How to process planting potatoes from phytophthora. How to deal with blight on potato folk remedies without harm to the harvest? The most resistant to late blight varieties.
Phytophthora is a fungal disease that most often affects plants from the group of nightshade. Potatoes and tomatoes are one of the most popular fruits that are grown in our latitudes, and which fall under the risk of being affected by this disease. Late blight (phytophthora) can take a tenth of the crop, and during years of widespread use, this number can go up to half. Therefore, there are many ways to combat the disease. Experienced Gardeners have already decided which of them is the most suitable for them (vitriol, improvised substances, chemicals). Beginners and people looking for new methods can learn a lot useful information from the presented article, and successfully fight the fungal formation.
How to process tomatoes from phytophthora
The active ingredient thiophenate methyl provides continuous monitoring of crop-carrying diseases in numerous re-testing and field studies. Incognito can be used alone or in combination with other registered fungicides to enhance protection against diseases.
Regalia stimulates plant protection, provides control over bacterial and fungal diseases, retards the development of resistance and helps minimize chemical residues in harvested products. Use regalia as a soil treatment and foliar spray to combat a wide range of pathogens on potatoes. After planting, turn on the regalia in your foliar spray to improve control of early burn, late burn, white mold and other leaf diseases. Phosphite: Phosphite is a fungicide with a reduced risk for use on potatoes.
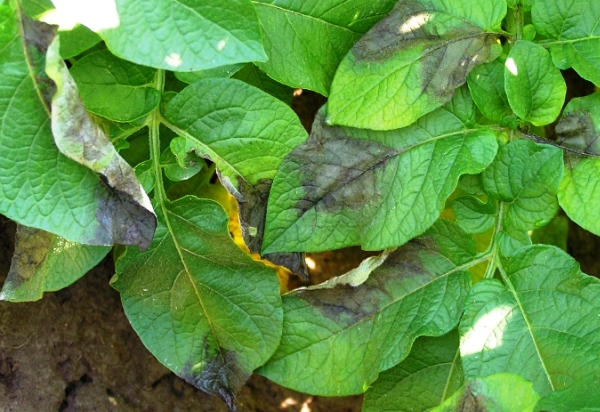
The first thing that needs to be done to defeat the pest is to correctly and timely diagnose the presence of fungal microorganisms. This is done quite easily - a dark patina appeared on the leaves of the potato. These are the first warning signs, after which you must immediately take up radical measures. If they are not taken, the defeat will expand throughout the plant, and then it will dry out altogether.
The active ingredient of phosphite is phosphoric acid, which is toxic to various fungi, such as phytophthora, pythia and fluffy mold. When used in accordance with the label phosphite can provide excellent protection against these diseases, while remaining safe for applicators and the environment.
It also works as a foliar and soil fungicide. Additional benefits include the ability of phosphate ions to promote the immune system on potato plants. Phosphite kills the disease on contact and helps to increase the natural protection of plants against further infection. Do not use phosphite in combination with copper products.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the inside of the sheet. If the potato is infected with blight, then there will be a whitish bloom, a little "fluffy." You need to be attentive even on the first shoots. Infection with the disease is possible in the early stages.
A few decades ago, infection occurred only in the middle or near the end of summer. Terms are shifting due to the adaptation of harmful microorganisms to the methods of struggle. There was a tendency to the emergence of new species that are more resistant to drugs and they manifest themselves much earlier in time.
Today's agricultural revolution for cleaner and safer food thanks to efficient products with low levels of chemical harm and disease control and innovative technologies for sustainable, high-performing agriculture and environmental improvement.
During the years of field trials, the impeccable efficiency of the moon was proved. Yield and quality losses are especially high if a late burn appears before or after line closure, respectively, as is the so-called late edema. Therefore, the main task for those working in this area is to prevent infection in the potato field as long as possible. Indeed, the weather, which is beyond our control, plays a crucial role in the beginning and in the development of infection. However, the potato farmer can take a number of measures to keep the infection low.
The first symptoms of phytophtora in potato tubers are grayish spots of a point character. Then they affect the entire area of the fruit, have a brown-red tint. As a result, they may rot with soft rot or remain affected for the whole winter, but not completely missing. Before planting, these tubers need to be sprayed or dipped in vitriol. There are cases of damage to the fetus in the center, and it is found only in winter.
Experienced farmers know that the planning of the first use of fungicides and the corresponding product decides the success of the fight against late fatigue. Spray fungicides should start from 7 to 12 days before a stain appears on the chart. In addition, for the cost-effectiveness of treatment, it is important that the choice of product be adjusted for the pressure of infection. Warning services and crop inspection are important tools for the timely planning of fungicide applications.
Why is soil moisture important for late decomposition?
Late purulent pathogen overwinters latently infected potato tubers. When this potato starts growing in spring, the mushroom expands into the stem. Extensive research activity in the Bavarian State Research Center for Agriculture in recent years has shown that another method of infection is possible with high soil moisture. Spores develop on a diseased tuber and are distributed through soil water. So you can infect neighboring plants or the stems of the same plant.
Ways of infection

There are many ways to spread and infect potatoes. Fungal microorganism living enough, to fight it is not easy. It is able to withstand low soil temperatures in winter and will reappear on new plantings. The most common routes of infection are:
In both cases, the plants detect infection of the trunk very early. That is why in years with dry weather in spring there is a much lower initial infection, and with this there is less exposure to infections than in wet years. But the type of soil indirectly affects the course of the disease. Light soils flow down faster, and the danger of early and severe invasion is much lower than on loamy soils.
Eliminate the source of infection!
Areas with high groundwater levels and areas with high rainfall are particularly vulnerable to very early and massive infection of the stems. But in the end the weather determines how hard the infection of the leaves will be. Lush pots for potatoes create a favorable microclimate in the culture and, therefore, represent a higher risk. What can those who work in this field do? In addition, the removal of potato volunteers and waste is a reasonable phytosanitary measure.
- The presence of fungus on the planting material. This occurs when the tubers are inattentively taken away for planting, and charged tubers are allowed. In this case, the disease quickly spreads to healthy plants.
- Sick tops have contact with tubers during harvest. Then the already harvested crop quickly falls into disrepair. To avoid such an unpleasant situation before harvesting the tops must be removed from the field.
- Infection from leaves and stems to the root occurs through moisture. Frequent rains and abundant dew carry the fungus from the surface part of the plant to the ground.
- Through weeds or other debris that has not been removed from the soil for the winter.
- Spread by airborne droplets from other infected plants. Studies have shown that in humid windy weather spores of the fungus can move 2-3 km. Therefore, it is better to plant vegetables from the family of Solanaceae as far as possible from each other.
How to fight
The phenomenon of phytophtora has long been known to mankind. Therefore, there are many approaches and methods of struggle. But a panacea that would completely and permanently rid your garden of fungus does not exist. Depending on the area of planting and personal beliefs, people use natural or chemical means.

But in both cases it is necessary to adhere to strict instructions and recommendations for dosages. In the first case, a low concentration of the main substance in the solution may not help. In the second - harm. And not only to the plant, but also to the health of people who will eat potatoes.
The use of chemicals can be at such stages:
- Soil preparation before planting, there may remain phytophtora mushrooms from last year. For such purposes, use "Thanos", "Ridomil", biofungicides.
- Processing potatoes intended for planting. It is produced by antifungal drugs. As an additional crop stimulator, growth regulators are used. The most popular ones are Agat 25, Zircon, etc. This is done by soaking or spraying.
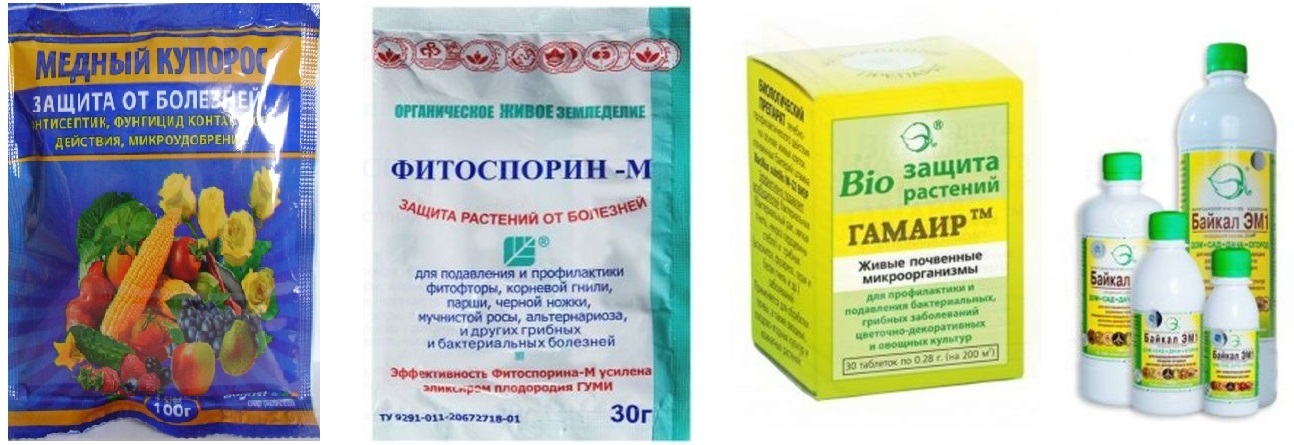
Spraying soil and plants with fungicides at different stages of plant growth:
- Before the closure of the rows. They use "Thanos", which effectively fights against Alternaria.
- The initial stage of budding. In this case, it is best to use systemic fungicides that enter the plant, plying through all its parts.
- Subsequent spraying in the amount of 4-5 times maximum, depending on the current situation. Carefully read the instructions, each drug has its own term of disintegration.
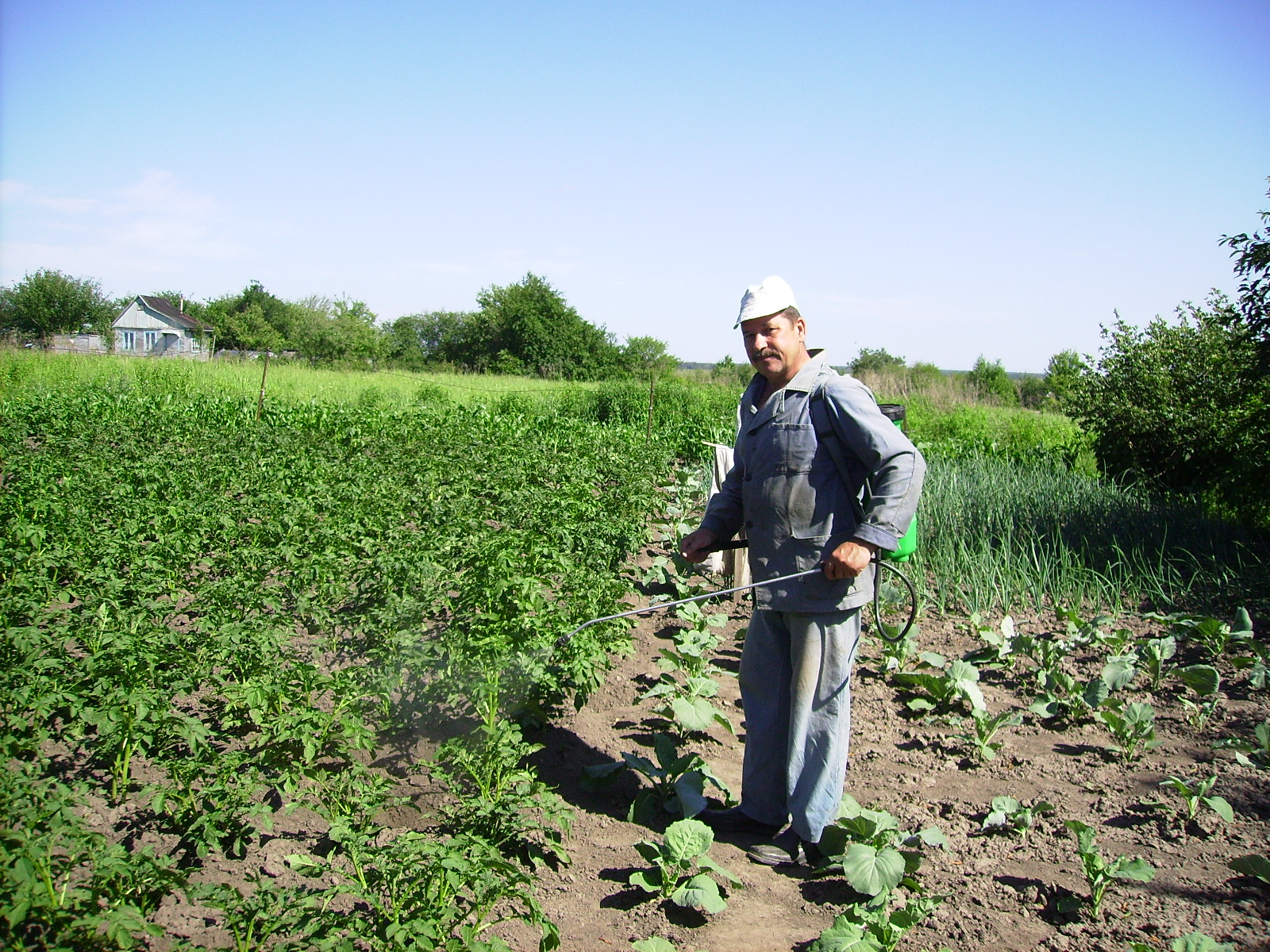

Best of all, the drug acts if it falls on the area of both sides of all leaves, even the lower ones. The active and repeated use of chemical agents is justified only in cases of epitophy (epidemics), which must be dealt with systematically.
Fans of natural products and a minimum of chemistry have their own ways of dealing with the ailments of plants. Gardeners successfully struggle with this disease with improvised means that are found at home or are easily bought in non-specialized stores.
Bordeaux mixture
This name has a copper sulphate mixed with quicklime. Based on 10 l of water, 100 g of vitriol and 120-150 grams of lime are taken. If the indicated proportions are not observed exactly, copper sulfate can cause burning of the plants. It is used at all stages of plant growth. It is dipped or sprayed tubers before planting, vitriol is treated during germination, 2 weeks after germination, and a month after planting.

- Garlic. 150 grams in any form (teeth, arrows or leaves) grind in a meat grinder and pour a glass of water. Strain, pour water in an amount of 10 liters, add 1 gram of potassium permanganate. Suitable for all plants Solanaceae family. Processing is done every 2 weeks.
- Horsetail. Take 1-2 kg, pour 10 liters of water and leave for 3-4 days. It is necessary to spray once a week. Horsetail is rich in silicon, which strengthens the immune system of plants.
- Ash. It is possible to use both dry for sprinkling, and solution for spraying. Proportions: 1 l ash, 10 l water, 200 grams of soap.
- Milk serum. Dilute with water in equal quantities. The first watering must be done in early July. Further as needed.
- Compost and urea. 1 kg and 1 tbsp. respectively. Proportions are calculated on 10 l of water. It is necessary to insist such a solution for 4-5 days, and spray once every two weeks.
- Trichopol tablets. 10 tablets, 10 liters of water, processed every 2 weeks.
Video "Protecting potatoes from late blight"
A very informative video about the methods of controlling late blight of potatoes.
Prevention
It is better to prevent time than to actively and then fight. There are special conditions that contribute to the rapid spread of harmful organisms. All these factors can not be prevented even by a professional. But to exclude most of them, even a novice can.

- The correct alternation of planting on the same field. If signs of phytophtora were noticed, then on this site re-landing can be done only after 3-4 years. Optimal processing of the soil is achieved by alternating potatoes with cruciferous and legumes.
- Choosing completely healthy planting material before landing. In special cases, infected tubers can be treated with a special agent (Pencozeb, Utan, vitriol, etc.). Sometimes germination is also produced, which generally increases the yield.
- Well influenced by high hilling. It is able to prevent infection of the fruit itself.
- The correct location on the plot - isolation from other plants of the family of the nightshade. And also need to get rid of weeds and debris.
- If there is such a possibility - to prevent dampness. It is also strictly forbidden to water by sprinkling in the evening.
- Use of organic fertilizers and nitrogen in moderate quantities.
- Harvesting is best done in dry weather, and then dried potatoes for at least 5 hours.
- It is recommended to cultivate between rows 3 or 5 days before harvesting. This procedure will improve the collection, eliminate excess moisture and reduce the number of weeds.
Proper prevention and timely response to the occurrence of the disease minimizes crop losses. Follow the above tips, use vitriol and other methods, and enjoy abundant harvests of clean potatoes.
Video "The best means of protection against phytophtors"
The author of the video tells about the most effective and safe means of protecting vegetables from phytophthora.