots. Thorns average, mostly located at the base of the stem. Resistant to diseases and pests. Resistance to heat is average. It can be cultivated in all regions of Russia.
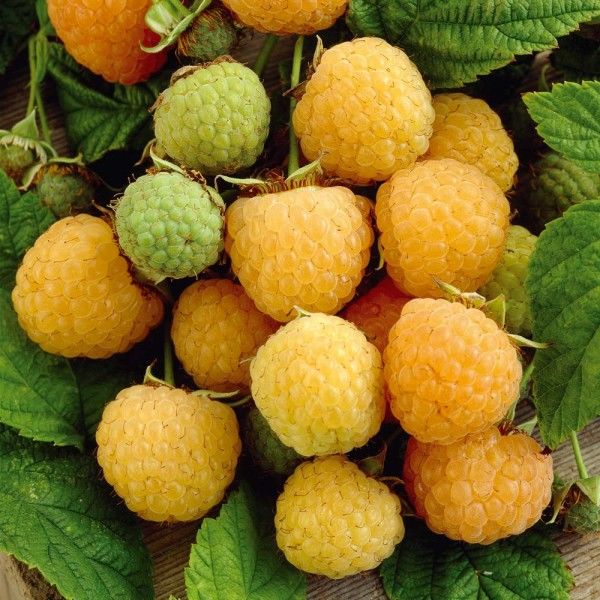
Amber
Universal variety, can be grown in all areas, including the northern. Bush powerful, medium height. A mass of bright orange berries - up to 7 g, spherical shape; the flesh is tender, has no flavor. Resistance to disease and drought is moderate. The spikes on the stem are only at the bottom. The number of formed shoots is average - 6-9 pcs. One- and two-year-old shoots of light brown color. Elegant.

The variety is known for its high yield - 140 kg / ha. The berries are small, on average 3.5 g. The bush is spreading, the stems are powerful. Annual shoots are green, biennial - light brown. Good resistance to diseases and pests of raspberries. Thorns mainly in the lower part of the stem. It is used for cultivation in the central regions of Russia.
Features of planting and feeding
The best time for planting is September-October, after the leaf fall and a month before the ground is freezing. During this period, cool and wet weather is established, contributing to better rooting, and the onset of cold weather delays the growing season. Seedlings have time to prepare for winter, and in the spring they begin to grow. By September, they have a good root system, which is a determining factor in their survival and resistance to drying.
The development of the roots continues to a temperature of -2 degrees. The length of the ground part of the planting material should be 25-30 cm. Seedlings should be carefully checked and if there are tuberous swelling on the roots (root cancer), cut them out and process with a one-percent solution of copper vitriol.

You can plant in early spring before the buds are blossomed. For this, wintering seedlings are instilled in the ground in an inclined position and watered. In the spring they are put on a permanent place. But such seedlings have an undeveloped root system, it is difficult for plants to provide themselves with enough moisture, and they develop more slowly. The short vegetative cycle of a plant determines the increased requirements of remontant raspberries for the preparation and quality of the soil.
Fertilizers
Before planting seedlings, 2-3 buckets of compost, manure or humus and universal mineral fertilizers with microelements should be applied - 1 cup per 1 square meter. m of soil. Next, a deep digging of the earth is carried out for 2 bayonet shovels (0.5-0.7 m), since remontant varieties develop a core root system reaching 1.5 m in length. When digging, remove all rhizomes of weeds.
Repairmen varieties respond very well to fertilizers, especially to nitrogenous ones: the more nutrition, the richer the harvest of berries. You can only use organic matter, but for this you need to double its amount and add ash in the amount of 0.8 kg / sq. m to replenish stocks of potassium in the soil.

Since fresh organic matter can be a source of phyto-diseases, it is better to dig holes and add fertilizers there 1.5-2 months before planting. Also, it is not necessary to apply fertilizer containing chlorine before planting, as the roots of the plant are sensitive to it.
Such fertilizers can be used under the autumn digging with, but at the same time, most of the useful substances are washed away with melt water.
Effective feeding of remontant raspberries during the planting season helps to preserve the soil yield for several years.

Ground Requirements
The best soil for all grades of raspberry is loose and nutritious. The plant loves well-lit places and warmth, which is necessary for the rapid ripening of berries. The root system does not tolerate high groundwater levels. They should lie no more than 1.5 m from the surface of the earth. Considering this, the southern slopes are the most favorable place for landing.
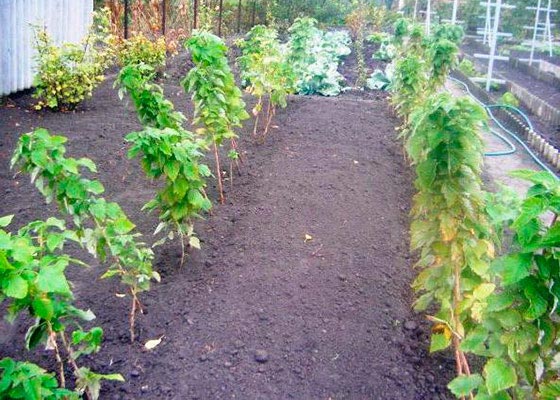

For heavy soils, it is acceptable to plant a remontant raspberry on prepared high ridges (with the addition of peat and sand), which are better warmed in spring and aerated. In the southern regions, such agrotechnical practices can lead to the drying of the soil.
Landing pattern
Under the seedlings dig holes with a diameter and a depth of 0.3 m at a distance of not less than 0.7 m from each other and 1.5 m between the rows. On poor soils, the distance between seedlings needs to be increased. The inline design provides the best light conditions and increases fruiting, as opposed to a solid planting.
The nesting method of planting with a step of 1.5-2 m also shows good results in the agricultural technology of raspberries. Fertilizers should be put in the wells: 1-2 buckets of organic and 4-5 tbsp. l mineral mixtures. The bottom of the hole can be sprinkled with earth for a more even distribution of the root system. When planting, it is not recommended to dig in the root of the cervix, a slight penetration is allowed in loose sandy and sandy soils.

Long-term cultivation of the same plant species at the site leads to the depletion of the soil and the accumulation of larvae pests. Therefore, to break a raspberry in place of the old should be no earlier than 5-7 years.
Since plants of the family Solanaceae and raspberries are susceptible to common diseases - mycoplasmosis and the witch's broom virus disease, it is not recommended to plant remontant varieties at the site of the previous growth of potatoes, peppers, eggplant, tobacco and tomato. These diseases spread rapidly among plants and lead to the formation of non-fertilizing shoots.
It is not necessary to place remontant varieties next to the ordinary ones, so that raspberry pests do not damage the seedlings. It is best to exclude the place of future planting from a crop rotation for one summer or pre-plant it with sideratami (lupine, vetch and oats, white mustard, phacelia), the green mass of which must be plowed for 1-1.5 months. before planting raspberry raspberry.
After planting, the seedlings must be watered in order to seal the earthy coma. The average water consumption for watering - 3-5 liters per plant. In dry weather, watering should be repeated in 2-3 weeks. The soil surface is mulched with humus, shavings, straw 5-10 cm thick. This allows you to retain moisture better, contributes to the aeration of the soil, and during autumn planting - protects the roots from freezing. Traditional pruning after planting for remontant varieties can not be done, since the presence of shoots contributes to better nutrition and vegetation of the plant in early summer.

Container "seedlings" allows you to extend the landing time in the summer season. Seedlings already have 5-8 leaves and grow faster than plants planted in the usual way. They require shading and more frequent watering in the first days after transplantation into the ground. After a couple of months, the plants already bear fruit and yield up to 1.5 kg / sq. m
Plant care
If the remontant raspberry is cultivated for the second year, then its development can be accelerated in the spring: for this purpose, snow is otgrebayut from the site and put on the ground covering material. This measure allows you to start growing season 10-14 days earlier.
Since the main part of the roots is shallow underground, the remontant raspberry is a moisture-loving plant. Watering should be done regularly and to prevent the earth coma from drying out, especially during the ripening of the berries. The best irrigation method is under the root, sprinkling is undesirable for all varieties of raspberries due to the possible development of fungal diseases.
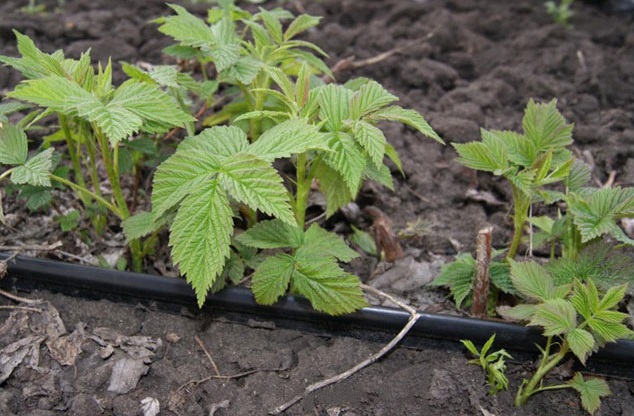

On the other hand, waterlogging of the soil for 2 weeks causes rotting of the roots and the death of the plant. Small root roots die and with a more short-term excess of moisture - within a few hours. As a result, the plant begins to "hurt", which affects its development and yield. Therefore, measures should be taken at the site to drain excess water and the soil should be loosened.
The need for watering is checked in a standard way - squeezing a lump of earth in a fist. If the ground does not stick, then it is time to moisten it. In those years when there is a dry autumn, regular watering is also needed when planting plants before winter. Mulching with sawdust, shavings, needles or freshly mowed grass contributes to preserving moisture and improving the air regime.
Cross-pollination of different remontant varieties provides higher yields. Therefore, for planting on a large area it is recommended to use several different varieties (without mixing them).
Loosening is carried out to a depth of 5-7 m at a distance of one meter around the bush of a raspberry, while care must be taken not to damage its surface roots. Aeration of the soil in late autumn and early spring contributes to the destruction of pests.
Fertilizers are applied in the second year according to the following scheme: in the beginning of summer, nitrogen fertilizers are used, which are necessary for the growing season of plants, and in the second half - complex mineral fertilizers. Usually used universal mixture, the dosage is calculated according to the instructions. Effective use of infusion of mullein or bird droppings, fermented for 10-14 days. Litter is diluted with water at a ratio of 1:20, and mullein - 1:10. Watering is carried out at the rate of 3-5 l / sq. m 1-2 times in early summer.
During the whole summer, it is necessary to ensure that the young shoots of raspberries do not clog up the plantings. When the repair raspberry plantation is thickened, the plants lack nutrients and light, the yield is reduced. Extra shoots and root shoots are cut at ground level. If the stalks of the plants are strongly stretched, their trellis garter is needed - the first garter is made when the plants reach half a meter in length, and the second - with their height of 1-1.5 m.
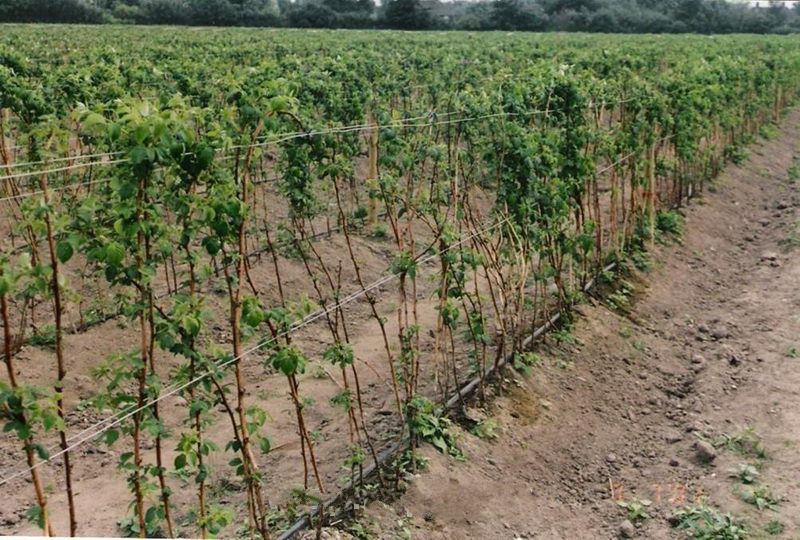

In late October, when the first snow falls, you need to prune the stalks, collect and dispose of old leaves and debris. Before winter you need to make watering, if the ground is dry; loosening and mulching. When cultivating remontant varieties in conditions of little snowy winters, sprouting shoots are recommended to be cut in early spring and not in autumn, in order to retain snow on the site and prevent freezing of the roots. For the same use the shelter of the roots with straw or roofing material.
Breeding
In the conditions of private gardening reproduction is possible in several ways:
- At the end of spring, young shoots, which begin to form roots on the bleached part of the stem, are carefully cut with a knife to a depth of 3-5 cm, and part of the leaves are removed to reduce the loss of moisture. The ground part of the green shoots should be no more than 3-5 cm. Work is done in the morning, in rainy weather. The shoots are wrapped in a damp cloth and stored in the shade before planting in a greenhouse, the roots are treated in wood ash. Larger shoots are left until fall to get lignified seedlings from them. To germinate the roots of green shoots, they plant in a mixture of river sand and peat, the thickness of which should be at least 10 cm over the ground. Rooting of shoots in a greenhouse occurs after 3 weeks at a temperature of 18-25 degrees. After the plants go to growth, you need to make fertilizing complex fertilizer and you can start hardening them, exposing the sun and the open air. After another two weeks, they are transplanted into containers or on a growing area.
- In late autumn, before the frost, they dig out the roots of raspberries and cut them into cuttings of 10-15 cm, spray them with water and put them into boxes with moss. They are placed in a cellar for winter storage, if necessary, periodically moistened. In early March, they are put in boxes in a peat-sand mixture and put in a greenhouse. Two weeks later shoots appear, which are cut with a piece of root bark. Further cultivation of seedlings produced by the first scheme.
- Less effective is the method of planting root cuttings directly into open ground in the autumn. For better survival, cuttings are protected by tops or lapnik from freezing, and in spring they are covered with a transparent film for 2 weeks. When shoots appear, the film is removed.
- For 2-3 years of cultivation, in the fall or spring, the central part of the shrub is cut and removed, and from the remaining roots in the ground by the end of the summer several seedlings are developed, which are seated in a permanent place.
- During reproduction of raspberries from seeds, the property of remanufacturing is preserved on average in 2/3 of the shoots. With this method, less viral and fungal diseases are transmitted. To do this, choose the largest berries, put them in a fabric bag and washed from the pulp under running water. Next, the seeds are dried and stored for 2 months in a refrigerator at a temperature of +2 - +4 degrees. They can survive in such conditions for several years. Before planting in the spring, the seeds are washed again, dried and rubbed for 5-10 minutes. between sheets of fine sandpaper for breaking their hard shell. Sowing in the seedling boxes produced at a depth of 0.5 cm, sprinkled with soil and monitor the humidity. After the 2nd true leaf, begin picking the plants and feeding them. A year later, you can plant seedlings on the site.
In laboratories, remontant varieties are propagated by micro-cloning, which provides protection against viral infections and the production of large quantities of planting material.
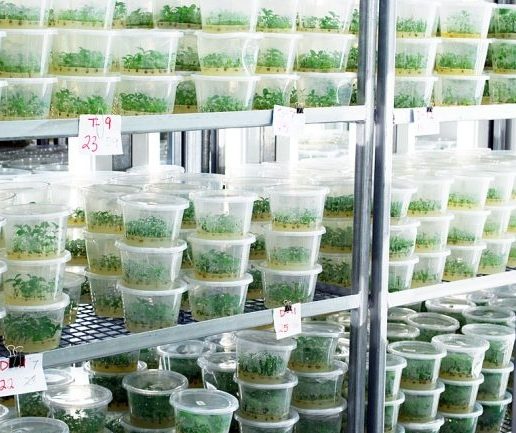

Pests and diseases of the repair raspberry
These raspberry varieties are less susceptible to pest damage than normal ones. The raspberry beetle goes into wintering before the autumn harvest of berries ripens. In the period from August to October, pests such as the red raspberry leaves and the fly stop their activity.
For using the same insecticidal preparations as for ordinary: Agrovertin, Fitosporin, Arrivo, Konfidor, Fufanon, Karate.

For the destruction of spider mites, which especially damages raspberries in dry weather, they use colloidal sulfur and its products: Tiovit Jet, Anti-mite, Akarin, Agrovertin, onion peel extracts, garlic and wood ash.
A 1% solution of Bordeaux liquids, HOM, Topaz preparations and preventive measures - thinning of the planting, preventing stagnant moisture in the soil, help to cope with fungal diseases.
Viral diseases: curliness, witch's broom, infectious chlorosis, mosaic, bushy dwarfism are eliminated by preventive control of insect pests, as they are carriers of these diseases, and treatment with copper-containing drugs (1% bordeaux liquid, copper chloroxide, HOM, Oxyh, Abiga -Peak).

Conclusion
Knowing how to properly care for remonty raspberries, you can get a good harvest of berries every season. These varieties are not picky and feel great in the Russian climate. The main thing for a gardener is to learn how to reproduce saplings correctly, and then all summer you can enjoy the wonderful taste and aroma of raspberries.