What do young hazelnut trees look like? How to grow hazelnuts from the nut at home
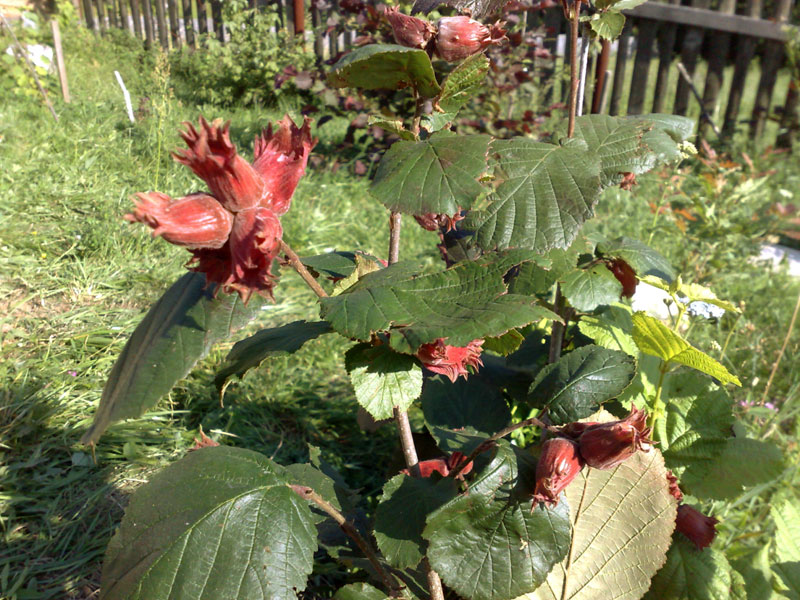
Hazelnuts are cultivated varieties of wild hazel or common hazel. This is a large shrub with a powerful branched root system. It grows as a multi-trunk shrub, forming a set of coppice shoots that propagates. The filbert is a wind-pollinated monoecious plant. It blooms very early, sometimes at the end of January, and mass flowering begins in February and early March - before the blooming of leaf buds. The hazelnut fruit is a nut covered with plyus. It is useful because of the high content of vitamins, fats, proteins, carbohydrates. Not only nuts are useful, but bark, leaves, plusus.
The benefits of hazelnuts
Hazelnuts are tasty, healthy and nutritious. They contain 65-73% of fats (oils), 18-22% of proteins, 2-5% of carbohydrates (starch and sugar). There are vitamins A, B, C, D, E, mineral salts. This causes its high caloric content as a food product. According to the caloric content of the hazelnut kernel, they exceed the pork by 1.5 times, soybean - 1.8 times, wheat bread - 3.5 times, beef - 3.8 times, chicken eggs - 4.5 times, potatoes - 8.5 times, apples - 15 times. For reference: 350-400 g of nuts satisfy the daily nutritional needs of an adult.
The hazelnut kernel contains all twenty amino acids, from which complete proteins are formed. It retains its taste during storage even under normal room conditions. Nuts are easily absorbed by our body, no matter how they are prepared. It is an unsurpassed high-quality product.
Hazelnut is rich in vitamin C in the roots and cucumber. Leaves and roots contain tannins.
AT traditional medicine hazelnuts (hazel) are used for urolithiasis, a decoction of dried pussies - for diarrhea, bark - against fever, leaves - as an antiseptic.
Walnut, pounded with water, is used for hemoptysis, flatulence, bronchitis, feverish conditions.
A decoction of hazelnut bark collected in the spring, used in malaria.
Walnut oil - antihelminthic (from ascaris).
Chopped fruits, mixed with egg white, used for burns.
Not only hazelnut nuts are useful. The bark has astringent, antidisintestinal, antipyretic properties. Infusions of the cortex are used for varicose veins, varicose ulcers, for tumors.
Hazelnut leaves (hazel) are used to treat intestinal diseases, anemia, vitamin deficiency, rickets. Broth - with hypertrophy of the prostate gland. Ointment - for cancer. Powder from dried plyus or decoction of the shell and plyus - with colitis.
In early spring, beekeepers often harvest hazelnut pollen or hazelnut to feed bee young. This pollen is very useful for people: these male vegetable genital products contain a lot of zinc, which is part of a variety of enzymes that help solve the problem of infertility, making sluggish sperm cells moving.
Healing properties of hazelnuts
And here are some popular recipes.
Jaundice
Fresh hazelnut or hazel leaves dry. One teaspoon of leaves, crushed to a powdery state, pour a glass of white wine, leave for the whole night. Divide into three parts, take daily before meals for three doses. After two weeks jaundice passes.
Varicose veins
- Hazelnut leaves to collect in May. Two tablespoons of leaves pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 2 hours. Drink half a cup 4 times daily before meals.
- One tablespoon of chopped hazelnut bark pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, cook for 10 minutes, strain. Drink half a cup 4 times daily before meals.
Adenoma
Hazelnut leaves collected in June, dried in the shade. One tablespoon of crushed leaves pour a glass of boiling water. Heat in a water bath for 15 minutes. Drink 1/3 cup per day.
Biological features


This is a relatively winter-hardy plant. We, in the Krasnodar Territory, did not notice the freezing of hazelnut wood, although in the plains regions frost damage occurred to male inflorescences. When propagating by seeds, the plant does not retain the properties of the parent plant, and fruiting with this method of reproduction occurs late.
Hazelnut fruits well on fairly fertile, moisture-rich soils. This may be flat areas or slopes. The southern slopes are not very suitable for its cultivation, since here the kidneys wake up too early - they can be damaged by return frost. Over-wetted, swampy areas are unfavorable for him. Hazelnut grows well on light soils.
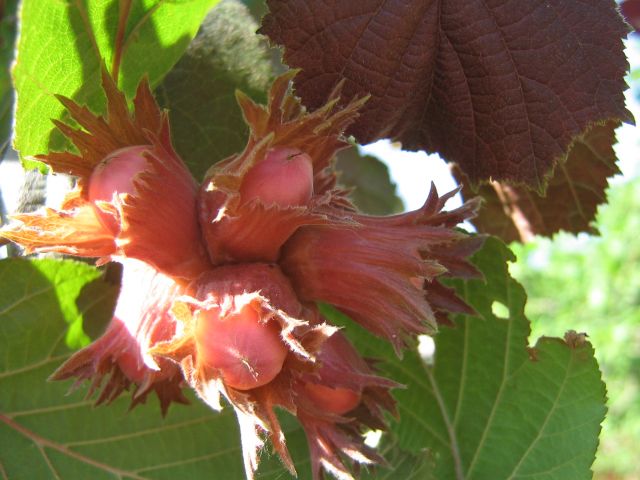
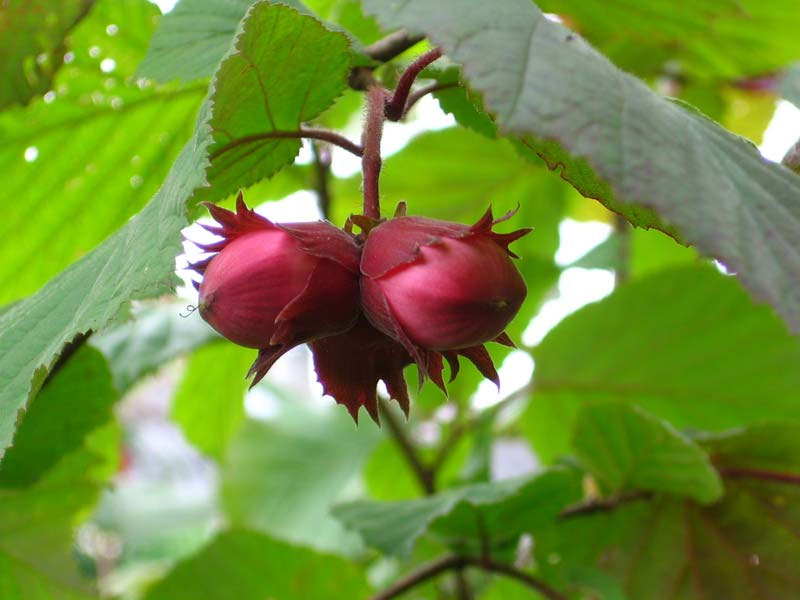
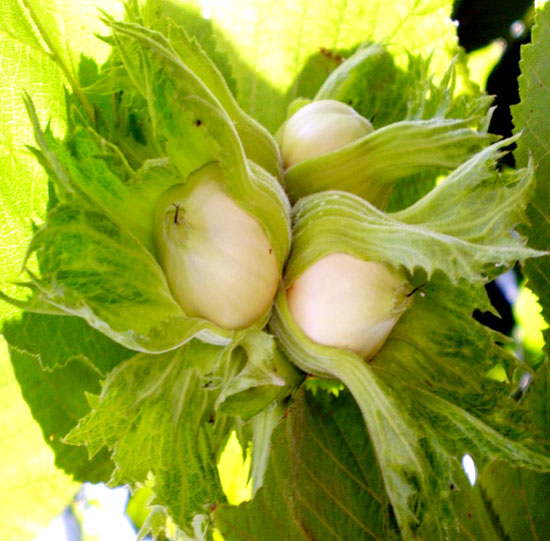
 The hazelnut fruit is a walnut covered with a ply wrap. Mass harvesting occurs at the end of August-beginning of September. An indicator of the physiological maturity of the fruit is the browning (yellowing) of the wrapper - the pluses and the loss of individual nuts.
The hazelnut fruit is a walnut covered with a ply wrap. Mass harvesting occurs at the end of August-beginning of September. An indicator of the physiological maturity of the fruit is the browning (yellowing) of the wrapper - the pluses and the loss of individual nuts.
The need for hazelnut fruit is very high. The harvest of nuts from a single bush with a high agrofone is 5-12 kg, in rainfed (arid) conditions on arable land - 3-5 kg, on unproductive - 2-3 kg.
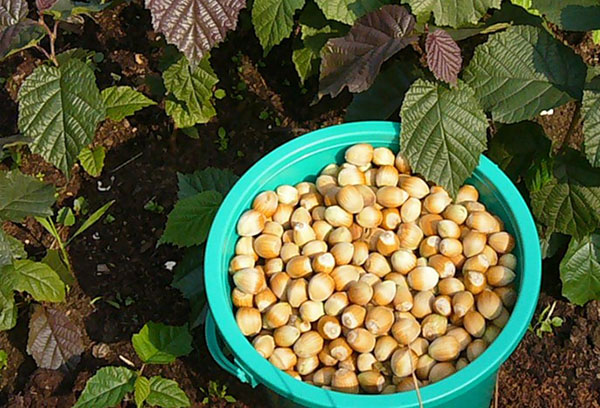
At my dacha I collected a bucket of nuts from one bush in a good year.
Hazelnut begins to bear fruit from 3-5 years old with vegetative propagation, from 6-10 - with seed. Greatest yields get when he reaches the age of 12-35 years.
The hazelnut bush annually forms a large number (up to 100-150) of zero basal shoots. To obtain a high yield, the number of basal branches (trunks) must be maintained at a level of 8-10, but not more than 12 pieces in a bush.
The durability of the bush due to the intensive formation of rhizomes practically unlimited. In general, the hazelnut is immortal. Almost the life of a bush is 150-180 years, without rejuvenation of the trunks - 60-80 years.
Thus, hazelnut shrubs can live in one place for a very long time. But the soil is gradually depleted, the soil is compacted: diseases, pests accumulate; reduced regenerative ability of plants (the ability to form new zero shoots). Yield reduction, drying of skeletal branches begins at the age of 20-25 years, and with irrigation 5-10 years later. In the first case, the rejuvenation of the bush will begin at 20, and in the second - at 30 years old. When rejuvenating, replace the basal branches (trunks) alternately, as they dry out, growing instead of shoots.
Scientists have experimented a lot to increase the yield of hazelnuts. The decision did not come immediately. They began to plant seedlings in 1-2 m in a row. Then only those plants were left which naturally bent downwards into a branch. The rest of the plants were cut. The lateral branches of the abandoned seedlings were not removed, so their crown began at a height of 50 cm from the ground. Productivity has increased dramatically to 40 kg / ha.
Probably, many experienced gardeners who have been engaged in gardening for a long time know that if a branch going upwards is tilted to the ground with a rope or a brick is hung on its end, the harvest will increase dramatically.
Hazelnut varieties
It is known that it is the variety that determines the level of productivity of plantations, the quality of the products obtained. It should be well adapted to local soil and climatic conditions. The following are considered the best varieties of hazelnuts in southern Russia.
Variety "Adygei-1"
Fruits - average weight - 2.1 g, wide, round, gathered in 3-4, less often in 5-8 pieces. It is recommended for cultivation on farmer, garden plots. Winter-hardy, drought-resistant, fruitful. Hazelnuts high taste. Medium resistant to pests, not sufficiently resistant to bacteriosis. On the Black Sea coast gives from 5 to 10 kg of nuts from one bush. Begins to bear fruit on the 6-7th year after planting. The fruits ripen in late August - early September.
Ata-Baba variety
The variety is medium resistant. Harvest gives annually. Fruits well. Nuts have an excellent presentation. Begins to bear fruit for 4 years. The average yield of 9.5 q / ha. Universal purpose. A vigorous hazelnut bush with a spherical, slightly flattened crown. Fruits weighing 2.5-3.0 g, rounded, slightly elongated. The shell is of medium thickness, light brown with dark stripes. The wrap is much longer than the nut. Resistant to major pests, diseases (except bacteriosis). The bush is very tall, with a rounded, slightly spreading crown.
Variety "Caucasus"
The breeding variety of the All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Floriculture and Subtropical Crops. The fruits are large, weighing 2.5 g. Peculiarity: good separability of the nut from the plyus. It is a good variety pollinator. Deserves testing in all zones of hazelnut cultivation. The shelf life of the fruit under normal room conditions up to two years.
Variety "Kuban"
Winter-hardy, high yield. Fruits are round, slightly flattened, slightly ribbed. The shell is medium, dense, smooth, slightly bumpy, shiny, with a barely noticeable bloom. The hazelnut fruits are very large, the average weight is 3.5 g. It is promising for cultivation in the Krasnodar Territory. Productivity - 8-9 kg from one bush (the Black Sea coast). Suitable for mechanized harvesting.
Variety "Louise"
Promising for growing in the Kuban. Differs in the increased resistance to low temperatures, regularly, well fructifies (7-10 kg from a bush). Gives nuts high commodity, taste merit.
Variety "Panahesky"
Medium ripening. Fruits are large or medium size (2.2 g), rounded oblong shape. Wrap longer than walnut, whole, sometimes dissected from one side. Highly frost-resistant hazelnuts, relatively resistant to pests and diseases. The grade is recommended for cultivation on personal or farmer sites.
Variety "President"
Distinctive features: large-fruited, simultaneous ripening of fruit, plusus easily separated from the pericarp, which allows to mechanize the process of collecting nuts. Grows best on the Black Sea coast.
Variety "Rome"
The fruits are large, weighing 3.2 -3.5 g, one-dimensional, flat-round, with a beautiful appearance. It has a high potential for annual, abundant fruiting, slightly affected by powdery mildew, bud mite, moderately resistant to bacteriosis. The disadvantages of the variety include poor winter hardiness, low resistance to fruit rot. At international exhibitions he was twice awarded gold medals.
Variety "Circassian"
It is characterized by relative resistance to pests, diseases. Relatively winter-hardy, drought-resistant. Universal purpose. Hazelnut fruit weighing 1.6 g, broadly oval, slightly flattened, pointed. The shell is thin, brown, with slight longitudinal stripes. The main industrial variety on the Black Sea coast. Well established among amateur gardeners.
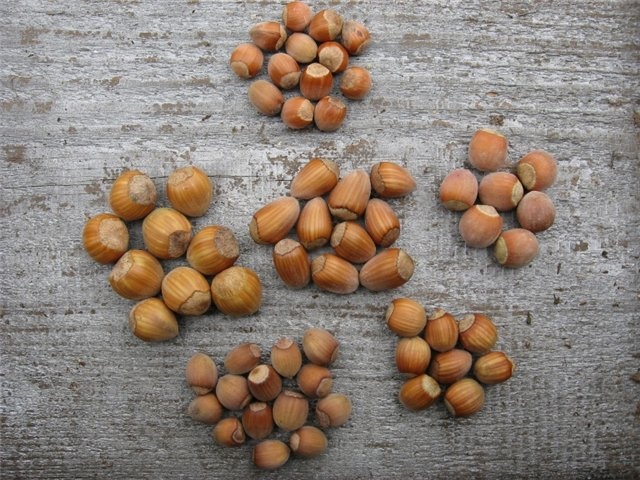
Hazelnut processing
Nuts are harvested when they begin to crumble. Purified them from plyus, stored in tight bags
Plyus is also dried. From the green young plyus you can make jam, it is with pleasant sourness, syrups that help in the treatment of scurvy, loosening of the gums, poor circulation, with increased pressure.
Hazelnut nuts are consumed raw, dried or toasted. From them you can make nut milk. To do this, fresh kernels are cleaned, crushed, soaked overnight in water, ground in a mortar. The resulting mass is diluted with nine times the amount of water, insist 4 hours, stirring from time to time. Then boil, filter or drain the liquid part, adding to taste salt, sugar. Nut milk, by the way, sour, gives the most delicious yogurt.
To receive nut butter hazelnut kernels are crushed, slightly diluted with water, heated. The heated mass is wrapped in a piece of clean cloth, placed under a screw press, under which a vessel is placed to collect oil. It is not inferior in quality almond, used in perfumery, confectionery, in the manufacture of high-quality artistic colors. Walnut oil has a light yellow color, a pleasant smell, well absorbed by the human body. The dough with the addition of peanut butter rises well, and the finished products do not get stale for a long time.
Hazelnut kernels are often used to make vegetable cream, milk and other products. To prepare nut cream, the kernels are cleaned from the shell, the skin, crushed, ground, gradually adding water in small portions. The pasty mass is diluted with warm water, whipped until a homogeneous mass is formed, resembling the taste of cream. Store hazelnut cream in the refrigerator. Nut cream is used in its natural form, they are prepared from them very tasty, nourishing cream for cakes, muffins, cakes.
The young leaves of hazelnuts are eaten for the preparation of cabbage rolls, soups and as a surrogate for tea.
Calorie nut is much higher than beans, soybeans, raisins, figs, milk, potatoes. Hazelnuts are widely used by the confectionery industry. Nutmeal and kernels are prepared toppings for sweets and other confectionery. The oilcake left after oil separation is processed for halva, chocolate, waffles.
Recipes
And finally, a few recipes.
Nut Cream Cake
Beat the eggs and sugar until thickened in a saucepan placed in a water bath, then cool, add butter, nut cream, grind thoroughly
Ingredients:
- eggs - 3 pcs.,
- butter - 150 g;
- sugar - 150 g;
- nut cream - 100 g
Nut drink
Soaked, chopped nuts pour water or milk for 4 hours, then strain. Infusion bring to a boil, add salt to taste, sugar.
Ingredients:
- hazelnuts - 200 g;
- milk or water - 1 liter;
- sugar, salt - to taste.
Nut coffee
Fry hazelnuts, grind coffee grinder or stupa, add ground black coffee. One teaspoon of the mixture brew 200 ml of boiling water, bring to a boil, let stand and brew. Add sugar to taste.
Walnut tea
One teaspoon of dried hazelnut leaves or hazelnut brew 200 ml of boiling water. Insist 15-20 minutes Sugar - to taste.
It is difficult to find someone who would not like chocolate or candy with hazelnuts. These small nuts not only have a pleasant taste, but also have a beneficial effect on the human body.. The high content of vitamins, chemical elements and amino acids improves health with anemia, chronic fatigue, diabetes, neurosis and heart disease. Hazelnut oil contained in nuts, supplying the body with vitamin E, returns vitality and has a rejuvenating effect. Eating hazelnuts for food is equally beneficial for both children and older people. Let's take a closer look at this plant, with the peculiarities of care and cultivation of hazel in the home.
Industrial cultivation of hazelnuts in our country is not conducted. Valuable fruits are imported mainly from Turkey, Italy, Spain and China. But hazelnut is not such an exotic plant as it seems. It is the cultural form of hazelwhich grows in natural conditions in the Caucasus, the Middle East, Ukraine and throughout European territory, up to northern latitudes. So why not grow this unpretentious and useful plant at your dacha, because planting hazelnuts is an excellent business prospect and investment in your health.
Growing hazelnuts for the gardener does not cause much trouble. No wonder the Italians call "cultural hazel" plant for the lazy. Hazelnut is a shrub reaching 2-5 m in height, depending on the variety, but can be formed by trimming in the form of a tree - the choice depends on the owner of the site.
The first harvest can be expected already for 3-4 year after planting. The plant does not need particularly careful care, because in nature, hazel grows well without human help. After planting, agrotechnics are reduced to watering, removal of basal shoots, annual pruning, and pest control, if necessary.
Hazelnuts planted on the site for decades will supply fruits with high nutritional properties and beneficial substances. The massive collection of nuts begins with 5-7 years of life of the plant and lasts for 10-15 years. After that, the plant is “rejuvenated” - for several years in a row 2-3 old branches are cut off, which are replaced with young ones and begin to bear fruit generously.
With each adult hazelnut subject to agronomic techniques get 5-12 kg of fruitsable to be stored for a long time (1-3 years) without sacrificing taste. If you plant on the site at least three plants, the annual harvest will look quite weighty.
Hazelnuts can grow in one place from 50 to 100 years. By planting a plant once, you will provide yourself and your children with valuable nuts for many years to come.
In addition to the benefits of harvesting, the plant has a high decorative effect. Hazelnut varieties have leaves of different colors and sizes.therefore, gardeners often practice planting a variety of leafy bushes in a row - with red, yellow and green foliage. Hazelnuts look impressive as a soliter plant formed in the form of a tree. Lovers of aesthetics will appreciate the beauty of the shrub that throws out spectacular earrings that attract bees in early spring.
Hazelnut reproduction at home
Fans to grow a tree from a nutlet may well resort to the seed method of reproduction. It is simple and, subject to the necessary requirements, will allow you to get a strong and healthy plant. However, this hazelnut will begin to bear fruit much later than the one that is grown from a seedling. If, when planting a seedling, the first nuts will appear for 3-4 years after planting, the plant grown
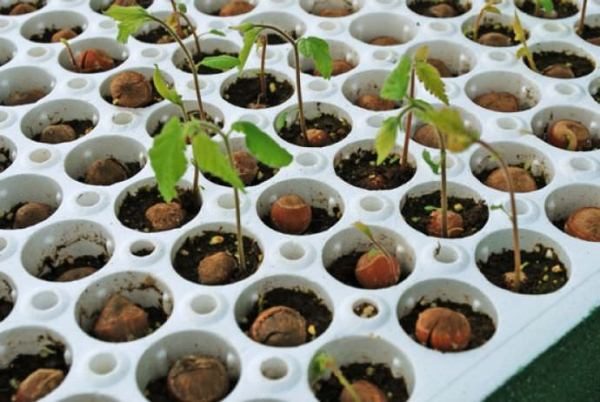

walnut fruit on 6 or even 10 year.
Therefore, gardeners often use planting seedlings. With this method of reproduction, in contrast to planting a nutlet, all the varietal signs of hazelnuts are preserved, on the basis of which they choose the plant that is suitable for certain conditions.
Selection of seedlings
For planting selected one or biennial seedlings. Preference is recommended to give winter-hardy and drought-resistant varieties. The purchase of a seedling at a local nursery guarantees the production of zoned varieties adapted to the climatic conditions of the region.
Choosing hazelnut seedlings in the nursery or garden center, you need to carefully examine the root system of the plant. It should be well developed, without damage. Slightly damaged roots cut to a healthy place.. If there is a lot of damage, the purchase of a sapling should be discarded, as a strong pruning can affect survival and lead to the death of the plant.
Choosing a landing site
Hazelnut is considered a plant, unpretentious to the composition of the soil and the terrain. A moderately fertile soil and a sufficient amount of moisture are favorable for the development of the plant and the future abundant fruiting. Gray forest soils, loamy, sandy and black soils of various types are most suitable for cultivation. Optimal groundwater occurrence - no closer than 1.2-1.5 m to the surface. During the spring thaw, the area should not be flooded with water - prolonged waterlogging leads to rotting and death of hazelnuts.
However, do not be upset with those who have a soil composition that is far from ideal. Hazelnuts are safely grown on almost all types of soils characteristic of the middle zone, except for very heavy clay, marshy, saline and dry sandy. When planting seedlings, black soil is facilitated by the introduction of sand and compost humus - this will improve the air and moisture permeability of the soil. The composition of acidic soils is improved by the addition of hydrated lime, ground chalk or wood ash.
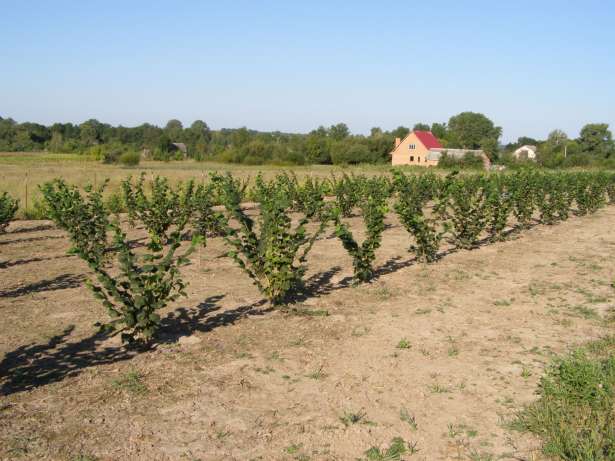

Hazelnut grows equally well on flat areas and mountain slopes. Due to the developed fibrous root system, the plant is planted specifically in places where it is necessary to prevent soil erosion. When planting on a plot under hazelnuts, you can take any place that is not suitable for other garden crops.
Experienced Gardeners in the first few years they practice planting different crops among the bushes of young hazelnuts, which improve the composition of the soil, yield crops and do not allow the place to be empty on the plot.
An important requirement that must be met when choosing a place to land is good illumination. Hazelnuts can grow in shady places, but then do not hope for good harvest . Only the presence of a large amount of natural light contributes to abundant fruiting.
When planting on the slopes for "cultural hazel" you can define a place on any side other than the south. It would seem that the south side is better lit and suitable for plants that love light. In fact, in early spring, in bright sunlight the flower buds bloom prematurely, and then die during the spring frosts.
Culture is sensitive to winds through, therefore when determining the place for landing choose the most protected from drafts areas. As protection against the wind, use the walls of buildings or hedges.
Planting several seedlings, the distance between them and the nearest trees with a volumetric crown can withstand at least 4-5 m, depending on the size of the future plant in adult condition.
Landing technology
According to the gardening reference information, seedlings of the “cultivated hazel” can be planted in early spring (March-April) or in autumn. The hazelnut has a short dormant period, its buds are advanced before other trees, and most of the plants planted in the spring do not take root.
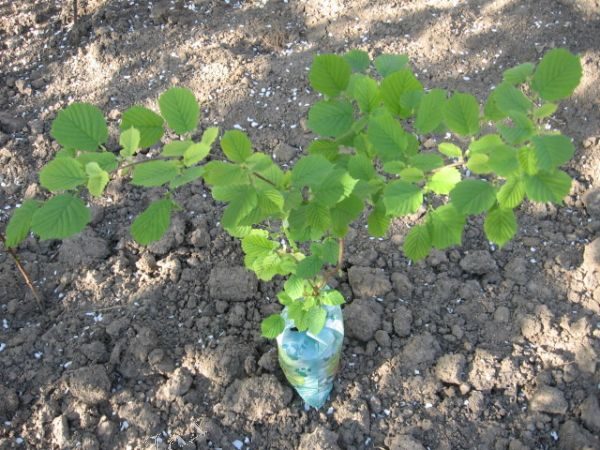

Experienced gardeners tend more to autumn planting - in October-November. Terms for each area are determined individually depending on weather conditions.. In any case, the autumn planting is carried out a month before the onset of frost.
In order to get a generous harvest of nuts, at least three shrubs of various mutually-polluting hazelnut varieties are planted on the site.
When planting in the fall landing pit for hazelnuts are cooked since springIf planting is planned for spring, then preparation is done in autumn. This technique allows you to rest the land, freed from weeds, and accumulate a sufficient amount of moisture. Often life makes adjustments to our plans, and if the decision to plant hazelnuts came spontaneously, the landing pit can be prepared at least two weeks before or immediately before planting.
The landing pit is excavated with a size of 0.6 x 0.6 x 0.6 m. Organic and mineral fertilizers are applied to the prepared pit and mixed well with the ground.:
- humus - 2-3 buckets;
- double superphosphate - 150-200 g;
- potassium sulfate - 50-70 g
It is more convenient to plant hazelnuts with an assistant: one holds the plant and straightens the root system, the other carries out all the necessary manipulations. Planting technology is simple:
- If the roots of the seedlings were processed in a clay mash, wash the clay from the roots. Dipping in the talker is only necessary to preserve moisture in the roots until planting.
- If the roots of the plant are slightly dried, pre immerse them in water for 1-2 days. The shriveled bark of shoots testifies to drying of roots.
- If the roots have dried significantly, then not only them, but the whole seedling is immersed in water for 1-2 days until the bark is smooth.
- Form a landing mound in the center of the pit, stick a peg into it.
- Put the seedling next to the peg, neatly spread the roots of the plant all over the pit. The root neck of the seedling at the time of planting should be just above the soil level. After watering the land will settle, and the root neck will be leveled. This is very important - when the root collar is buried in the ground, hazelnuts will develop poorly, and may not produce any fruit at all.
- Fall asleep pit in two rounds. First, half of the hole covered with soil, a little tamped earth and generously watered. Then fall asleep the rest of the pit, tamped again and watered again. The total amount of water under each seedling is at least 25 liters, optimally depending on weather conditions - 30-40 liters.
- Check the level of the root collar - as much as possible allowable excess above ground is 1-3 cm.
- The seedling is tied to a peg and cut over 5-6 kidney . The height of the aerial parts should be 20-25 cm. Pruning contributes to the development of several fruitful shoots during the growing season.
Care for a young seedling
A pristvolny circle with a radius of 0.5 m is mulched with peat, humus, manure or sawdust, leaving a free space of 5 cm near the stem. The layer of mulch is usually 7-10 cm.
Hazelnut does not tolerate stagnant water, but at the same time is a moisture-loving plant. Therefore, at first after planting, regular and abundant watering is of great importance for the growth of a seedling. The first time the plant is watered one week after planting, a 7-10-day break is taken and watered again. After that, you can be sure that the planting unit forms a single whole with the rest of the soil and will be able to retain the necessary moisture.
In the first 2-3 winters, hazelnut seedlings are covered with lutrasil or spanbond.. This protects the plant from freezing and breaking open undripe shoots.
Further care and cultivation
From planting to fruiting, depending on the variety, you will have to wait 3-4 years. At first the harvest will be small, but after 1-3 years the collection of nuts will please with its abundance, and in 10 years from each bush it will turn out to collect a bucket of nuts. One can hope for abundant fruiting if the necessary measures for the care of hazelnuts are carried out.
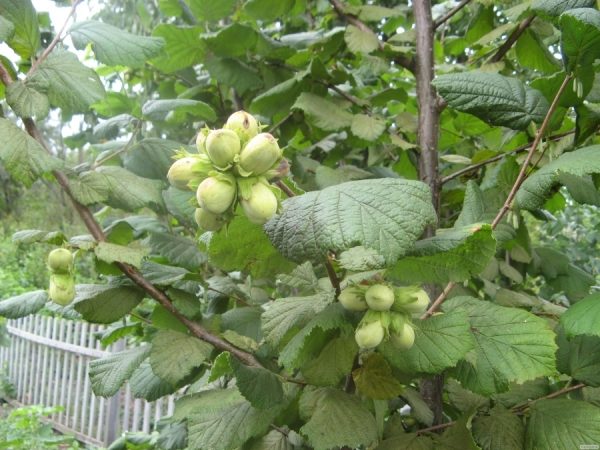

Watering
During the growing season the plant is watered 1-2 times a month, the total number of irrigations, starting from April, is 5-6 times. The last time the shrub is watered is after leaf fall - this will create in the soil the necessary moisture for the plant next spring. In June and July, the need for moisture increases due to the growth of fruits and the laying of the generative organs of the crop of the next season, so the hazelnuts are watered twice during these months. For irrigation use 40-50 liters of warm water for each bush.
Weeding and Mulching
Weeding contributes to the destruction of weeds and the saturation of the root system with air. When loosening the soil, it is necessary to take into account that most of the roots come close to the surface. Damaged hazelnut roots are not restored, therefore weeding depth is 8-10 cm. The soil of pristvolny circles is mulched with peat, sawdust, dry grass.
Pruning
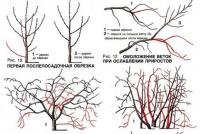
 Hazelnut trimming scheme: on the left - before trimming, on the right - after trimming
Hazelnut trimming scheme: on the left - before trimming, on the right - after trimming Pruning is necessary for the formation of shrubs. During each summer season, extra shoots are cut out, leaving 8-10 of the strongest. They try to remove the shoots located inside the bush, as well as weak and damaged.
Hazel Pest Control
For hazelnuts from pests, the hazel weevil and the hazelnut barbel are dangerous. Signs of their appearance are "worminess" and premature drying of the fruit. In the fight against insects using systemic insecticides, conducting processing in early May, when the beetles appear en masse, and in mid-June, when the nuts are pushed out. Of the diseases most commonly found are powdery mildew, which can be disposed of by treatment with colloidal sulfur, lime-sulfur decoction or store fungicidal agents, as well as the timely harvesting of infected fruit and fallen leaves.
The reader may have the deceptive impression that planting and growing hazelnuts is a rather troublesome task. In this article we have tried to give maximum information useful for the owners of summer cottages and their own estates. The filbert does not need a special temperature mode, it can grow on almost any soil and withstand the lack of dressings. It is enough to make a minimum of effort, and the plant will thank for the generous harvest of tasty and healthy nuts.
"The variety decides the success of the case" I. V. Michurin
Hazelnut varieties and cultivated hazel forms
Common hazel (hazelnut, hazelnut, hazelnut) has been used by man since ancient times. First, the nuts were collected in the wild thickets, then such thickets were specially cultivated by thinning, while the bushes with the largest, tasty nuts with a thin shell were left in them. Gradually, varieties were created by selection. To create varieties by hybridization and subsequent selection, other species were used, in particular, Pontian filbert (S. pontiaca) and large or Lombard filbert (C. maxima). Hazelnuts today call all varietal hazel grown on plantations, as well as their fruits, although originally this name was applied exclusively to large hazel. Seeds of varietal hazel and nuts grown on them are called semi-hazelnut.
Promising frost-resistant red-leaved hybrid varieties of hazelnuts were obtained by the followers of I. V. Michurin - I. S. Gorshkov, A. S. Yablokov, R. F. Kudasheva, S. G. Vanicheva and others. These new hybrids and varieties easily tolerate winter hardships and plantations of domestic hazel in Central Russia have been around for 30 years. The strength of fruiting, winter hardiness and especially the quality of the nuts, even without strict adherence to agricultural technology, indicate the possibility of successful cultivation of nuts in this zone.
Most of the varieties of the Moscow-Tambov selection krasnolistna. All passed many years of testing and now you can safely land in the recommended areas. The main reference point: where common hazel grows wild, then there can also be planted hybrid red-leaved frost-resistant hazelnuts, because common hazelnut was involved in the selection process. The description of the most promising varieties is given below.
Popular varieties of hazel (hazelnuts) for Central Russia

Variety of hazel Catherine (hybrid 12-34) - red-leaved hybrid hazelnuts, obtained in 1961 by R. F. Kudasheva from crossing the selective form of common hazelnut No. 454, selected in the forests of the Steppe forestry enterprise of the Tambov region, with the red-leaved hybrid hazelnut No. 236, which was allocated to the elite from the hybrid stock of A. S. Yablokov. The vigorous shrub with red leaf coloring, the wrapper and nuts are pinkish to dark crimson. Walnut wrap often cut on the one hand, it is much smaller than a nut, carved, thin. The nut is long, very large - (length 30, width 19, thickness 18 mm). The top is slightly wider, the base is convex, even, smooth, the top is not pointed, the shell is very thin. The core yield is 54%. Variety Catherine - dessert. This variety can grow in Central Russia and in the South. In the southern regions has a late ripening of nuts.
The most large-fruited variety of all red-leaved hybrid hazelnuts, weight up to 5 grams. In a bunch of up to 8 nuts. Ripens at the end of September, the yield is good. For all the time of observation, it has never froze. Like all red-leaf hybrids, it requires pollination by frost-resistant green-leaved varieties (Tambov Early, Tambov Late and Firstborn).
Advantages: the most large-fruited of all hybrid hazelnuts.
Disadvantages: during reproduction, the root system forms weakly.
Variety of hazel Isaevsky - obtained R.F. Kudasheva from the crossing of the Tambov hazel with the red-leaved variety Academician Yablokov (Ivanteevsky nursery). The variety is considered one of the most valuable hazelnuts. Fruits are large, light brown with dark brown stripes, have excellent taste. The variety is very frost resistant. This hybrid was abundantly fruiting even after the harsh and destructive winter of 1978/79 for apple trees. Frosts in the Moscow Region reached -42? C.
Advantages: the most valuable "amateur" variety - according to the words of R. F. Kudasheva.
Hazelle grade Masha - a spontaneous hybrid of the red-leaved form, obtained by R. F. Kudasheva from free pollination of the hazelnut of Tambov early variety with red-leaved hybrid hazelnuts, obtained in the Ivanteevsky nursery of VNIILM (now RNIILM). The fruits are elongated, medium size, excellent taste with a thin shell. Winter-hardy and fruitful.
Variety of hazel Moscow Ruby (VLM-2) (hazelnuts) - Hybrid red-leaved hazelnut breeding R. F. Kudasheva. It was obtained in 1957, the crossings were carried out in the Zakatala nut farm of Azerbaijan. As the mother plant used large-fruited variety of hazelnuts called Nottingham. Pollination was carried out with a mixture of pollen from red-leaved hybrid hazelnuts №№ 154, 155, 162 and 167 (selection A.S. Yablokova). Selection of hybrid plants was carried out in the Moscow region. ? The Moscow Ruby variety is larger than the original forms, including the southern maternal grade hazelnuts. The average size of a hybrid nut is 28 × 18 × 16 mm, weighing 3.0-3.5g. Its volume reaches 5 cm ³. The color of its leaves, spruce and the nut itself at the beginning of summer is bright crimson, by the end of summer - dark crimson. In the seedlings 7-8, and sometimes up to 15 large nuts. Plus size is equal to or slightly longer than a nut, bivalved. The shell of a nut is of medium thickness, the bottom is smooth, even, convex. The top of the nut is dulled. Above the nut is slightly wider than at the base. The core is tender, excellent dessert taste, its output is more than 52%, the fat content is 63%. Tasting score 4.3 points. The core is in a silky smooth light shell. In the Moscow region nuts ripen in the first decade of October. The bush is a vigorous, powerful, up to 4.5 m., Winter-hardy, fruitful. It may be the main variety and pollinator variety. The bush forms a large number of male earrings, it is literally strewn with them and they are very dusty, the pollen fertility is 92%. It is the best pollinator from krasnolistnyh varieties. Fruits almost every year - 3-4 kg from a bush. In the south, this variety is distinguished by a later ripening of nuts. Good pollinators for the Moscow Ruby are the Tambov Late, the Tambov Early and the Firstborn.

At the state test since 1982. Included in the state register in 1994 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-West and North-Caucasus regions.
Advantages: High winter hardiness (up to −40? C). It is a good pollinator for hazelnut varieties.
Disadvantages:
Variety of hazel Academician Yablokov - Memory of Yablokov (hybrid 328) - hybrid hazelnut, red-leaved, isolated in 1961 R. F. Kudasheva from the hybrid stock of A. S. Yablokova, medium-tall - 3.7 m, frost-resistant, fruitful. The maternal plant was small-fruited, red-leaved hybrid hazelnut No. 86 (red-leaved hazel x Barcelona hazelnut). The father of the plant was the largest Turkish hazelnut variety in the world - Trapezund (20 × 26 × 24). At a young age, male earrings are almost not formed on this hybrid, although it is early and abundantly tied with nuts. Earlier bushes make earrings, but they almost always freeze slightly, especially in winters with unstable temperatures. Grade Akademik Yablokov is characterized by abundant formation of fruit buds (a lot of female flowers). In artificial pollination of the Akademik Yablokov cultivar with hazel pollen from the Tambov late cultivar, up to 100% of the ovary is obtained. Plants varieties Akademik Yablokov very beautiful.

The number of germinating pollen grains reaches 92%. Female inflorescences have maroon, almost black stigmas, so during the spring flowering there is always the impression that they froze to death, but by the middle of June this impression was dissipated by the appearance of an abundant amount of tying nuts. Stem fruit densely crimson color, with 7-12 nuts of the same color or even brighter than plus. The walnut wrapper is heavily pubescent with dark crimson glandular hairs, monocotyledonous, with a slit to the inner side, about 1.5 times longer than the walnut, very fleshy. Nuts large 2.5-3.4 grams. (26 × 17 × 17 mm), elongated in the form of an acorn. Tasting score 4.5 points. They are very different from the nuts of the parent plants. The nut shell is very thin - 0.8 mm, brown in color with darker longitudinal stripes (“zebra”), shiny, fragile, light, smooth inside. Vertex evenly narrowed, slightly pubescent. The bottom is convex, smooth, smooth, large. The core of excellent taste in a light, thin, silky film is up to 56% of the weight of the nut and contains more than 65% fat. Under the conditions of the Moscow region, the nuts ripen late (late September - early October). An overly thin shell contributes to severe damage to nuts by the weevil. Variety late maturity - requires a pollinator late bloom and, accordingly, late maturity.
Pollinators for this variety are Tambov later, as well as the Firstborn.
Winter hardiness is average - male inflorescences and one-year growth freeze slightly. Female inflorescences withstand spring frosts to minus 6-7? C. The bush has a beautiful cup shape.
At the state test since 1975. Included in the state register in 1994 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-West, Middle Volga and North-Caucasus regions.
Advantages: in the presence of pollinator s.Tambovskii late yield up to 10 kg. The most productive variety.
Disadvantages: average winter hardiness. Due to thin shells can be damaged by the weevil.
Variety of hazel firstborn (hybrid number 1241) - interspecific green-leaved hybrid, obtained in 1957 by R. F. Kudasheva in the Ivanteevsky nursery of VNIILM (now RNIILM) from crossing the Far Eastern diverse hazelnut (S. heterophylla) with a large-fruited hazelnut, apparently, named, by mistake, Nottingham () from the Zakatalsky Nut Farm of Azerbaijan), although its nuts are in shape and in size closer to the nuts of hazelnut varieties Sikler and Gustav. Earrings are reddish, like those of the mother plant, but they are much larger and more abundant in dust, collected in several pieces in the form of a brush. Bark of gray trunks. Sprawling bush, srednerosly, height 3.5 m, the increase is small. Gives a lot of shoots at the very base of the stem. The wrapper is carved, curly, the edges are bent outward, like that of hazel leaves. It is 1.5 times as long as the nut, bichromatic, light green in color. In compound fruit, there are 2-5 large nuts of 27 × 21 × 16 mm in size, weighing up to 2.5 g. The walnut volume reaches 4.5 cm³, (for leafy leaves - 0.9 cm³, for paternal nut - 3.5 cm³). The shape of the nut is elongated, similar to the shape of the father nut, but larger. The nut shell is of medium thickness, even thinner than that of southern hazelnuts. The surface of the shell is smooth, evenly colored in golden yellow color. The bottom is convex. The core in a light, thin, silky film, the weight of the nut is more than 50%, contains 65% fat. Tasting score of 4.5 points. The grade is highly winter-hardy and fruitful. Productivity up to 6 kg from a bush (8-18 c / ha.) Fruits almost every year. Universal purpose. Differs in abundant formation of male and female inflorescences. The flowering time of male and female inflorescences is the same. Female flowers have stigmas bright crimson. It has a high viability of pollen (70-80%). Men's earrings are abundantly dusty, and the period of dusting is more extended than that of other hybrids. Therefore, it is a good pollinator for red-leaved forms of hazelnuts. This results from the fact that they ripen at different times. Female flowers are blooming at different times. This is very important for preserving them from short-term spring frosts, which, obviously, is the cause of the abundant annual harvest of nuts. The variety is recommended for breeding throughout the area of hazel. It can be a good pollinator for many varieties of hazelnuts. The average ripening period - in the Moscow region ripen in 2-3 decade of September. Kidneys are not damaged by the hazel mite at all.
At the state test since 1975. Included in the state register in 1995 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-West and North-Caucasus regions.
Advantages: High winter-hardy (up to −40? C). It is a good pollinator for all varieties and forms of hazelnuts.
Disadvantages: abundant formation of root shoots.

Variety of hazel Pushkin red. Hybrid krasnolistny hazelnut. Received at the Nut Fundarisation NGO of the All-Russian Research Institute for Forestry and Forestry Mechanization. Selected from the Yablokov hybrid fund. Medium ripening. Winter hardiness is high. The average yield is 4.4 c / ha, the maximum - 9.1 c / ha. It is a good pollinator for green leaf forms. Universal purpose. Fruit size 23 × 17 × 17mm - fruit weighing up to 2.3 g, wide-ribbed, oblong, gathered in the stem of up to 10 pieces. The peel is medium, smooth, with thin stripes, brown, to the top - light brown. The leaves are large, burgundy (dark burgundy) in color, by autumn the leaves are dark green, obovoid-shaped. Very decorative look. The Pushkin red and Ivanteevsky red varieties are like twin brothers, only Pushkin red is slightly darker (more noticeable).
Disadvantages:
Varieties of hazel Ivanteevsky red. Hybrid krasnolistny hazelnut-obtained by crossing the variety F-705 and hybrid 468 (seedling F-129). Received at the Nut Fundarisation NGO of the All-Russian Research Institute for Forestry and Forestry Mechanization. Medium ripening. Winter hardiness is high. The average yield is 4.4 c / ha, the maximum - 9.1 c / ha. It is a good pollinator for green leaf forms. Universal purpose.
The bush is 4.5 m high with a thick, narrow pyramidal below, from the middle of the bush an expanded crown. The leaves are large, red in color (by autumn leaves are dark green), obovoid-shaped. Fruit size 23 × 17 × 17mm - fruit weighing up to 2.3 g, wide-ribbed, oblong. The peel is medium, smooth, with thin stripes, brown, to the top - light brown. The output of the core is 46%, the fat content is 64%. Tasting score 4 points.
At the state test since 1995. Included in the state register in 1996 in the Central, Central - Chernozem, North-West, Mid-Volga regions.
Advantages: High winter hardiness. It is a good pollinator for green leaf forms of hazelnuts.
Disadvantages: -

Variety of hazelnut Moscow early. Selective shape of common hazel. Received at the Nut Fundarisation NGO of the All-Russian Research Institute for Forestry and Forestry Mechanization. Early ripening - 2nd decade of August. Highly resistant. The average yield is up to 3 kg from a bush (6-9 c / ha). Universal purpose.
The bush is of medium height (up to 3.0 m) with a compact, slightly rounded crown. Leaves purple color. Fruits of average size weighing 1,9 g (19 × 14 × 14 mm), rounded oblong, average one-dimensionality, with a shell of average thickness. The output of the core is 50%, the fat content is 64%. Good taste, tasting score 4.5 points. The Tambov Early, Tambov Late and Firstborn are used as pollinators. The early Moscow variety forms many male earrings that hang on very long petioles, which gives the bush a special expressiveness in the leafless state.
On the state test since 1994. Included in the state register in 1995 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-West, Middle-Volga regions.
Advantages: The most frost-resistant (up to −40? C) of all krasnolistnyh forms.
Disadvantages:
Variety of hazel Kudrayf. Red-leaved seedling from free pollination of the Moscow Ruby variety, i.e., selective seedling form. The variety is named in honor of Raisa Fedorovna Kudasheva - the most active breeder of hybrid red-leaved hazelnuts. Received at the Nut Fundarisation NGO of the All-Russian Research Institute for Forestry and Forestry Mechanization. The average maturity (1-2nd decade of September). Winter-hardy, productive, with good quality fruits. The average yield is 3-4 kg per bush, (6.4 c / ha - 11.6 c / ha). Universal purpose. Low-growing bush - 3.5 m high with a rounded, medium-dense crown, branches depart from the trunk at an acute angle. The leaves are large, smooth, shiny, pinkish-red, back - ovate.
Fruit weighing 2-2.3 g, slightly elongated, with a pointed tip. The shell is of medium thickness, smooth, with weak stripes, yellowish-brown. The core yield is 51.8%, the fat content is 68.2%. Tasting score of 4.5 points.
At the state test since 1995. Included in the state register in 1996 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-West, Middle-Volga regions.
Pluses: Winter-hardy.
Disadvantages:
Grade hazel Purple. Hybrid krasnolistny hazelnut. Obtained by crossing varieties F-86 (purpure-leaved hazel and Barcelona) and Trapezund. Received at the Nut Fundarisation NGO of the All-Russian Research Institute for Forestry and Forestry Mechanization. The average ripening period (late August-September). High resistance and highly drought resistant. The average yield is 6 q / ha, the maximum - 9 q / ha (up to 3 kg per bush). It is a good pollinator for green leaf forms. Universal purpose. The bush is of medium growth power, height 3.5 m with a sprawling, very decorative crown (with dark purple leaf color), the branches depart from the trunk at an acute angle. Fruits are small (1.5 g), well executed, oblong (18 × 16 × 16 mm), obovoid. The shell is of medium thickness, smooth, shiny, with thin stripes. The output of the core is 45%, the fat content is 62%. Tasting score 4.6 points. Good pollinators for him are the Tambov early and firstborn.
At the state test since 1995. Included in the state register in 1997 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-West and Mid-Volga regions.
Advantages: one of the most decorative varieties. It is a good pollinator for green leaf forms.
Disadvantages:
Variety of hazel sugary - hybrid hazelnut, krasnolistnogo forms. Productivity, frost resistance and winter resistance are high. The quality of round, medium-sized, thin-shelled nuts is excellent. The yield of the kernel (51%) is only slightly lower than the grade of Academician Yablokov, but it exceeds the content of oil (71%) and sugar (16.9%), which is the highest quality (taste) of the harvested fruit. This hazelnut has a very intense dark cherry color and leaves, and plyus, and nuts (before removal from the bush). Nuts are medium in size. The harvest is 3-4 kg from a bush, ripens in mid-September.
Advantages: to taste exceeds all varieties listed here.
Variety of hazelnut Sugar. Hybrid krasnolistny hazelnuts obtained by crossing the variety F-86 (purple hazelnut hazelnut Barcelona hazelnut) x hazelnut Trapezund. Certified by the Nut Fundarisation NGO of the All-Russian Research Institute of Forestry and Forestry Mechanization. Red leaf form, medium ripening (late August - early September). Universal purpose. Winter hardiness is high. Forms male earrings a lot and they do not freeze slightly, is a good pollinator for other varieties. For pollinators, green leafy forms are used for it ((Tambov Early and Firstborn). The bush is of medium growth power (3-3.5m) with a spreading, dense crown.

Productivity makes up to 3-4 kg from a bush. Fruits of mass (1.8 g), medium unidimensionality (17 × 18 × 16 mm), rounded with a thin shell. The output of the core is 48%, the fat content is 71%, of excellent taste - hence the name - “Sugar”. Tasting score 4.5 points. The main color of the nuts is golden brown, with slightly pronounced stripes. The wrapper is equal to the length of the nut. The variety is very decorative - leaves and nuts on a bush of dark cherry color. The highest quality of the harvested fruit - surpasses all other varieties in oil and sugar content.
On the state test since 1994. Included in the state register in 1995 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-West and North-Caucasus regions.
Advantages: High winter hardiness (up to −40? C).
Disadvantages:
Variety of hazelnut Northern 42 - Hybrid green leaf hazelnut breeding Academician A. S. Yablokova. Obtained from the crossing of a southern variety (hazelnuts of Barcelona) with hazel near Moscow, produced in 1935 in Sochi. Hybrid offspring grown near Moscow. Winter-hardy plant, withstands the harsh winters of Central Russia and has nuts like southern hazelnuts. In appearance, the nuts of this variety are not similar to the nuts of the mother plant. They are large, but have an oblong shape, their size is 22 × 16 × 14 mm. Hazelnut North 42 inherited paternal winter hardiness and good quality cultivated nuts of maternal hazelnuts Barcelona. The nuts of this variety are dark brown, large, slightly flat. The bottom is rounded, convex, smooth and even. The top of the nut is pointed. The weight of one nut reaches 2.5 g in the Moscow Region and 3.8 g in the Caucasus. The core yield is 47%, the fat content is 69%. The shell of the nut is of medium thickness. The bush is a vigorous, reaches a height of 4-5 m, the diameter of the main stem up to 7 cm. The variety is a good pollinator. The ability to fertilize its pollen by the number of germinated pollen grains reaches 95%. The size of pollen grains is 30 microns, the length of pollen tubes during germination in a 20% sucrose solution is 130 microns. The flowering time of men's earrings and female inflorescences does not match. Under the conditions of the Moscow region, men's earrings sometimes freeze slightly; this variety needs pollinators for industrial plantings. Female flowers - stigmas are painted in a deep crimson color. The nut wrapper is single and bipartite, deep-cut, a little larger than the size of the nut. Variety can be bred in Central Russia.
Variety of hazelnut Northern 31 - hybrid hazelnut selection A. S. Yablokova. Obtained in 1935 from distant crossing - hazelnut Barcelona x leschina near Moscow. This variety has smaller, rounded nuts. The nut shell is of medium thickness, light brown in color, shiny. The core is in a thin film, its output is more than 45%, its fat content is 70.5%. The variety is drought-resistant, vigorous shrub, reaches 5 m in height, the diameter of the main stem is 6 cm. The leaves are dark green, large. Earrings in the Moscow region sometimes freeze slightly, so a pollinator is required for this variety. The stigmas are colored bright crimson. Pollen has a viability of 95%. In the process of testing in the conditions of the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus at the age of 8 years, a harvest of 3-4 kg of dry walnut from a bush was obtained. This variety can be bred in the Moscow region and in more southern areas.
Variety of hazelnut Northern 9 - hazelnut breeding A. S. Yablokova (Ivanteevsky nursery), received from the same parents as the Northern 31 and at the same time. Bushes of this variety are vigorous, annually bear fruit. Under the conditions of the Moscow Region, up to 3-4 kg of clean, dry nuts from a bush are given. Plyuska is equal to or slightly longer than a nut. Nuts are large, oblong, slightly flattened. Shell average thickness - 1.5 mm. The output of the core is 48%, the fat content is 65-67%. Winter-hardy. Can grow throughout the area of hazel.

Variety of hazel Severny 14 - hazelnut selection A. S. Yablokova (Ivanteevsky nursery), a hybrid from the same family. Bush vigorous. Nuts are large - 22 × 22 × 18 mm, plus the nut is equal to, strongly carved. The shell is of medium thickness. The core yield is about 50%, the fat content is 65-66%. 3-4 kg of pure nuts are collected from the bush. Dessert variety. It can grow in central Russia and in the south.
Variety of hazelnut Northern 40 - hazelnut selection A. S. Yablokova (Ivanteevsky nursery). The bush is vigorous, winter-hardy. Fruits annually, harvest 3-4 kg from a bush. Plyuska is equal to a nut, carved. Nuts of medium size - 18 × 18 × 16 mm, rounded. The shell is 1 mm thick. The output of the core is 45-48%, the fat content is 65-67%. The variety can be cultivated in Central Russia and in the south.
Variety of hazel Smolin - obtained R.F. Kudasheva from crossing green-leaved hazelnuts with red-leaved hazelnuts of the Yablokov selection (Ivanteevsky nursery). From his father's plant, he inherited the red color of leaves and nuts. The bush is quite vigorous, winter-hardy, fruitful. Nuts of medium size, oblong shape, very thin, assembled in seedlings of 10-12 pieces.
Variety of hazel Tambov early (hazel No. 700) is a green leafy form, accepted into state variety testing since 1969. The bush was selected in the forests of the Tambov region at the Roundhouse Steppe forestry enterprise in 1956. R. F. Kudasheva. The height of the bush is up to 4 m, the diameter of the main stem is 3.5 cm. The leaves are large, light green, the shape of the bush is narrow pyramidal. Plus large, of two slices, almost 2 times longer than the nut and is 40% of the raw weight of nuts. Nuts oblong, golden yellow in color, average size 21 × 12 × 11 mm. The shell is thin - 0.8 mm thick. Fruits weighing 2 grams, tasting score 4.5 points, dessert destination.
The yield of the core is 51%, the fat content in the core is 73%. The most oily variety. According to the biochemical composition, the oil of this hazel is better than the popular Turkish hazelnuts. The core in a light thin film, tender, sweetish, in normal room conditions, it remains in good condition, almost without losing its taste, for 3-4 years. The flowering time of men's earrings and female inflorescences is the same, which is very important for the harvest. The stigmas are bright crimson color. The Tambov early variety can grow throughout the whole range of common hazel. It is frost-resistant, withstands temperatures down to −42 ° С. In industrial plantings it can be diluted as a pollinator for all varieties of hazelnut and hazelnut. The time of ripening of its nuts begins in the Moscow and Tambov regions on August 15-20. In the pudding is from 2 to 10 nuts. Harvest from a bush aged 10 or more years up to 4 kg, from 1 hectare to 16 centners. Seedling from free pollination of local forms (Tambov region) common hazel. Early ripening. Winter hardiness is very high. It forms many male inflorescences and is a good pollinator for other varieties. Included in the state register in 1994 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-Western and Middle Volga regions.
Advantages: high winter hardiness, is the main variety - pollinator. In 1978/79 g in the territory of the Moscow and Tambov region. stood the test of frost −42? C and even fruited, while the wild forest hazel was mostly frozen out.
Disadvantages:
Variety of hazel Tambov late (hazel no. 575) —green leaf form, selected by R.F. Kudasheva in 1956 in square 13 of the “Round” dacha of the Steppe Forestry in the Tambov Region. The height of the bush is 3.5 m, the diameter of the main stem is 3 cm, the number of trunks is more than 200 in one bush. Stem bark gray. The shape of the bush is spreading, the leaves are dark green, large. Nuts in stems from 3 to 32 pieces. Plyuska is very small in the form of a cup, only about 18% of the raw weight of nuts. The nuts are slightly larger than those of the Tambov Early - length 22 mm, width 17 mm, thickness 16 mm, slightly elongated, pointed to the top, weighing 2.5 g, shell thin less than 1 mm. The nut end is wide, convex, smooth. The shell is thin, shiny, golden brown with dark longitudinal stripes. To the top, the nut is slightly pubescent. The core is in a dark cherry smooth shell, sweetish, excellent taste. The yield of the core in full biological ripeness is about 50%, the fat content is about 65%, the protein is 15.4%, the sugars are 12.5%. Late variety (nuts ripen in the second half of September), high-yielding, (yield slightly higher than the Tambov early variety). At the age of 10 years or more, yields up to 5 kg from a bush, about 20 centners per hectare. This variety is an excellent pollinator. Stigmas are pale pink in color. In 1969, this variety was accepted into state variety testing. In industrial plantings, it can be used as the main one throughout the whole range of hazelnut and beyond, and as a pollinator. Very frost-resistant, can withstand temperatures up to 42 ° C. Forms a lot of male inflorescences and they do not freeze slightly and abundantly dust, is a good pollinator for other varieties. Included in the state register in 1994 in the Central, Central Black Earth, North-West and Middle-Volga regions.
Advantages: high winter hardiness, is one of the best varieties - pollinators. In 1978/79 g in the territory of the Moscow and Tambov region. stood the test of frost -42? C and even fruited, while the local forest hazel was mostly frozen out. It is a fact.
Disadvantages:
Hybrid number 4219. Hazelnut hybrid green leaf (from North 42). Cupped bush with burdock leaves and huge (26 × 24 × 21 mm) nuts. Good pollinator. If we consider that the largest hazelnut fruit in the world is the Turkish variety of hazelnuts Trapezund (20 × 26 × 24 mm), and hybrid No. 4219 (26 × 24 × 21 mm). Are we the biggest !?
Hazel number 72a. Dedicated to the Institute of Forestry and Forestry Mechanization. The height of the bush up to 4 m., Green leaf. The nut is almost round, with a diameter of 17-18 mm, with a very thin shell. The amount of fat in the core is 65%.
Hybrid number 468 Red leafy, large-fruited. Very decorative crown - from crimson - pink spring to crimson-violet at the end of summer.
Hybrid number 490. Red-leaved, early ripe and very fruitful. Fruits almost every year
In addition to the listed varieties of red-leaved hybrid hazelnuts, R. Kudasheva to amateur gardeners recommended many other equally valuable ones, such as the Miracle of the Vsesvyatsky, Maria Makarevich, the Memory of Khomyakov, Vera, Nelly, Nina.
As a result of crossing red-leaved hybrid hazelnuts with green-leafed hazel, extremely ornamental plants with leaves colored red-green. And it happens that the plant as a whole is red-leaved, but on some branches the leaves are red, in the middle they seem to have leaves of the same shape, but smaller, green. And there are red leaves with green stripes or green spots (for example, in the hybrid Ivan-da-Marya).
Alida (selective form of seedlings of the Moscow Ruby variety) is distinguished by very beautiful reddish large leaves. In the seedlings 4-6 nuts. Ripen in early September. Red leaf form. Ryabushkina Valentina Grigorievna
Lentina (selective form of seedlings of Tambov Early variety) - green leaf form. The bush is compact. Nuts of medium size, with a thin peel. The core is in a light silky film, tasty, tender. Full maturity comes in mid-August, and they themselves fall off. In the stage of milky ripeness suitable for use in early August. In the seedlings 3-7 nuts. Ryabushkina Valentina Grigorievna.
Variety of hazel Lena. Green leaf form. Selected form of seedlings of southern varieties. Under the conditions of the Moscow Region, according to V. Kolotilov, one of the most high-yielding varieties - up to 7 kg from a bush.
Popular hazelnut varieties for the southern regions of Russia
Adygei 1 (hazelnut)
Seedling from free pollination of local form. Received at the Kuban State Agrarian University. Early - middle (third decade of August) ripening. Author: N. A. Tkhagushev. It is characterized by high frost resistance, relative resistance to drought, pests and diseases are damaged a little. The average yield is 22.1 c / ha. Universal purpose. Bush with a crown of medium density and articulated, olive-yellow, pubescent shoots. Fruits with an average weight of 2.1 g, wide-round, collected in 3-4, less often in 5-8 pieces. Wrap whole, slightly longer than the nut. The core yield is 49.3%, the fat content is 65.6%. Tasting score 3.9 points.
At the state test since 1967. Included in the state register in 1973 in the North Caucasus region.
Advantages: It is characterized by high frost resistance for the southern region, relative resistance to drought, pests and diseases are damaged a little.
Disadvantages:
Panahesky (hazelnut)
Seedling from free pollination of local form. Received at the Kuban State Agrarian University. Author: N. A. Tkhagushev. Medium ripening. Highly frost-resistant, relatively resistant to pests and diseases. The average yield of 20.2 c / ha. Universal purpose. A shrub with articulated shoots of light brown color. Fruits are large and medium size (2.2 g), rounded oblong shape. The wrap is twice as long as the nut, whole, sometimes dissected from one side. The core yield is 48.7%, the fat content is 66.1%, and the protein content is 17.9%. Tasting score 4.4 points.
Adopted for state variety testing in 1967. Included in the state register in 1973 in the North Caucasus region.
disadvantages
Circassian 2 (Circassian round, Shapsugsky, Kerassundsky round, Kichmaysky, Adygei) (hazelnuts)
Local Adyghean variety. Originator is not registered. Early ripening. The average yield of 22.3 c / ha. It is characterized by relative resistance to pests and diseases. Relatively winter-hardy and drought-resistant. Universal purpose.
Vigorous shrub with a spreading crown. Fruits weighing 1.6 g, broadly oval, slightly flattened, pointed. The wrapper is integral, longer than the nut, divided into uneven jagged lobes. The shell is thin, brown, with slight longitudinal stripes. The yield of the core is 45.2%, the fat content is about 70%. Tasting score of 4.5 points.
Admitted to state variety testing in 1950. Included in the state register in 1959 in the North Caucasus region.
Advantages: Relative resistance to pests and diseases.
Disadvantages:
Kuban (hazelnuts)

Spontaneous somatic mutant (clone) of the Circassian variety 2. Obtained from the All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Floriculture and Subtropical Crops. Medium ripening. Winter hardy high-yielding variety. The average yield is 24 kg / ha, the maximum - 27 kg / ha. Universal purpose.
A bush 3 m high with a willow crown of average density. The leaves are large, slightly elongated, dark green, wrinkled. The fruits are very large, with an average weight of 3.5 g, round, slightly flattened, slightly finned. The peel is of medium thickness, dense, smooth, slightly bumpy, shining with a barely noticeable patina. The output of the core is 48%, the fat content is 67%, the protein is 19%. Tasting score 4.6 points.
Adopted for state variety testing in 1995. Included in the state register in 1999 for the North Caucasus region.
Advantages: Winter-hardy, high-yielding variety.
Disadvantages:
Perestroika (hazelnuts)
Obtained by crossing varieties Kudryavchik and Trebizond. Obtained at the All-Russian Research Institute of Floriculture and Subtropical Crops. Early ripening. Universal purpose.
Spreading-willowy shrub 2.5 m high with a rounded crown of medium thickness. Fruits are large (2.2 g), round, slightly ribbed. The output of the core is 50%. Fat content 73%. Tasting score of 5 points.
Adopted for state variety testing in 1989. Included in the state register in 1999 in the North Caucasus region.
Advantages: The highest tasting score. Large fruits.
Disadvantages:
Rome (hazelnut)
Received in Italy. Medium ripening. Resistant to pests and diseases. Weakly affected by powdery mildew. Frost resistance is average. The average yield of 30 - 35 kg / ha. Universal purpose.
The fruits are large, weighing 3.2 - 3.5 g, one-dimensional, flat-round, with a beautiful appearance. The thickness of the shell is 0.9 - 1.0 mm. The yield of the core is 43 - 47%, the fat content is 68%, protein - 14.6%.
Adopted for state variety testing in 1968. Included in the state register in 1973 in the North Caucasus region.
Pluses: Resistant to pests and diseases. Weakly affected by powdery mildew. The fruits are large, with a beautiful appearance.
Disadvantages: Average frost resistance.
Foots (hazelnuts)
Local Georgian variety. Originator is not registered. Early ripening. Highly drought resistant, not damaged by pests and diseases. The average yield of 17.6 c / ha. Self-infertile, the best pollinator is the Nems variety. Universal purpose.
Spreading srednerosly bush forming abundant root growth. Fruits are large (2.8 g), well executed, rounded. The output of the core is 50%, the fat content is 65-68%. Tasting score of 4.5 points.
Admitted to state variety testing in 1954.
Advantages: Highly drought resistant, not damaged by pests and diseases.
Disadvantages: Self-infested, forms abundant root shoots.
Popular varieties of common hazel species
Fuscorubra. Large wide vertical shrub with numerous trunks, height and width from 4 to 6 m. With age, the crown of plants becomes umbrella-shaped. Initially, this variety of hazel grows slowly, then faster. The leaves of the plants are large, heart-shaped, red-brown when blooming, later brownish-green.
Contorta. Common Hazel “Kontorta” is a slow-growing shrub with twisted trunks and branches, with a height and width of 1.5 to 2.5 m. The Hazel Filbert is distinguished by asymmetrical, somewhat twisted leaves. Appearing on the plant ordinary shoots should be immediately removed.
Aurea. Large, dense, upright shrub height and width from 3 to 5 m; grows slowly. The leaves of the Aurea hazel variety when blooming are golden yellow, later lemon green, in autumn - yellow.
Variety of hazel large purpurea. Large, wide, vertical, multi-barreled, slow-growing shrub with a height and width of 4 to 6 m. Crohn of adult plants is umbrella-shaped. Purple hazel has rounded heart-shaped leaves (when blooming is dark red, with a metallic sheen; in summer the color becomes less saturated; in the shade the leaves are reddish-green).
For planting, it is necessary to purchase small hazelnut saplings from reliable vendors at a young age - so that you can see that the source was a cutting (fibrous root form), and not a seedling (semi-hazelnut), which has a strictly stem form of the roots. See the “Reproduction” section of the photo of root systems of a half-hazelnut seedling and a seedling from a cutting.
In the fluffy bushes of hazel, or hazel, advantageously combines a high decorative effect and productivity. For a dacha, it is better to choose its domesticated form - hazelnuts: it is unpretentious, and planting and caring for them will not cause difficulties even in the absence of significant experience in gardening. Its spreading bushes with bright foliage and powerful roots reach a height of 3 m, and their life expectancy reaches 80 years. Each of them can ripen up to 8-10 kg of nuts. But to achieve this, you need to comply with the technology of cultivation of culture.
Suitable plot
Hazelnuts - master adaptation. It can adapt to any conditions, but this nut develops best of all in sunny or slightly shaded areas. The lack of light reflects badly on the yield of shrubs. The hazelnut ornamentation suffers in the thick shadow: the young branches wither and the leaves lose their intensity. The place for cultivation of crops should be chosen warm and not blown by winds and drafts, without stagnation of cold air in spring.
The soil can be any, but the most generous crop is a nut in a fertile wet soil with a neutral reaction. The most unfavorable option for him is the quickly drying earth and sand. Sour and podzolic soil before planting shrubs will have to lime. Make it better in advance - a year before the procedure, but you can before it. Having scattered lime on the site (at the rate of 0.5 kg of substance per 1 m²), the soil is dug up, going deeper by 1.5 bayonet shovels.
The terrain does not matter. Hazelnuts are found in lowlands, on steep and gentle slopes, on elevations, near the banks of reservoirs — everywhere it grows equally well. You can plant a nut on a plot next to a shed or hozblok, along a fence, at a gate or wicket, at a house wall casting a shadow. Hazelnut hedges are spectacular and elegant.

Timing and landing scheme
Place shrubs on the site better in the fall. After winter, the plant quickly wakes up, so they start spring planting very early - at the end of February - March, otherwise the hazelnut will not take root. If the cottage is in middle lane or in the Urals, it is advisable to postpone the procedure until the beginning of October. Then the injured roots of the seedling will have time to heal before the cold weather, and with the advent of heat, it will begin to grow actively.
Space for the development of hazelnut need to leave a lot. Use several schemes for its placement:
- 6x6 m;
- 5x6 m;
- 4x6 m;
- 4x5 m
Thickening planting is impractical: the bushes grow weak, and nuts on them mature enough.
Can be placed hazelnut nesting method. Having outlined a circle with a diameter of 1.5 m, 5-6 plants are planted along it, adhering to the 6x6 m scheme. Later they are formed into 1 trunk, getting rid of the entire root growth.
The soil begins to be prepared 6 months before the seedlings are placed in it. During this time, it must be steamed in order to accumulate as much moisture as possible. Its purity is monitored by regularly weeding and cultivating weeds. It is advisable to treat the deep layers of the soil, plunging into it by 50-60 cm. In the oxygen-rich, loose earth, the roots of the shrub will grow faster, it will take root easier. If the soil is not fertile, it is enriched with phosphorus-potassium compounds.
In order to achieve abundant fruiting of hazelnuts, several of its bushes are planted (at least 2-3), necessarily belonging to different varieties. Only in the presence of numerous neighbors plants will be able to fully pollinate. The dependence here is direct: the more varieties of culture planted in the country, the more nuts are harvested from them.
Landing technique
A landing pit is dug at least 2 weeks before the plants are placed in it. Its optimum depth is 60 cm, and its width is 50 cm. Fertile soil is poured into the pit, adding fertilizer to it:
- humus (2-3 buckets) or manure (5-8 kg);
- superphosphate (150-200 g);
- potassium salt (50 g).
The supply of nutrients should be in the middle and upper part of the recess. With such a refueling in the first 3-4 years of life in a new place, no hazelnuts will need to be fed. In the center of the pit set wooden stake. He will support for the young bush.
Hazelnut saplings at the age of 2 years best take root. Having straightened the roots of the plant, they are dipped in a mash from clay or earth. A seedling is put on a mound, but first a couple of handful soil with mycorrhiza taken from under a hazelnut is placed under it (to a depth of about 15 cm). In order for the roots to branch and actively develop, the root neck of the bush must be 2-3 cm below the ground level. But it’s impossible to sprinkle it with earth. Well compacted soil over the roots, spend abundant watering (3-5 buckets of water).
The surface of the hole is mulched. Any organic material is suitable for this:
- sawdust;
- straw;
- needles;
- peat;
- humus;
- manure;
- compost.
In order for the seedlings to settle down faster, after 5-7 days they re-water. This is especially important when spring planting hazelnuts. In damp soil, its roots will quickly grow, and the hairs formed on them will help them to more actively absorb water and nutrients necessary for the development of the aerial part of the bush. To connect the soil capillaries need 2-3 watering. When this happens, the landing gear will become inseparable from the rest of the soil. This will prevent it from drying out.
Watering and feeding
Further care of plantings involves standard procedures:
- watering;
- soil loosening;
- top dressing;
- weed removal;
- pruning.
Hazelnut loves moisture and does not tolerate drought. Water it 5-6 times per season. Be sure to moisturize the soil when the nut fades, during intensive growth of ovaries and planting flower buds of the next year (in July) and after the flying of foliage. Watering should be abundant. They spend it with warm water, spending 40-50 liters per each adult plant.
After moistening, the soil under the bushes is loosened. This should be done carefully, going deep into the soil by a maximum of 10-15 cm, so as not to damage the roots located almost near the surface. Experienced gardeners prefer not to risk and instead of loosening, they lay down near-stem circles with mowed grass. Pereprev, such mulch will be for plants an additional source of nutrients. This technique is also useful because the grass attracts worms, as a result of whose vital activity the soil fertility increases.
Growing hazelnuts will not be successful without regular dressings - they are needed throughout the growing season. In autumn, the soil in tree trunks is enriched with wood ash. This dressing speeds up fruiting and increases the yield of hazelnuts. In spring and summer, plantings are fed by adding the following components to the soil:
- manure or compost;
- humus;
- ammonium nitrate;
- phosphate and potash fertilizers.
When the ovary begins to form, the bushes are watered with a solution of urea.
Before feeding the soil moistened. After scattering nutrient compositions on it, they are buried in the soil by shallow loosening. Pristvolny circle again watered and mulch. The introduction of nitrogen fertilizers must be approached carefully: on poor soils, they will provoke an intensive growth of green mass, and the ovaries on plants will be little. Excess nutrients hazelnuts will not benefit. Its bushes will actively grow, but the shoots will not have time to ripen and will suffer from frost in winter.
Trimming and preparation for winter
Usually hazelnut shape of a bush. Most importantly, the young shoots - they form the ovary. From the lower branches choose 7-10 - they form the skeleton of a bush. Extra branches cut out. Abandoned shoots should be strong, well developed and as far as possible from each other. Be sure to get rid of diseased and damaged branches. Overgrow bush should not: it reduces its yield and creates a favorable environment for pathogens and pests. Therefore, care for an adult plant is in its thinning, removal of dry branches and the gradual rejuvenation of the bush.
The formation of hazelnuts in the form of a tree involves regular pruning of all lateral shoots while preserving the main trunk.
There is a little trick that will save time and effort. A part of the plant stem (5-6 cm above the soil with the obligatory grip of the root collar) is wrapped with a film, digging its bottom edge into the ground. Under it, root shoots will not be able to form.
The filbert well transfers the neighborhood of vegetable and melon cultures, and also wild strawberry. They can be planted between his young bushes so that the place on the site is not empty. When they grow up, having closed their crowns (in 5-6 years), it is better to sow the soil under them with perennial grasses. For soil with a neutral reaction suitable cereal crops. If the earth is sour, lupine should be planted in tree circles. Improving the structure of alkaline soil will help sow the oatmeal mix. Grown grass will have to mow periodically.
In the fall, when the shrub leaves off, they are raked and burned. This is an excellent powdery mildew prevention. It is advisable to dig up the soil in tree trunks by 10-15 cm. Hazelnut is a frost-resistant culture, but it is better to winter with skeletal branches on the ground. So his male earrings will be protected from the cold. To the soil shoots pressed snow. When it melts, the branches raise.
In the cultivation of hazelnuts is nothing complicated. Rare watering and dressing in combination with the correct pruning will allow him to regularly please the owners with useful and nutritious nuts. And in lean years, the disappointment of a small number of ovaries will smooth out the elegant look of the plant, which you can admire from early spring to late autumn.
- reduce the body's immune defense
- drowsiness
- frequent fatigue
- depressed
- headaches, as well as various pains and cramps in the internal organs
If you feel frequent ailments, you just need to clean the body. How to do it
Hazelnut saplings are recommended to be placed on the basis of the following planting schemes: 6x6, 5x6, 4x6 and 4x5 m. The more places you allocate for the plant, the more powerful it will grow and the greater the harvest. There is also a nested landing method. At the same time on a circle of one and a half meters up to 6 plants are placed using the planting scheme 6x6 meters. Root growth is removed in order that the bush went to 1 trunk.
If we talk about the preparation of the soil, it is necessary to loosen before planting. If the potassium and phosphorus are low, you need to add fertilizer. Nitrogen is introduced as a top dressing during the growing season. It is also worth to plow the soil and breakdown for landing. Hazelnut saplings are sunk by 60 centimeters. In order for the roots to develop well, several buckets of humus or fertile soil are brought in. In this case, the nut will begin to fruit much earlier.
How to care, grow; when to replant (photo)
Nursing is no different from caring for other cultures. The soil near the trunk circles loosens, but it is not necessary to touch the roots. Walnut is watered several times per season to increase yields.
Watering is required mainly in June-July. A significant role is played by fertilizers, fruiting also depends on them. The best option - compost and manure, they make 2 times a year. Every year make mineral dressing. During fruit set-up, urea is fertilized.
Any varieties of hazelnuts increase the crop gradually, from the 3rd year of life. A bucket of nuts from one bush can only be obtained from the 15th year of life.
Fruits ripen from late August. Their collection occurs after they acquire a light brown color. Then the nuts are dried and stored in a well-ventilated room.
How is the formation of the bush by trimming
Getting a good harvest helps the proper formation of the bush. In the first years, the underground part of the plant develops better than the aboveground part. After 3 years, active growth of shoots begins. Of them form the trunks of the crown. Those branches that are to be removed, cut right at the base of the bush.
Growing hazelnuts involves the removal of excess shoots from the bush throughout life. At the same time, the young branches are left, and the barren stalks are eliminated.
Starting from the 11th year, the bush is rejuvenated, while 3 old trunks are removed, and new shoots are shortened. Carry out the action should be before the leaves bloom.
Top dressing, watering and other care
Hazelnut saplings have a delicate root system. Therefore, if loosening pristvolnyh circles, you should proceed with caution so as not to hurt them. It is better to use mulching with mowed grass. Worms develop well under it, which makes the soil more fertile. Improving yield helps ash in the soil.
Growing walnut involves the implementation of irrigation. It is also necessary to make humus - 2 buckets per year per plant. In the summer there is additional feeding with ashes, in the spring - with ammonium sulphate and ammonium nitrate.
Nut Reproduction
Propagate different varieties of hazelnuts in different ways.
Dividing bush
The easiest way, all characteristics of the variety are preserved. The pre-excavated plant is divided into parts so as to produce 15-centimeter hemp. At the same time on the parts must remain the roots and soil.
Propagation by the bow
In this case, annual shoots are rooted, but they do not separate them from the plant. It is impossible to take older layers, do not take root. During reproduction by digging, dig holes with a depth of 15 cm, their length should be about 40 cm. Shoots are placed in the grooves and fixed with wooden hooks. The upper part of the layers is attached to the pegs. In the place where there is a bend, make a cut and pollinate with the help of a root. Next, the grooves sprinkle with soil and produce watering. So the soil is compacted. From one escape only one rooted layering will result.
Horizontal layouts
Time consuming, but effective way. With one shoot, you can get up to 5 layers. Laying goes into the grooves horizontally. Layers pinned, but do not fall asleep. From the vegetative shoots vertically grow shoots, then they mulch. During the summer period, the layers are sprinkled several times with earth.
Among other things, watering is done. As a result, hillocks are obtained above the layering. The growth is shortened to 50 cm in order to enhance the formation of roots. On next year horizontal layers are dug out and divided into parts.
Vertical layouts
Excellent results are obtained with the rejuvenation of the entire bush. From juvenile buds of the root zone, juvenile shoots are obtained. In the process of hilling leaves from the bottom of the shoots are removed. In the fall of the rooted shoots cut. In the process of growing shoots hauling occurs. As a result, he takes roots and by the autumn reaches 1 meter in height. In place of constriction shoots break off with the help of wire.
Seeds
When sowing seeds, different offspring is formed that does not resemble the mother plant. Such reproduction is usually used for breeding purposes. The presented method makes it possible to obtain new improved varieties. Nuts are selected well developed and large. They are pre-stratified. When spring planting beds must be dried dry leaves.
Cuttings
After 5 years, the ability to root the cuttings is close to one hundred percent. At the same time, one third of the cuttings first take root, and already two thirds of it.
Rhizome shoots
In horticulture, coppice breeding is actively used. The lower part of the bush for a long time retains the ability to resume, which is very important. Walnut shrubs grow in a circle with the help of rhizomes. Growth in hazelnuts formed in the 3rd year. For breeding, use 2-3-year-old shoots, which are separated with an ax. They are called otdirkami. When transplanting shoots, cuts are made to ensure better survival.
Graft
Propagation by vaccination is difficult to produce. Often, bear nut and hazel seedlings are used for this purpose. Vaccination is carried out in early spring. It is tied and applied garden var. Also installed a special cap made of polyvinyl chloride film. After the kidneys are formed on the handle, the cap is opened, two weeks are waiting for and removed altogether. After the graft grows together, all the shoots are removed from the stock.
Diseases and pests
Hazelnuts prefer to eat animals such as boars, squirrels, woodpeckers, mouse-like rodents, and nuts. Virtually all nut bushes are sooner or later exposed to diseases and pests. The main pests are caterpillars, butterflies, beetles, hares, weevils.
Greater danger is a walnut weevil and barbel. They struggle with it in the following way: they dig the soil, remove the wormy nuts, insects shake off the film and process it with toxic chemicals. Mealy dew may appear in the second half of the summer. Affected leaves must be collected and sprayed with lime-sulfur decoction. Colloidal sulfur is also treated.
The filbert which advantage is not subject to doubt is unpretentious to a place of landing and leaving a plant. Reproduction goes different ways - cuttings, rhizomes, layering, etc. The crop is usually large, but it is necessary to protect the bush from diseases and pests.
Growing hazelnuts (video)
In order not to lose the material, be sure to save it to yourself in the social network Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki, Facebook, simply by clicking on the button below:
Attention, only TODAY!
Feedback and Comments
Did you find a mistake in the text? Please select it and press Ctrl + Enter. Thank!
0 Yuri 03/26/2016 8:10
I quote Sergey:
I do not know how many hazelnuts I planted, and I could not grow it. That dries, it does not bear fruit. Who has grown, and gave birth to hazelnuts, write how you did it. I will be very grateful. the product is very useful, and grow it does not work.
First of all, it is necessary to find hazel or hazelnut layering, water more often, mulch, because root system superficial. Rooting takes 2 years to remove the ovary. For a stable harvest, you need to plant several copies. different varieties hazelnut, hazelnut or bear nut.